Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
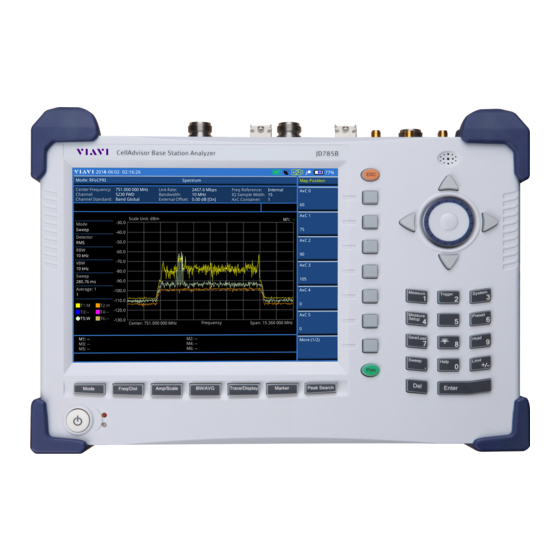
Enabling Australia's Field Technicians to build, troubleshoot
and maintain better communications networks.
This reference material is provided by TMG Test Equipment,
VIAVI's only Master Distributor for Contractors in Australia
Industry Best Pricing
Short to Medium Project-Based Rental Solutions
Dedicated Technical & After-Sales Support
In-house Diagnostics, Repair & NATA Calibration Laboratory
FREECALL
Finance Available
1800 680 680
Advertisement
Table of Contents

















Need help?
Do you have a question about the CellAdvisor JD700B Series and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers