Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Copyright
Copyright © 2019 MiTAC International Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of
this manual may be reproduced or translated without prior written consent from
MiTAC International Corporation.
Trademark
All registered and unregistered trademarks and company names contained in this
manual are property of their respective owners including, but not limited to the
following.
®
TYAN
is a trademark of MiTAC International Corporation.
®
Intel
is a trademark of Intel
AMI, AMI BIOS are trademarks of AMI Technologies.
®
Microsoft
, Windows
®
Winbond
is a trademark of Winbond Electronics Corporation.
Notice
Information contained in this document is furnished by MiTAC International
Corporation and has been reviewed for accuracy and reliability prior to printing.
MiTAC assumes no liability whatsoever, and disclaims any express or implied
warranty, relating to sale and/or use of TYAN
warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose or merchantability. MiTAC
retains the right to make changes to product descriptions and/or specifications at
any time, without notice. In no event will MiTAC be held liable for any direct or
indirect, incidental or consequential damage, loss of use, loss of data or other
malady resulting from errors or inaccuracies of information contained in this
document.
S5557
Version 1.0
®
Corporation.
®
are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
http://www.tyan.com
®
products including liability or
1
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for MiTAC TYAN S5557
-
Page 1: S5557
In no event will MiTAC be held liable for any direct or indirect, incidental or consequential damage, loss of use, loss of data or other malady resulting from errors or inaccuracies of information contained in this document. -
Page 2: Table Of Contents
Contents S5557 ......................1 Before you begin… ..................3 Chapter 1: Instruction ................4 1.1 Congratulations ................. 4 1.2 Hardware Specifications ..............4 Chapter 2: Board Installation ..............7 2.1 Board Image ..................8 2.2 Block Diagram ................... 9 2.3 Motherboard Mechanical Drawing ........... 10 2.4 Board Parts, Jumpers and Connectors ........... -
Page 3: Before You Begin
Before you begin… Check the box contents! The retail motherboard package should contain the following: S5557 Motherboard x 1 SATA Signal Cable x 2 SATA Power Cable x 1 Rear IO shielding x 1 S5557 Quick Installation Guide x 1 IMPORTANT NOTE: 1. -
Page 4: Chapter 1: Instruction
Chapter 1: Instruction 1.1 Congratulations ® ® You have purchased the powerful TYAN S5557 motherboard, based on the Intel ® Core™ i3/i5/i7 series H310 chipset. The S5557 is designed to support Intel Processors, and support Unbuffered DDR4 SO-DIMM 2666/2400 up to 32GB ®... - Page 5 Connector (2) SATA + (1) SATADOM Controller Intel H310 Storage SATA Speed 6.0 Gb/s RAID Connector type (2) Display port 1.2 Graphic Chipset Intel Processor Graphics (pGFX) Resolution Up to 4096x2304 @60Hz (2) USB3.1 Gen1 ports (at rear) (2) USB3.1 Gen1 ports (via Cable) RJ-45 (2) GbE ports Input...
- Page 6 Motherboard (1) S5557 Motherboard Manual (1) Quick Installation Guide Package I/O Shield (1) I/O Shield Contains (1) SATA power cable SATA Cable (2) SATA signal cables http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 7: Chapter 2: Board Installation
Unplug the power from your computer power supply and then touch a safely grounded object to release static charge (i.e. power supply case). For the safest conditions, MiTAC recommends wearing a static safety wrist strap. (2) Hold the motherboard by its edges and do not touch the bottom of the board, or flex the board in any way. -
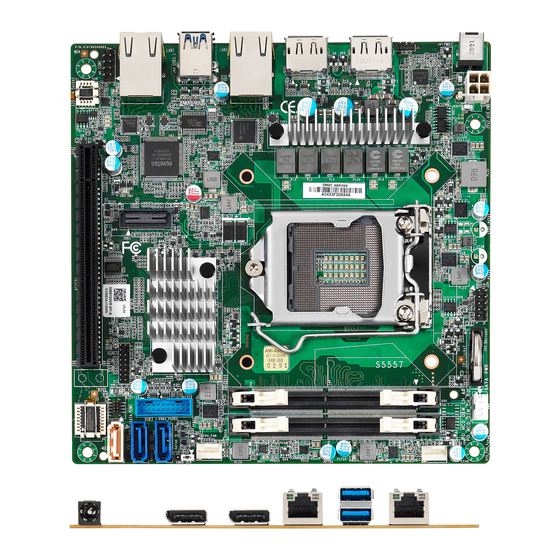
Page 8: Board Image
2.1 Board Image S5557 This picture is representative of the latest board revision available at the time of publishing. The board you receive may not look exactly like the above picture. http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 9: Block Diagram
2.2 Block Diagram S5557 Block Diagram http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 10: Motherboard Mechanical Drawing
2.3 Motherboard Mechanical Drawing http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 11: Board Parts, Jumpers And Connectors
2.4 Board Parts, Jumpers and Connectors This diagram is representative of the latest board revision available at the time of publishing. The board you receive may not look exactly like the above diagram. The DIMM slot numbers shown above can be used as a reference when reviewing the DIMM population guidelines shown later in the manual. - Page 12 Motherboard Components Connectors 1. DC 12V Jack (J87) 2. Display Port#1 (DP1) 3. Display Port#2 (DP2) Ports 4. LAN1 Connector (LAN1) 5. USB3.1Connector (J93) 6. LAN2 Connector (LAN2) 7. TYAN Module Header (DBG_HD1) 12. CPU FAN Connector (CPU_FAN) 13. System FAN Connector 8.
- Page 13 CPU FAN/ SYS_FAN_1: 4-pin Fan Connector Signal VCC12 FAN_TACH Use this header to connect the cooling fan to your motherboard to keep the system stable and reliable. Note: A 4-pin fan is required for fan support 4pin Control PW9: SATA HDD Power Connector Signal Signal VCC5V...
- Page 14 DBG_HD1: TYAN Module Header Signal Signal P3V3 FRAME_N LAD0 LAD1 PLT_RST_N LAD2 LAD3 CLK_33M DBG_SERIRQ DBG_PRES_N VCC3_AUX P3V3(NI) / GND RST_ESPI_RESET_N USB3_FPIO1: Front USB3.0 Connector Signal Signal P0_RX_N P0_RX_P P0_TX_N P0_TX_P P0_N P0_P OC_N P1_P P1_N P1_TX_P P1_TX_N P1_RX_P P1_RX_N J60: Clear CMOS Jumper Signal...
-
Page 15: Installing The Processor And Heatsink
Intel processors for this specific motherboard. NOTE: MiTAC is not liable for damage as a result of operating an unsupported configuration. Processor Installation (Single LGA1151 Socket for Intel Coffee lake-S CPU) Follow the steps below to install the processors and heat sinks. - Page 16 3. Open the CPU socket cover to the fully position. 4. Install the processor and make sure the golden arrow is located in the right direction. 5. Close the CPU socket cover. 6. Close the socket lever. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 17 Heat sink Installation After installing the processor, you will need to proceed to install the heat sink. The CPU heat sink will ensure that the processor do not overheat and continue to operate at maximum performance for as long as you own them. An overheated processor is dangerous to the motherboard.
- Page 18 Secure the heatsink screws. Connect the heatsink fan cable. http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 19: Tips On Installing Motherboard In Chassis
2.6 Tips on Installing Motherboard in Chassis Before installing your motherboard, make sure your chassis has the necessary motherboard support studs installed. These studs are usually metal and are gold in color. Usually, the chassis manufacturer will pre-install the support studs. If you are unsure of stud placement, simply lay the motherboard inside the chassis and align the screw holes of the motherboard to the studs inside the case. - Page 20 Some chassis include plastic studs instead of metal. Although the plastic studs are usable, MiTAC recommends using metal studs with screws that will fasten the motherboard more securely in place. Below is a chart detailing what the most common motherboard studs look like and how they should be installed.
-
Page 21: Installing The Memory
2.7 Installing the Memory Before installing memory, ensure that the memory you have is compatible with the motherboard and processor. Check the TYAN Web site at http://www.tyan.com details of the type of memory recommended for your motherboard. Support (1) DIMM slots per channel ... - Page 22 Recommended Memory Population Table (Single CPU) Quantity of memory installed Single CPU Installed (CPU0 only) P0_MC0_DIM_Ch_A0 √ √ P0_MC0_DIM_Ch_B0 √ NOTE: 1. √ indicates a populated DIMM slot. 2. Use paired memory installation for max performance. 3. Populate the same DIMM type in each channel, specifically - Use the same DIMM size - Use the same # of ranks per DIMM Intel Xeon Coffee lake-S Memory Support...
- Page 23 (S5557G2NR support as following) DDR4 Supported Memory Modules and Devices Supported DDR4 SO-DIMM Module Configurations (S-Processor Lines) Raw Card Version DIMM 16GB Capacity DRAM Device Technology DRAM 512Mx8 1024Mx8 512Mx8 1024Mx8 256Mx16 512Mx16 Organization # of DRAM Devices #of Ranks #of Row/Col 15/10 16/10...
- Page 24 Memory Installation Procedure Follow these instructions to install memory modules into the S5557. Unlock a DIMM socket by Press the retaining clip outwardly in the following illustration. Align the memory module with the socket,such that the DIMM NOTCH match the KEY SLOT on the socket. Seat the module firmly into the socket by gently pressing down until it sits flush with the socket.
-
Page 25: Attaching Drive Cables
2.8 Attaching Drive Cables The following illustrates how to make a SATA Cable connection. If you are in need of SATA/SAS cables or power adapters please contact your local sales representative. Attaching SATA Power Cable Attaching SATA Cable http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 26: Installing Add-In Cards
2.9 Installing Add-In Cards Before installing add-in cards, it’s helpful to know if they are fully compatible with your motherboard. For this reason, we’ve provided the diagrams below, showing the slots that may appear on your motherboard. PCIE3.0 SLOT x16 (w/ x16 link) ... -
Page 27: Connecting External Devices
2.10 Connecting External Devices Connecting external devices to the motherboard is an easy task. The motherboard supports a number of different interfaces through connecting peripherals. See the following diagrams for the details. Display Display LAN1 USB3.1x2 LAN2 12V DC Jack Port 1 Port 2 Onboard LAN LED Color Definition... -
Page 28: Installing The Ac/Dc Adapter
2.11 Installing the AC/DC Adapter There is One (1) power connector on your S5557 motherboard. The S5557 supports DC Input 12V/90W DC Adapter. 2.12 Finishing Up Congratulations on making it this far! You have finished setting up the hardware aspect of your computer. Before closing up your chassis, make sure that all cables and wires are connected properly, especially SATA cables and most importantly, jumpers. -
Page 29: Chapter 3: Bios Setup
Chapter 3: BIOS Setup 3.1 About the BIOS The BIOS is the basic input/output system, the firmware on the motherboard that enables your hardware to interface with your software. The BIOS determines what a computer can do without accessing programs from a disk. The BIOS contains all the code required to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial communications, and a number of miscellaneous functions. - Page 30 Chipset section unless you are absolutely sure of what you are doing. The Chipset defaults have been carefully chosen either by MiTAC or your system manufacturer for best performance and reliability. Even a seemingly small change to the Chipset setup options may cause the system to become unstable or unusable.
-
Page 31: Main Menu
3.2 Main Menu In this section, you can alter general features such as the date and time. Note that the options listed below are for options that can directly be changed within the Main Setup screen. BIOS Information It displays BIOS related information. Product Name It displays Product information. -
Page 32: Advanced Menu
System Time Adjust the system clock. HH (24 hours format): MM (Minutes): SS (Seconds) Access Level Adminstrator 3.3 Advanced Menu This section facilitates configuring advanced BIOS options for your system. CPU Configuration CPU Configuration parameters SATA Configuration SATA Device Option Settings PCH-FW Configuration Configure Management Engine Technology Parameters ACPI Settings... - Page 33 Hardware Health Configuration Hardware Health Configuration S5 RTC Wake Settings S5 RTC Wake Settings Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU This formset allows the user to manage Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU Trusted Computing Trusted Computing settings. Option ROM Dispatch Policy Option ROM Dispatch Policy Parameters PCI Subsystem Settings PCI, PCI-X and PCI Express Settings...
- Page 34 3.3.1 CPU Configuration Software Guard Extensions (SGX) Enable/ Disable Software Guard Extensions (SGX) Disabled / Enabled/ Software controlled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 35 Intel (VMX) Virtualization Technology When enabled, a VMM can utilize the additional hardware capabilities provided by Vanderpool Technology. Disabled / Enabled Active Processor Cores Number of cores to enable in each processor package. All / 1 Hyper- threading Enabled or Disabled Hyper-Threading Technology. Disabled / Enabled Boot performance Mode Select the performance state that the BIOS will set starting from reset vector.
- Page 36 3.3.2 SATA Configuration SATA Mode Selection Determines how SATA controller(s) operate. AHCI Serial ATA Port 0/1/2 Hot Plug Designates this port as Hot Pluggable. Disabled / Enabled SATA Device Type Identify the SATA port is connected to Solid State Drive or Hard Dish Drive. Hard Disk Drive / Solid State Drive http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 37 3.3.3 PCH-FW Configuration ME State When Disabled ME will be not into ME Temporarily Disabled Mode. Disabled / Enabled Firmware Update Configuration Configure Management Engine Technology Parameters. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 38 3.3.3.1 Firmware Update Configuration Me FW Image Re-Flash Enable/Disable Me FW Image Re- Flash function. Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 39 3.3.4 ACPI Settings Enable ACPI Auto Configuration Enable or Disables BIOS ACPI Auto Configuration. Disabled / Enabled Enable Hibernation Enables or Disables System ability to Hibernate (OS/S4 Sleep State). This option may not be effective with some operating systems. Disabled / Enabled ACPI Sleep State Select the highest ACPI sleep state the system will enter when the SUSPEND button is pressed.
- Page 40 3.3.5 Watchdog Timer Configuration Watchdog Mode The duration of enabling Watchdog Timer. When Watchdog time-out occurs, System will roboot immediately. Disabled / POST / OS / Power ON http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 41 3.3.6 Hardware Health Configuration Auto Fan Control Auto Fan Control help. Disabled / Enabled NOTE: Auto Fan Control must be set to [Enabled] PWM Minimal Duty Cycle menu will appear. PWM Minimal Duty Cycle Duty Cycle control range 30% Duty Cycle / 45% Duty Cycle / 60% Duty Cycle http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 42 3.3.6.1 Sensor Data Register Monitoring http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 43 3.3.7 S5 RTC Wake Settings Wake system from S5 Enable or disable system wake on alarm event. Select Fixed time, system will wake on the hr::min::sec specified. Select dynamic time, system will wake on the current time+ increase minute(s) Disabled / Fixed time / Dynamic time http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 44 3.3.8 Option ROM Dispatch Policy Onboard LAN1 (I210) Enable or disable onboard LAN1 OPROM. Disabled / Enabled Onboard LAN2 (I219) Enable or disable onboard LAN1 OPROM. Disabled / Enabled PCIE#1 Empty Enable or Disable Option ROM execution for selected Slot. Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 45 3.3.9 PCI Subsystem Settings Above 4G Decoding Enables or Disables 64bit capable Devices to be decoded in Above 4G Address Space(Only if System supports 64 bit PCI decoding). Enabled / Disabled BME DMA Mitigation Re-enable Bus Master Attribute disabled during Pci enumeration for PCI Bridges after SMM locked Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 46 3.3.10 USB Configuration Legacy USB Support Enables USB legacy support. AUTO option disables legacy support if no USB devices are connected. DISABLE option will keep USB devices available only for EFI applications. Enabled / Disabled / Auto XHCI Hand-off This is a workaround for OSes without XHCI hand-off support. The XHCI ownership change should be claimed by XHCI driver.
- Page 47 Device reset time-out USB mass storage device Start Unit command time-out. 10 sec / 20 sec / 30 sec / 40 sec Device power-up delay Maximum time the device will take before it properly reports itself to the Host Controller. ‘AUTO’ uses default value: for a Root port it is 100 ms, for a Hub port the delay is taken from Hub descriptor.
- Page 48 Boot option filter This option controls Legacy/UEFI ROMs priority UEFI and Legacy / Legacy only / UEFI only Network Controls the execution of UEFI and legacy PXE OpROM UEFI / legacy Storage Controls the execution of UEFI and legacy PXE OpROM UEFI / legacy Video Controls the execution of UEFI and legacy PXE OpROM...
- Page 49 3.3.12 NVMe Configuration No NVMe Device Found http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 50 3.3.13 Onboard Device Configuration LAN1 (I210) Enable or disable onboard LAN1 (I210). Disabled / Enabled LAN2 (I219) Enable or disable onboard LAN2 (I219) Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 51 3.3.14 Network Stack Configuration Network Stack Enable / Disable UEFI Network Stack. Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 52 3.3.15 iSCSI Configuration Step 0. Connect to iSCSI Server Step 1. Option ROM Dispatch Policy Settings: Advanced>Option ROM Dispatch Policy >Onboard LAN1 (I210) [Enabled] Advanced>Option ROM Dispatch Policy>Onboard LAN1Option ROM type [iSCSI] Step 2. Network Stack Configuration Settings: Set Advanced >Network Stack Configuration>> Network Stack [Enabled] Step 3.
- Page 53 3.3.15.1 Add an Attempt Read only. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 54 3.3.15.1.1 MAC A0:42:3F:3A:F7:F0 iSCSI Mode Disabled, Enabled, Enabled for MPIO. Disabled / Enabled / Enabled for MPIO http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 55 Internet Protocol Initiator IP address is system assigned in IP6 mode. In Autoconfigure mode, iSCSI driver will attempt to connect iSCSI target via IPv4 stack, if failed then attempt IPv6 stack. IP4 / IP6 / Autoconfigure Connection Retry Count The minimum value is 0 and the maximum is 16. 0 means no retry. Connection Establishing Timeout The timeout value in milliseconds.
- Page 56 Authentication Type Authentication method: CHAP, Kerberos, or None. CHAP / None Save Changes Must reboot system manually for changes to take place. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 57 3.3.15.2 Delete Attempts Commit Changes and Exit Commit Changes and Exit. Discard Changes and Exit Discard Changes and Exit. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 58 3.3.15.3 Change Attempt Order Commit Changes and Exit Commit Changes and Exit. Discard Changes and Exit Discard Changes and Exit. http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 59: Chipset Menu
3.4 Chipset Menu North Bridge System Agent (SA) Parameters. South Bridge PCH Parameters http://www.tyan.com... - Page 60 3.4.1 North Bridge Configuration VT-d VT-d capability Disabled / Enabled Memory Configuration Memory Configuration Parameters Graphics Configuration Graphics Configuration DMI/ OPI Configuration Control various DMI functions. PEG Port Configuration PEG Port Options http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 61 3.4.1.1 Memory Configuration Maximum Memory Frequency Maximum Memory Frequency Selections in Mhz. Valid values should match the refclk, i.e. divide by 133 or 100 Auto / 2133 / 2400 / 2666 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 62 3.4.1.2 Graphics Configuration Primary Display Select which of IGFX/PEG/ PCI Graphics device should be Primary Display or select SG for Switchable Gfx. Auto / IGFX / PEG Internal Graphics Keep IGFX enabled based on the setup options. Auto / Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 63 3.4.1.3 DMI/OPI Configuration DMI Max Link Speed Set DMI Speed Gen1/Gen2/Gen3 Auto / Gen1 / Gen2 / Gen3 DMI Link ASPM Control Enable/Disable the control of Active State Power Management on SA side of the DMI Link. Disabled / L0s / L1 / L0sL1 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 64 3.4.1.4 PEG Port Configuration Enable Root Port Enable or Disable the Root Port Disabled / Enabled / Auto Max Link Speed Configure PEG 0:1:0 Max Speed Auto / Gen1 / Gen2 / Gen3 Max Link Width Force PEG link to retrain to X1/2/4/8 Auto / Force X1 / Force X2 / Force X4 / Force X8 ASPM Control ASPM support for the PEG 0.
- Page 65 3.4.2 South Bridge Configuration HD Audio Configuration HD Audio Subsystem Configuration Settings DeepSx Power Configure the DeepSx Mode configuration. Disabled Enabled in S4-S5 Wake on LAN Enable/Disable integrated LAN to wake the system. Enabled / Disabled High Precision Timer Enable or Disable the High Precision Event Timer Disabled Enabled Restore AC Power Loss...
- Page 66 3.4.2.1 HD Audio Configuration HD Audio Control Detection of the HD- Audio device. Disabled = HAD will be unconditionally disabled Enabled = HAD will be unconditionally enabled. Disabled Enabled Audio DSP Enable/Disable Audio DSP. Disabled Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 67: Security
3.5 Security Administrator Password Set Administrator Password. User Password Set User Password. Security Frozen Mode Enable or disable HDD security freeze lock. Disable to support secure erase function. For AHCI SATA ports only. Disabled / Enabled Secure Boot Customizable Secure Boot settings http://www.tyan.com... - Page 68 3.5.1 Secure Boot Configuration Submenu Secure Boot Secure Boot feature is Active if Secure Boot is Enabled, Platform Key (PK) is enrolled and the System is in User mode. The mode change requires platform reset Disabled / Enabled Secure Boot Mode Secure Boot mode selector.
- Page 69 3.5.1.1 Restore Factory Keys Submenu Restore Factory Keys Force System to User Mode. Install factory default Secure Boot Key databases. When Press ‘Yes’ to proceed When Press ‘No’ to cancel http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 70 3.5.1.2 Reset To Setup Mode Submenu Reset To Setup Mode Delete all Secure Boot key databases from NVRAM Deleting all variables will reset the System to setup Mode When Press ‘Yes’ to proceed When Press ‘No’ to cancel Key Management Enables experienced users to modify Secure Boot variables http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 71 3.5.2 Key Management Factory Keys Provision Install factory default Secure Boot Keys after the platform reset and while the System is in Setup Mode. Disabled / Enabled When the Factory Keys Provision set to [Enabled],the following items will be able to log Restore Factory Keys Force System to User Mode.
- Page 72 Remove ‘UEFI CA’ from DB Device Guard ready system must not list ‘ Microsoft’ UEFI CA’ Certificate in Authorized Signature database (db) Restore DB defaults Restore DB variable to Factory defaults Platform Key (PK) Enroll Factory Defaults or load certificates from a file: 1.
- Page 73 Forbidden Signatures Enroll Factory Defaults or load certificates from a file: 1. Public Key Certificate in: a) EFI_SIGNATURE_LIST b) EFI_CERT_X509 (DER encoded) c) EFI_CERT_RSA2048 (bin) d) EFI_CERT_SHA256,384,512 2. Authenticated UEFI Variable 3. EFI PE/COFF Image(SHA256) Key Source: Default, External, Mixed, Test Authorized TimeStamps Enroll Factory Defaults or load certificates from a file: 1.
-
Page 74: Boot
3.6 Boot Setup Prompt Timeout Number of seconds to wait for setup activation key. 65535 (0xFFFF) means indefinite waiting. Bootup NumLock State Select the keyboard NumLock state. Off / On Quiet Boot Enable or disable Quiet Boot option. Disabled / Enabled Boot Option #1 Sets the system boot order Device Name / Disabled... -
Page 75: Save & Exit
3.7 Save & Exit Save Changes and Exit Exit system setup after saving the changes. Discard Changes and Exit Exit system setup without saving any changes. Save Changes and Reset Reset the system after saving the changes. Discard Changes and Reset Reset system setup without saving any changes. - Page 76 Boot Override Device Name http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 77: Chapter 4: Diagnostics
Chapter 4: Diagnostics NOTE: if you experience problems with setting up your system, always check the following things in the following order: Memory, Video, CPU By checking these items, you will most likely find out what the problem might have been when setting up your system. -
Page 78: Amibios Post Code (Aptio)
4.2 AMIBIOS Post Code (Aptio) The POST code checkpoints are the largest set of checkpoints during the BIOS pre- boot process. The following table describes the type of checkpoints that may occur during the POST portion of the BIOS: Checkpoint Ranges Status Code Range Description 0x01 –... - Page 79 SEC Error Codes 0x0C – 0x0D Reserved for future AMI SEC error codes 0x0E Microcode not found 0x0F Microcode not found SEC Phase None PEI Phase Status Code Description Progress Codes 0x10 PCI Core is started 0x11 Pre-memory CPU initialization is started 0x12 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific) 0x13...
- Page 80 Status Code Description CPU post-memory initialization. Boot Strap Processor (BSP) 0x35 selection CPU post-memory initialization. System Management Mode (SMM) 0x36 initialization 0x37 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization is started. Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module 0x38 specific) Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module 0x39 specific) Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module...
- Page 81 Status Code Description S3 Resume Error Codes 0xE8 S3 Resume failed 0xE9 S3 Resume PPI not found 0xEA S3 Resume Boot Script error 0xEB S3 OS wake error 0xEC – 0xEF Reserved for future AMI error codes Recovery Progress Codes 0xF0 Recovery condition triggered by firmware (Auto recovery) 0xF1...
- Page 82 Status Code Description 0x63 CPU DXE initialization is started. 0x64 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific) 0x65 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific) 0x66 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific) 0x67 CPU DXE initialization (CPU module specific) 0x68 PCI host bridge initialization 0x69 North Bridge DXE initialization is started.
- Page 83 Status Code Description 0x9B USB Reset 0x9C USB Detect 0x9D USB Enable 0x9E -0x9F Reserved for future AMI codes 0xA0 IDE initialization is started 0xA1 IDE Reset 0xA2 IDE Detect 0xA3 IDE Enable 0xA4 SCSI initialization is started. 0xA5 SCSI Reset 0xA6 SCSI Detect 0xA7...
- Page 84 Status Code Description 0xD5 No Space for Legacy Option ROM 0xD6 No Console Output Devices are found. 0xD7 No Console Input Devices are found. 0xD8 Invalid password 0xD9 Error loading Boot Option (LoadImage returned error) 0xDA Boot Option is failed (StartImage returned error). 0xDB Flash update is failed.
-
Page 85: Appendix I: Fan And Temp Sensors
Appendix I: Fan and Temp Sensors This section aims to help readers identify the locations of some specific FAN and Temp Sensors on the motherboard. A table of BIOS Temp sensor name explanation is also included for readers’ reference. NOTE: The red dot indicates the sensor. - Page 86 BIOS Temp Sensor Name Explanation: CPU_DTS_Temp Temperature of the CPU_DTS CPU_PECI_Value Temperature of the CPU_PECI_Value P_MOS_Area Temperature of the P MOS_Area PCH_Temp Temperature of the PCH P0_MC0_DIM_CH_A The highest temperature of CPU DIMM channel A slot P0_MC0_DIM_CH_B The highest temperature of CPU DIMM channel B slot BIOS FAN Sensor Name Explanation CPU_FAN...
- Page 87 NOTE http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 88: Glossary
Glossary ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface): a power management specification that allows the operating system to control the amount of power distributed to the computer’s devices. Devices not in use can be turned off, reducing unnecessary power expenditure. AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): a PCI-based interface which was designed specifically for demands of 3D graphics applications. - Page 89 Bus: a data pathway. The term is used especially to refer to the connection between the processor and system memory, and between the processor and PCI or ISA local buses. Bus mastering: allows peripheral devices and IDEs to access the system memory without going through the CPU (similar to DMA channels).
- Page 90 DRAM (Dynamic RAM): widely available, very affordable form of RAM which looses data if it is not recharged regularly (every few milliseconds). This refresh requirement makes DRAM three to ten times slower than non-recharged RAM such as SRAM. ECC (Error Correction Code or Error Checking and Correcting): allows data to be checked for errors during run-time.
- Page 91 I/O (Input/Output): the connection between your computer and another piece of hardware (mouse, keyboard, etc.) IRQ (Interrupt Request): an electronic request that runs from a hardware device to the CPU. The interrupt controller assigns priorities to incoming requests and delivers them to the CPU. It is important that there is only one device hooked up to each IRQ line;...
- Page 92 RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): a way for the same data to be stored in different places on many hard drives. By using this method, the data is stored redundantly and multiple hard drives will appear as a single drive to the operating system.
- Page 93 Standby mode: in this mode, the video and hard drives shut down; all other devices continue to operate normally. UltraDMA-33/66/100: a fast version of the old DMA channel. UltraDMA is also called UltraATA. Without a proper UltraDMA controller, your system cannot take advantage of higher data transfer rates of the new UltraDMA/UltraATA hard drives.
-
Page 94: Technical Support
Technical Support If a problem arises with your system, you should first turn to your dealer for direct support. Your system has most likely been configured or designed by them and they should have the best idea of what hardware and software your system contains. - Page 95 NOTE: A receipt or copy of your invoice marked with the date of purchase is required before any warranty service can be rendered. You may obtain service by calling the manufacturer for a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number. The RMA number Should be prominently displayed on the outside of the shipping carton and the package should be mailed prepaid.
















Need help?
Do you have a question about the TYAN S5557 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers