Summary of Contents for Rohde & Schwarz R&S FSW-K106
- Page 1 ® R&S FSW-K106 LTE NB-IoT Measurement Application (Downlink) User Manual (;ÜÉU2) 1178593702 Version 16...
- Page 2 This manual applies to the following FSW models with firmware version 6.00 and later: ● R&S ® FSW8 (1331.5003K08 / 1312.8000K08) ● ® R&S FSW13 (1331.5003K13 / 1312.8000K13) ● ® R&S FSW26 (1331.5003K26 / 1312.8000K26) ● R&S ® FSW43 (1331.5003K43 / 1312.8000K43) ●...
-
Page 3: Table Of Contents
® Contents R&S FSW-K106 Contents 1 Documentation overview...............7 Getting started manual....................7 User manuals and help....................7 Service manual......................7 Instrument security procedures.................. 8 Printed safety instructions...................8 Specifications and brochures..................8 Release notes and open-source acknowledgment (OSA).........8 Application notes, application cards, white papers, etc........... 9 Videos..........................9 2 Welcome to the LTE NB-IoT measurement application.... - Page 4 ® Contents R&S FSW-K106 4.2.6 Input source configuration.....................44 4.2.7 Frequency configuration....................50 4.2.8 Amplitude configuration....................51 4.2.9 Configuring the data capture..................55 4.2.10 Trigger configuration..................... 57 4.2.11 Parameter estimation and tracking................58 4.2.12 Configuring demodulation parameters................60 4.2.13 Automatic configuration....................61 Time alignment error measurements................ 62 Frequency sweep measurements................62 4.4.1 ACLR signal description....................62...
- Page 5 ® Contents R&S FSW-K106 Status register......................79 NB-IoT application selection..................80 Screen layout.......................84 6.5.1 General layout.......................84 6.5.2 Layout of a single channel.................... 85 Measurement control....................93 6.6.1 Measurements......................93 6.6.2 Measurement sequences....................95 Trace data readout...................... 97 6.7.1 The TRACe[:DATA] command..................97 6.7.2 Result readout......................108 Numeric result readout.....................109 6.8.1...
- Page 6 ® Contents R&S FSW-K106 User Manual 1178.5937.02 ─ 16...
-
Page 7: Documentation Overview
® Documentation overview R&S FSW-K106 Service manual 1 Documentation overview This section provides an overview of the FSW user documentation. Unless specified otherwise, you find the documents at: www.rohde-schwarz.com/manual/FSW Further documents are available at: www.rohde-schwarz.com/product/FSW 1.1 Getting started manual Introduces the FSW and describes how to set up and start working with the product. Includes basic operations, typical measurement examples, and general information, e.g. -
Page 8: Instrument Security Procedures
® Documentation overview R&S FSW-K106 Release notes and open-source acknowledgment (OSA) The service manual is available for registered users on the global Rohde & Schwarz information system (GLORIS): https://gloris.rohde-schwarz.com 1.4 Instrument security procedures Deals with security issues when working with the FSW in secure areas. It is available for download on the internet. -
Page 9: Application Notes, Application Cards, White Papers, Etc
® Documentation overview R&S FSW-K106 Videos 1.8 Application notes, application cards, white papers, etc. These documents deal with special applications or background information on particu- lar topics. www.rohde-schwarz.com/application/FSW 1.9 Videos Find various videos on Rohde & Schwarz products and test and measurement topics on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@RohdeundSchwarz User Manual 1178.5937.02 ─... -
Page 10: Welcome To The Lte Nb-Iot Measurement Application
® Welcome to the LTE NB-IoT measurement application R&S FSW-K106 Starting the LTE NB-IoT measurement application 2 Welcome to the LTE NB-IoT measurement application The LTE NB-IoT measurement application is a firmware application that adds function- ality to measure on NB-IoT signals according to the 3GPP standard to the FSW. This user manual contains a description of the functionality that the application pro- vides, including remote control operation. -
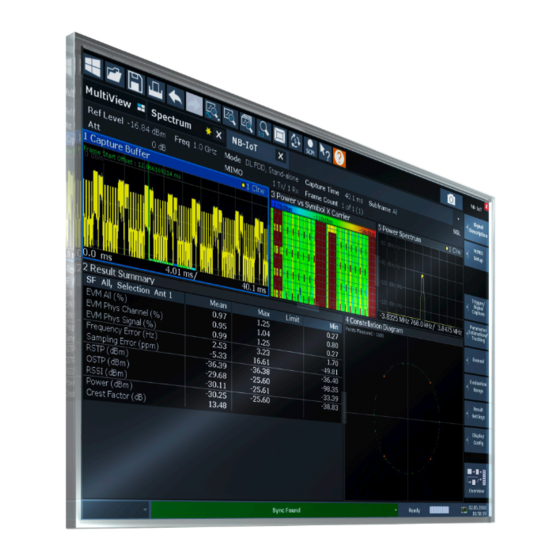
Page 11: Understanding The Display Information
® Welcome to the LTE NB-IoT measurement application R&S FSW-K106 Understanding the display information 2.3 Understanding the display information The following figure shows a measurement diagram during NB-IoT operation. All differ- ent information areas are labeled. They are explained in more detail in the following sections. - Page 12 ® Welcome to the LTE NB-IoT measurement application R&S FSW-K106 Understanding the display information Frame Count Number of frames that have been captured Subframe Subframe considered in the signal analysis In addition, the channel bar displays information on instrument settings that affect the measurement results even though this is not immediately apparent from the display of the measured values (for example trigger settings).
-
Page 13: Measurements And Result Displays
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 Selecting measurements 3 Measurements and result displays The LTE NB-IoT measurement application measures and analyzes various aspects of an NB-IoT signal. It features several measurements and result displays. Measurements represent differ- ent ways of processing the captured data during the digital signal processing. Result displays are different representations of the measurement results. -
Page 14: Selecting Result Displays
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 Selecting result displays Time alignment error Time alignment error (TAE) measurements record, process and demodulate the sig- nal's I/Q data. The result displays available for TAE measurements indicate how well the antennas in a multi-antenna system are aligned. For TAE measurements, you can combine the result displays in any way. -
Page 15: Performing Measurements
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 Selecting the operating mode From that predefined state, add and remove result displays as you like from the Smart- Grid menu. Remote command: on page 86 LAYout:ADD[:WINDow]? 3.3 Performing measurements By default, the application measures the signal continuously. In "Continuous Sweep" mode, the FSW captures and analyzes the data again and again. -
Page 16: I/Q Measurements
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements The analysis interval is automatically determined according to the Capture Time have defined. The analysis interval cannot be edited directly in the NB-IoT application, but is changed automatically when you change the evaluation range. The currently used analysis interval (in seconds, related to capture buffer start) is indicated in the window header for each result display. - Page 17 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Power vs Symbol x Carrier....................26 Allocation ID vs Symbol x Carrier..................27 Result Summary......................27 Marker Table......................... 29 Capture Buffer The "Capture Buffer" shows the complete range of captured data for the last data cap- ture.
- Page 18 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Figure 3-2: Capture buffer after a zoom has been applied Remote command: Selection: LAY:ADD ? '1',LEFT,CBUF Query (y-axis): TRACe:DATA? Query (x-axis): on page 107 TRACe<n>[:DATA]:X? Subframe start offset: on page 114 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:TFRame? EVM vs Carrier The "EVM vs Carrier"...
- Page 19 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Remote command: Selection LAY:ADD ? '1',LEFT,EVCA Query (y-axis): TRACe:DATA? Query (x-axis): on page 107 TRACe<n>[:DATA]:X? EVM vs Symbol The "EVM vs Symbol" result display shows the error vector magnitude (EVM) of the OFDM symbols.
- Page 20 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements EVM vs Subframe The "EVM vs Subframe" result display shows the Error Vector Magnitude (EVM) for each subframe. You can use it as a debugging technique to identify a subframe whose EVM is too high.
- Page 21 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Remote command: Selection: LAY:ADD ? '1',LEFT,FEVS Query (y-axis): TRACe:DATA? Query (x-axis): on page 107 TRACe<n>[:DATA]:X? Power Spectrum The "Power Spectrum" shows the power density of the complete capture buffer in dBm/Hz. The displayed bandwidth is always 7.68 MHz.
- Page 22 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Group Delay This "Group Delay" shows the group delay of each subcarrier. The measurement is evaluated over the currently selected slot in the currently selected subframe. The currently selected subframe depends on your selection. The x-axis represents the frequency.
- Page 23 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements In the default state, the result display evaluates the full range of the measured input data. Each color represents a modulation type. ● : BPSK ● : RBPSK ● : MIXTURE ●...
- Page 24 ® R&S FSW-K106 Measurements and result displays I/Q measurements Mean Mean power Peak Peak power Crest Crest factor (peak power – mean power) 10 % 10 % probability that the level exceeds mean power + [x] dB 1 % probability that the level exceeds mean power + [x] dB 0.1 % 0.1 % probability that the level exceeds mean power + [x] dB 0.01 %...
- Page 25 ® R&S FSW-K106 Measurements and result displays I/Q measurements Remote command: Selection: LAY:ADD ? '1',LEFT,ASUM Query: TRACe:DATA? Bitstream The "Bitstream" shows the demodulated data stream for the data allocations. At the end of the table is a summary of the bitstream for certain configurations. ●...
- Page 26 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Indicates the position of the table row's first bit or symbol within the complete stream. ● Bit Stream The actual bit stream. Remote command: Selection: LAY:ADD ? '1',LEFT,BSTR EVM vs Symbol x Carrier The "EVM vs Symbol x Carrier"...
- Page 27 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Allocation ID vs Symbol x Carrier The "Allocation ID vs Symbol x Carrier" result display is a graphical representation of the structure of the analyzed frame. It shows the allocation type of each subcarrier in each symbol of the received signal.
- Page 28 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements In addition to the red font, the application also puts a red star ( ) in front of failed results. By default, all EVM results are in %. To view the EVM results in dB, change the Unit.
- Page 29 ® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements NB-IoT Power Shows the power of all resource elements used by NB-IoT. on page 113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:NBPower[:AVERage]? Crest Factor Shows the peak-to-average power ratio of captured signal. on page 110 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:CRESt[:AVERage]? Marker Table Displays a table with the current marker values for the active markers.
-
Page 30: Time Alignment Error
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 Time alignment error 3.6 Time alignment error Access: "Overview" > "Select Measurement" > "Time Alignment" The time alignment error measurement captures and analyzes new I/Q data when you select it. The time alignment error measurement only works under the following conditions: ●... -
Page 31: Frequency Sweep Measurements
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 Frequency sweep measurements You can select the reference antenna from the dropdown menu in the result display. You can also select the reference antenna in the MIMO Setup - if you change them in one place, they are also changed in the other. -
Page 32: Result Display Selection: Layout:add[:Window]? On Page 86 Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio (Aclr)
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 Frequency sweep measurements Remote command: Measurement selection: on page 120 CONFigure[:LTE]:MEASurement Result display selection: on page 86 LAYout:ADD[:WINDow]? Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio (ACLR)..............32 └ Result diagram....................32 └ Result summary....................32 Spectrum Emission Mask (SEM).................. -
Page 33: Spectrum Emission Mask (Sem)
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 Frequency sweep measurements ● Channel Shows the channel type (Tx, adjacent or alternate channel). ● Bandwidth Shows the channel bandwidth. ● Offset Shows the channel spacing. ● Power Shows the power of the Tx channel. ●... -
Page 34: Marker Peak List
® Measurements and result displays R&S FSW-K106 Frequency sweep measurements Shows the absolute frequency whose power measurement being closest to the limit line for the corresponding frequency segment. ● Power Abs Shows the absolute measured power of the frequency whose power is closest to the limit. -
Page 35: Configuration
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 Configuration overview 4 Configuration LTE NB-IoT measurements require a special application on the FSW, which you can select by adding a new measurement channel or replacing an existing one. When you start the LTE NB-IoT application, the FSW starts to measure the input signal with the default configuration or the configuration of the last measurement (if you haven't performed a preset since then). - Page 36 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 Configuration overview In addition to the main measurement settings, the "Overview" provides quick access to the main settings dialog boxes. The individual configuration steps are displayed in the order of the data flow. Thus, you can easily configure an entire measurement channel from input over processing to output and analysis by stepping through the dialog boxes as indicated in the "Overview".
-
Page 37: I/Q Measurements
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Note: Do not confuse "Preset Channel" with the [Preset] key, which restores the entire instrument to its default values and thus closes all channels on the FSW (except for the default channel)! Remote command: on page 121 SYSTem:PRESet:CHANnel[:EXEC] Select Measurement... - Page 38 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements The contents of the "Signal Description" dialog box depend on the deployment you have selected. The remote commands required to configure the physical signal characteristics are described in "Physical settings" on page 122. Selecting the NB-IoT mode...................
- Page 39 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements The application supports the following deployments. ● "Stand Alone" The NB-IoT signal uses a dedicated spectrum outside of an LTE band, for example a frequency band currently used by GSM. With a carrier bandwidth of 200 kHz in GSM, there is enough room for an NB-IoT carrier (180 kHz), including a guard interval of 10 kHz on both sides of the carrier.
- Page 40 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Note that the 1.4 MHz bandwidth is not supported for in band transmission of NB- IoT signals. ● "E-UTRA CRS Sequence Info" Cell-specific reference signal sequence. The sequence defines the assignment of resources between LTE and NB-IoT. These sequences are defined in 3GPP 36.213, chapter 16.8.
- Page 41 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements In addition, the application shows various physical properties of the NB-IoT signal. ● "NB-IoT Channel Bandwidth", which is currently always 200 kHz. ● "NB-IoT Center Frequency", which is calculated from the E-UTRA channel charac- teristics.
-
Page 42: Test Scenarios
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements 4.2.2 Test scenarios Access: "Overview" > "Signal Description" > "Test Models" Test scenarios are descriptions of specific NB-IoT signals for standardized testing of DUTs. These test scenarios are stored in .allocation files. You can select, manage and create test scenarios in the "Test Models"... -
Page 43: Npdsch Settings
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Remote command: on page 129 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:MIMO:CONFig Tx Antenna Selection The "Tx Antenna Selection" selects the antenna(s) you want to analyze. The number of menu items depends on the number of antennas in the system. Each antenna corresponds to a cell-specific reference signal. -
Page 44: Configuring The Control Channel
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements This information about the NPDSCH is required to distinguish between NPDSCH and NPDCCH information, which in turn is required to calculate bit error information in the bitstream result display. Remote command: State: on page 130 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:NPDSch:DMODulation Subframes: on page 130... - Page 45 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements ● "Impedance" on page 55 Direct Path........................45 High Pass Filter 1 to 3 GHz...................45 YIG-Preselector......................45 Input Connector......................46 Direct Path Enables or disables the use of the direct path for small frequencies. In spectrum analyzers, passive analog mixers are used for the first conversion of the input signal.
- Page 46 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Note: Note that the YIG-preselector is active only on frequencies greater than 8 GHz. Therefore, switching the YIG-preselector on or off has no effect if the frequency is below that value. To use the optional 90 GHz frequency extension (R&S FSW-B90G), the YIG-preselec- tor must be disabled.
- Page 47 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements "Digital I/Q" is only available if the optional "Digital Baseband" is installed. Remote command: on page 137 INPut:SELect Input Sample Rate Defines the sample rate of the digital I/Q signal source. This sample rate must corre- spond with the sample rate provided by the connected device, e.g.
- Page 48 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements 4.2.6.4 Analog baseband Access: "Overview" > "Input / Frontend" > "Input Source" > "Analog BB" Analog Baseband Input State..................48 Mode........................48 Input Configuration......................48 High Accuracy Timing Trigger - Baseband - RF............49 Analog Baseband Input State Enables or disable the use of the "Analog Baseband"...
- Page 49 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Remote command: on page 136 INPut:IQ:BALanced[:STATe] High Accuracy Timing Trigger - Baseband - RF Activates a mode with enhanced timing accuracy between analog baseband, RF and external trigger signals. Note: Prerequisites for previous models of FSW. For FSW models with a serial number lower than 103000, special prerequisites and restrictions apply for high accuracy timing: ●...
-
Page 50: Frequency Configuration
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements I/Q Input File State Enables input from the selected I/Q input file. If enabled, the application performs measurements on the data from this file. Thus, most measurement settings related to data acquisition (attenuation, center frequency, measurement bandwidth, sample rate) cannot be changed. -
Page 51: Amplitude Configuration
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements The remote commands required to configure the frequency are described in Chap- ter 6.9.2.3, "Frequency configuration", on page 139. Signal Frequency......................51 └ Center Frequency................... 51 └ Frequency Stepsize..................51 Signal Frequency For measurements with an RF input source, you have to match the center frequency of the analyzer to the frequency of the signal. - Page 52 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements The remote commands required to configure the amplitude are described in Chap- ter 6.9.2.4, "Amplitude configuration", on page 141. Reference Level......................52 └ Auto Level....................... 52 └ Reference Level Offset................... 53 Attenuating the Signal....................53 └...
- Page 53 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements The application shows the current reference level (including RF and external attenua- tion) in the channel bar. Remote command: Automatic: on page 156 [SENSe:]ADJust:LEVel<ant> Auto level mode: [SENSe:]ADJust:CONFigure:LEVel:DURation:MODE on page 156 Auto level time: on page 155 [SENSe:]ADJust:CONFigure:LEVel:DURation Reference Level Offset ←...
- Page 54 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Remote command: State: on page 142 INPut:ATTenuation<ant>:AUTO Level: on page 142 INPut:ATTenuation<ant> Electronic Attenuation ← Attenuating the Signal Controls the optional electronic attenuator. If you select automatic signal attenuation, the attenuation level is coupled to the refer- ence level.
-
Page 55: Configuring The Data Capture
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements For an active external frontend, input coupling is always DC. Not available for input from the optional "Analog Baseband" interface. Not available for input from the optional "Digital Baseband" interface. AC coupling blocks any DC voltage from the input signal. AC coupling is activated by default to prevent damage to the instrument. - Page 56 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Capture Time The "Capture Time" corresponds to the time of one measurement. Therefore, it defines the amount of data the application captures during a single measurement (or sweep). By default, the application captures 20.1 ms of data to make sure that at least one complete NB-IoT frame is captured in the measurement.
-
Page 57: Trigger Configuration
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements ● If you capture the data according to the standard. Remote command: on page 145 [SENSe:][LTE:]FRAMe:COUNt 4.2.10 Trigger configuration Access: "Overview" > "Trig / Sig Capture" > "Trigger" A trigger allows you to capture those parts of the signal that you are really interested While the application runs freely and analyzes all signal data in its default state, no matter if the signal contains information or not, a trigger initiates a measurement only under certain circumstances (the trigger event). -
Page 58: Parameter Estimation And Tracking
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements ● IF Power The trigger event is the level of the intermediate frequency (IF). The measurement starts when the level of the IF meets or exceeds the trigger level. ● RF Power The trigger event is the level measured at the RF input. The measurement starts when the level of the signal meets or exceeds the trigger level. - Page 59 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Boosting Estimation...................... 59 Channel Estimation....................... 59 Phase..........................59 Time Tracking........................59 Boosting Estimation Turns boosting estimation on and off. Boosting estimation, when you turn it on, automatically sets the relative power settings of all physical channels, the NPSS and NSSS by analyzing the signal. Boosting estimation is always active.
-
Page 60: Configuring Demodulation Parameters
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements Remote command: on page 155 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:TRACking:TIME 4.2.12 Configuring demodulation parameters Access: "Overview" > "Demodulation" Demodulation settings contain settings that describe signal processing and the way the signal is measured. The remote commands required to configure the demodulation are described in Chap- ter 6.9.2.7, "Demodulation",... -
Page 61: Automatic Configuration
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 I/Q measurements "At Optimal Calculates the EVM using the optimal timing position. Timing Posi- tion" Remote command: on page 153 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:DEMod:EVMCalc NPDSCH Reference Data Selects the type of reference data to calculate the EVM for the NPDSCH. By default, the FSW automatically detects the NPDSCH reference values and maps the measured values to the nearest reference point. -
Page 62: Time Alignment Error Measurements
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 Frequency sweep measurements Auto Scaling Scales the y-axis for best viewing results. Also see "Automatic scaling of the y-axis" on page 67. Remote command: DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:TRACe<t>:Y[:SCALe]:AUTO on page 164 4.3 Time alignment error measurements Several settings supported by time alignment error measurements are the same as those for I/Q measurements. -
Page 63: Sem Signal Description
® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 Frequency sweep measurements The SEM measurement and its settings are basically the same as in the spectrum application of the FSW. For a comprehensive description, see the FSW user manual. In addition, the ACLR measurement in the NB-IoT application has several exclusive settings not available in the spectrum application. - Page 64 ® Configuration R&S FSW-K106 Frequency sweep measurements In addition to the base station category, the shape of the limit line depends on the power of the NB-IoT carrier. For medium range base stations, the shape of the limit line also depends on the power of the transmission channel.
-
Page 65: Analysis
® Analysis R&S FSW-K106 General analysis tools 5 Analysis The FSW provides various tools to analyze the measurement results. ● General analysis tools.....................65 ● Analysis tools for I/Q measurements..............68 ● Analysis tools for frequency sweep measurements..........72 5.1 General analysis tools The general analysis tools are tools available for all measurements. -
Page 66: Microservice Export
® Analysis R&S FSW-K106 General analysis tools 2. Select "Export" > "I/Q Export". 3. Define a file name and location for the I/Q data. The default file type is iq.tar. 4. Later on, you can import the I/Q data using the I/Q file input source. -
Page 67: Zoom
® Analysis R&S FSW-K106 General analysis tools You can restore the original scale anytime with "Restore Scale". Remote command: DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:TRACe<t>:Y[:SCALe]:MAXimum on page 164 DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:TRACe<t>:Y[:SCALe]:MINimum on page 164 Automatic scaling of the y-axis Usually, the best way to view the results is if they fit ideally in the diagram area and display the complete trace. -
Page 68: Analysis Tools For I/Q Measurements
® Analysis R&S FSW-K106 Analysis tools for I/Q measurements For I/Q measurement, the FSW supports up to four markers, for frequency sweep measurements there are more. Markers give either absolute values (normal markers) or values relative to the first marker (deltamarkers). If a result display has more than one trace, for example the "EVM vs Symbol"... -
Page 69: Evaluation Range
® Analysis R&S FSW-K106 Analysis tools for I/Q measurements Add and remove columns as required. 5.2.2 Evaluation range Access: "Overview" > "Evaluation Range" The evaluation range defines the signal parts that are considered during signal analy- sis. Subframe Selection.......................69 Evaluation range for the constellation diagram............. - Page 70 ® Analysis R&S FSW-K106 Analysis tools for I/Q measurements You can apply the filter to the following result displays. ● Result Summary ● EVM vs Carrier / EVM vs Symbol / EVM vs Symbol X Carrier ● Group Delay ● Power vs Symbol X Carrier ●...
-
Page 71: Result Settings
® Analysis R&S FSW-K106 Analysis tools for I/Q measurements 5.2.3 Result settings Access: "Overview" > "Analysis" > "Result Settings" Result settings define the way certain measurement results are displayed. Unit........................71 Bit Stream Format......................71 Carrier Axes........................71 Marker Coupling......................72 EVM Unit The "EVM Unit"... -
Page 72: Analysis Tools For Frequency Sweep Measurements
® Analysis R&S FSW-K106 Analysis tools for frequency sweep measurements X-axis shows the results in terms of the subcarrier number. Remote command: on page 166 UNIT:CAXes Marker Coupling Couples or decouples markers that are active in multiple result displays. When you turn on this feature, the application moves the marker to its new position in all active result displays. -
Page 73: Remote Control
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Common suffixes 6 Remote control The following remote control commands are required to configure and perform LTE NB-IoT measurements in a remote environment. The FSW must already be set up for remote operation in a network as described in the base unit manual. Universal functionality Note that basic tasks that are also performed in the base unit in the same way are not described here. -
Page 74: Introduction
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Introduction Table 6-1: Common suffixes used in remote commands in the LTE NB-IoT measurement application Suffix Value range Description <m> 1..4 Marker <n> 1..16 Window (in the currently selected channel) <t> 1..6 Trace <li> 1 to 8 Limit line <ant>... -
Page 75: Long And Short Form
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Introduction If not specified otherwise, commands can be used both for setting and for querying parameters. If a command can be used for setting or querying only, or if it initiates an event, the usage is stated explicitly. ●... -
Page 76: Optional Keywords
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Introduction If you do not quote a suffix for keywords that support one, a 1 is assumed. Example: DISPlay[:WINDow<1...4>]:ZOOM:STATe enables the zoom in a particular mea- surement window, selected by the suffix at WINDow. DISPlay:WINDow4:ZOOM:STATe ON refers to window 4. 6.2.4 Optional keywords Some keywords are optional and are only part of the syntax because of SCPI compli- ance. - Page 77 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Introduction Example: LAYout:ADD:WINDow Spectrum,LEFT,MTABle Parameters can have different forms of values. ● Numeric values....................... 77 ● Boolean........................78 ● Character data......................78 ● Character strings.....................78 ● Block data....................... 78 6.2.6.1 Numeric values Numeric values can be entered in any form, i.e. with sign, decimal point or exponent. For physical quantities, you can also add the unit.
- Page 78 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Introduction ● INF/NINF Infinity or negative infinity. Represents the numeric values 9.9E37 or -9.9E37. ● Not a number. Represents the numeric value 9.91E37. NAN is returned if errors occur. 6.2.6.2 Boolean Boolean parameters represent two states. The "on" state (logically true) is represented by "ON"...
-
Page 79: Status Register
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Status register The ASCII character # introduces the data block. The next number indicates how many of the following digits describe the length of the data block. The data bytes follow. Dur- ing the transmission of these data bytes, all end or other control signs are ignored until all bytes are transmitted. -
Page 80: Nb-Iot Application Selection
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 NB-IoT application selection Bit No. Meaning 9 to 14 Unused This bit is always 0 6.4 NB-IoT application selection ..................80 INSTrument:CREate:DUPLicate ....................80 INSTrument:CREate[:NEW] ..................81 INSTrument:CREate:REPLace ......................81 INSTrument:DELete ......................81 INSTrument:LIST? .......................83 INSTrument:REName ......................83 INSTrument[:SELect]... - Page 81 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 NB-IoT application selection INSTrument:CREate:REPLace <ChannelName1>, <ChannelType>, <ChannelName2> Replaces a channel with another one. Setting parameters: <ChannelName1> String containing the name of the channel you want to replace. <ChannelType> Channel type of the new channel. For a list of available channel types, see INSTrument:LIST? on page 81.
- Page 82 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 NB-IoT application selection Example: INST:LIST? Result for 3 channels: 'ADEM','Analog Demod','IQ','IQ Analyzer','IQ','IQ Analyzer2' Usage: Query only Table 6-3: Available channel types and default channel names in Signal and Spectrum Analyzer mode Application <ChannelType> Default Channel name*) parameter Spectrum SANALYZER...
- Page 83 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 NB-IoT application selection Application <ChannelType> Default Channel name*) parameter Pulse (FSW-K6) PULSE Pulse "Real-Time Spectrum" RTIM "Real-Time Spectrum" TD-SCDMA BTS (FSW-K76) BTDS TD-SCDMA BTS TD-SCDMA UE (FSW-K77) MTDS TD-SCDMA UE Transient Analysis (FSW-K60) Transient Analysis Verizon 5GTF Measurement Application (V5GTF, V5GT V5GT...
-
Page 84: Screen Layout
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout 6.5 Screen layout ● General layout......................84 ● Layout of a single channel..................85 6.5.1 General layout The following commands are required to configure general window layout, independent of the application. Note that the suffix <n> always refers to the window in the currently selected measure- ment channel. -
Page 85: Layout Of A Single Channel
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout Example: DISP:WIND2:SIZE LARG DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:SELect Sets the focus on the selected result display window. This window is then the active window. For measurements with multiple results in subwindows, the command also selects the subwindow. Use this command to select the (sub)window before querying trace data. Suffix: <n>... - Page 86 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout ....................89 LAYout:REMove[:WINDow] ....................89 LAYout:REPLace[:WINDow] ........................89 LAYout:SPLitter ....................91 LAYout:WINDow<n>:ADD? ..................91 LAYout:WINDow<n>:IDENtify? ....................92 LAYout:WINDow<n>:REMove ..................92 LAYout:WINDow<n>:REPLace ....................93 LAYout:WINDow<n>:TYPE LAYout:ADD[:WINDow]? <WindowName>, <Direction>, <WindowType> Adds a window to the display in the active channel. Is always used as a query so that you immediately obtain the name of the new window as a result.
- Page 87 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout Manual operation: "Capture Buffer" on page 17 "EVM vs Carrier" on page 18 "EVM vs Symbol" on page 19 "EVM vs Subframe" on page 20 "Frequency Error vs Symbol" on page 20 "Power Spectrum" on page 21 "Channel Flatness"...
- Page 88 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout Parameter value Window type CBUF "Capture Buffer" MTAB "Marker Table" PSPE "Power Spectrum" "Time Alignment Error" ACLR and SEM measurements DIAG "Diagram" PEAK "Peak List" MTAB "Marker Table" RSUM "Result Summary" LAYout:CATalog[:WINDow]? Queries the name and index of all active windows in the active channel from top left to bottom right.
- Page 89 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout Example: LAY:IDEN:WIND? '2' Queries the index of the result display named '2'. Response: Usage: Query only LAYout:REMove[:WINDow] <WindowName> Removes a window from the display in the active channel. Setting parameters: <WindowName> String containing the name of the window. In the default state, the name of the window is its index.
- Page 90 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout Note that windows must have a certain minimum size. If the position you define con- flicts with the minimum size of any of the affected windows, the command does not work, but does not return an error. Figure 6-1: SmartGrid coordinates for remote control of the splitters Setting parameters: <Index1>...
- Page 91 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout Example: LAY:SPL 1,4,70 Moves the splitter between window 1 ('Frequency Sweep') and 3 ('"Marker Peak List"') towards the top (70%) of the screen. The following commands have the exact same effect, as any combination of windows above and below the splitter moves the splitter vertically.
- Page 92 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Screen layout Suffix: <n> Window Return values: <WindowName> String containing the name of a window. In the default state, the name of the window is its index. Example: LAY:WIND2:IDEN? Queries the name of the result display in window 2. Response: Usage: Query only...
-
Page 93: Measurement Control
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Measurement control LAYout:WINDow<n>:TYPE <WindowType> Queries or defines the window type of the window specified by the index <n>. The win- dow type determines which results are displayed. For a list of possible window types, on page 86. LAYout:ADD[:WINDow]? Note that this command is not available in all applications and measurements. - Page 94 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Measurement control Now you can send the ABORt command on the remote channel performing the mea- surement. Example: ABOR;:INIT:IMM Aborts the current measurement and immediately starts a new one. Example: ABOR;*WAI INIT:IMM Aborts the current measurement and starts a new one once abortion has been completed.
-
Page 95: Measurement Sequences
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Measurement control [SENSe:]SYNC[:CC<cc>][:STATe]? Queries the current synchronization state. Suffix: <cc> irrelevant Return values: <State> The string contains the following information: A zero represents a failure and a one represents a successful synchronization. Example: //Query synchronization state SYNC:STAT? Would return, e.g. - Page 96 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Measurement control INITiate:SEQuencer:MODE <Mode> Defines the capture mode for the entire measurement sequence and all measurement groups and channels it contains. Note: To synchronize to the end of a measurement sequence using *OPC, *OPC? or *WAI, use SINGle Sequencer mode.
-
Page 97: Trace Data Readout
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout 6.7 Trace data readout ● The TRACe[:DATA] command................97 ● Result readout.......................108 6.7.1 The TRACe[:DATA] command This chapter contains information on the TRACe:DATA command and a detailed description of the characteristics of that command. The TRACe:DATA command queries the trace data or results of the currently active measurement or result display. -
Page 98: Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout ● EVM vs symbol..................... 103 ● EVM vs symbol x carrier..................103 ● Frequency error vs symbol..................104 ● Power spectrum....................104 ● Power vs symbol x carrier..................104 ● Spectrum emission mask..................105 ●... - Page 99 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout The return values have the following characteristics. ● The <allocation ID is encoded. For the code assignment, see Chapter 6.7.1.19, "Return value codes", on page 105. ● The unit for <relative power> is always dB. ●...
-
Page 100: Bit Stream
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout (...) //ALL for all subframes -2,-2,,,,,2.13196434228374E-06 6.7.1.4 Bit stream For the bitstream result display, the number of return values depends on the parame- ter. ● TRACE:DATA TRACE1 Returns several values and the bitstream for each line of the table. <subframe>, <allocation ID>, <codeword>, <modulation>, <# of symbols/bits>, <hexadecimal/binary numbers>,... -
Page 101: Ccdf
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout The following parameters are supported. ● TRAC:DATA TRACE1 Note that the command returns positive peak values only. 6.7.1.6 CCDF For the CCDF result display, the type of return values depends on the parameter. ●... -
Page 102: Group Delay
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout Returns the average power over all subframes. ● TRAC:DATA TRACE2 Returns the minimum power found over all subframes. If you are analyzing a partic- ular subframe, it returns nothing. ● TRAC:DATA TRACE3 Returns the maximum power found over all subframes. -
Page 103: Evm Vs Carrier
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout 6.7.1.11 EVM vs carrier For the EVM vs carrier result display, the command returns one value for each subcar- rier that has been analyzed. <EVM>, ... The unit depends on UNIT:EVM. The following parameters are supported. ●... -
Page 104: Frequency Error Vs Symbol
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout <EVM[Symbol(1),Carrier(1)]>, ..., <EVM[Symbol(1),Carrier(n)]>, <EVM[Symbol(n),Carrier(1)]>, ..., <EVM[Symbol(n),Carrier(n)]>, The unit depends on UNIT:EVM. Resource elements that are unused return NAN. The following parameters are supported. ● TRAC:DATA TRACE1 6.7.1.15 Frequency error vs symbol For the frequency error vs symbol result display, the command returns one value for each OFDM symbol that has been analyzed. -
Page 105: Spectrum Emission Mask
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout The following parameters are supported. ● TRAC:DATA TRACE1 6.7.1.18 Spectrum emission mask For the SEM measurement, the number and type of returns values depend on the parameter. ● TRAC:DATA TRACE1 Returns one value for each trace point. <absolute power>, ... - Page 106 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout ● 2 = alternate channel <codeword> Represents the codeword of an allocation. The range is {0...6}. ● 0 = 1/1 ● 1 = 1/2 ● 2 = 2/2 ● 3 = 1/4 ●...
- Page 107 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout Query parameters: <TraceNumber> TRACE1 | TRACE2 | TRACE3 Queries the trace data of the corresponding trace. LIST Queries the results for the SEM measurement. Return values: <TraceData> For more information about the type of return values in the differ- ent result displays, see Chapter 6.7.1, "The TRACe[:DATA] com- mand",...
-
Page 108: Result Readout
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Trace data readout 6.7.2 Result readout ......108 CALCulate<n>:MARKer<m>:FUNCtion:POWer<sb>:RESult[:CURRent]? CALCulate<n>:MARKer<m>:FUNCtion:POWer<sb>:RESult[:CURRent]? [<Measurement>] Queries the results of the ACLR measurement or the total signal power level of the SEM measurement. To get a valid result, you have to perform a complete measurement with synchroniza- tion to the end of the measurement before reading out the result. -
Page 109: Numeric Result Readout
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout Results for the ACLR measurements: Relative power levels of the ACLR channels. The number of return values depends on the number of transmission and adja- cent channels. The order of return values is: •... - Page 110 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout ..............111 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:FERRor[:AVERage]? ..............112 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:OSTP:MAXimum? ..............112 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:OSTP:MINimum? ..............112 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:OSTP[:AVERage]? ............... 112 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:POWer:MAXimum? ..............112 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:POWer:MINimum? ...............112 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:POWer[:AVERage]? ..............113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:NBP:MAXimum? ..............113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:NBP:MINimum? ............113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:NBPower[:AVERage]? ..............113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSSI:MAXimum? ..............113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSSI:MINimum? ..............113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSSI[:AVERage]? ..............
-
Page 111: Fetch[:Cc
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout Example: //Query EVM FETC:SUMM:EVM? Usage: Query only FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:EVM:PCHannel:MAXimum? FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:EVM:PCHannel:MINimum? FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:EVM:PCHannel[:AVERage]? Queries the EVM of all physical channel resource elements. Suffix: <cc> Component Carrier Return values: <EVM> <numeric value> EVM in % or dB, depending on the unit you have set. Example: //Query EVM FETC:SUMM:EVM:PCH?]:Summary:ferror[:Average] -
Page 112: Fetch[:Cc
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout Return values: <FrequencyError> <numeric value> Minimum, maximum or average frequency error, depending on the last command syntax element. Default unit: Hz Example: //Query average frequency error FETC:SUMM:FERR? Usage: Query only FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:OSTP:MAXimum? FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:OSTP:MINimum? FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:OSTP[:AVERage]? Queries the OSTP.]:Summary:ostp:maximum -
Page 113: Fetch[:Cc
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:NBP:MAXimum? FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:NBP:MINimum? FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:NBPower[:AVERage]? Queries the NB-IoT power. Suffix: <cc> irrelevant Return values: <Power> <numeric value> Minimum, maximum or average power, depending on the last command syntax element. Default unit: dBm Example: //Query NB-IoT power FETC:SUMM:NBP? Usage: Query only...]:Summary:nbp:maximum -
Page 114: Time Alignment Error
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout Example: //Query RSTP FETC:SUMM:RSTP? Usage: Query only FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:SERRor:MAXimum? FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:SERRor:MINimum? FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:SERRor[:AVERage]? Queries the sampling error. Suffix: <cc> Component Carrier Return values: <SamplingError> <numeric value> Minimum, maximum or average sampling error, depending on the last command syntax element. Default unit: ppm Example: //Query average sampling error... -
Page 115: Marker Table
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout FETCh:FERRor[:CC<cc>][:AVERage]? Queries the carrier frequency error. Suffix: <cc> Component Carrier Return values: <FrequencyError> <numeric value> Average, minimum or maximum frequency error, depending on the command syntax. Default unit: Hz Example: //Query frequency error. FETC:FERR? Usage: Query only... - Page 116 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout If necessary, the command activates the delta marker and positions a reference marker to the peak power. Suffix: <n> Window <m> Marker Parameters: <Position> Numeric value that defines the marker position on the x-axis. Range: The value range and unit depend on the measure- ment and scale of the x-axis.
- Page 117 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout If the marker has been used as a delta marker, the command turns it into a normal marker. Suffix: <n> Window <m> Marker Note that 3D diagrams only support one marker. Parameters: <Position>...
- Page 118 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout Manual operation: "Marker Table" on page 29 "Marker Peak List" on page 34 CALCulate<n>:MARKer<m>:Z? Queries the marker position on the z-axis of three-dimensional result displays. Returns the type of value displayed in the selected result display (EVM, Power or Allo- cation ID).
-
Page 119: Ccdf Table
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Numeric result readout Manual operation: "Marker Table" on page 29 6.8.4 CCDF table ................119 CALCulate<n>:STATistics:CCDF:X<t>? ................119 CALCulate<n>:STATistics:RESult<res>? CALCulate<n>:STATistics:CCDF:X<t>? <Probability> Queries the results of the CCDF. Suffix: <n> Window <t> Trace Query parameters: <Probability> P0_01 Level value for 0.01 % probability P0_1... -
Page 120: Configuration
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration CFACtor Determined crest factor (= ratio of peak power to average power) in dB. Results of all three measurements mentioned before, separated by commas: <mean power>,<peak power>,<crest factor> Example: CALC:STAT:RES2? ALL Reads out the three measurement results of trace 2. Example of answer string: 5.56,19.25,13.69 i.e. -
Page 121: I/Q Measurements
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Example: //Select measurement CONF:MEAS EVM Manual operation: "EVM" on page 13 "Time alignment error" on page 14 "Channel power ACLR" on page 14 "SEM" on page 14 "Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio (ACLR)" on page 32 "Spectrum Emission Mask (SEM)"... - Page 122 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration ● Demodulation......................152 ● Estimation & compensation...................154 ● Automatic configuration..................155 6.9.2.1 Signal characteristics ● Physical settings....................122 ● MIMO configuration....................129 ● NPDSCH settings....................130 ● Control channel.....................131 Physical settings Commands to configure physical settings described elsewhere. ●...
- Page 123 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration CONFigure[:LTE]:EUTRa:FREQuency <Frequency> Defines the center frequency of an E-UTRA channel. Prerequisites for this command ● Select in band deployment of an NB-IoT carrier (CONFigure[:LTE]: DEPLoyment). Parameters: <Frequency> <numeric value> Default unit: Hz Example: //Define E-UTRA channel center frequency CONF:DEPL INB CONF:EUTR:FREQ 1GHZ Manual operation:...
- Page 124 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:FREQuency:OFFSet <Frequency> Defines the location of the NB-IoT carrier in the E-UTRA guard band. Prerequisites for this command ● Select guard band deployment of an NB-IoT carrier (CONFigure[:LTE]: DEPLoyment). ● Select user defined location (CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:FREQuency:GINDex). Parameters: <Frequency>...
- Page 125 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Parameters: <Sequence> <numeric value> (integer only) *RST: depends on the E-UTRA channel bandwidth Example: //Define E-UTRA CRS sequence CONF:DEPL INB CONF:DL:BW BW10_00 CONF:DL:SINF 20 Manual operation: "Defining physical settings for NB-IoT inband deployment" on page 39 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:BW <Bandwidth>...
- Page 126 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration <numeric value> (integer only) Number of the cell ID. Range: 0 to 503 Example: //Select cell ID CONF:DL:PLC:CID 15 Manual operation: "Configuring the Physical Layer Cell Identity" on page 41 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:PLC:CIDGroup <GroupNumber> Selects the cell ID group. Suffix: <cc>...
- Page 127 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration CONFigure[:LTE]:TYPE <Type> Selects the NB-IoT carrier type. Parameters: <Type> ANCHor NPSS, NSSS, NPBCH and SIB-NB transmission assumed. NANChor NPSS, NSSS, NPBCH and SIB-NB transmission not assumed. *RST: ANCHor Example: //Select carrier type CONF:TYPE ANCH Manual operation: "Carrier Type"...
- Page 128 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration MMEMory:LOAD[:CC<cc>]:DEModsetting <File> Restores previously saved demodulation settings. The file must be of type .allocation and depends on the link direction that was cur- rently selected when the file was saved. You can load only files with correct link direc- tions.
- Page 129 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Manual operation: "User defined test scenarios" on page 42 MIMO configuration ............129 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:MIMO:ASELection ..............129 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:MIMO:CONFig CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:MIMO:ASELection <Antenna> Selects the antenna for measurements with MIMO setups. For time alignment error measurements, the command selects the reference antenna. Suffix: <cc>...
- Page 130 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration NPDSCH settings ..............130 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:NPDSch:DMODulation ................130 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:NPDSch:SFList ................130 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:NPDSch:UEID CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:NPDSch:DMODulation <State> Turns automatic NPDSCH and NPDCCH demodulation on and off. Parameters: <State> ON | OFF | 1 | 0 *RST: Example: //Turn on automatic demodulation CONF:DL:NPDS:DMOD ON Manual operation: "NPDSCH Demodulation"...
- Page 131 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Example: // Select NPDSCH N_RNTI CONF:DL:NPDS:DMOD OFF CONF:DL:NPDS:UEID 16 Manual operation: "NPDSCH Demodulation" on page 43 Control channel ................. 131 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:PSOFfset CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:PSOFfset <Offset> Defines the symbol offset for NPDSCH allocations relative to the start of the subframe. The offset applies to all subframes.
- Page 132 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration ....................136 INPut:FILTer:YIG[:STATe] .................... 136 INPut:IQ:BALanced[:STATe] ......................137 INPut:IQ:TYPE .........................137 INPut:SELect ........................138 INPut:TYPE ..................138 MMEMory:LOAD:IQ:STReam ................139 MMEMory:LOAD:IQ:STReam:AUTO ................139 MMEMory:LOAD:IQ:STReam:LIST? .................. 139 TRACe:IQ:FILE:REPetition:COUNt CALibration:AIQ:HATiming[:STATe] <State> Activates a mode with enhanced timing accuracy between analog baseband, RF and external trigger signals.
- Page 133 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Return values: <Value> Example: INP:DIQ:CDEV? Result: 1,SMW200A,101190,BBMM 1 OUT, 100000000,200000000,Passed,Passed,1,1.#QNAN Manual operation: "Connected Instrument" on page 47 INPut:DIQ:RANGe:COUPling <State> If enabled, the reference level for digital input is adjusted to the full scale level automat- ically if the full scale level changes.
- Page 134 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration INPut:DIQ:RANGe[:UPPer]:UNIT <Level> Defines the unit of the full scale level. The availability of units depends on the mea- surement application you are using. Is only available if the optional "Digital Baseband" interface is installed. Parameters: <Level>...
- Page 135 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Example: INP:DPAT OFF Manual operation: "Direct Path" on page 45 INPut:FILE:PATH <FileName>[, <AnalysisBW>] Selects the I/Q data file to be used as input for further measurements. The I/Q data file must be in one of the following supported formats: ●...
- Page 136 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration INPut:FILTer:HPASs[:STATe] <State> Activates an additional internal high-pass filter for RF input signals from 1 GHz to 3 GHz. This filter is used to remove the harmonics of the FSW to measure the harmon- ics for a DUT, for example. Requires an additional high-pass filter hardware option.
- Page 137 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration INPut:IQ:TYPE <DataType> Defines the format of the input signal. Parameters: <DataType> IQ | I | Q The input signal is filtered and resampled to the sample rate of the application. Two input channels are required for each input signal, one for the in-phase component, and one for the quadrature compo- nent.
- Page 138 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Analog Baseband signal (only available with optional "Analog Baseband" interface) Not available for Input2. *RST: Example: INP:TYPE INP1 For FSW85 models with two RF input connectors: selects the 1.00 mm RF input connector for configuration. INP:SEL RF Manual operation: "Digital I/Q Input State"...
- Page 139 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration MMEMory:LOAD:IQ:STReam:AUTO <State> Only available for files that contain more than one data stream from multiple channels: automatically defines which data stream in the file is used as input for the channel. Parameters: <State> ON | OFF | 0 | 1 OFF | 0 The data stream specified by MMEMory:LOAD:IQ:STReam...
- Page 140 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Note that the [:CC<cc>] part of the syntax is not supported. Suffix: <cc> Component Carrier Parameters: <Frequency> <numeric value> Range: fmin to fmax *RST: 1 GHz Default unit: Hz Example: //Define frequency for measurement on one carrier: FREQ:CENT 1GHZ Manual operation: "Defining physical settings for NB-IoT inband deployment"...
- Page 141 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Example: //Set the center frequency to 110 MHz. FREQ:CENT 100 MHz FREQ:CENT:STEP 10 MHz FREQ:CENT UP Manual operation: "Frequency Stepsize" on page 51 6.9.2.4 Amplitude configuration ......141 DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:TRACe<t>:Y[:SCALe]:RLEVel ....141 DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:TRACe<t>:Y[:SCALe]:RLEVel:OFFSet ....................142 INPut:ATTenuation<ant> ..................
- Page 142 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Suffix: <n> irrelevant <w> subwindow Not supported by all applications <t> irrelevant Parameters: <Offset> Range: -200 dB to 200 dB *RST: Default unit: DB Example: DISP:TRAC:Y:RLEV:OFFS -10dB Manual operation: "Reference Level Offset" on page 53 INPut:ATTenuation<ant>...
- Page 143 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration INPut:COUPling <CouplingType> Selects the coupling type of the RF input. If an external frontend is active, the coupling is automatically set to AC. Parameters: <CouplingType> AC | DC AC coupling DC coupling *RST: Example: INP:COUP DC Manual operation: "Input Coupling"...
- Page 144 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration The command requires the additional preamplifier hardware option. Parameters: <Gain> For all FSW models except for FSW85, the following settings are available: 15 dB and 30 dB All other values are rounded to the nearest of these two. For FSW85 models: FSW43 or higher: 30 dB...
- Page 145 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration INPut:EATT<ant>:AUTO <State> Turns automatic selection of the electronic attenuation on and off. If on, electronic attenuation reduces the mechanical attenuation whenever possible. Is available with the optional electronic attenuator, but not if you are using the optional digital baseband Input.
- Page 146 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Prerequisites for this command ● Turn on overall frame count ([SENSe:][LTE:]FRAMe:COUNt:STATe). ● Turn on manual selection of frames to analyze ([SENSe:][LTE:]FRAMe:COUNt: AUTO). Parameters: <Subframes> <numeric value> (integer only) *RST: Example: //Define number of frames to analyze manually FRAM:COUN:STAT ON FRAM:COUN:AUTO OFF FRAM:COUN 20...
- Page 147 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Parameters: <State> ON | OFF | 1 | 0 *RST: Example: //Swap I and Q branches SWAP ON Manual operation: "Swap I/Q" on page 56 [SENSe:]SWEep:TIME <CaptureLength> Defines the capture time. Parameters: <CaptureLength> <numeric value> *RST: 20.1 ms Default unit: s...
- Page 148 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Parameters: <DropoutTime> Dropout time of the trigger. Range: 0 s to 10.0 s *RST: Default unit: S Manual operation: "Trigger Source" on page 57 TRIGger[:SEQuence]:HOLDoff<ant>[:TIME] <Offset> Defines the trigger offset. Suffix: <ant> Instrument Parameters: <Offset>...
- Page 149 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Example: TRIG:SOUR IFP Sets the IF power trigger source. TRIG:IFP:HYST 10DB Sets the hysteresis limit value. Manual operation: "Trigger Source" on page 57 TRIGger[:SEQuence]:LEVel<ant>[:EXTernal<tp>] <Level> Defines the level for an external trigger. Suffix: <ant> Instrument <tp>...
- Page 150 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Note that any RF attenuation or preamplification is considered when the trigger level is analyzed. If defined, a reference level offset is also considered. Suffix: <ant> Instrument Parameters: <Level> <numeric value> Range: -130 dBm to 30 dBm *RST: -20 dBm Default unit: dBm...
- Page 151 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Example: //Select trigger port 1 TRIG:PORT PORT1 TRIGger[:SEQuence]:SLOPe <Type> Selects the trigger slope. Parameters: <Type> POSitive | NEGative POSitive Triggers when the signal rises to the trigger level (rising edge). NEGative Triggers when the signal drops to the trigger level (falling edge). *RST: POSitive Example:...
- Page 152 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration IFPower Measurement starts when the second intermediate frequency exceeds a certain level. Not available for input from the optional digital baseband inter- face. For input from the optional analog baseband interface, this parameter is interpreted as BBPower for compatibility reasons. IQPower Measurement starts when the sampled I/Q data exceeds a cer- tain magnitude.
- Page 153 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Manual operation: "Compensate Crosstalk" on page 61 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:DEMod:CBSCrambling <State> Turns scrambling of coded bits on and off. Parameters: <State> ON | OFF | 1 | 0 *RST: Example: //Descramble coded bits DL:DEM:CBSC ON Manual operation: "Scrambling of Coded Bits"...
- Page 154 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration ALL0 Reference data is 0, according to the test model definition. Example: //Select reference data for NPDSCH demodulation DL:DEM:PRD ALL0 Manual operation: "NPDSCH Reference Data" on page 61 6.9.2.8 Estimation & compensation Parameter estimation ................
- Page 155 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:TRACking:PHASe <Type> Selects the phase tracking type. Parameters: <Type> Deactivate phase tracking Pilot only PILP Pilot and payload *RST: Example: //Select phase tracking type DL:TRAC:PHAS PILPAY Manual operation: "Phase" on page 59 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:TRACking:TIME <State> Turns timing tracking on and off.
-
Page 156: Time Alignment Error Measurements
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Example: ADJ:CONF:DUR:MODE MAN Selects manual definition of the measurement length. ADJ:CONF:LEV:DUR 5ms Length of the measurement is 5 ms. Manual operation: "Auto Level" on page 52 [SENSe:]ADJust:CONFigure:LEVel:DURation:MODE <Mode> To determine the ideal reference level, the FSW performs a measurement on the cur- rent input data. -
Page 157: Frequency Sweep Measurements
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration ● Commands in Chapter 6.9.2.7, "Demodulation", on page 152. ● Commands in Chapter 6.9.2.2, "Input configuration", on page 131. ● Commands in Chapter 6.9.2.3, "Frequency configuration", on page 139. ● Commands in Chapter 6.9.2.4, "Amplitude configuration", on page 141. - Page 158 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Configuration Parameters: <Power> <numeric value> Default unit: dBm Example: //Define base station power POW:SEM:CAT MED POW:SEM:CHBS:AMP:AUTO OFF POW:SEM:CHBS:AMP 0 Manual operation: "Tx Power" on page 64 [SENSe:]POWer:SEM:CHBS:AMPower:AUTO <State> Turn automatic detection of the TX channel power on and off. Prerequisites for this command ●...
-
Page 159: Analysis
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Analysis [SENSe:]POWer:SEM:PIOV <Power> Defines the power of the NB-IoT carrier on which the calculation of the SEM limits is based. Prerequisites for this command ● Select manual SEM limit calculation mode ([SENSe:]POWer:SEM:PIOM). Parameters: <Power> <numeric value> *RST: Example: //Define NB-IoT power manually... -
Page 160: Format:dexport:header
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Analysis FORMat:DEXPort:HEADer <State> If enabled, additional instrument and measurement settings are included in the header of the export file for result data. If disabled, only the pure result data from the selected traces and tables is exported. Parameters: <State>... -
Page 161: Microservice Export
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Analysis Example: MMEM:STOR1:TRAC 1,'C:\TEST.ASC' Stores trace 1 from window 1 in the file TEST.ASC. 6.10.2 Microservice export ..................161 MMEMory:STORe<n>:MSERvice MMEMory:STORe<n>:MSERvice <FileName> Exports the signal configuration to the microservice. Suffix: <n> irrelevant Parameters: <FileName> String containing the path and name of the file. The file extension is .m5g. - Page 162 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Analysis [SENSe:][LTE:][CC<cc>:]CARRier:SELect <Carrier> Filters the results in the constellation diagram by a certain subcarrier. Suffix: <cc> Component Carrier Parameters: <Carrier> Shows the results for all subcarriers. <numeric_value> (integer only) Shows the results for a single subcarrier. *RST: Example: //Display results for subcarrier 1...
-
Page 163: Y-Axis Scale
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Analysis *RST: Example: //Display results for all elements with a QPSK modulation MOD:SEL 2 Manual operation: "Evaluation range for the constellation diagram" on page 70 [SENSe:][LTE:][CC<cc>:]SUBFrame:SELect <Subframe> Selects the subframe to be analyzed. Suffix: <cc> Component Carrier Parameters: <Subframe>... - Page 164 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Analysis DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:TRACe<t>:Y[:SCALe]:AUTO <ONCE> Automatically scales the y-axis of a diagram based on the displayed results. Suffix: <n> Window <w> Subwindow <t> irrelevant Setting parameters: <ONCE> Scales the y-axis in all windows for an ideal viewing experience. DEFault Restores the default scale of the y-axis.
-
Page 165: Result Settings
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Analysis Suffix: <n> Window <w> Subwindow <t> irrelevant Parameters: <Value> Minimum displayed value. The unit and value range depend on the selected diagram. Example: //Define minimum value on y-axis in subwindow 2 of window 2 DISP:WIND2:SUBW2:TRAC:Y:MIN -50 Manual operation: "Manual scaling of the y-axis"... -
Page 166: Reading Out Status Register
® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Reading out status register Manual operation: "Bit Stream Format" on page 71 UNIT:CAXes <Unit> Selects the scale of the x-axis for result displays that show subcarrier results. Parameters: <Unit> CARR Shows the number of the subcarriers on the x-axis. Shows the frequency of the subcarriers on the x-axis. - Page 167 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Reading out status register The command also deletes the contents of the EVENt section. Query parameters: <ChannelName> String containing the name of the channel. The parameter is optional. If you omit it, the command works for the currently active channel.
- Page 168 ® Remote control R&S FSW-K106 Reading out status register STATus:QUEStionable:SYNC:PTRansition <BitDefinition>[,<ChannelName>] These commands control the Positive TRansition part of a register. Setting a bit causes a 0 to 1 transition in the corresponding bit of the associated regis- ter. The transition also writes a 1 into the associated bit of the corresponding EVENt register.
-
Page 169: Annex
® Performing time alignment measurements R&S FSW-K106 Annex A Performing time alignment measurements The measurement application allows you to perform time alignment measurements between different antennas. The measurement supports setups of up to two Tx antennas. The result of the measurement is the time alignment error. The time alignment error is the time offset between a reference antenna (for example antenna 1) and another antenna. -
Page 170: List Of Commands (Nb-Iot Downlink)
® List of commands (NB-IoT downlink) R&S FSW-K106 List of commands (NB-IoT downlink) [SENSe:][LTE:][CC<cc>:]ALLocation:SELect....................161 [SENSe:][LTE:][CC<cc>:]CARRier:SELect....................162 [SENSe:][LTE:][CC<cc>:]LOCation:SELect....................162 [SENSe:][LTE:][CC<cc>:]MODulation:SELect....................162 [SENSe:][LTE:][CC<cc>:]SUBFrame:SELect....................163 [SENSe:][LTE:][CC<cc>:]SYMBol:SELect..................... 163 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:DEMod:BESTimation....................... 154 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:DEMod:CBSCrambling....................153 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:DEMod:CESTimation....................... 154 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:DEMod:EVMCalc......................153 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:DEMod:MCFilter.......................153 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:DEMod:PRData........................153 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:TRACking:PHASe......................155 [SENSe:][LTE:]DL:TRACking:TIME....................... 155 [SENSe:][LTE:]FRAMe:COUNt........................145 [SENSe:][LTE:]FRAMe:COUNt:AUTO...................... - Page 171 ® List of commands (NB-IoT downlink) R&S FSW-K106 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:NPDSch:SFList......................130 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:NPDSch:UEID......................130 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:PINDex........................124 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL:SINFo...........................124 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:BW....................... 125 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:MIMO:ASELection..................129 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:MIMO:CONFig..................... 129 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:MIMO:CROSstalk..................152 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:PLC:CID.......................125 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:PLC:CIDGroup.....................126 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:PLC:PLID.....................126 CONFigure[:LTE]:DL[:CC<cc>]:PSOFfset..................... 131 CONFigure[:LTE]:EUTRa:FREQuency......................123 CONFigure[:LTE]:MEASurement........................120 CONFigure[:LTE]:TYPE..........................127 DISPlay:FORMat............................. 84 DISPlay[:WINDow<n>]:SIZE..........................84 DISPlay[:WINDow<n>]:TAB<tab>:SELect....................... 85 DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:SELect..................85 DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:TRACe<t>:Y[:SCALe]:AUTO............164 DISPlay[:WINDow<n>][:SUBWindow<w>]:TRACe<t>:Y[:SCALe]:MAXimum..........
- Page 172 ® List of commands (NB-IoT downlink) R&S FSW-K106 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:POWer:MINimum?....................112 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:POWer[:AVERage]?..................112 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSSI:MAXimum?....................113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSSI:MINimum?....................113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSSI[:AVERage]?.....................113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSTP:MAXimum?.....................113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSTP:MINimum?....................113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:RSTP[:AVERage]?....................113 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:SERRor:MAXimum?..................114 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:SERRor:MINimum?..................114 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:SERRor[:AVERage]?..................114 FETCh[:CC<cc>]:SUMMary:TFRame?......................114 FORMat:DEXPort:DSEParator........................159 FORMat:DEXPort:HEADer..........................160 FORMat:DEXPort:TRACes..........................160 FORMat[:DATA]............................. 106 INITiate:SEQuencer:ABORt..........................95 INITiate:SEQuencer:IMMediate........................95 INITiate:SEQuencer:MODE..........................96 INITiate<n>:CONTinuous..........................94 INITiate<n>[:IMMediate]..........................94 INPut:ATTenuation<ant>..........................142 INPut:ATTenuation<ant>:AUTO........................142 INPut:CONNector............................
- Page 173 ® List of commands (NB-IoT downlink) R&S FSW-K106 INSTrument:LIST?............................81 INSTrument:REName............................83 INSTrument[:SELect]............................83 LAYout:ADD[:WINDow]?..........................86 LAYout:CATalog[:WINDow]?..........................88 LAYout:IDENtify[:WINDow]?..........................88 LAYout:REMove[:WINDow]..........................89 LAYout:REPLace[:WINDow]..........................89 LAYout:SPLitter..............................89 LAYout:WINDow<n>:ADD?..........................91 LAYout:WINDow<n>:IDENtify?........................91 LAYout:WINDow<n>:REMove..........................92 LAYout:WINDow<n>:REPLace........................92 LAYout:WINDow<n>:TYPE..........................93 MMEMory:LOAD:IQ:STReam........................138 MMEMory:LOAD:IQ:STReam:AUTO......................139 MMEMory:LOAD:IQ:STReam:LIST?......................139 MMEMory:LOAD[:CC<cc>]:DEModsetting....................128 MMEMory:LOAD[:CC<cc>]:TMOD:DL......................128 MMEMory:STORe<n>:IQ:STATe........................121 MMEMory:STORe<n>:MSERvice........................161 MMEMory:STORe<n>:TRACe........................160 MMEMory:STORe<n>[:CC<cc>]:DEModsetting....................128 STATus:QUEStionable:SYNC:CONDition?....................167...
-
Page 174: Index
® Index R&S FSW-K106 Index Copying Channel (remote) ............80 AC/DC coupling ..............54 CRS sequence ..............39 ACLR ................31, 32 Add channel ..............10 Allocation Data capture ..............55 Filter by ............... 70 Data format Allocation ID vs symbol x carrier ........27 Remote .............. - Page 175 ® Index R&S FSW-K106 Guard band deployment I/Q ................16 Configuration .............. 40 numerical ..............27 power spectrum ............21 power vs sym x carr ............ 26 Refresh ............... 15 Hardware settings ..............11 Result displays ............14 High-pass filter result summary ............27 RF input ..............
- Page 176 ® Index R&S FSW-K106 Strings ................. 78 Subframe selection ............69 Suffixes ............... 75 Suffixes Restoring Common ..............73 Channel settings ............36 Remote commands ............. 75 Result displays ..............14 Swap I/Q ................56 Marker table ..............29 Symbol Peak list ..............

















Need help?
Do you have a question about the R&S FSW-K106 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers