Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for LSI MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 RAID Controller Series 520
-
Page 1: Raid Controller
HARDWARE GUIDE ® MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 RAID Controller S e p t e m b e r 2 0 0 2 ®... - Page 2 LSI Logic; nor does the purchase or use of a product from LSI Logic convey a license under any patent rights, copyrights, trademark rights, or any other of the intellectual property rights of LSI Logic or third parties.
- Page 3 LSI LOGIC with this product. The complete list of tested jumper settings, system configurations, peripheral devices, and memory modules are documented in the LSI LOGIC Compatibility Report for this product.
- Page 4 Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 5: Features
Preface This book is the primary reference and Hardware Guide for the LSI Logic MegaRAID the MegaRAID controller and for configuring RAID arrays. It also contains background information on RAID. The MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 controller supports single-ended and low- voltage differential (LVD) SCSI devices on an Ultra320 and Wide SCSI channel with data transfer rates up to 320 Mbytes/s. - Page 6 320-1 Controller, you may be able to find the information you need at the MegaRAID support page at If this does not resolve your problem, you can call your LSI Logic OEM Technical Support representative at 678-728-1250. Before you call, please complete the MegaRAID Problem Report form.
- Page 7 Use this form to record the configuration details for your logical drives. Logical Drive Configuration Logical RAID Stripe Drive Level Size Preface Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. BIOS Date: Video Adapter: CPU Type/Speed: System Memory: Other adapter cards Installed: Logical Drive Cache...
- Page 8 LD17 LD18 LD19 LD20 LD21 LD22 LD23 LD24 LD25 LD26 LD27 LD28 LD29 LD30 LD31 viii Preface Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Logical Drive Cache Read Size Policy Policy Write # of Physical Policy Drives...
- Page 9 Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Preface Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Logical Drive Cache Read Size Policy Policy Channel 0 Write # of Physical...
- Page 10 Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Preface Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Channel 0...
- Page 11 Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Preface Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Channel 0...
- Page 12 Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Preface Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Channel 0...
-
Page 13: Table Of Contents
RAID Overview 2.3.1 2.3.2 2.3.3 2.3.4 2.3.5 MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide MegaRAID Configuration Software Guide MegaRAID Operating System Driver Installation Guide Improved I/O Increased Reliability... - Page 14 Operating System Software Drivers MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Specifications 4.9.1 4.9.2 4.9.3 4.9.4 4.9.5 4.9.6 Contents Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Disk Mirroring Disk Spanning Parity Hot Spares Hot Swapping Disk Rebuild Logical Drive States SCSI Drive States...
- Page 15 Chapter 6 Hardware Installation Hardware Requirements Installation Steps 6.2.1 6.2.2 6.2.3 Contents Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. SCSI Termination SCSI Firmware MegaRAID BIOS Configuration Utility WebBIOS Configuration Utility Power Console Plus MegaRAID Manager Server Management...
- Page 16 Appendix B Audible Warnings Appendix C Glossary Contents Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Step 4: Set Termination Step 5: Install MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Step 6: Connect SCSI Devices Step 7: Set Target IDs Step 8: Power Up...
-
Page 17: Customer Feedback
Index Customer Feedback Contents xvii Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. - Page 18 Contents Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 19: Scsi Connectors
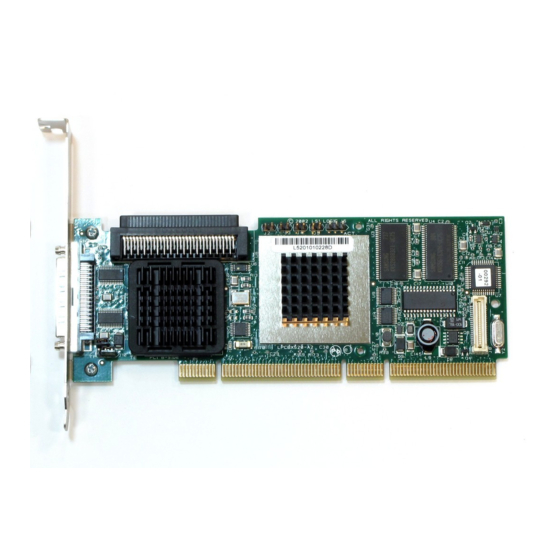
The MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 is part of the LSI Logic Intel GC80302-based MegaRAID controller family. The MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 is an entry level- to mid-range RAID controller solution. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 offers a cost-effective way to implement RAID in a server. -
Page 20: Features
SCSI Channel The MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 upgrade card includes one Ultra3 SCSI channel. The channel is powered by an LSI Logic 53C1020 Ultra320 SCSI processor. NVRAM and Flash ROM A 32 KB x 8 NVRAM stores RAID system configuration information. The MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 firmware is stored in flash ROM for easy upgrade. -
Page 21: Single-Ended And Differential Scsi Buses
Wide Ultra160 SCSI Ultra320 Ultra320 Single-Ended and Differential SCSI Buses Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists the maximum SCSI cable length and number of disk drives Maximum Cable Length for SCSI Standards Single Ended SCSI 1.5 m... -
Page 22: Scsi Bus Widths And Maximum Throughput
This manual describes the software configuration utilities that you can use to configure and modify RAID systems. Overview Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists the SCSI bus widths and maximum throughput, based on SCSI Bus Widths and Maximum Throughput... -
Page 23: Megaraid Operating System Driver Installation Guide
1.8.3 MegaRAID Operating System Driver Installation Guide This manual provides detailed information about installing the MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 operating system drivers. Documentation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. - Page 24 Overview Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 25: Introduction To Raid
RAID provides a way to achieve much better data throughput. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 26: Increased Reliability
The sustained data transfer rate of the SCSI devices · The number of SCSI channels · The number of SCSI disk drives Host-based solutions must provide operating system-specific drivers. Introduction to RAID Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 27: Scsi-To-Scsi External Raid
· An entire physical array · More than one entire physical array · A part of an array · Parts of more than one array RAID Overview Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 28: Consistency Check
2.3.5 Disk Striping Disk striping writes data across multiple disk drives instead of just one disk drive, as shown in Introduction to RAID Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Figure 2.1. - Page 29 Stripe width is a measure of the number of disks involved in an array where striping is implemented. For example, a four-disk array with disk striping has a stripe width of four. RAID Overview Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Disk Striping MegaRAID Controller Segment 2...
-
Page 30: Disk Mirroring
Either drive can act as the operational drive. Although disk mirroring provides 100% redundancy, it is expensive because each drive in the system must be duplicated. Introduction to RAID Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Disk Mirroring MegaRAID Controller Segment 1 Duplicated... -
Page 31: Disk Spanning
RAID 10 array. Figure 2.3 Segment 1 Segment 3 Segment 5 RAID Overview Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Figure 2.3, two RAID 1 arrays are turned into Disk Spanning MegaRAID Controller Data Flow RAID 1... -
Page 32: Parity
MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 controller assigns the hot spare that Introduction to RAID Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. describes how disk spanning is used for RAID 10 and RAID 50. Spanning for RAID 10 and RAID 50 Configure RAID 10 by spanning two contiguous RAID 1 logical drives. -
Page 33: Hot Swapping
RAID Overview Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Hot spares are employed only in arrays with redundancy— for example, RAID levels 1, 5, 10, and 50. A hot spare... -
Page 34: Logical Drive States
Fail (FAIL) Rebuild (REB) 2-10 Introduction to RAID Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. describes the logical drive states. Logical Drive States Description The drive operating condition is good. All configured drives are online. The drive operating condition is not optimal. One of the configured drives has failed or is offline. -
Page 35: Disk Array Types
Enclosure management increases the fault tolerance of the disk subsystem. RAID Overview Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. describes the RAID disk array types. Disk Array Types... - Page 36 2-12 Introduction to RAID Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 37: Raid Levels
The capacity of the drives in the array · The need for data redundancy · The disk performance requirements Note: MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. The SCSI 320-1 controller supports a maximum of 15 physical drives. -
Page 38: Raid
Weak Points Drives Figure 3.1 RAID Levels Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. RAID 0 provides high data throughput, especially for large files. Suitable for any environment that does not require fault tolerance. Provides increased data throughput for large files. No capacity loss penalty for parity. -
Page 39: Raid
Uses Strong Points Weak Points Drives Figure 3.2 RAID 1 Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. RAID 0 Array MegaRAID Controller Segment 2 Segment 6 Segment 10 Use RAID 1 for small databases or any other environment that requires fault tolerance but small capacity. - Page 40 In addition, robust caching algorithms and hardware based RAID Levels Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. RAID 1 Array MegaRAID Controller Segment 1 Duplicated...
- Page 41 Segment 8 Parity (9–12) RAID 5 Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Provides high data throughput, especially for large files. Use RAID 5 for transaction processing applications, because each drive can read and write independently. If a drive fails, the MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 uses the parity drive to recreate all missing information.
- Page 42 Drives Figure 3.4 RAID Levels Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Works best for data storage that must have 100% redundancy of mirrored arrays and that also needs the enhanced I/O performance of RAID 0 (striped arrays). RAID...
-
Page 43: Raid
The size of each block is determined by the stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation of the RAID set. RAID 50 Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. RAID 10 Array MegaRAID Controller... - Page 44 Parity (5-6) Parity (9-10) Segment 9 RAID Levels Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Works best when used with data that requires high reliability, high request rates, high data transfer, and medium to large capacity. Provides high data throughput, data redundancy, and very good performance.
-
Page 45: Features
The MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Self Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) detects up to 70% of all predictable drive failures. SMART monitors the internal performance of all motors, heads, and drive electronics. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 46: Cache Memory
Maximum number of MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 controllers per system Online capacity expansion Hot spare support Features Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. contains the configuration features for the MegaRAID 320-1. Configuration Features Feature 0, 1, 5, 10, and 50 PCI 2.2... -
Page 47: Array Performance Features
Table 4.2 Specification Host data transfer rate Drive data transfer rate Stripe sizes Array Performance Features Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Configuration Features (Cont.) lists the array performance features. Array Performance Features Feature 533 Mbytes/s... -
Page 48: Raid Management Features
Enclosure management Drive failure detection Drive rebuild using hot spares Parity generation for RAID Features Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists the RAID management features. RAID Management Features lists the fault tolerance features. Fault Tolerance Features... -
Page 49: Software Utilities
DOS version 6.xx or later The DOS drivers for MegaRAID are contained in the firmware on the MegaRAID controller, except for the DOS ASPI and CD drivers. Call your LSI OEM support representative or access the web site at www.lsilogic.com systems. -
Page 50: Megaraid Scsi 320-1 Specifications
SCSI device types supported RAID levels supported Features Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists the specifications for the SCSI 320-1. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Specifications Specification Low profile PCI Adapter card size (6.875" X 2.5") Intel GC80302 64-bit RISC processor at 100 MHz PCI 2.2... -
Page 51: Scsi Connectors
The BIOS resides on a 1 MB × 8 flash ROM for easy upgrade. The MegaRAID BIOS supports INT 13h calls to boot DOS without special MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Specifications Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Specifications (Cont.) Specification One 68-pin internal high-density connector for 16-bit SCSI devices. -
Page 52: Serial Port
4.9.7 SCSI Termination The MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 uses active termination on the SCSI bus, conforming to Alternative 2 of the SCSI-2 specifications. Termination enable/disable is automatic through cable detection. Features Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 53: Scsi Firmware
The BIOS Configuration Utility (<Ctrl><M>) is used to configure and maintain RAID arrays, format hard drives, and manage the RAID system. RAID Management Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. SCSI Firmware Description Optimizes SCSI bus seek... -
Page 54: Webbios Configuration Utility
As a simple network management protocol (SNMP) agent, MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 supports all SNMP managers. 4.11.2 SCSI Device Compatibility MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 supports SCSI hard drives, CD drives, and tape drives. 4-10 Features Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 55: Software
4.11.3 Software All SCSI backup and utility software should work with MegaRAID SCSI 320-1. This software is not provided with MegaRAID SCSI 320-1. Compatibility 4-11 Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. - Page 56 4-12 Features Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 57: Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, And Logical Drives
When replacing a failed drive, make sure that the replacement drive has a capacity that is at least as large as the drive being replaced. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 58: Current Physical Device Configuration
Table 5.1 SCSI ID Device Description Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, and Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Be sure to back up your data regularly, even when using RAID. to record the current configuration for your physical... -
Page 59: Logical Drive Configuration
LD14 LD15 LD16 LD17 LD18 LD19 LD20 LD21 Configuring SCSI Physical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. to record the configuration for your logical drives. Logical Drive Cache Size Policy Read Write # of Physical... - Page 60 LD30 LD31 LD32 LD33 LD34 LD35 LD36 LD37 LD38 LD39 Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, and Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Logical Drive Cache Size Policy Read Write # of Physical Policy Policy Drives...
-
Page 61: Physical Device Layout
Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Configuring SCSI Physical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. to record the physical device layout. Physical Device Layout Channel 1... - Page 62 Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, and Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Physical Device Layout (Cont.) Channel 1...
- Page 63 Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Target ID Device type Logical drive number/Drive number Manufacturer/Model number Firmware level Configuring SCSI Physical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Channel 1...
-
Page 64: Configuring Arrays
Any drive that is present, formatted, and initialized, but is not included in a array or logical drive is automatically designated as a hot spare. Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, and Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Physical Device Layout (Cont.) Channel 1... -
Page 65: Creating Logical Drives
Table 5.4 RAID Level Creating Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Table 5.4 describes the RAID levels, including the number of Capacity for RAID Levels Drives Description Required Striping 1 –... - Page 66 A basic guideline of the performance 5-10 Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, and Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Capacity for RAID Levels (Cont.) Drives Description...
-
Page 67: Assigning Raid Levels
Table 5.7 RAID Level Note: Creating Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Performance Characteristics for RAID Levels Performance Characteristics Excellent for all types of I/O activity, but provides no data security. Provides data redundancy and good performance. -
Page 68: Configuring Logical Drives
You must first define the major purpose of the disk array. Will this disk array increase the system storage capacity for general-purpose file and print servers? Does this disk array support any software system that 5-12 Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, and Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 69: Planning The Array Configuration
RAID 1 requires two drives, RAID 10 at least four, and RAID 50 at least six. Planning the Array Configuration Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Table 5.8 to help plan this array. - Page 70 Table 5.9 Table 5.9 # of Drives 5-14 Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, and Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. to plan the array configuration. Array Configuration Planner Possible Relative RAID Levels Performance None Excellent...
- Page 71 Array Configuration Planner (Cont.) Possible # of Drives RAID Levels RAID 0 RAID 5 RAID 10 RAID 50 Planning the Array Configuration Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Relative Fault Performance Tolerance Excellent Good Good Good...
- Page 72 5-16 Configuring Physical Drives, Arrays, and Logical Drives Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 73: Hardware Installation
Ultra320, Ultra, Fast SCSI 2 or Wide SCSI hard disk drives MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. A motherboard with 5 V/3.3 V PCI expansion slots that has an available expansion slot Support for PCI version 2.2 or later... -
Page 74: Installation Steps
Table 6.1 detail in the following pages. Table 6.1 Step Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists the hardware installation steps. Each step is described in Hardware Installation Steps Action Unpack the MegaRAID controller and inspect for damage. -
Page 75: Step 1: Unpack
MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 controller card from the anti-static bag and inspect it for damage. If the card appears damaged, or if any item listed below is missing, contact LSI Logic or your MegaRAID OEM support representative. The MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 controller is shipped with the following: ·... - Page 76 LED on the computer enclosure. The LED will be lit when data in the cache has not yet been written to the storage device. Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Jumpers for the MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Description...
- Page 77 J9 is a 2-pin jumper. The factory setting is pins 1-2 shorted. Leave at the default setting (jumper installed) for J9 to allow the PCI bus to provide termination power. Installation Steps Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Table 6.3 shows the jumper settings. Pinout for J4 BIOS Enable...
-
Page 78: Step 4: Set Termination
SCSI device that internally terminates the SCSI bus at the end of the SCSI channel. Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Table 6.4. Leave at the default setting Pinout for J10 Termination Enable... - Page 79 Terminating Internal SCSI Disk Arrays Set the termination so that SCSI termination and termination power are intact when any hard drive is removed from a SCSI channel, as shown Figure Installation Steps Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. 6.2.
- Page 80 Figure 6.2 Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Termination of Internal SCSI Disk Arrays Termination Enabled ID1 – No Termination ID0 – Boot Drive No Termination MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 SCSI ID 7...
- Page 81 You can use both internal and external drives with the MegaRAID SCSI 320-1. You still must make sure that the proper SCSI termination and termination power is preserved, as shown in Installation Steps Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. 6.3: Terminating External Disk Arrays Termination...
- Page 82 ID 4 ID 5 ID 6* Note: *Termination enabled from last SCSI drive 6-10 Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Host Computer Terminator ID1 – No Termination ID0 – Boot Drive No Termination SCSI 320-1...
- Page 83 External SCSI CD-ROM Drive Installation Steps Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Since all non-disk SCSI devices are single ended, it is not advisable to attach a non-disk device to a MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 RAID controller if LVD disk drives are also attached.
-
Page 84: Step 5: Install Megaraid Scsi
Attach the bracket to the computer frame with the bracket screw. 6-12 Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Figure 6.6 3.3 V and 5 V PCI Slots shows the differences... -
Page 85: Step 6: Connect Scsi Devices
1. Disable termination on any SCSI device that does not sit at the end of the SCSI bus. Installation Steps Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Installing the MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Controller Bracket Screw 32-bit Slots (3.3 V) -
Page 86: Step 7: Set Target Ids
0 to 15. The arbitration priority for a SCSI device depends on its TID. Table 6.5 Table 6.5 Priority 6-14 Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. shows the relative priority of each Target ID: Priority of Target IDs Highest Lowest... - Page 87 Example of MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 ID Mapping Table 6.6 Table 6.6 Installation Steps Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. unique SCSI IDs regardless of the channel they are connected to. provides an example of ID mapping for the SCSI 320-1.
-
Page 88: Step 8: Power Up
Press <Ctrl><M> to run MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 BIOS Configuration Utility 6-16 Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. shows the target IDs as presented to the operating system. Target IDs as Presented to the Operating System Device... -
Page 89: Step 9: Run The Megaraid Bios Configuration Utility
Novell NetWare 5.1, 6.0 · Red Hat Linux 7.2, 7.3 Note: Installation Steps Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Refer to the MegaRAID Driver Installation Guide for the procedures used to install operating system drivers. 6-17... - Page 90 WebBIOS Configuration Utility MegaRAID Manager Power Console Plus 6-18 Hardware Installation Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Table 6.8 lists the utility programs for configuring MegaRAID Configuration Utilities and Operating Systems Operating System Independent of the operating system Independent of the operating system Red Hat Linux 7.2, 7.3...
-
Page 91: Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
One of the hard drives in the array fails often. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists the general problems that can occur, along with suggested Suggested Solution Check the system BIOS configuration for PCI interrupt assignments. -
Page 92: Type
What SCSI IDs can a non-hard disk device have and what is maximum number allowed per adapter? Troubleshooting Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Suggested Solution Check the drives IDs on each channel to make sure each device has a different ID. -
Page 93: Bios Boot Error Messages
Degraded drives signed on in a degraded state. BIOS Boot Error Messages Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. describes BIOS error messages that can display when you Suggested Solution Enable the BIOS using the MegaRAID BIOS Configuration Utility. -
Page 94: Other Bios Error Messages
MegaRAID cannot determine the drive that has the duplicate information. Troubleshooting Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Suggested Solution Make sure all physical drives are properly connected and are powered on. Run MegaRAID Manager to find out if any physical drives are not responding. -
Page 95: Other Potential Problems
MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 supports one logical unit number (LUN) per each target ID. No multiple LUN devices are supported. Other Potential Problems Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Suggested Solution 1. Press a key to run MegaRAID Manager. - Page 96 In some cases, Windows NT Setup repeatedly prompts to swap disks. Windows NT will recognize any devices attached to this adapter. 6. Repeat this step for each host adapter not already recognized by Windows NT Setup. Troubleshooting Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 97: Scsi Cables And Connectors
The cable assemblies that interface with the 68-pin connector are: · Flat ribbon or twisted pair cable for connecting internal Wide SCSI devices · Round shielded cable for connecting external Wide SCSI devices MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. -
Page 98: Cable Assembly For Internal Wide Scsi Devices
Pin 1 Pin 1 Pin 1 SCSI Cables and Connectors Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Connectors: 68 Position Plug (Male) AMP – 786090-7 Cable: Flat Ribbon or Twisted-Pair Flat Cable 68 Conductor 0.025 Centerline... -
Page 99: Connecting Internal And External Wide Devices
SCSI devices is shown below. Pin 1 Pin 1 Pin 1 68-Pin High-Density SCSI Internal Connector Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Connector A: 68 Position Panel Mount Receptacle with 4-40 Holes (Female) AMP – 786096-7... -
Page 100: Converting Internal Wide To Internal Non-Wide
(Type 2) SCSI connectors is shown below. 68 Position Connector Contact Number Table 1: Connector Contact Connection for Wide to Non-Wide Conversion SCSI Cables and Connectors Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. 50 Position Connector Contact Number Open Open Open Pin 1... -
Page 101: Converting Internal Wide To Internal Non-Wide
(Type 3) SCSI connectors is shown below. Pin 1 Pin 1 68-Pin High-Density SCSI Internal Connector Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Connector A: 68 Position Plug (Male) AMP– 749925-5 Connector B: 50 Position Plug (Male) AMP –... -
Page 102: Scsi Cable And Connector Vendors
Table A.2 Table A.2 Manufacturer Fujitsu Honda SCSI Cables and Connectors Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists SCSI cable vendors, and contact information. SCSI Cable Vendors Telephone Number Voice: 800-826-7904 Fax: 800-331-2841 Voice: 800-877-1985 Voice: 714-835-1081 Voice: 800-659-1599 table lists SCSI connector vendors. -
Page 103: High-Density 68-Pin Connector Pinout For Se Scsi
TERMPWR Reserved Ground Ground High-Density 68-Pin Connector Pinout for SE SCSI Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists the pinout for the high-density 68-pin connector for single- High-Density 68-Pin Connector Pinout (SE SCSI) Connector Cable Cable... - Page 104 -DB (14), -DB 15), and -DB (P1). · All other signals should be connected as defined. Caution: SCSI Cables and Connectors Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. High-Density 68-Pin Connector Pinout (SE SCSI) Connector Cable Cable...
-
Page 105: 68-Pin Connector Pinout For Lvd Scsi
TERMPWR Reserved Ground +ATN Ground 68-Pin Connector Pinout for LVD SCSI Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. lists the pinout for the 68-pin connector for LVD SCSI. 68-Pin Connector Pinout for LVD SCSI Connector Cable Cable... - Page 106 +DB(9) +DB(10) +DB(11) Note: A-10 SCSI Cables and Connectors Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. 68-Pin Connector Pinout for LVD SCSI (Cont.) Connector Cable Cable The conductor number refers to the conductor position when using flat-ribbon cable.
-
Page 107: Appendix B Audible Warnings
MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Examples One or more drives in a RAID 0 configuration failed. Two or more drives in a RAID 1, or 5 configuration failed. - Page 108 Audible Warnings Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 109: Appendix C Glossary
(or not started.) If the data is not cached (a cache miss), it is fetched from main memory and saved in cache memory. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. - Page 110 See also Array Spanning and Spanning. Disk Striping A type of disk array mapping. Consecutive stripes of data are mapped round-robin to consecutive array members. A striped array (RAID 0) Glossary Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 111 Gigabyte. Shorthand for 1,000,000,000 (10 to the ninth power) bytes. One Gbyte is equivalent to 1,000 Mbytes. Host-based A disk array with an array management software in its host computer Array rather than in a disk subsystem. Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 112 The conversion between multiple data addressing schemes, especially conversions between member disk block addresses and block addresses of the virtual disks presented to the operating environment by array management software. Glossary Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 113 High level protocols deal with the data formatting, including the message syntax, the terminal- to-computer dialogue, character sets, and sequencing of messages. Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 114 The percentage of CPU resources devoted to rebuilding. Reconstruct The act of remaking a logical drive after changing RAID levels or adding a physical drive to an existing array. Glossary Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 115 Hot Spare: Powered-on stand-by disk drive, ready for use if an online disk fails. · Fail: Out of service, due to a fault occurring on the drive. · Rebuild: Currently being rebuilt with data from a failed drive. Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 116 A resistor connected to a signal wire in a bus or network for impedance matching to prevent reflections—for example, a 50 ohm resistor connected across the end of an Ethernet cable. SCSI buses and some LocalTalk wiring schemes also require terminators. Glossary Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 117 A variant on the SCSI-2 interface. Wide SCSI uses a 16-bit bus, double the width of the original SCSI-1. Wide SCSI devices cannot be connected to a SCSI-1 bus. Like Fast SCSI, Wide SCSI supports transfer rates up to 20 Mbytes/s. Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 118 C-10 Glossary Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
- Page 119 Converting from internal Wide to internal non-Wide (Type 3) Converting internal Wide to internal non-Wide Converting internal Wide to internal non-Wide (Type 30) MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Creating hot spares Creating logical drives Data redundancy...
- Page 120 Operating system software drivers Operating voltage Optimal 2-10 Optimizing Data Storage 5-12 IX-2 Index Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. Other BIOS error messages Parity Partition PCI controller Physical array Physical disk Physical disk roaming Physical drive...
- Page 121 1-vi Termination disable Terminator Troubleshooting Ultra3-SCSI (320M) Unpack Virtual sizing WebBIOS Configuration Utility 4-10 Wide SCSI Windows .NET 6-17 Windows 2000 6-17 Windows NT 6-17 Windows XP 6-17 Index Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. IX-3...
- Page 122 IX-4 Index Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
Page 123: Customer Feedback
Thank you for your help in improving the quality of our documents. MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 Hardware Guide Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. - Page 124 Name Telephone Title Department Company Name Street City, State, Zip Customer Feedback Copyright © 2002 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved. LSI Logic Corporation Technical Publications M/S E-198 Fax: 408.433.4333 Excellent Good Average ____ ____ ____...


Need help?
Do you have a question about the MegaRAID SCSI 320-1 RAID Controller Series 520 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers