Summary of Contents for HighPoint RocketRAID 3522 SATAII
- Page 1 RocketRAID 3522 SATAII Host Adapter User’s Guide Revision: 1.0 Date: January 2008 HighPoint Technologies, Inc.
- Page 2 HighPoint’s products and use at your own risk. In no event shall HighPoint be liable for any loss of profits, or for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages arising from any defect or error in HighPoint’s products or manuals.
-
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Table of Contents Table of Content Chapter 1 Introduction About this Guide ....................... 1-1 Introducing the RocketRAID 3522 Host Adapter ............1-1 RocketRAID 3522 – Features and Specifications ............1-2 Understanding RAID Concepts and Terminology ............. 1-4 Network Features ........................1-5 Chapter 2 RocketRAID 3522 Hardware Description/Installation 1 - RocketRAID 3522 Adapter Layout ................ - Page 4 Table of Contents Driver and Software CD ..................... 4-1 Windows Driver Installation ..................4-3 Chapter 5 RocketRAID 3522 Web-RAID Management Interface 1 - Web RAID Management Interface ................ 5-1 2 - Preparing Hard disks ..................... 5-2 3 - Array Management ....................5-3 4 - Device Management .....................
-
Page 5: Introducing The Rocketraid 3522 Host Adapter
Chapter 1 Introduction Contents of this Chapter: About this guide Introducing the RocketRAID 3522 Host Adapter RocketRAID 3522 Features and Specifications Understanding RAID Concepts and Terminology Network Features (Web Management/BIOS Utilities) -
Page 6: Introduction
RAID arrays hosted by the adapter. Introducing the RocketRAID 3522 Host Adapter The HighPoint RocketRAID 3522 is an 8-channel PCI-E x8 to Serial ATA II RAID controller. The RocketRAID 3522 solution designed for enterprise storage applica- tions such as NAS solutions, workgroup and web servers, video streaming / video editing workstations, data archiving/back up, and security systems. -
Page 7: Rocketraid 3522 - Features And Specifications
Introduction Onboard Cache and Optional Battery Backup for optimal performance and added security 256MB of DDR SDRAM with ECC protection is integrated into the RocketRAID 3522 for improved performance, and provides additional security in the case of critical system failure, when used in conjunction with the optional battery back up unit. RocketRAID 3522 –... - Page 8 Introduction Array Monitors, Alerts and Indicators • SMTP for email notification • Alarm / Buzzer alerts for array activity • SAF-TE support • Ethernet Board for (OBM) Out of Band Management • NTP (Network Time Protocol) RAID Management • TerabyteSaver™ and TerabyteGuard™ for Data Protection and Reliability •...
-
Page 9: Understanding Raid Concepts And Terminology
When you create a redundant array using the RocketRAID 3522 controller’s BIOS Configuration Utility, it will automatically start the initialization process. When creating an array using the HighPoint RAID Management Console software, you can specify an initialization option (Skip initialization, foreground and background). -
Page 10: Network Features
Introduction Online RAID Level Migration This term describes the ability to change one type of array (RAID level), into a different type of array (changing a RAID 1 array into a RAID 10 array for example). Data is still accessible during the migration process, and a base level of security is still active. OCE, ORLM and the RocketRAID 3522 The RocketRAID 3522 supports both Online Capacity Expansion (OCE), and Online RAID Level Migration (ORLM). -
Page 11: Rocketraid 3522 Hardware Description/Installation
Chapter 2 RocketRAID 3522 Hardware Description/Installation Contents of this Chapter: RocketRAID 3522 Hardware 1 - RocketRAID 3522 Adapter Layout 2 - Installing the RocketRAID 3522 Host Adapter 3 - Verifying Installation 4 - Battery Backup... -
Page 12: Rocketraid 3522 Adapter Layout
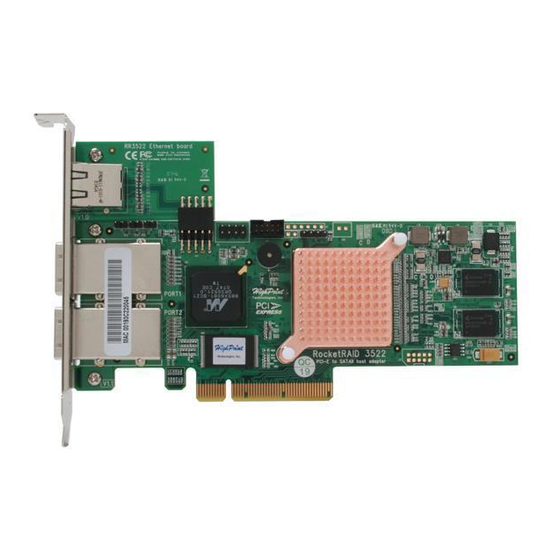
RocketRAID 3522 Hardware Description/Installation RocketRAID 3522 Hardware 1 - RocketRAID 3522 Adapter Layout Port1, Port2 These represent the RocketRAID 3522’s two External Mini-SAS ports. Each port can support up to 4 hard disks. J1 - SAF-TE connector BEEP1 – Speaker Alarm (speaker): the speaker emits and audible alarm in the case of disk/array failure. -
Page 13: Installing The Rocketraid 3522 Host Adapter
RocketRAID 3522 Hardware Description/Installation 2 - Installing the RocketRAID 3522 Host Adapter Note: Make sure the system is powered-off before installing the RocketRAID 3522 host adapter. The RocketRAID 3522 includes both standard and low-profile brackets. It may be necessary to attach the low-profile bracket in place of the standard bracket, depend- ing upon the chassis design. -
Page 14: Verifying Installation
RocketRAID 3522 Hardware Description/Installation 3 - Verifying Installation Once the RocketRAID 3522 host adapter and hard disks have been installed into the disk enclosure, boot-up the system to verify that the hardware is properly recognized. Power on the system. If the system detects the presence of the adapter, the RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility will be displayed during bootup. -
Page 15: Battery Backup
RocketRAID 3522 Hardware Description/Installation 4 - Battery Backup A battery backup option will be available as an optional add-on component. The battery provides additional data security in case of a critical system failure. Data normally lost during a major system fault, such as a power outage or CPU failure, which was in transit at the time of the failure (stored in the card’s onboard cache), will remain viable for up to 72 hours. -
Page 16: Rocketraid 3522 Bios Utility
Chapter 3 RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility Contents of this Chapter: RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility 1 - BIOS Command Overview 2 - Disk Menu 3 - Array Menu 4 - Controller Menu... -
Page 17: Bios Command Overview
RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility The RocketRAID 3522’s BIOS Utility can be accessed using the “Ctrl+H” command. This command should be displayed automatically when the RocketRAID 3522’s BIOS screen appears during the system’s boot up procedure. 1 - BIOS Command Overview The RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility provides a wide selection of RAID related commands. -
Page 18: Disk Menu
RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility Press [ALT + S] to open the “System” menu in the figure 1; then select “Supervisor mode”, and press ENTER. This will open the user authentication interface. Enter the appropriate password and then press ENTER. The initial password is “hpt”. 2 - Disk Menu Press [ALT + D] to access the “Disk”... -
Page 19: Array Menu
RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility Note: If the selected disk has already been initialized, the BIOS utility will display a warning message, but will continue to initialize the remaining disks. Warning: Initializing a disk may result in data loss – do not initialize disks that contain critical data. - Page 20 RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility Note: Variable Sector Size (VSS) for over 2TB support in 32bit LBA OS. It changes the sector size from default 512 Bytes to 4k Bytes etc. the maximum volume capacity up to 16TB. This option works under Windows platform only. And it CANNOT be converted to Dynamic Disk, because 4k sector size is not a standard format.
-
Page 21: Controller Menu
RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility Start Task – select this option to schedule specific RAID maintenance tasks such as RAID Verification. Stop Task – use this option to terminate scheduled tasks. Set boot - use this option to set an array to act as a boot volume. Note: This setting is dependent on the motherboard’s BIOS configuration. - Page 22 RocketRAID 3522 BIOS Utility Network Setting Use this menu to configure the RocketRAID card’s network settings. Access the Controller menu, select “Network” and press ENTER. You can select “Use automatic config” to request the network information from the system, or configure the settings manually.
- Page 23 Chapter 4 RocketRAID 3522 Driver and Software Installation Microsoft Windows (2000, XP, 2003 Server, Vista) Contents of this Chapter: Driver and Software CD Windows Driver Installation...
-
Page 24: Driver And Software Cd
RocketRAID 3522 Driver and Software Installation Driver and Software CD The RocketRAID 3522 retail box includes a Driver and Software CD. This CD can be used to generate driver diskettes, and install the RAID Management software for a variety of operating systems. To create a driver diskette: Insert the CD into the system’s CD/DVD drive. - Page 25 RocketRAID 3522 Driver and Software Installation Click on the “Please Select the Diskette you want to create” drop-down button, and select the appropriate OS from the list. Click on the “OK” button to create the driver diskette. To install the RAID software: Click on “Install RAID Management Software”.
-
Page 26: Windows Driver Installation
RocketRAID 3522 Driver and Software Installation Windows Driver Installation Before installing the RocketRAID 3522 device driver, make sure the RocketRAID 3522 host adapter and all required hard disks have been installed into the system’s chassis (refer to the Hardware Installation section, pages 2-2, 2-3). Installing the RocketRAID 3522 driver for an existing Windows XP/2003/x64 system After the operating system has booted, Windows will automatically detect the RocketRAID 3522, and request that a device driver be installed. - Page 27 RocketRAID 3522 Driver and Software Installation Installing the RocketRAID 3522 driver during a fresh Windows 2000/XP/2003/x64 installation After booting from the Windows 2000/XP/2003 CD-ROM, when the Windows Setup blue screen appears, look towards the bottom of the screen. Windows will prompt you to press the F6 key if you want to install a third party SCSI or RAID driver.
- Page 28 RocketRAID 3522 Driver and Software Installation When asked: “Would you like to install this driver software?”, select “Install”. Reboot the system when prompted. The RocketRAID 3522 will be available for use after Vista reboots. Installation Verification After the driver has been installed, and the system has been restarted: Click the Start button, then right-click My Computer icon.
-
Page 29: Web Raid Management Interface
Chapter 5 RocketRAID 3522 Web RAID Management Interface Contents of this Chapter: 1 - Web RAID Management Interface 2 - Preparing Hard disks 3 - Array Management 4 - Device Management 5 - Configuring Spare Disks 6 - Managing Events and Tasks 7 - Settings... -
Page 30: Web Raid Management Interface
1 Web RAID Management Interface There are two methods to access the RocketRAID 3522’s web-based RAID management interface: Use HighPoint In-band Management Service or use the adapter’s Ethernet port (out-of-band management). The Web RAID Management interface is a firmware-based utility. If you are using the adapter’s Ethernet port, you need no additional software and configuration on the host... -
Page 31: Preparing Hard Disks
Web RAID Management Interface The in-band management software provides an access URL for each controller on the system. You can access the RAID management interface for each controller through its access URL. Then Select the controller’s Access URL by click the link http://127.0.0.1:7412 You will be asked for the User and Password to login. -
Page 32: Array Management
Web RAID Management Interface 3) Checkmark each disk you wish to initialize, and click the Submit button. Warning: initializing disks may delete data stored on the selected disks. Legacy Disks Disks that already contain data or have been partitioned will be recognized as “Legacy Disks”. - Page 33 Web RAID Management Interface If you are creating a redundant RAID array (RAID1, 5, 6, 10, 50), select an initialization option for the array. Note: An un-initialized RAID1 or RAID10 array can still provide redundancy in case of a disk failure. A RAID5 array, however, is not fault-tolerant until initializa- tion is finished.
- Page 34 Web RAID Management Interface 3) Click the Delete button. Note: An array in use by the operating system cannot be deleted. Any data stored on a deleted array will be inaccessible Array Maintenance – Rebuilding/Verifying/Modifying RAID arrays Rebuilding a Failed Array When an array member in a redundant array fails, the array will be listed as broken.
- Page 35 Web RAID Management Interface 2) Highlight the desired RAID array 3) Click the “Maintenance” button. Click the Verify button to start the verify process. OCE/ORLM – modifying existing RAID arrays Expanding/Migrating an Array With the OCE/ORLM function, you can migrate an array from one RAID level to another RAID level and/or expand the array dynamically, even under I/O load.
- Page 36 Web RAID Management Interface An unexpected system crash may result in data loss while performing OCE/ORLM on an array. We strongly recommend backing up data before starting the OCE/ORLM process. After the OCE/ORLM procedure has completed, reboot the system. Other RAID related Functions Renaming an Array You are free to rename RAID arrays.
-
Page 37: Device Management
Web RAID Management Interface 4 Device Management Select the “Manage - Device” function to access the device management page. Change Device Settings Depending upon the capabilities RAID controller and hard disks drives in use, several configurable device settings may be available: Read Ahead, Write Cache, TCQ, and NCQ. - Page 38 Web RAID Management Interface User can also use the Web RAID management to upgrade controller’s firmware. SHI – Storage Health Inspector The primary SHI interface displays a brief “health” summary of each hard disk. Controller ID Which controller /card the disk is attached to. Port # Port location of the hard disk...
- Page 39 Web RAID Management Interface Device SSN# Serial number of the hard disk RAID RAID/Non-RAID status Temperature (in Fahrenheit) of the hard disk (Celsius is displayed under the SMART status) Bad Sectors/Found & Repaired The card is capable of repairing bad sectors – a summary of this activity is presented here.
- Page 40 Web RAID Management Interface Note: S.M.A.R.T attribute data is drive-specific. The software includes a list of definitions for popular drive models/manufacturers. Unknown S.M.A.R.T. attributes will be shown as “unknown”. You can add the attribute definitions for your drive in the file smart.def (which resides in the software installation directory). Rescan Devices When you physically add drives to the controller while the system is running, you can rescan the controller to reflect the change.
-
Page 41: Configuring Spare Disks
Web RAID Management Interface To rescan the devices: 1) Select menu “Manage - Device”. 2) Click “Rescan Devices” button. Note: When you are hot-plugging an entire array, run rescan only after all array members (hard disks) have been physically plugged or unplugged from the system. You can rescan all the devices at once using the Rescan function on the Array Management page. -
Page 42: Managing Events And Tasks
Managing Tasks With the HighPoint RAID Management Software, you can configure and schedule back- ground rebuild and verify tasks to help maintain the integrity of your drives and data. You can select menu “Task” to enter Task Management page. -
Page 43: Settings
Web RAID Management Interface Scheduling a Task To add a task schedule: 1) Select the array that you want to verify or rebuild. 2) Enter a name for the task. 3) Configure the frequency for the task. 4) Check the Submit button. Delete a Scheduled Task To delete a task schedule: 1) Select a task from the Tasks List. - Page 44 Web RAID Management Interface Settings>System The System Setting page include SAF-TE config file setting, Audible Alarm setting, Staggered Spinup setting, Spindown Idle Disk setting, Rebuild priority setting and Auto Rebuild setting. The Upload SAF-TE config file option allow user to upload the special SAF-TE config files.
- Page 45 Web RAID Management Interface Settings>User This setting allows you to alter the default password (when logging on). Enter a new password and click the “Change Password” button to change the current user’s password. Settings>Email Enabling E-mail notification: To configure E-mail notification: 1) Select the “Enable Event Notification”...
- Page 46 Web RAID Management Interface To test E-mail notification: 1) Enter the necessary information for the recipient. 2) Click the Test button. If the software is unable to send a test message, an error will be displayed. Double check the recipient entries and make sure the information is correct. Settings>SNMP You can set three SNMP Trap IP address and trap type, this setting will be saved in the flash.
-
Page 47: Linux Driver Support
Chapter 6 Linux Driver Support Contents of this Chapter: Fedora 7 Linux installation Overview Red Hat Enterprise 5 Overview SuSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) installation Overview... - Page 48 Linux Driver Support 1 - Fedora 7 Linux installation Overview This section provides instructions describing how to install and utilize the RocketRAID host adapter on a Fedora 7 Linux system. 2 - Installing Fedora 7 on the RocketRAID 3522 Host Adapter Note: If the OS is running kernel that differs from the one supported by the precompiled driver, the precompiled drivers cannot be used.
- Page 49 Linux Driver Support 3 - Installing the RocketRAID 3522 driver for an Exist- ing System Note: If a SCSI adapter is used to boot the system, make sure the RocketRAID host adapter BIOS loads/posts after the SCSI adapter’s BIOS. It may be necessary to move the adapter(s) to another PCI slot.
- Page 50 Linux Driver Support Then, instruct the system to load the module when booting. Use the following commands: #echo “modprobe hptiop” > /etc/init.d/hptdriver #chmod 755 /etc/init.d/hptdriver #ln –sf /etc/init.d/hptdriver /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S01hptdriver #ln –sf /etc/init.d/hptdriver /etc/rc.d/rc4.d/S01hptdriver #ln –sf /etc/init.d/hptdriver /etc/rc.d/rc5.d/S01hptdriver Step 4 Configure System to Mount Volumes during Startup The system can be instructed to automatically mount the array(s) during startup by modifying the file”/etc/fstab”.
- Page 51 Linux Driver Support 1 - Red Hat Enterprise 5 Installation Overview This section provides instructions describing how to install and utilize the RocketRAID host adapter on a Red Hat Enterprise 3 Linux system. 2 - Installing Red Hat Enterprise 5 (AS, ES, WS) Linux on the RocketRAID 3522 controller To install Red Hat Enterprise Linux onto disks or RAID arrays attached to RocketRAID host adapter:...
- Page 52 Linux Driver Support Note: 1. The system device mapping order is the same as the order shown in RocketRAID BIOS Setting Utility. If no other SCSI adapters are installed, the device marked as “BOOT” or “HDD0”will identified as /dev/sda, “HDD1” as /dev/sdb, “HDD2” as /dev/sdc, etc.
- Page 53 Linux Driver Support Step 3 Configure System to Automatically Load the Driver To avoid typing in “insmod hptiop.ko” each time the operating system is booted, the system must be instructed to automatically load the module during bootup. To install the module, type in the following commands (first change to the directory where the proper hptiop.ko file is located): # install -d /lib/modules/‘uname –r‘/kernel/drivers/scsi # install -c hptiop.ko /lib/modules/‘uname –r‘/kernel/drivers/scsi...
- Page 54 Linux Driver Support Example: # gzip -dc /boot/initrd-xxx.img > /tmp/initrd.ext2 # mkdir /mnt/initrd # mount -o loop /tmp/initrd.ext2 /mnt/initrd # cp /tmp/hptiop.ko /mnt/initrd/lib/hptiop_00.ko # umount /mnt/initrd # gzip -c /tmp/initrd.ext2 > /boot/initrd-xxx.img If you are using lilo to boot the system, use “lilo” to reinstall the RAM disk: # lilo Update hptiop.ko in /lib/modules: # cp /tmp/hptiop.ko /lib/modules/‘uname –r‘/kernel/drivers/scsi/hptiop.ko...
- Page 55 Linux Driver Support 1 - SuSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) installation Overview This section provides instructions describing how to install and utilize the RocketRAID host adapter on a SuSE (SLES) Linux system. 2 - Installing SLES Linux on the RocketRAID 3522 Host Adapter Note: If the OS is running kernel that differs from the one supported by the precompiled driver, the precompiled drivers cannot be used.
- Page 56 Linux Driver Support Additional Installation Notes: The system device mapping order is the same as the order shown in RocketRAID host adapter’s BIOS Setting Utility. If no other SCSI adapters are installed, the device marked as “BOOT” or “HDD0” will be identified as /dev/sda, “HDD1” as /dev/sdb, “HDD2”...
- Page 57 Linux Driver Support # mount /dev/fd0 /mnt/floppy # cd / # tar xfz /mnt/floppy/linux/suse/i386-sles9/install/update.tar.gz The driver modules will be extracted to the directory /lib/modules/[kernel-ver]/kernel/ drivers/scsi/ . After you have extracted the driver module, you can load it by following commands: # modprobe sd_mod # insmod hptiop.ko Then you can access the arrays attached to the controller as SCSI devices (e.g.
- Page 58 Linux Driver Support 2. Run the “depmod” command to update the module configuration: # depmod 3. Next, run the “mkinitrd” command to update the initrd file: # mkinitrd 4. If you are using the lilo boot loader, run lilo again: # lilo Step 5 Configure System to Mount Volumes during Startup The system can be instructed to automatically mount the array(s) during startup by...
-
Page 59: Freebsd Driver Support
Chapter 7 FreeBSD Driver Support Contents of this Chapter: 1 - Installing FreeBSD on the RocketRAID 3522 Controller 2 - Installing the RocketRAID 3522 Driver on an Existing System 3 - Updating the Driver 4 - Uninstalling the Driver... -
Page 60: Installing Freebsd On The Rocketraid 3522 Controller
FreeBSD Driver Support 1 - Installing FreeBSD on the RocketRAID 3522 Con- troller If you would like to install FreeBSD onto arrays attached to the RocketRAID host adapter, please follow the steps below. Step 1 Prepare the Driver Diskette When installing FreeBSD to a disk or array attached to the RocketRAID host adapter, you must prepare a driver diskette before starting the installation procedure. - Page 61 FreeBSD Driver Support B o o t i n g [ k e r n e l ] s e c o n d s … < - p r e s s S P A C E k e y A prompted label “ok”...
- Page 62 FreeBSD Driver Support for FreeBSD 5.1-RELEASE ok load disk0:hptiop-5.1.ko for FreeBSD 5.2.1-RELEASE ok load disk0:hptiop-5.2.1.ko for FreeBSD 5.3-RELEASE ok load disk0:hptiop-5.3.ko for FreeBSD 5.4-RELEASE ok load disk0:hptiop-5.4.ko for FreeBSD 5.3-AMD64-RELEASE ok load disk0:hptiop-5.3-amd64.ko for FreeBSD 5.4-AMD64-RELEASE ok load disk0:hptiop-5.4-amd64.ko for FreeBSD 6.0-AMD64-RELEASE ok load disk0:hptiop-6.0-amd64.ko for FreeBSD 6.1-RELEASE ok load disk0: hptiop-6.1.ko...
-
Page 63: Installing The Rocketraid 3522 Driver On An Existing System
FreeBSD Driver Support Before exiting installation, an additional step must be taken to copy the RocketRAID driver module to the system. On the driver diskette, there is a setup script labeled “postinstall”, which will complete this task. Before rebooting the system, press Alt-F4 to enter the command shell, and type the following commands: # mount –o ro /dev/fd0 /mnt... - Page 64 FreeBSD Driver Support For FreeBSD 5.x: # mdconfig –a –t vnode –f freebsd_5.x.img –u 0 # mount /dev/md0 /mnt # cp /mnt/hptiop-xxx.ko /boot/kernel/hptiop.ko # umount /mnt # mdconfig –d –u md0 Step 2 Test the Driver Module Test the driver module to ensure that it works with the system, by loading it during bootup.
-
Page 65: Updating The Driver
FreeBSD Driver Support Note: If you have configured a RAID 10 using 4 disks, it will be registered to system as device /dev/da0. You can use “/stand/sysinstall” to create partitions and disklabels (like da0s1e) on da0. Then, create a new filesystem using “newfs /dev/ da0s1e”. -
Page 66: Mac Osx Driver
Chapter 8 Mac OSX Driver Contents of this Chapter: Installing the driver and RAID utility... -
Page 67: Installing The Driver And Raid Utility
Mac OSX Driver 1 Installing the driver and RAID utility Installing the package 1) Double click the package labeled “rr3xxx_4xxx-MacOSX-universal-vxxx.dmg” to start the installation process (“xxx” refers to the revision of the driver). This will open the driver and software packag. 2) Double click the “rr3xxx_4xxx-MacOSX-universal-vxxx.dmg”... -
Page 68: Appendix
Appendix Customer Support... - Page 69 Customer Support Customer Support If you encounter any problems while utilizing the RocketRAID 3522, or have any questions about this or any other HighPoint product, feel free to contact our Customer Support Department. Troubleshooting Checklist Before contacting our Customer Support department: Make sure the latest BIOS, driver and RAID Software have been installed for the RocketRAID 3522.
- Page 70 FCC Part 15 Class B Radio Frequency Interference statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
















Need help?
Do you have a question about the RocketRAID 3522 SATAII and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers