Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Download this manual
See also:
Owner's Manual
Advertisement
Table of Contents
Troubleshooting

Summary of Contents for KTM 250 SX-F 2006
- Page 1 REPAIRMANUAL2005-2006 250 SX-F REPARATURANLEITUNG MANUALE DI RIPARAZIONE MANUEL DE RÉPARATION MANUAL DE REPARACIÓN...
- Page 3 KTM Group Partner...
- Page 5 1 SERVICE-INFORMATIONS 2 GENERAL INFORMATION 3 REMOVING AND REFITTING ENGINE 4 DISASSEMBLING ENGINE 5 SERVICING INDIVIDUAL COMPONENTS 6 ASSEMBLING ENGINE 7 ELECTRICAL 8 FUEL SYSTEM 9 TROUBLE SHOOTING 10 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS 11 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE 12 WIRING DIAGRAMS...
- Page 7 X P L A N A T I O N P D A T I N G 3.206.027-E Repair Manual 250 SX-F Basicversion Modelyear 2005 5/2005 Edition: 05/2005...
- Page 9 „NOTE” POINTS OUT USEFUL TIPS. Use only ORIGINAL KTM SPARE PARTS when replacing parts. The KTM high performance engine is only able to meet user expectations if the maintenance work is performed regularly and professionally. In accordance with the international quality management ISO 9001 standard, KTM uses quality assurance processes that lead to the highest possible product quality.
- Page 11 REPLY FAX FOR REPAIR MANUALS We have made every effort to make our repair manuals as accurate as possible but it is always possible for a mistake or two to creep in. To keep improving the quality of our repair manuals, we request mechanics and shop foremen to assist us as follows: If you find any errors or inaccuracies in one of our repair manual –...
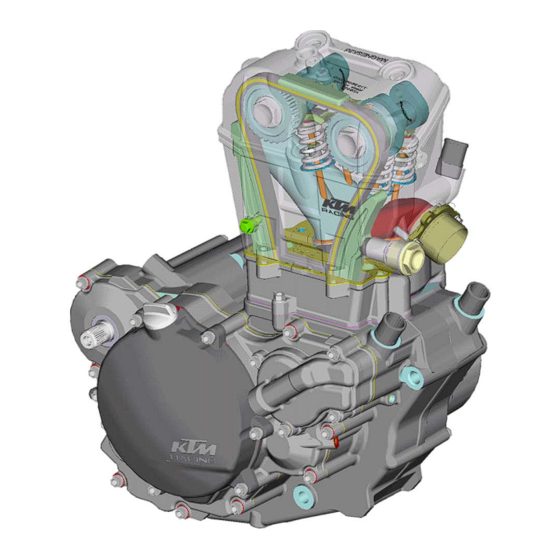
- Page 13 GENERAL INFORMATION INDEX BLEEDING THE COOLING SYSTEM ........2-2 CHANGING THE OIL FILTER .
- Page 15 Bleeding the cooling system The cooling liquid can be drained by removing the screw on the water pump cover. To bleed the cooling system add approx. 1 liter of cooling liquid and remove the bleeder screw . Do not replace the bleeder screw until cooling liquid starts to leak out of the hole without bubbles.
- Page 16 Oil circuit Oil circuit The oil pump draws the engine oil from the transmission oil sump through the long oil screen and conveys it to the oil filter , where any contamination is filtered out. The cleansed engine oil is pumped past the bypass valve through the hole in the crankshaft to the conrod bearing...
- Page 17 Checking the oil level of the hydraulic clutch To check the oil level in the master cylinder of the clutch remove the cover. For this purpose, remove bolts and cover together with the rubber boot . The oil level in the horizontal-standing master cylinder should be 4 mm (0,157 in) below the upper edge.
- Page 18 SPECIAL TOOLS – ENGINE 250 SX-F...
- Page 19 SPECIAL TOOLS – ENGINE 250 SX-F PART NO. DESCRIPTION 560.12.001.000 Universal engine work stand 770.29.002.000 Engine holder for engine work stand 770.29.003.000 Engine holder for engine work stand 503.29.050.000 Bleeding syringe for hydraulic clutch 600.29.073.000 Spark plug wrench 16 mm 770.29.026.000 Limit plug gauge 5 mm 590.29.034.000...
- Page 21 REMOVING AND REFITTING ENGINE INDEX DISMOUNTING THE ENGINE ........3-2 MOUNTING THE ENGINE .
- Page 23 Dismounting the engine – Thoroughly clean the motorcycle and jack up on a suitable assembly stand. Make sure it cannot tip over. – Remove the seat and tank with the spoiler. – Remove the frame protector on both sides. NOTE: you do not need to take the screws on the outside of the swing arm pivot all the way out.
- Page 24 – Pull the manifold pipe forward and remove from the motorcycle. – Open the drain plug on the water pump and allow the cooling liquid to drain into a suitable vessel. – Loosen the hose clamp and pull the radiator hoses off of the engine.
- Page 25 – Disconnect generator connector throttle potentiometer connector – Unscrew the hot start control from the carburetor. – Remove both upper engine braces – Carefully disconnect the engine vent and remove from the motorcycle together with the hose. NOTE: only pull the connection upwards, otherwise it can easily break. –...
- Page 26 – Loosen the chain guide and tilt upwards. – Remove the front and lower engine fixing screws and lift the engine out of the frame from the left side. CAUTION AKE SURE THE MOTORCYCLE CANNOT TIP OVER...
- Page 27 Mounting the engine – Lift the engine into the frame from the left, position and screw in the lower and the front engine fixing screws but do not tighten them yet. – Mount the chain guide and tighten the screw. –...
- Page 28 – Mount the engine vent – Mount both upper engine braces but do not tighten the screws yet. NOTE: the hose the engine vent should run between the two engine braces. – Screw the hot start control into the carburetor. –...
- Page 29 – Connect the radiator hoses to the engine and tighten the hose clamp – Attach the manifold pipe to the front of the motorcycle and slide into the main silencer. – Mount the fixing screw for the manifold pipe with washers the rubber sleeve –...
- Page 30 – Mount the foot brake cylinder , apply Loctite 243 to the screws and tighten to 10 Nm. – Apply Loctite 243 to the ball joint of the pushrod and tighten to 10 – Attach the return spring for the foot brake lever. –...
- Page 31 DISASSEMBLING THE ENGINE INDEX PREPARATORY WORK ......... . .4-2 MOVING THE ENGINE INTO THE TDC POSITION .
- Page 33 Preparatory work – Thoroughly clean the outside of the engine and screw onto the engine work stand 560.12.001.000 with both engine holders 770.29.002.000 and 770.29.003.000. – Unscrew the shift lever, drain the oil and remove the oil filter cover. Discard the O-ring in the oil filter cover and the seal ring on the oil drain plug.
- Page 34 – Remove the valve cover. Moving the engine into the TDC position – Turn the crankshaft until the two marks on the camshaft gears are aligned and precisely above the dividing line between the two camshaft bearing bridges. – Unscrew the engine locking screw , remove the seal ring and screw the engine locking screw back in (tightening torque 20 Nm).
- Page 35 Removing the camshafts – Open the plug on the chain tensioner and pull out the chain tensioner – Discard the sealing washer on the plug and the O-ring on the chain tensioner. – Loosen all of the screws and nuts on the upper camshaft bearing bridge and carefully remove the camshaft bearing bridge.
- Page 36 Removing the cylinder head and piston – Remove the lower camshaft bearing bridge , remove the dowels. – Take the shims out of the spring retainers and mark their mounted positions. NOTE: you will only need to check the valve clearance after assembling;...
- Page 37 – Lift off the cylinder head, paying attention to the chain tensioning rail. – Discard the cylinder head gasket, remove the dowels. – Lift off the cylinder, paying attention to the chain tensioning rail. – Discard the cylinder base gasket, remove the dowels. –...
- Page 38 Removing the clutch cover – Loosen the rotor nut and remove together with the detent edged lock washer. – Screw the special tool 580.12.009.000 on the rotor, hold with a wrench and pull the rotor off the crankshaft by turning in the ejector screw.
- Page 39 Dismantling the clutch – Pull out the pushrod. – Loosen the screws on the pressure cap crosswise and remove together with the washers and springs. – Remove the pressure cap. – Take the clutch disks out of the outer clutch hub. –...
- Page 40 – Remove the outer clutch hub with the needle bearing and inner ring. Removing the chain drive and primary gear – Push the timing chain towards the rear sprocket and pull the rear sprocket off the timing train idler shaft. –...
- Page 41 4-10 Dismantling the shift mechanism – Push back the shift rail and pull out the shift shaft together with the stop disk underneath. – Remove the screw on the shift lock , push back the locking lever and pull off the shift lock; let go of the locking lever. –...
- Page 42 4-11 Removing the oil pumps – Remove the oil pump gear and the oil pump idler. – Pull the needle roller out of the oil pump shaft – Remove the screws and remove the pump cover from the pressure pump –...
- Page 43 4-12 Separating the casing halves, removing the crankshaft and transmission shafts – Turn the engine over and remove all of the casing screws as well as both nuts on the engine work stand holders. – Lift off the left casing half; if necessary, gently tap on the shaft with a plastic hammer.
- Page 45 SERVICING INDIVIDUAL COMPONENTS INDEX LEFT CASING HALF ..........5-2 RIGHT CASING HALF .
- Page 46 IMPORTANT NOTE REGARDS WORKING ON ENGINE HOUSING Read through the following section before commencing work. Then determine the assembly sequence so that the engine housing halves only need to be heated up once before replacing the bearings. Having first removed the dowels, in order to expel the bearings or remove them with light mallet blows, the housing halves must be placed on a suitably large plane surface, supporting the whole of the sealing surface without damaging it.
- Page 47 Left casing half Remove all shaft seal rings and the bearing fixing screws, heat the casing half in the oven to approx. 150° C. – Roller bearing for the crankshaft Press in the roller bearing from the outside with a suitable driver. Press in a new roller bearing from the inside up to the stop.
- Page 48 Right casing half Remove the shaft seal ring and the bearing fixing screws, heat the casing half in the oven to approx. 150° C. – Roller bearing for the crankshaft Press in the roller bearing from the outside with a suitable driver. Press in a new roller bearing from the inside up to the stop.
- Page 49 Bypass valve – Check the valve piston, sealing seat and pressure spring for damage. Minimum length of the pressure spring : 23.5 mm NOTE: if the length of the pressure spring is less than 23.5 mm, the opening pressure of the bypass valve will be reduced. This will lead to a drop in the oil pressure and consequently to increased wear.
- Page 50 Crankshaft If replacing the conrod bearing, make sure the crank pin is in the right position. The holes in the crankshaft web must align with the holes in the crank pin CAUTION F YOU PRESS IN THE CRANK PIN IN THE WRONG POSITION THE CONROD BEARING WILL NOT BE SUPPLIED WITH ENGINE OIL WHICH WILL RESULT IN DAMAGE TO THE...
- Page 51 Measuring the outside dimension of the crankshaft webs – Measure the outside dimension of the crankshaft webs using a sliding gauge, as illustrated. Outside dimension of the crankshaft webs = 54 mm ± 0.05 mm Crankshaft bearings – Fix the crankshaft in the vise with protective jaws. –...
- Page 52 Nikasil cylinder coating Nikasil is the brand name for a cylinder coating process developed by the Mahle piston company. The name is derived from the two materials used in the process - one layer of nickel in which the exceptionally hard silicon carbite is embedded.
- Page 53 Piston – Replace the piston if oil consumption is high or the piston skirt is excessively grooved. – If the piston is to be remounted: 1. Check the piston bearing surface for damage 2. Piston ring grooves: the piston rings must move freely in the groove. Use old piston rings or sandpaper (400 grit) to clean the piston ring grooves.
- Page 54 Lubricating system – Replace the O-rings and sealing washer each time you change the oil filter. – Replace the oil filter each time you change the oil. – Check whether the O-rings are brittle and replace if necessary; always replace the O-rings when you repair the engine. –...
- Page 55 5-10 Camshaft bearing – Clamp the camshaft in a vise with protective aluminum jaws. Position one of the cams so that the camshaft cannot be turned. – Loosen the camshaft gear (A/F 21) and remove the screw. – Pull off the camshaft gear using the extractor 590.29.033.000 and pressure tool 770.29.035.000.
- Page 56 5-11 Camshafts – Check pivot points and cams for wear and damage. – Check the toothing of the camshaft gears for wear and damage. – Replace the camshaft bearings (see pages 5-10). Automatic decompression – Remove the camshaft gear and camshaft bearing (see pages 5-10). –...
- Page 57 5-12 Camshaft bearing bridges – Check both camshaft bearing bridges for wear, seizing marks and damage. – Pull out the cam lever shafts ; they are inserted loosely, and can easily be removed by tapping gently on the camshaft bearing bridge. NOTE: if remounting the cam lever, write down the installation position.
- Page 58 5-13 Timing chain tensioner CAUTION F YOU DO NOT FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS THE TIMING CHAIN WILL NOT BE TENSIONED CORRECTLY AND WILL SKIP RESULTING IN ENGINE DAMAGE NOTE: – The timing chain tensioner operates with spring force and with oil pressure.
- Page 59 5-14 Timing train Thoroughly clean all parts and check for wear. – Check the toothing of the control idler for breakout and wear. – Check the timing chain tensioning rail for seizing marks and damage. – Check the timing chain guide for seizing marks and damage.
- Page 60 5-15 Cylinder head – Loosen the screws and remove the exhaust flange together with the gasket. – Remove the shims from the valve spring retainers (if still mounted). – Dismount the valve keys using the special tools 590.29.019.000 and 770.29.041.000 and relieve the valve springs. NOTE: Used valves must be remounted in the same valve guide as before.
- Page 61 5-16 – Remove the valve spring retainer and valve springs from the cylinder head. – Pull the valve stem sealing off the valve guides and take out the spring washers – Check the sealing areas of the spark plug thread and the valve seats for damage and cracks.
- Page 62 5-17 Clutch – Check the pressure piece for seizing marks and smooth operation. – Check the axial bearing for damage. – Lay the pushrod on an even surface and check for runout. – Check the length of the clutch springs ;...
- Page 63 5-18 Kickstarter – Remove all parts from the kickstarter shaft and clean. – Check the toothing on the kickstarter pinion for wear and the clearance of the mounting. – Check the toothing of the kickstarter idler for wear and the clearance of the mounting.
- Page 64 5-19...
- Page 65 5-20 Shift mechanism – Check the shift forks on the leaf for wear. The forks have a thickness of 4.8 to 4.9 mm when new, the wear limit is 4.6 mm. – Check the shift grooves on the shift drum for wear.
- Page 66 5-21 General information on servicing the transmission Clamp the main shaft or countershaft in a vise (use protective jaws). Remove the gear wheels and check the following parts for wear and seizing marks: – Bearings – Pivot points on the main shaft and countershaft and pivot points on the idler gears –...
- Page 67 5-22 General information on servicing the transmission Clamp the main shaft or countershaft in the vise (use protective jaws). Remove the gears and check the following parts for wear and seizing marks: – Bearings – Pivot points on the main and countershaft and pivot points on idler gears –...
- Page 69 ASSEMBLING THE ENGINE INDEX INSTALLING THE TRANSMISSION SHAFTS AND CRANKSHAFT, ASSEMBLING THE CASING HALVES . . .6-2 ........6-4 MOUNTING THE OIL PUMPS MOUNTING THE SHIFT MECHANISM .
- Page 71 Installing the transmission shafts and crankshaft, assembling the casing halves – Place the right casing half on the engine work stand in an upright position. – Put the two transmission shafts together and insert in the casing half with one hand while you guide the transmission shafts into the bearings with the other hand.
- Page 72 – Mount the crankshaft. NOTE: the cone for the rotor must face up. – Degrease the entire sealing area and apply a thin coat of permanently elastic sealing compound (309 098). – Mount the dowels; do not forget the stop disk for the main shaft. –...
- Page 73 Mounting the oil pumps – Mount the oil pump shaft with the pressure pump rotors and the needle roller as illustrated. The marks on both rotors must be opposite the needle roller. – Slide the preassembled oil pump shaft into the right engine case half.
- Page 74 – Mount the suction pump rotors with the marks facing the case. The marks should no longer be visible when mounted. – Insert the needle roller in the recess of the oil pump shaft and inner rotor. – Fill the oil pump with engine oil. –...
- Page 75 Mounting the shift mechanism – Mount the locking lever with the washer , bushing spring . Apply Loctite 243 to the screw and tighten to 6 Nm. – Press the locking lever away from the shift drum and slip on the shift lock.
- Page 76 Mounting the primary pinion and the chain drive – Move the crankshaft into the TDC position and lock in place with the locking screw (20 Nm). – Mount the woodruff key (if previously removed). – Mount the primary gear, detent edged lock washer and nut (+ Loctite 243, A/F 27, LH thread).
- Page 77 Mounting the clutch – Slide the inner ring , needle bearing and outer clutch hub on the main shaft. NOTE: Turn the starter idler , oil pump gear and outer clutch hub back and forth until the toothing engages. – Slide on the stop disk and driver. –...
- Page 78 – Mount the pressure cap and gradually tighten the screws with the washers and springs crosswise to 10 Nm. Mounting the clutch cover – Mount a new gasket and the clutch cover (do not forget the dowels). – Turn in the screws as illustrated and tighten to 10 Nm. M6x35 M6x25 M6x55...
- Page 79 6-10 – Insert the woodruff key in the crankshaft groove. – Slip on the rotor. – Mount the spring washer and nut. Tighten the nut to 60 Nm. Mounting the piston and cylinder head – Place the well-oiled piston on the cylinder and clamp the piston rings together with the piston ring compressor 600.29.015.000.
- Page 80 6-11 – Attach thrust bushings to the cylinder and mount a new cylinder head gasket. – Pull the timing chain through the timing chain compartment with the cable clips and mount the cylinder head, being careful not to damage the chain tensioning rail. –...
- Page 81 6-12 – Place the shims in the spring retainers in accordance with their mounted position. NOTE: check the valve clearance after assembling; adjust the valve clearance if valves or other parts in the valve control were replaced. – Mount the thrust bushings and pull the timing chain up. –...
- Page 82 6-13 Mounting the camshafts – Place the intake camshaft in the bearing seat, mark aligned with the dividing edge between the camshaft bearing bridges, and run the chain over the camshaft gear such that the chain is tensioned on the intake side. NOTE: –...
- Page 83 6-14 Mounting the chain tensioner – Press the chain tensioner together up to the first notch and lock in this position. Slide into the hole in the cylinder heads together with a new O-ring. NOTE: – Check and lock the chain tensioner: see Chapter 5. –...
- Page 84 6-15 Assembling the engine – Mount the valve cover with a new gasket and tighten the screws. – Place the oil screen on a pin wrench approx. 300 mm long. Insert the pin wrench through the opening in the bore of the opposite engine case wall and slide the oil screen all the way into the engine case.
- Page 85 ELECTRICAL INDEX CDI UNIT ........... .7-2 CHECKING THE IGNITION COIL .
- Page 87 CDI unit Check the cables and socket connections to the CDI unit. The CDI unit can only be tested on an ignition test bench. CAUTION EVER TEST THE UNIT WITH A CONVENTIONAL MEASURING DEVICE IGHLY SENSITIVE ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS COULD BE DESTROYED Checking the ignition coil –...
- Page 88 Ignition system General information The measurements described below will only detect serious defects. Short circuits in the coil that lead to a weak ignition spark or poor generator capacity can be established with the peak voltage adapter 584.29.042.000. In case of a defect, check the cable and the plug and socket connections in the ignition system first.
- Page 89 Measuring with the peak voltage adapter 584.29.042.000: static ignition values Kokusan 4K-3A Measuring conditions: – cold engine – seat and tank removed – all plug and socket connectors and the ground connection in a non-corroding condition, plugs tightly connected – depress the kickstarter forcefully at least 5 times for each measurement Connecting the peak voltage adapter and setting the multimeter The peak voltage adapter is equipped with 4 cables: 2 red and 2 black.
- Page 91 FUEL SYSTEM INDEX DISMOUNTING AND INSTALLING THE CARBURETOR ..... .8-3 DISASSEMBLING THE CARBURETOR ....... . .8-4 CHOKE KNOB AND HOT START SLIDE .
- Page 93 CARBURATOR - KEIHIN FCR-MX 39 550 mm 630 mm 550 mm 400 mm 630 mm...
- Page 94 Dismounting and mounting the carburetor NOTE: clean the motorcycle thoroughly before you start to work on the carburetor. – Remove the seat and tank with the spoilers. – Remove the carburetor cover – Loosen the 2 nuts and disconnect both throttle cables from the carburetor.
- Page 95 Disassembling the carburetor NOTE: Before you start disassembling the carburetor, you should look for a clean workplace. It should offer you enough space to lay out all individual components of the carburetor in perfect order. – Dismount the carburetor and remove any coarse dirt. –...
- Page 96 – Turn the carburetor around, remove the 3 screws and remove the cover of the accelerator pump. NOTE: When dismounting the cover, watch out for the spring and the sealing rings as they may get lost easily. – Remove the 2 sealing rings, the spring and the diaphragm from the pump housing.
- Page 97 – Remove screws and the throttle sensor NOTE: the throttle sensor should only be dismounted if defective. If the screws are loosened, the throttle sensor must be adjusted again. – Remove screw and pull the connecting piece out of the carburetor.
- Page 98 Checking the choke knob and hot start slide Choke knob: The choke knob must be easy to actuate . The piston of the choke knob must not have any pronounced score marks or deposits. Hot start slide: The hot start slide must be easily actuated. The piston on the hot start slide may not have any scores or deposits.
- Page 99 Assembling the carburetor – Mount the idle-air jet and the main air jet – Place the O-ring in the groove and secure the intake trumpet to the carburetor by means of the 2 screws. – Insert the fuel port in the carburetor and fix with screw NOTE: In the mounted state, the connection piece must be easy to turn.
- Page 100 – Position the float and the float needle valve and mount the float hinge pin – Check the float level (see page 8-14). – Mount the float chamber and the gasket, position the bracket for the adjustment screw and fix the float chamber with the screws NOTE: When positioning the float chamber, make sure that the push of the accelerator pump slides into the bore.
- Page 101 8-10 – Apply Loctite 243 to the screw and tighten. – Mount the jet needle and fix with the screw – Position the slide cover with the gasket and fasten with the 2 screws – Fix the vent hoses on the float chamber with the 2 screws...
- Page 102 8-11 Adjusting the position of the throttle valve sensor NOTE: Before checking the position of the throttle valve sensor, you have to adjust the idle speed correctly. – Disengage the plug-and-socket connection of the throttle valve sensor. – Connect a multimeter (measuring range Ω x 1k) to the blue (+) and the black (-) cable of the throttle valve sensor and measure the throttle valve resistance.
- Page 103 8-12 Checking the throttle valve sensor NOTE: The following measurement must be taken at a component temperature of approx. 20°C. – Open the plug-and-socket connection of the throttle valve sensor. – Connect a multimeter (measuring range Ω x 1k) to the blue (+) and the black (-) cable of the throttle valve sensor.
- Page 104 8-13 CARBURETOR – Adjust idling Idling adjustment of the carburetor strongly affects the engine’s starting behavior. That is, an engine whose idling speed is adjusted correctly will be easier to start than one whose idling speed has not been adjusted correctly. The idle speed is controlled by means of the adjusting wheel the mixture control screw .
- Page 105 8-14 Checking the float level (float height) For this purpose, dismount the carburetor and remove the float chamber. Hold the carburetor in a slanted position such that the float will abut the float needle valve but not compress it. In this position, the edge of the float should be parallel with the float chamber sealing surface (see illustration).
- Page 107 TROUBLE SHOOTING INDEX TROUBLE SHOOTING ..........9-2...
- Page 109 ERROR CAUSE REMEDY Open the fuel tap, refuel, do not actuate the choke, follow Engine does not switch on Motorcycle has not been used for a start-up instructions (see driving instructions) longer period of time, leaving old fuel in the float chamber The highly inflammable constituents in the new fuel volatize if left standing over longer periods of time.
- Page 110 ERROR CAUSE REMEDY Disassemble the carburetor and check for wear Engine won't rev up Carburetor overflows because the float needle is soiled or worn Tighten the jets Loose carburetor jets Electronic ignition advance Have the ignition system checked defective Clean and check the fuel system and carburetor Engine does have...
- Page 111 10-1 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS INDEX ENGINE ........... . 11-2 CHASSIS .
- Page 113 10-2 TECHNICAL DATA – ENGINE 250 SX-F Design Liquid-cooled single cylinder 4-stroke engine Displacement 249.51 ccm Bore/Stroke 76 / 55 mm Ratio 12.8 : 1 Fuel unleaded fuel with at least RON 95 Valve timing 4 valves controlled by finger levers and 2 camshafts, driven by a pair of spur gears and a tooth-type chain Camshaft Valve diameter Intake...
- Page 114 10-3 TECHNICAL DATA – CHASSIS 250 SX-F Chassis 250 SXF Frame Central tube chrome-moly-steel frame Fork 4860 MA/PA Wheel travel front/rear 300/335 mm Rear suspension WP Progressive Damping System shock absorber, aluminium swing arm Front brake Disk brake with carbon-steel brake disc Ø 260 mm, brake caliper floated Rear brake Disk brake with carbon-steel brake disc Ø...
- Page 115 10-4 ASSEMBLY CLEARANCE, WEAR LIMIT Crankshaft axial clearance 0.25 - 0.35 mm run out of crank stud max 0.15 mm crankshaft webs - measure outer dimension 54 mm ± 0.05 mm Conrod bearing radial clearance max. 0.03 mm axial clearance max.
- Page 116 10-5 TIGHTENING TORQUES - ENGINE Oil drain plug M12x1.5 20 Nm HH plug, long oil screen M20x1.5 15 Nm AH plug, short oil screen M16x1.5 oil + 15 Nm Pressure relief valve plug M12x1.5 20 Nm HH/AH screws on oil pump cover Loctite 222 + 6 Nm Cylinder head screws oil + 40/50 Nm...
- Page 117 10-6 TIGHTENING TORQUES - CHASSIS HH collar screw on front wheel spindle M24x1,5 40 Nm HH collar screws on front brake caliper Loctite 243 + 25 Nm HH collar screws on front/rear brake disks Loctite 243 + 10 Nm HH collar screws on upper triple clamp 15 Nm HH collar screws on lower triple clamp 10 Nm...
- Page 119 11-1 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE INDEX 250 SX-F ...........12-2...
- Page 120 IF MOTORCYCLE IS USED FOR COMPETITION 10 HOURS SERVICE SHOULD BE CARRIED OUT AFTER EVERY RACE. Service intervalls should never be exceeded by more than 2 hours or 15 liters of fuel. Maintenance work done by KTM authorised workshops is not a substitute for care and checks done by the rider.
- Page 121 Treat blank metal parts (with the exception of brake and exhaust system) with wax-based anti corrosion agent Check tightness of screws, nuts and hose clamps regularly RECOMMENDED INSPECTIONS OR MAINTENANCE WORK BY THE AUTHORIZED KTM WORKSHOP FOR COMPETITIVE RACING (ADDITIONAL ORDER FOR THE KTM WORKSHOP) every...
- Page 123 12-1 WIRING DIAGRAMS INDEX WIRING DIAGRAM ..........13-2 CABLE COLORS .
- Page 124 12-2...
- Page 125 12-3 Cable colours bl: black ye: yellow bu: blue gn: green re: red wh: white br: brown or: orange pi: pink gr: grey pu: purple...