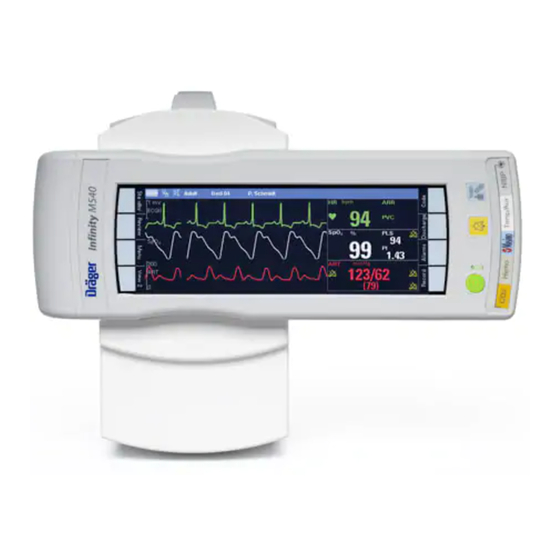
Dräger Infinity M540 Instructions For Use Manual
Acute care system
Hide thumbs
Also See for Infinity M540:
- Instructions for use manual (350 pages) ,
- Quick reference manual (24 pages) ,
- Quick reference manual (24 pages)













Need help?
Do you have a question about the Infinity M540 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers