Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for WÄRTSILÄ WÄRTSILÄ 50DF
- Page 1 WÄRTSILÄ 50DF PRODUCT GUIDE...
- Page 2 © Copyright by WÄRTSILÄ FINLAND Oy All rights reserved. No part of this booklet may be reproduced or copied in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, graphic, photocopying, recording, taping or other information retrieval systems) without the prior written permission of the copyright owner.
- Page 3 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Introduction Introduction This Product Guide provides data and system proposals for the early design phase of marine engine installations. For contracted projects specific instructions for planning the installation are always delivered. Any data and information herein is subject to revision without notice. This 2/2016 issue replaces all previous issues of the Wärtsilä...
-
Page 4: Table Of Contents
Table of contents Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Table of contents Main Data and Outputs ........................Maximum continuous output ....................... Output limitations in gas mode ....................Reference conditions ........................Operation in inclined position ...................... Dimensions and weights ......................Operating Ranges ..........................Engine operating range ....................... - Page 5 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Table of contents Compressed Air System ........................Instrument air quality ........................Internal compressed air system ....................External compressed air system ....................Cooling Water System ......................... Water quality ..........................Internal cooling water system ...................... External cooling water system ....................10.
- Page 6 Table of contents Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 18. Engine Room Layout ........................... 18-1 18.1 Crankshaft distances ........................18-1 18.2 Space requirements for maintenance ..................18-2 18.3 Transportation and storage of spare parts and tools ..............18-4 18.4 Required deck area for service work ................... 18-4 19.
-
Page 7: Main Data And Outputs
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 1. Main Data and Outputs Main Data and Outputs The Wärtsilä 50DF is a 4-stroke, non-reversible, turbocharged and inter-cooled dual fuel engine with direct injection of liquid fuel and indirect injection of gas fuel. The engine can be operated in gas mode or in diesel mode. -
Page 8: Output Limitations In Gas Mode
1. Main Data and Outputs Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Output limitations in gas mode 1.2.1 Output limitations due to methane number Fig 1-1 Output limitations due to methane number Notes: Compensating a low methane number gas by The dew point shall be calculated for the specific lowering the receiver temperature below 45°C is site conditions. - Page 9 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 1. Main Data and Outputs 1.2.2 Output limitations due to gas feed pressure and lower heating value Fig 1-2 Output limitation factor due to gas feed pressure / LHV Notes: The above given values for gas feed pressure No compensation (uprating) of the engine output (absolute pressure) are at engine inlet.
-
Page 10: Reference Conditions
1. Main Data and Outputs Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Reference conditions The output is available within a range of ambient conditions and coolant temperatures specified in the chapter Technical Data. The required fuel quality for maximum output is specified in the section Fuel characteristics. -
Page 11: Dimensions And Weights
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 1. Main Data and Outputs Dimensions and weights Fig 1-3 In-line engines (DAAE000316d) Engine LE1* LE3* LE5* W 6L50DF NA357 8205 8310 6170 1295 1295 3580 4000 TPL71 8120 8310 6170 1295 1295 3475 4000 W 8L50DF TPL76 10270 7810... - Page 12 1. Main Data and Outputs Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 1-4 V-engines (DAAE000413c) Engine LE1* LE3* LE5* W 12V50DF NA357 10410 10540 7850 1840 1840 4055 3600 1500 TPL71 10425 10540 7850 1840 1840 4240 3600 1500 W 16V50DF TPL76 13830 13200 10050...
- Page 13 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 1. Main Data and Outputs Fig 1-5 Example of total installation lengths, in-line engines (DAAE000489) Fig 1-6 Example of total installation lengths, V-engines (DAAE000489) Engine Genset weight [ton] W 6L50DF 12940 4940 2235 1090 W 8L50DF 15060 5060 2825...
- Page 14 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 15: Operating Ranges
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 2. Operating Ranges Operating Ranges Engine operating range Below nominal speed the load must be limited according to the diagrams in this chapter in order to maintain engine operating parameters within acceptable limits. Operation in the shaded area is permitted only temporarily during transients. -
Page 16: Loading Capacity
2. Operating Ranges Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 2-1 Operating field for CP-propeller, 975 kW/cyl, rated speed 514 rpm Remarks: The maximum output may have to be reduced depending on gas properties and gas pressure, refer to section "Derating of output in gas mode". The permissible output will in such case be reduced with same percentage at all revolution speeds. - Page 17 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 2. Operating Ranges The load should always be applied gradually in normal operation. Acceptable load increments are smaller in gas mode than in diesel mode and also smaller at high load, which must be taken into account in applications with sudden load changes. The time between load increments must be such that the maximum loading rate is not exceeded.
- Page 18 2. Operating Ranges Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 2.2.2 Constant speed applications Fig 2-3 Maximum load increase rates for engines operating at nominal speed The propulsion control and the power management system must not permit faster load reduction than 20 s from 100% to 0% without automatic transfer to diesel first. In electric propulsion applications loading ramps are implemented both in the propulsion control and in the power management system, or in the engine speed control in case isochronous load sharing is applied.
- Page 19 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 2. Operating Ranges Gas mode Fig 2-4 Maximum instant load steps in % of MCR in gas mode ● Maximum step-wise load increases according to figure ● Steady-state frequency band ≤ 1.5 % ● Maximum speed drop 10 % ●...
-
Page 20: Operation At Low Load And Idling
2. Operating Ranges Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Operation at low load and idling Absolute idling (declutched main engine, disconnected generator): ● Maximum 10 minutes if the engine is to be stopped after the idling. 3-5 minutes idling before stop is recommended. ●... -
Page 21: Technical Data
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Technical Data Introduction This chapter contains technical data of the engine (heat balance, flows, pressures etc.) for design of ancillary systems. Further design criteria for external equipment and system layouts are presented in the respective chapter. Separate data is given for engines driving propellers “ME”... -
Page 22: Wärtsilä 6L50Df
3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 6L50DF Wärtsilä 6L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Engine output 5700 5850 5850 Mean effective pressure IMO compliance Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2... - Page 23 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 6L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Fuel oil system Pressure before injection pumps (PT 101) 800±50 800±50 800±50 Fuel oil flow to engine, approx HFO viscosity before the engine 16...24 16...24...
- Page 24 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 6L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Pressure from expansion tank 70...150 70...150 70...150 Water volume in engine 0.95 0.95 0.95 LT cooling water system Pressure at engine, after pump, nom.
-
Page 25: Wärtsilä 8L50Df
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 8L50DF Wärtsilä 8L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Engine output 7600 7800 7800 Mean effective pressure IMO compliance Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2... - Page 26 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 8L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Fuel oil system Pressure before injection pumps (PT 101) 800±50 800±50 800±50 Fuel oil flow to engine, approx HFO viscosity before the engine 16...24 16...24...
- Page 27 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 8L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Pressure from expansion tank 70...150 70...150 70...150 Water volume in engine 1.35 1.35 1.35 LT cooling water system Pressure at engine, after pump, nom.
-
Page 28: Wärtsilä 9L50Df
3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 9L50DF Wärtsilä 9L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Engine output 8550 8775 8775 Mean effective pressure IMO compliance Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2... - Page 29 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 9L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Fuel oil system Pressure before injection pumps (PT 101) 800±50 800±50 800±50 Fuel oil flow to engine, approx HFO viscosity before the engine 16...24 16...24...
- Page 30 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 9L50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Pressure from expansion tank 70...150 70...150 70...150 Water volume in engine LT cooling water system Pressure at engine, after pump, nom. (PT 471) 250+ static 250+ static 250+ static...
-
Page 31: Wärtsilä 12V50Df
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 12V50DF Wärtsilä 12V50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Engine output 11400 11700 11700 Mean effective pressure IMO compliance Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2... - Page 32 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 12V50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Fuel oil system Pressure before injection pumps (PT 101) 800±50 800±50 800±50 Fuel oil flow to engine, approx 12.0 12.4 12.5...
- Page 33 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 12V50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Pressure from expansion tank 70...150 70...150 70...150 Water volume in engine LT cooling water system Pressure at engine, after pump, nom. (PT 471) 250+ static 250+ static 250+ static...
-
Page 34: Wärtsilä 16V50Df
3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 16V50DF Wärtsilä 16V50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Engine output 15200 15600 15600 Mean effective pressure IMO compliance Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2... - Page 35 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 16V50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Fuel oil system Pressure before injection pumps (PT 101) 800±50 800±50 800±50 Fuel oil flow to engine, approx 16.0 16.6 16.6...
- Page 36 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 16V50DF Diesel Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Pressure from expansion tank 70...150 70...150 70...150 Water volume in engine LT cooling water system Pressure at engine, after pump, nom. (PT 471) 250+ static 250+ static 250+ static...
-
Page 37: Wärtsilä 18V50Df
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 18V50DF Wärtsilä 18V50DF Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Engine output 17100 17550 Mean effective pressure IMO compliance Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 2 Combustion air system (Note 1) Flow at 100% load kg/s 27.5... - Page 38 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Wärtsilä 18V50DF Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Fuel oil system Pressure before injection pumps (PT 101) 800±50 800±50 Fuel oil flow to engine, approx 18.0 18.6 HFO viscosity before the engine 16...24 16...24 Max.
- Page 39 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 3. Technical Data Wärtsilä 18V50DF Diesel Diesel mode mode mode mode Cylinder output Engine speed Pressure from expansion tank 70...150 70...150 Water volume in engine LT cooling water system Pressure at engine, after pump, nom. (PT 471) 250+ static 250+ static Pressure at engine, after pump, max.
- Page 40 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 41: Description Of The Engine
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 4. Description of the Engine Description of the Engine Definitions Fig 4-1 In-line engine and V-engine definitions (1V93C0029 / 1V93C0028) Main components and systems Main dimensions and weights are presented in chapter Main Data and Outputs. 4.2.1 Engine Block The engine block, made of nodular cast iron, is cast in one piece for all cylinder numbers. -
Page 42: Cylinder Liner
4. Description of the Engine Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The crankshaft is forged in one piece and mounted on the engine block in an under-slung way. In V-engines the connecting rods are arranged side-by-side on the same crank pin in order to obtain a high degree of standardization. -
Page 43: Camshaft And Valve Mechanism
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 4. Description of the Engine together with the upper deck and the side walls form a box section in the four corners of which the hydraulically tightened cylinder head bolts are situated. The cylinder head features two inlet and two exhaust valves per cylinder. All valves are equipped with valve rotators. - Page 44 4. Description of the Engine Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The venting valve of the gas common rail pipe is used to release the gas from the common rail pipe when the engine is transferred from gas operating mode to diesel operating mode. The valve is pneumatically actuated and controlled by the engine control system.
-
Page 45: Lubricating System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 4. Description of the Engine and well protected inside the hot box. The feed pipes distribute the pilot fuel from the common rail to the injection valves. The pilot diesel injection part of the twin fuel oil injection valve has a needle actuated by a solenoid, which is controlled by the engine control system. - Page 46 4. Description of the Engine Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide mounted on the engine. The engine safety module handles fundamental safety, for example overspeed and low lubricating oil pressure shutdown. The safety module also performs fault detection on critical signals and alerts the alarm system about detected failures. The local control panel has push buttons for local start/stop and shutdown reset, as well as a display showing the most important operating parameters.
-
Page 47: Cross Section Of The Engine
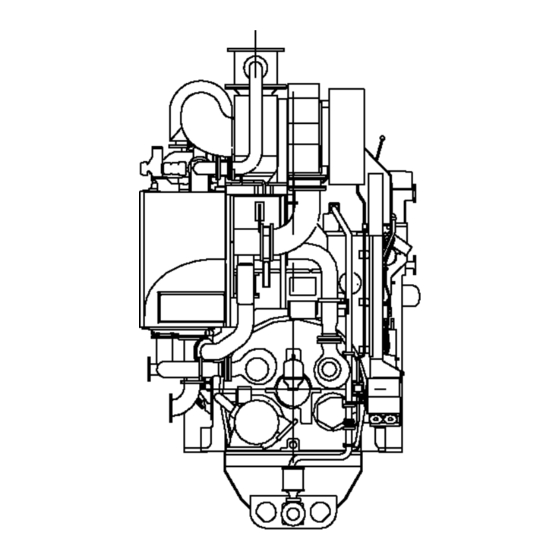
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 4. Description of the Engine Cross section of the engine Fig 4-2 Cross section of the in-line engine (1V58B2480) Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016... - Page 48 4. Description of the Engine Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 4-3 Cross section of the V-engine (1V58B2523) Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
-
Page 49: Free End Cover
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 4. Description of the Engine Free end cover All engine driven pumps are installed on the free end cover. The torsional vibration damper, if fitted, is fully covered by the free end cover. Fig 4-4 Built-on pumps at the free ends of the in-line and V-engines Wärtsilä... -
Page 50: Overhaul Intervals And Expected Life Times
4. Description of the Engine Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Overhaul intervals and expected life times The following overhaul intervals and lifetimes are for guidance only. Actual figures will be different depending on operating conditions, average loading of the engine, fuel quality used, fuel handling system, performance of maintenance etc. -
Page 51: Piping Design, Treatment And Installation
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation Piping Design, Treatment and Installation This chapter provides general guidelines for the design, construction and planning of piping systems, however, not excluding other solutions of at least equal standard. Installation related instructions are included in the project specific instructions delivered for each installation. -
Page 52: Trace Heating
5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Table 5-1 Recommended maximum velocities on pump delivery side for guidance Piping Pipe material Max velocity [m/s] LNG piping Stainless steel Fuel gas piping Stainless steel / Carbon steel Fuel oil piping (MDF and HFO) Black steel Lubricating oil piping Black steel... -
Page 53: Pipe Class
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation The pressure in the system can: ● Originate from a positive displacement pump ● Be a combination of the static pressure and the pressure on the highest point of the pump curve for a centrifugal pump ●... -
Page 54: Insulation
5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide ● Ship Rules Part 6 Chapter 13, Gas Fuelled Engine Installations Table 5-2 Classes of piping systems as per DNV rules Media Class I Class II Class III MPa (bar) °C MPa (bar) °C... -
Page 55: Flexible Pipe Connections
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation System Methods Starting air A,B,C Cooling water A,B,C Exhaust gas A,B,C Charge air A,B,C In case of carbon steel pipes Methods applied during prefabrication of pipe spools A = Washing with alkaline solution in hot water at 80°C for degreasing (only if pipes have been greased) B = Removal of rust and scale with steel brush (not required for seamless precision tubes) D = Pickling (not required for seamless precision tubes) Methods applied after installation onboard... -
Page 56: Clamping Of Pipes
5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 5-1 Flexible hoses Clamping of pipes It is very important to fix the pipes to rigid structures next to flexible pipe connections in order to prevent damage caused by vibration. The following guidelines should be applied: ●... - Page 57 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 5. Piping Design, Treatment and Installation Fig 5-2 Flange supports of flexible pipe connections (4V60L0796) Fig 5-3 Pipe clamp for fixed support (4V61H0842) Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
- Page 58 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 59: Fuel System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fuel System Acceptable fuel characteristics 6.1.1 Gas fuel specification As a dual fuel engine, the Wärtsilä 50DF engine is designed for continuous operation in gas operating mode or diesel operating mode. For continuous operation without reduction in the rated output, the gas used as main fuel in gas operating mode has to fulfill the below mentioned quality requirements. - Page 60 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The distillate grades mentioned above can be described as follows: ● DMX: A fuel which is suitable for use at ambient temperatures down to -15°C without heating the fuel. Especially in merchant marine applications its use is restricted to lifeboat engines and certain emergency equipment due to the reduced flash point.
- Page 61 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System It shall be ensured that the pour point is suitable for the equipment on board, especially if the ship operates in cold climates. If the sample is dyed and not transparent, then the water limit and test method ISO 12937 shall apply. If the sample is not clear and bright, the test cannot be undertaken and hence the lubricity limit shall not apply.
- Page 62 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Remarks: Additional properties specified by Wärtsilä, which are not included in the ISO specification. Max. 1010 kg/m³ at 15°C provided that the fuel treatment system can remove water and solids (sediment, sodium, aluminium, silicon) before the engine to specified levels.
- Page 63 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System 6.1.3 Liquid bio fuels The engine can be operated on liquid bio fuels according to the specifications in tables "6-4 Straight liquid bio fuel specification" or "6-5 Biodiesel specification based on EN 14214:2012 standard".
- Page 64 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Table 6-5 Biodiesel specification based on EN 14214:2012 standard Property Unit Limit Test method ref. Viscosity at 40°C, min...max. 3.5...5 ISO 3104 Viscosity, before injection pumps, min. Density at 15°C, min...max. kg/m³ 860...900 ISO 3675 / 12185 Cetane number, min.
-
Page 65: Operating Principles
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Operating principles Wärtsilä 50DF engines are usually installed for dual fuel operation meaning the engine can be run either in gas or diesel operating mode. The operating mode can be changed while the engine is running, within certain limits, without interruption of power generation. -
Page 66: Fuel Gas System
6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fuel gas system 6.3.1 Internal fuel gas system Internal fuel gas system for in-line engines Fig 6-1 Internal fuel gas system, in-line engines (DAAE010198b) System components: Safety filter Cylinder Gas admission valve Venting valve Pipe connections: Size Pressure class... - Page 67 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Internal fuel gas system for V-engines Fig 6-2 Internal fuel gas system,V-engines (DAAE010199c) System components Safety filter Cylinder Gas admission valve Venting valve Sensors and indicators SE614A/B...SE6#4A/B Knock sensor PT901 Gas pressure Pipe connections Size Pressure class Standard...
- Page 68 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide When operating the engine in gas mode, the gas is injected through gas admission valves into the inlet channel of each cylinder. The gas is mixed with the combustion air immediately upstream of the inlet valve in the cylinder head. Since the gas valve is timed independently of the inlet valve, scavenging of the cylinder is possible without risk that unburned gas is escaping directly from the inlet to the exhaust.
- Page 69 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System 6.3.2 External fuel gas system Fuel gas system, with instrument cabinet Fig 6-3 Example of fuel gas system with instrument cabinet (DAAF022750D) System components Pipe connections Gas detector Gas inlet Gas double wall system ventilation fan Gas system ventilation 10N05 Gas valve unit...
- Page 70 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fuel gas system, with solenoid valve cabinet Fig 6-4 Example of fuel gas system with solenoid valve cabinet (DAAF077105) System components Pipe connections Gas detector Gas inlet Gas double wall system ventilation fan Gas system ventilation 10N05 Gas valve unit...
- Page 71 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System The fuel gas can typically be contained as CNG, LNG at atmospheric pressure, or pressurized LNG. The design of the external fuel gas feed system may vary, but every system should provide natural gas with the correct temperature and pressure to each engine. Double wall gas piping and the ventilation of the piping The annular space in double wall piping is ventilated artificially by underpressure created by ventilation fans.
- Page 72 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Gas valve unit (10N05) Before the gas is supplied to the engine it passes through a Gas Valve Unit (GVU). The GVU include a gas pressure control valve and a series of block and bleed valves to ensure reliable and safe operation on gas.
- Page 73 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fig 6-6 Gas valve unit P&I diagram (DAAF051037C) Unit components: Gas filter First block valve Shut off valve Control air filter Vent valve Shut off valve Inert gas filter Second block valve Pressure regulator Manual shut off valve Gas control valve CV-V0#...
- Page 74 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Pipe size DN65 DN80 DN100 PN10 10mm 10mm 10mm Fig 6-7 Main dimensions of the enclosed GVU for W50DF (DAAF060741) Fig 6-8 Main dimensions of the open GVU for W50DF (DAAF075752A) 6-16 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
- Page 75 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fig 6-9 Gas valve unit, open type (DAAF072567) System components: Gas filter First block valve Shut off valve Control air filter Vent valve Shut off valve Inert gas filter Second block valve Pressure regulator Manual shut off valve Gas control valve CV-V0#...
- Page 76 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide It is always recommended to have one main shut-off valve directly outside the engine room and valve room in any kind of installation. Fuel gas venting In certain situations during normal operation of a DF-engine, as well as due to possible faults, there is a need to safely ventilate the fuel gas piping.
- Page 77 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Gas feed pressure The required fuel gas feed pressure depends on the expected minimum lower heating value (LHV) of the fuel gas, as well as the pressure losses in the feed system to the engine. The LHV of the fuel gas has to be above 28 MJ/m at 0°C and 101.3 kPa.
-
Page 78: Fuel Oil System
6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fuel oil system 6.4.1 Internal fuel oil system Internal fuel oil system for in-line engines Fig 6-10 Internal fuel oil system, in-line engines (3V69E8745-1i) System components: Injection pump Pilot fuel pump Injection valve with pilot solenoid and nozzle Pilot fuel safety valve Pressure control valve Fuel leakage collector... - Page 79 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Internal fuel oil system for V-engines Fig 6-11 Internal fuel oil system, V-engines (3V69E8746-1h) System components: Injection pump Pilot fuel filter Fuel leakage collector Injection valve with pilot solenoid Pilot fuel pump Water separator and nozzle Pressure control valve Pilot fuel safety valve...
- Page 80 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide There are separate pipe connections for the main fuel oil and pilot fuel oil. Main fuel oil can be Marine Diesel Fuel (MDF) or Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO). Pilot fuel oil is always MDF and the pilot fuel system is in operation in both gas- and diesel mode operation.
-
Page 81: Fuel Tanks
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fig 6-12 Fuel oil viscosity-temperature diagram for determining the pre-heating temperatures of fuel oils (4V92G0071b) Example 1: A fuel oil with a viscosity of 380 cSt (A) at 50°C (B) or 80 cSt at 80°C (C) must be pre-heated to 115 - 130°C (D-E) before the fuel injection pumps, to 98°C (F) at the separator and to minimum 40°C (G) in the bunker tanks. - Page 82 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide To ensure sufficient time for settling (water and sediment separation), the capacity of each tank should be sufficient for min. 24 hours operation at maximum fuel consumption. The tanks should be provided with internal baffles to achieve efficient settling and have a sloped bottom for proper draining.
- Page 83 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fuel treatment Separation Heavy fuel (residual, and mixtures of residuals and distillates) must be cleaned in an efficient centrifugal separator before it is transferred to the day tank. Classification rules require the separator arrangement to be redundant so that required capacity is maintained with any one unit out of operation.
- Page 84 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide ● Feed pump (1P02) ● Pre-heater (1E01) ● Sludge tank (1T05) ● Separator (1S01/1S02) ● Sludge pump ● Control cabinets including motor starters and monitoring Fig 6-13 Fuel transfer and separating system (V76F6626F) Separator feed pumps (1P02) Feed pumps should be dimensioned for the actual fuel quality and recommended throughput of the separator.
- Page 85 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Separator pre-heater (1E01) The pre-heater is dimensioned according to the feed pump capacity and a given settling tank temperature. The surface temperature in the heater must not be too high in order to avoid cracking of the fuel.
- Page 86 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Sludge tank (1T05) The sludge tank should be located directly beneath the separators, or as close as possible below the separators, unless it is integrated in the separator unit. The sludge pipe must be continuously falling.
- Page 87 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fuel feed system - MDF installations Fig 6-14 Example of fuel feed system, single L-engine installation (DAAF335502) System components: WL50DF 1P03 Circulation pump (MDF) 1E04 Cooler (MDF) 1T04 Leak fuel tank (clean fuel) 1F05 Fine filter (MDF) 1T06...
- Page 88 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 6-15 Example of fuel feed system, single V-engine installation (DAAF335503) System components: WV50DF 1P03 Circulation pump (MDF) 1E04 Cooler (MDF) 1T04 Leak fuel tank (clean fuel) 1F05 Fine filter (MDF) 1T06 Day tank (MDF) 1F07 Suction strainer (MDF) 1T07...
- Page 89 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fig 6-16 Example of fuel feed system, multiple engine installation (DAAE015150D) System components: 1E04 Cooler (MDF) 1P03 Circulation pump (MDF) 1F05 Fine filter (MDF) 1T06 Day tank (MDF) 1F07 Suction strainer (MDF) 1T11 Mixing tank, min.
- Page 90 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 6-17 Example of fuel feed system, multiple engine with stand-by pump (DAAF335504) System components: WL50DF 1P03 Circulation pump (MDF) WV50DF 1P08 Stand-by pump (MDF) 1E04 Cooler (MDF) 1T04 Leak fuel tank (clean fuel) 1F05 Fine filter (MDF) 1T06...
- Page 91 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System If the engines are to be operated on MDF only, heating of the fuel is normally not necessary. In such case it is sufficient to install the equipment listed below. Some of the equipment listed below is also to be installed in the MDF part of a HFO fuel oil system.
- Page 92 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide MDF cooler (1E04) The fuel viscosity may not drop below the minimum value stated in Technical data. When operating on MDF, the practical consequence is that the fuel oil inlet temperature must be kept below 45°C.
- Page 93 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fuel feed system - HFO installations Fig 6-18 Example of fuel oil system (HFO), single main engine (DAAF335564) System components: WL50DF 1P04 Fuel feed pump (booster unit) WV50DF 1P06 Circulation pump (booster unit) 1E02 Heater (booster unit) 1P13...
- Page 94 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 6-19 Example of fuel oil system (HFO), separate booster units (DAAF335565) System components: WL50DF 1N13 Black start fuel oil pump unit WV50DF 1P04 Fuel feed pump (booster unit) 1E02 Heater (booster unit) 1P06 Circulation pump (booster unit) 1E03...
- Page 95 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Fig 6-20 Example of fuel oil system (HFO), one booster unit (DAAF335566) System components: WL50DF 1N13 Black start fuel oil pump unit WV50DF 1P04 Fuel feed pump (booster unit) 1E02 Heater (booster unit) 1P06 Circulation pump (booster unit) 1E03...
- Page 96 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide HFO pipes shall be properly insulated. If the viscosity of the fuel is 180 cSt/50°C or higher, the pipes must be equipped with trace heating. It sha ll be possible to shut off the heating of the pipes when operating on MDF (trace heating to be grouped logically).
- Page 97 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System ● One control valve for steam or thermal oil heaters, a control cabinet for electric heaters ● One thermostatic valve for emergency control of the heaters ● One control cabinet including starters for pumps ●...
- Page 98 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Total consumption of the connected engines added with Capacity the flush quantity of the automatic filter (1F08) Design pressure 1.6 MPa (16 bar) Max. total pressure (safety valve) 0.7 MPa (7 bar) Design temperature 100°C Viscosity for dimensioning of electric motor 1000 cSt...
- Page 99 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System There should be a by-pass line around the consumption meter, which opens automatically in case of excessive pressure drop. If the consumption meter is provided with a prefilter, an alarm for high pressure difference across the filter is recommended.
- Page 100 6. Fuel System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Viscosimeter, booster unit (1I02) The heater is to be controlled by a viscosimeter. The viscosimeter should be of a design that can withstand the pressure peaks caused by the injection pumps of the diesel engine. Design data: Operating range 0...50 cSt...
- Page 101 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 6. Fuel System Design pressure 1.6 MPa (16 bar) Filter fineness 37 μm (absolute mesh size) Maximum permitted pressure drops at 14 cSt: - clean filter 20 kPa (0.2 bar) - alarm 80 kPa (0.8 bar) Overflow valve, HFO (1V05) When several engines are connected to the same feeder/booster unit an overflow valve is needed between the feed line and the return line.
- Page 102 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 103: Lubricating Oil System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System Lubricating Oil System Lubricating oil requirements 7.1.1 Engine lubricating oil The lubricating oil must be of viscosity class SAE 40 and have a viscosity index (VI) of minimum 95. The lubricating oil alkalinity (BN) is tied to the fuel grade, as shown in the table below. BN is an abbreviation of Base Number. - Page 104 7. Lubricating Oil System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7.1.2 Oil in speed governor or actuator An oil of viscosity class SAE 30 or SAE 40 is acceptable in normal operating conditions. Usually the same oil as in the engine can be used. At low ambient temperatures it may be necessary to use a multigrade oil (e.g.
-
Page 105: Internal Lubricating Oil System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System Internal lubricating oil system 7.2.1 Internal LO system, in-line engines Fig 7-1 Internal lubricating oil system, in-line engines (3V69E8745-2i) System components: Oil sump Turbocharger Lubricating oil main pump Sampling cock Crankcase breather Pressure control valve Running-in filter 1) To be removed after commisioning... - Page 106 7. Lubricating Oil System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7.2.2 Internal LO system, V-engines Fig 7-2 Internal lubricating oil system, V-engines (3V69E8746-2h) System components: Oil sump Turbocharger Lubricating oil main pump Sampling cock Crankcase breather Pressure control valve Running-in filter 1) To be removed after commisioning Sensors and indicators: PTZ201 Lubricating oil inlet pressure...
- Page 107 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System The oil sump is of dry sump type. There are two oil outlets at each end of the engine. One outlet at the free end and both outlets at the driving end must be connected to the system oil tank.
-
Page 108: External Lubricating Oil System
7. Lubricating Oil System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide External lubricating oil system 7.3.1 External LO system with engine driven pumps Fig 7-3 Example of lubricating oil system, with engine driven pumps (DAAE021746B) System components: 2E01 Lubricating oil cooler 2N01 Separator unit 2F01 Suction strainer (main lubricating oil pump) 2P02... - Page 109 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System 7.3.2 External LO system without engine driven pumps Fig 7-4 Example of lubricating oil system, without engine driven pumps (DAAF001973A) System components: 2E01 Lubricating oil cooler 2P03 Separator pump (separator unit) 2E02 Heater (separator unit) 2P04 Stand-by pump...
- Page 110 7. Lubricating Oil System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7.3.3 Separation system Separator unit (2N01) Each main engine must have a dedicated lubricating oil separator and the separators shall be dimensioned for continuous separating. If the installation is designed to operate on gas/MDF only, then intermittent separating might be sufficient.
- Page 111 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System engine output [kW] number of through-flows of tank volume per day: 5 for HFO, 4 for MDF operating time [h/day]: 24 for continuous separator operation, 23 for normal dimensioning Sludge tank (2T06) The sludge tank should be located directly beneath the separators, or as close as possible below the separators, unless it is integrated in the separator unit.
- Page 112 7. Lubricating Oil System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 7-5 Example of system oil tank arrangement (DAAE007020e) Design data: Oil tank volume 1.2...1.5 l/kW, see also Technical data Oil level at service 75...80% of tank volume Oil level alarm 60% of tank volume 7.3.5 Gravity tank (2T02) In installations without engine driven pump it is required to have a lubricating oil gravity tank,...
- Page 113 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System 16-, 18V50DF 7.3.6 Suction strainers (2F01, 2F04, 2F06) It is recommended to install a suction strainer before each pump to protect the pump from damage. The suction strainer and the suction pipe must be amply dimensioned to minimize pressure losses.
- Page 114 7. Lubricating Oil System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Water temperature before cooler 45°C Oil temperature before engine 63°C Design pressure 1.0 MPa (10 bar) Margin (heat rate, fouling) min. 15% Fig 7-6 Main dimensions of the lubricating oil cooler Dimensions [mm] Weight, dry Engine [kg]...
- Page 115 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System A viscosity of 50 cSt at 60°C can be used for evaluation of the pressure drop (SAE 40, VI 95). Design data: Temperature before engine, nom 63°C Design pressure 1.0 MPa (10 bar) Pressure drop, max 50 kPa (0.5 bar) 7.3.10...
-
Page 116: Crankcase Ventilation System
7. Lubricating Oil System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7.3.12 Lubricating oil damper (2R03) The 12V engine is delivered with a damper to be installed in the external piping. Fig 7-7 Lubricating oil damper arrangement to external piping (3V35L3112) Crankcase ventilation system The purpose of the crankcase ventilation is to evacuate gases from the crankcase in order to keep the pressure in the crankcase within acceptable limits. - Page 117 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System The size of the ventilation pipe (D2) out from the condensate trap should be bigger than the ventilation pipe (D) com- ing from the engine. For more information about ventilation pipe (D) size, see the external lubricating oil system drawing.
-
Page 118: Flushing Instructions
7. Lubricating Oil System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Flushing instructions Flushing instructions in this Product Guide are for guidance only. For contracted projects, read the specific instructions included in the installation planning instructions (IPI). 7.5.1 Piping and equipment built on the engine Flushing of the piping and equipment built on the engine is not required and flushing oil shall not be pumped through the engine oil system (which is flushed and clean from the factory). - Page 119 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 7. Lubricating Oil System Lubricating oil sample To verify the cleanliness a LO sample shall be taken by the shipyard after the flushing is completed. The properties to be analyzed are Viscosity, BN, AN, Insolubles, Fe and Particle Count.
- Page 120 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 121: Compressed Air System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 8. Compressed Air System Compressed Air System Compressed air is used to start engines and to provide actuating energy for safety and control devices. The use of starting air for other purposes is limited by the classification regulations. To ensure the functionality of the components in the compressed air system, the compressed air has to be free from solid particles and oil. - Page 122 8. Compressed Air System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 8.2.1 Internal compressed air system for in-line engines Fig 8-1 Internal compressed air system, in-line engines (3V69E8745-3i) System components: Starting air master valve Valve for automatic draining Pressure control valve High pressure filter Starting booster for speed governor Air container Flame arrester...
- Page 123 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 8. Compressed Air System 8.2.2 Internal compressed air system for V-engines Fig 8-2 Internal compressed air system, V-engines (3V69E8746-3h) System components: Starting air master valve Valve for automatic draining Pressure control valve High pressure filter Slow turning valve Air container Starting booster for speed governor Stop valve...
-
Page 124: External Compressed Air System
8. Compressed Air System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide External compressed air system The design of the starting air system is partly determined by classification regulations. Most classification societies require that the total capacity is divided into two equally sized starting air receivers and starting air compressors. - Page 125 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 8. Compressed Air System 8.3.2 Oil and water separator (3S01) An oil and water separator should always be installed in the pipe between the compressor and the air vessel. Depending on the operation conditions of the installation, an oil and water separator may be needed in the pipe between the air vessel and the engine.
- Page 126 8. Compressed Air System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide where: total starting air vessel volume [m normal barometric pressure (NTP condition) = 0.1 MPa air consumption per start [Nm ] See Technical data required number of starts according to the classification society maximum starting air pressure = 3 MPa Rmax minimum starting air pressure = See Technical data...
-
Page 127: Cooling Water System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System Cooling Water System Water quality The fresh water in the cooling water system of the engine must fulfil the following requirements: p H ....... min. 6.5...8.5 Hardness ..... max. 10 °dH Chlorides ..... max. -
Page 128: Internal Cooling Water System
9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Internal cooling water system 9.2.1 Internal cooling water system for in-line engines Fig 9-1 Internal cooling water system, in-line engines (3V69E8745-4i) System components: Charge air cooler (HT) HT-water pump Charge air cooler (LT) LT-water pump Sensors and indicators: PT401... - Page 129 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System 9.2.2 Internal cooling water system for V-engines Fig 9-2 Internal cooling water system, V-engines (3V69E8746-4h) System components: Charge air cooler (HT) HT-water pump Charge air cooler (LT) LT-water pump Sensors and indicators: PT401 HT-water inlet pressure TSZ403...
- Page 130 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The fresh water cooling system is divided into a high temperature (HT) and a low temperature (LT) circuit. The HT water circulates through cylinder jackets, cylinder heads and the 1st stage of the charge air cooler. The HT water passes through the cylinder jackets before it enters the HT-stage of the charge air cooler.
- Page 131 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System Fig 9-5 Wärtsilä 50DF 514 rpm in- Fig 9-6 Wärtsilä 50DF 514 rpm V- line engine HT and LT cool- engine HT and LT cooling ing water pump curves water pump curves (4V19L0332A) (4V19L0333A) Wärtsilä...
-
Page 132: External Cooling Water System
9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide External cooling water system 9.3.1 CW system for in-line engine in common circuit built-on pumps and evaporator Fig 9-7 Cooling water system, in-line engine in common circuit built-on pumps and evaporator (DAAF072992) System components: 1E04 Cooler (MDF return line) - Page 133 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System 9.3.2 CW system for engines in dedicated circuits with built-on pumps, generator cooling and evaporator Fig 9-8 Cooling water system, in-line and V-engines in dedicated circuits with built-on pumps, generator cooling and evaporator (DAAF072974) System components: 1E04 Cooler (MDF return line)
- Page 134 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9.3.3 CW system system for in-line engine with combined LT/HT cooling systems Fig 9-9 Cooling water system, in-line engines with combined LT/HT cooling systems (DAAF333647) System components: WL50DF 4S01 Air venting 2E01 Lube oil cooler 4T03 Additive dosing tank...
- Page 135 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System 9.3.4 CW system system for V-engine with combined LT/HT cooling systems Fig 9-10 Cooling water system, V-engines with combined LT/HT cooling systems (DAAF333651) System components: WV50DF TC/FE 4P09 Transfer pump WV50DF TC/DE 4S01 Air venting 2E01...
- Page 136 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9.3.5 CW system system for V-engine with separate LT/HT cooling systems Fig 9-11 Cooling water system, V-engines with separate LT/HT cooling systems (DAAF333806) System components: WV50DF TC/FE 4S02 Air daerator (HT) WV50DF TC/DE 4S03 Air daerator (LT) 2E01...
- Page 137 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System 9.3.6 CW system system for multiple engines with separate LT/HT cooling systems Fig 9-12 Cooling water system, multiple engines with separate LT/HT cooling systems (DAAF333808) System components: Wärtsilä L50DF 4P15 Circulating pump (LT) Wärtsilä...
- Page 138 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9.3.7 CW system system for multiple engines with combined LT/HT cooling systems Fig 9-13 Cooling water system, multiple engines with combined LT/HT cooling systems (DAAF333807) System components: WL50DF 4P09 Transfer pump WV50DF 4P15 Circulating pump (LT) 2E01...
- Page 139 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System 9.3.8 CW system system for in-line engine, single main engine Fig 9-14 Cooling water system for in-line single main engine (DAAF333648) System components: WL50DF 4P09 Transfer pump 2E01 Lube oil cooler 4S01 Air venting 4E05 Heater (preheater)
- Page 140 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9.3.9 CW system system for V-engine, single main engine Fig 9-15 Cooling water system for V-engine, single main engine (DAAF333652) System components: WV50DF TC/FE 4P05 Stand-by pump (LT) WV50DF TC/DE 4P09 Transfer pump 2E01 Lube oil cooler 4S01...
- Page 141 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System It is recommended to divide the engines into several circuits in multi-engine installations. One reason is of course redundancy, but it is also easier to tune the individual flows in a smaller system.
- Page 142 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The charge air temperature is controlled according to engine load. 9.3.14 Temperature control valve for heat recovery (4V02) The temperature control valve after the heat recovery controls the maximum temperature of the water that is mixed with HT water from the engine outlet before the HT pump. The control valve can be either self-actuated or electrically actuated.
- Page 143 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System Fig 9-16 Central cooler main dimensions (4V47F0004). Example for guidance only Number of cylinders A [mm] B [mm] C [mm] H [mm] T [mm] Weight [kg] 1910 1135 1350 1910 1135 1400 1910 1435 1430...
- Page 144 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Air separator (4S01) It is recommended to install efficient air separators in addition to the vent pipes from the engine to ensure fast evacuation of entrained air. These separators should be installed: 1 Directly after the HT water outlet on the engine.
- Page 145 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System The expansion tank should be equipped with an inspection hatch, a level gauge, a low level alarm and necessary means for dosing of cooling water additives. The vent pipes should enter the tank below the water level. The vent pipes must be drawn separately to the tank (see air venting) and the pipes should be provided with labels at the expansion tank.
- Page 146 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide on heavy fuel, but strongly recommended also for engines that operate exclusively on marine diesel fuel. The energy required for preheating of the HT cooling water can be supplied by a separate source or by a running engine, often a combination of both.
- Page 147 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System ● Electric or steam heaters ● Circulating pump ● Control cabinet for heaters and pump ● Set of thermometers ● Non-return valve ● Safety valve Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 9-21...
- Page 148 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 9-18 Example of preheating unit, electric (4V47K0045) Table 9-2 Example of preheating unit Capacity [kW] Water content [kg] Weight [kg] 1455 1455 1445 1000 1645 1000 1100 1640 1100 1100 1640 1100 1100 1710...
- Page 149 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9. Cooling Water System Fig 9-19 Example of preheating unit, steam Type L1 [mm] L2 [mm] Dry weight [kg] KVDS-72 1160 KVDS-96 1160 KVDS-108 1160 KVDS-135 1210 KVDS-150 1210 KVDS-170 1190 1210 KVDS-200 1190 1260 KVDS-240 1190 1260 KVDS-270...
- Page 150 9. Cooling Water System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 9.3.25 Thermometers and pressure gauges Local thermometers should be installed wherever there is a temperature change, i.e. before and after heat exchangers etc. Local pressure gauges should be installed on the suction and discharge side of each pump. 9-24 Wärtsilä...
-
Page 151: Combustion Air System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 10. Combustion Air System Combustion Air System 10.1 Engine room ventilation To maintain acceptable operating conditions for the engines and to ensure trouble free operation of all equipment, attention to shall be paid to the engine room ventilation and the supply of combustion air. -
Page 152: Combustion Air System Design
10. Combustion Air System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide It is good practice to provide areas with significant heat sources, such as separator rooms with their own air supply and extractors. Under-cooling of the engine room should be avoided during all conditions (service conditions, slow steaming and in port). - Page 153 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 10. Combustion Air System from the engine, when the intake air is cold, so that the air is allowed to heat up in the engine room. 10.2.1 Charge air shut-off valve, "rigsaver" (optional) In installations where it is possible that the combustion air includes combustible gas or vapour the engines can be equipped with charge air shut-off valve.
- Page 154 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 155: Exhaust Gas System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 11. Exhaust Gas System Exhaust Gas System 11.1 Internal exhaust gas system 11.1.1 Internal combustion air and exhaust gas system for in-line engines Fig 11-1 Internal combustion air and exhaust gas system, in-line engines (3V69E8745-5i) System components: Air filter Water separator Waste gate valve... - Page 156 11. Exhaust Gas System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 11.1.2 Internal combustion air and exhaust gas system for V-engines Fig 11-2 Internal combustion air and exhaust gas system, V-engines (3V69E8746-5h) System components: Air filter Water separator Waste gate valve Turbocharger Restrictor Charge air shut-off valve (optional) Charge air cooler Cylinder...
-
Page 157: Exhaust Gas Outlet
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 11. Exhaust Gas System 11.2 Exhaust gas outlet Fig 11-3 Exhaust pipe connection,(4V58F0057d, -58d) Fig 11-4 Exhaust pipe, diameters and support Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 11-3... - Page 158 11. Exhaust Gas System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Engine type TC type A [mm] B [mm] W 6L50DF TPL71 DN600 NA357 DN450 W 8L50DF TPL76C DN800 1000 W 9L50DF TPL76 DN800 1000 W 12V50DF TPL71 DN600 1200 NA357 DN450 1200 W 16V50DF TPL76 DN800...
-
Page 159: External Exhaust Gas System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 11. Exhaust Gas System 11.3 External exhaust gas system Each engine should have its own exhaust pipe into open air. Backpressure, thermal expansion and supporting are some of the decisive design factors. Flexible bellows must be installed directly on the turbocharger outlet, to compensate for thermal expansion and prevent damages to the turbocharger due to vibrations. - Page 160 11. Exhaust Gas System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide ● The combustion in all cylinders is continuously monitored and should it be detected that all cylinders are not firing reliably, then the engine will automatically trip to diesel mode. ● The exhaust gas system is ventilated by a fan after the engine has stopped, if the engine was operating in gas mode prior to the stop.
- Page 161 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 11. Exhaust Gas System 11.3.4 Piping The piping should be as short and straight as possible. Pipe bends and expansions should be smooth to minimise the backpressure. The diameter of the exhaust pipe should be increased directly after the bellows on the turbocharger.
- Page 162 11. Exhaust Gas System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The supporting must allow thermal expansion and ship’s structural deflections. 11.3.6 Back pressure The maximum permissible exhaust gas back pressure is stated in chapter Technical Data. The back pressure in the system must be calculated by the shipyard based on the actual piping design and the resistance of the components in the exhaust system.
- Page 163 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 11. Exhaust Gas System Fig 11-8 Exhaust gas silencer (4V49E0156A) Table 11-1 Typical dimensions of exhaust gas silencers, Attenuation 35 dB (A) L [mm] D [mm] B [mm] Weight [kg] 7470 1800 1190 4600 1000 8000 1900 1280 5300...
- Page 164 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 165: Turbocharger Cleaning
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 12. Turbocharger Cleaning Turbocharger Cleaning Regular water cleaning of the turbine and the compressor reduces the formation of deposits and extends the time between overhauls. Fresh water is injected into the turbocharger during operation. Additives, solvents or salt water must not be used and the cleaning instructions in the operation manual must be carefully followed. -
Page 166: Abb Turbochargers
12. Turbocharger Cleaning Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide System components Pipe connections Size Rubber hose 12.2 ABB turbochargers Engines equipped with TPL turbochargers are delivered with an automatic cleaning system, which comprises a valve unit mounted in the engine room close to the turbocharger and a common control unit for up to six engines. - Page 167 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 12. Turbocharger Cleaning Fig 12-2 Valve unit Fig 12-3 Control unit Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 12-3...
- Page 168 12. Turbocharger Cleaning Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 12-4 Turbocharger cleaning system (DAAE066685A). System components Diesel engine Flow meter Valve unit Pressure control valve Control unit Flexible hose (Flexible hose length 1.3m) Pipe connections on engine Size Pressure class Standard Cleaning water to turbine DN32 PN40...
-
Page 169: Turbocharger Cleaning System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 12. Turbocharger Cleaning Wärtsilä 50DF engines are delivered with an automatic cleaning system, which comprises a valve unit mounted in the engine room close to the turbocharger and a common control unit for up to six engines. Cleaning is started from the control panel on the control unit and the cleaning sequence is then controlled automatically. -
Page 170: Wärtsilä Control Unit For Four Engines, Unic
12. Turbocharger Cleaning Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Engine Turbocharger Water inlet press Nom water inlet Water inlet flow Water consump- System air for (0-80 l/min) before contr. press after press rate (l/min) tion/wash (l) scavening at low valve (bar) contr. valve load (l/min) 6L50DF TPL71-C... -
Page 171: Exhaust Emissions
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 13. Exhaust Emissions Exhaust Emissions Exhaust emissions from the dual fuel engine mainly consist of nitrogen, carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapour with smaller quantities of carbon monoxide (CO), sulphur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), partially reacted and non-combusted hydrocarbons and particulates. 13.1 Dual fuel engine exhaust components Due to the high efficiency and the clean fuel used in a dual fuel engine in gas mode, the exhaust... - Page 172 13. Exhaust Emissions Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Table 13-1 ISO 8178 test cycles D2: Constant-speed Speed (%) auxiliary engine applica- Power (%) tion Weighting 0.05 0.25 factor E2: Constant-speed Speed (%) main propulsion applica- Power (%) tion including diesel- electric drive and all Weighting 0.15 0.15...
- Page 173 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 13. Exhaust Emissions The IMO Tier 3 NO emission standard effective date starts from year 2016. The Tier 3 standard will apply in designated emission control areas (ECA). The ECAs are to be defined by the IMO. So far, the North American ECA and the US Caribbean Sea ECA have been defined and will be effective for marine diesel engines installed in ships constructed on or after 1.1.2016.
- Page 174 13. Exhaust Emissions Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The IMO Tier 3 NO emission level corresponds to an 80% reduction from the IMO Tier 2 NOx emission standard. The reduction can be reached by applying a secondary exhaust gas emission control system. A Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system is an efficient way for diesel engines to reach the NOx reduction needed for the IMO Tier 3 standard.
-
Page 175: Methods To Reduce Exhaust Emissions
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 13. Exhaust Emissions 13.2.2 Other Legislations There are also other local legislations in force in particular regions. 13.3 Methods to reduce exhaust emissions All standard Wärtsilä engines meet the NOx emission level set by the IMO (International Maritime Organisation) and most of the local emission levels without any modifications. - Page 176 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 177: Automation System
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 14. Automation System Automation System Wärtsilä Unified Controls – UNIC is a modular embedded automation system. UNIC C3 is used for engines with electronically controlled fuel injection and has a hardwired interface for control functions and a bus communication interface for alarm and monitoring. 14.1 UNIC C3 UNIC C3 is a fully embedded and distributed engine management system, which handles all... - Page 178 14. Automation System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Local Display Unit offers a set of menus for retrieval and graphical display of operating data, calculated data and event history. The module also handles communication with external systems over Modbus TCP. Power Distribution Module handles fusing, power distribution, earth fault monitoring and EMC filtration in the system.
-
Page 179: Power Unit
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 14. Automation System Fig 14-2 Local control panel and local display unit 14.1.2 Engine safety system The engine safety module handles fundamental safety functions, for example overspeed protection. It is also the interface to the shutdown devices on the engine for all other parts of the control system. - Page 180 14. Automation System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The power unit contains redundant power converters, each converter dimensioned for 100% load. At least one of the two incoming supplies must be connected to a UPS. The power unit supplies the equipment on the engine with 2 x 24 VDC and 2 x 110 VDC. Power supply from ship's system: ●...
- Page 181 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 14. Automation System Cable From <=> To Cable types (typical) Engine <=> Propulsion Control System 1 x 2 x 0.75 mm Engine <=> Power Management System / Main Switch- 1 x 2 x 0.75 mm board 1 x 2 x 0.75 mm 24 x 0.75 mm 24 x 0.75 mm...
- Page 182 14. Automation System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 14-4 Signal overview (Main engine) 14-6 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
-
Page 183: Functions
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 14. Automation System Fig 14-5 Signal overview (Generating set) 14.2 Functions 14.2.1 Engine operating modes The operator can select four different fuel operating modes: ● Gas operating mode (gas fuel + pilot fuel injection) ● Diesel operating mode (conventional diesel fuel injection + pilot fuel injection) ●... - Page 184 14. Automation System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide automatically trip from gas- into diesel operating mode (gas trip) in several alarm situations. Request for diesel operating mode will always override request for gas operating mode. The engine control system automatically forces the engine to backup operating mode (regardless of operator choice of operating mode) in two cases: ●...
- Page 185 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 14. Automation System The engine efficiency change depending on fuel mix ratio and engine load, please contact Wärtsilä for further information. Fig 14-7 Fuel mixing ratio 14.2.2 Start Start blocking Starting is inhibited by the following functions: ●...
- Page 186 14. Automation System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide ● A combustion check (verify that all cylinders are firing) ● Gas admission is started and engine speed is raised to nominal The start mode is interrupted in case of abnormalities during the start sequence. The start sequence takes about 1.5 minutes to complete.
-
Page 187: Shutdown Mode
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 14. Automation System Fig 14-8 Operating modes are load dependent Points for consideration when selecting fuels When selecting the fuel operating mode for the engine, or before transferring between operating modes, the operator should consider the following: ●... -
Page 188: Alarm And Monitoring Signals
14. Automation System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Emergency stop mode The sequence of engine stopping in emergency stop mode is similar to shutdown mode, except that also the pilot fuel injection is de-activated immediately upon stop signal. Emergency stop is the fastest way of manually shutting down the engine. In case the emergency stop push-button is pressed, the button is automatically locked in pressed position. -
Page 189: Electrical Consumers
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 14. Automation System 14.4 Electrical consumers 14.4.1 Motor starters and operation of electrically driven pumps Separators, preheaters, compressors and fuel feed units are normally supplied as pre-assembled units with the necessary motor starters included. The engine turning device and various electrically driven pumps require separate motor starters. - Page 190 14. Automation System Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Stand-by pump, HT cooling water (if installed) (4P03) The engine control system starts the pump automatically via a motor starter, if the cooling water pressure drops below a preset level when the engine is running. There is a dedicated sensor on the engine for this purpose.
-
Page 191: Foundation
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 15. Foundation Foundation Engines can be either rigidly mounted on chocks, or resiliently mounted on rubber elements. If resilient mounting is considered, Wärtsilä must be informed about existing excitations such as propeller blade passing frequency. Dynamic forces caused by the engine are shown in the chapter Vibration and noise. - Page 192 15. Foundation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide The tool included in the standard set of engine tools is used for hydraulic tightening of the holding down bolts. The piston area of the tools is 72.7 cm² and the hydraulic tightening pressures mentioned in the following sections only apply when using this tool. Lateral supports must be installed for all engines.
- Page 193 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 15. Foundation The size of the wedge type chocks should be 200x360 mm. The chocks should always cover two bolts to prevent it from turning (except the chock closest to the flywheel, which has a single hole). The material may be cast iron or steel. The supporting surface of the seating top plate should be machined so that a bearing surface of at least 75% is obtained.
- Page 194 15. Foundation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 15-1 Seating and fastening, rigidly mounted in-line engines on steel chocks (1V69L1651a) 15-4 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
- Page 195 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 15. Foundation Number of pieces per engine Component W 6L50DF W 8L50DF W 9L50DF Fitted bolt Clearance bolt Adjusting screw Distance sleeve Round nut Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 15-5...
- Page 196 15. Foundation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 15-2 Seating and fastening, rigidly mounted V-engines on steel chocks (1V69L1659a) 15-6 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
- Page 197 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 15. Foundation Number of pieces per engine Component W 12V50DF W 16V50DF W 18V50DF Fitted bolt Clearance bolt Adjusting screw Distance sleeve Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 15-7...
- Page 198 15. Foundation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Number of pieces per engine Component W 12V50DF W 16V50DF W 18V50DF Round nut 15-8 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
- Page 199 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 15. Foundation Fig 15-3 Seating and fastening, rigidly mounted in-line engines on resin chocks (1V69L0082c) Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 15-9...
- Page 200 15. Foundation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Number of pieces per engine Component W 6L50DF W 8L50DF W 9L50DF Fitted bolt Clearance bolt Adjusting screw Distance sleeve Round nut 15-10 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
- Page 201 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 15. Foundation Fig 15-4 Seating and fastening, rigidly mounted V-engines on resin chocks (1V69L0083c) Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 15-11...
- Page 202 15. Foundation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Number of pieces per engine Component W 12V50DF W 16V50DF W 18V50DF Fitted bolt Clearance bolt Adjusting screw Distance sleeve Round nut 15-12 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
- Page 203 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 15. Foundation 15.2.2 Resilient mounting In order to reduce vibrations and structure borne noise, engines may be resiliently mounted on rubber elements. The engine block is so rigid that no intermediate base frame is required. Rubber mounts are fixed to the engine feet by means of a fixing rail.
-
Page 204: Flexible Pipe Connections
15. Foundation Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 15-6 Seating and fastening, resiliently mounted V-engine (DAAE001882) The machining tool permits a maximum distance of 85mm between the fixing rail and the top plate. The brackets of the side and end buffers are welded to the foundation. Due to the soft mounting the engine will move when passing resonance speeds at start and stop. -
Page 205: Vibration And Noise
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 16. Vibration and Noise Vibration and Noise Wärtsilä 50DF engines comply with vibration levels according to ISO 10816-6 Class 5. 16.1 External forces and couples Some cylinder configurations produce external forces and couples. These are listed in the tables below. -
Page 206: Torque Variations
16. Vibration and Noise Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Table 16-2 External couples Engine Speed Frequency Frequency Frequency [rpm] [Hz] [Hz] [Hz] [ k N m ] [ k N m ] [ k N m ] [ k N m ] [ k N m ] [ k N m ] W 9L50DF... -
Page 207: Structure Borne Noise
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 16. Vibration and Noise Polar mass moment of inertia J [kgm W 6L50DF 3020 2900 W 8L50DF 3570 3540 W 9L50DF 4580 4580 W 12V50DF 5310 5310 W 16V50DF 7250 6790 W 18V50DF 8820 8820 16.4 Structure borne noise Fig 16-2 Typical structure borne noise levels... -
Page 208: Air Borne Noise
16. Vibration and Noise Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 16.5 Air borne noise The airborne noise of the engine is measured as a sound power level according to ISO 9614-2. Noise level is given as sound power emitted by the whole engine, reference level 1 pW. The values presented in the graphs below are typical values, cylinder specific graphs are included in the Installation Planning Instructions (IPI) delivered for all contracted projects. -
Page 209: Exhaust Noise
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 16. Vibration and Noise Fig 16-4 Typical sound power level for W V50DF 16.6 Exhaust noise The exhaust noise of the engine is measured as the sound power emitted from the turbocharger outlet without exhaust gas piping connected. Reference value 1 pW. The values presented in the graphs below are typical values, cylinder specific graphs are included in the Installation Planning Instructions (IPI) delivered for all contracted projects. - Page 210 16. Vibration and Noise Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 16-5 Typical sound power level for exhaust noise, W L50DF Fig 16-6 Typical sound power level for exhaust noise, W V50DF 16-6 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
-
Page 211: Power Transmission
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 17. Power Transmission Power Transmission 17.1 Flexible coupling The power transmission of propulsion engines is accomplished through a flexible coupling or a combined flexible coupling and clutch mounted on the flywheel. The crankshaft is equipped with an additional shield bearing at the flywheel end. Therefore also a rather heavy coupling can be mounted on the flywheel without intermediate bearings. -
Page 212: Input Data For Torsional Vibration Calculations
17. Power Transmission Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 17-1 Shaft locking device and brake disc with calipers 17.5 Input data for torsional vibration calculations A torsional vibration calculation is made for each installation. For this purpose exact data of all components included in the shaft system are required. See list below. Installation ●... -
Page 213: Turning Gear
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 17. Power Transmission ● Generator output, speed and sense of rotation ● Mass moment of inertia of all rotating parts or a total inertia value of the rotor, including the shaft ● Torsional stiffness or dimensions of the shaft ●... - Page 214 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 215: Engine Room Layout
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 18. Engine Room Layout Engine Room Layout 18.1 Crankshaft distances Minimum crankshaft distances have to be followed in order to provide sufficient space between engines for maintenance and operation. 18.1.1 In-line engines Fig 18-1 Crankshaft distances, in-line engines (3V69C0320b) Engine type Min. -
Page 216: Space Requirements For Maintenance
18. Engine Room Layout Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Minimum [mm] Recommended [mm] Engine type W 16V50DF 5600 5800 1100 W 18V50DF 5600 5800 1100 18.2 Space requirements for maintenance 18.2.1 Working space around the engine The required working space around the engine is mainly determined by the dismounting dimensions of engine components, and space requirement of some special tools. - Page 217 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 18. Engine Room Layout 18.2.3 Maintenance platforms In order to enable efficient maintenance work on the engine, it is advised to build the maintenance platforms on recommended elevations. The width of the platforms should be at minimum 800 mm to allow adequate working space.
-
Page 218: Transportation And Storage Of Spare Parts And Tools
18. Engine Room Layout Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 18-4 Maintenance platforms, V-engine (3V69C0244) 18.3 Transportation and storage of spare parts and tools Transportation arrangements from engine room to workshop and storage locations must be provided for heavy engine components, for example by means of several chain blocks on rails, or by suitable routes for trolleys. - Page 219 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 18. Engine Room Layout 18.4.1 Service space requirement for the in-line engine Fig 18-5 Service space requirement (DAAE093286C) Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 18-5...
- Page 220 18. Engine Room Layout Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Services spaces in mm 6L50DF 8L-9L50DF Height needed for overhauling cylinder head freely over injection pump 3370 3370 Height needed for transporting cylinder head freely over adjacent cylinder head covers 4000 4000 Height needed for overhauling cylinder head freely over exhaust gas insulation box 4300 4300...
- Page 221 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 18. Engine Room Layout 18.4.2 Service space requirement for the V-engine Fig 18-6 Service space requirement (DAAE093288A) Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 18-7...
- Page 222 18. Engine Room Layout Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Services spaces in mm 12V50DF 16V-, 18V50DF Height needed for overhauling cylinder head freely over injection pump 3150 3150 Height needed for overhauling cylinder head freely over adjacent cylinder head covers 4000 4000 Height needed for overhauling cylinder head freely over exhaust gas insulation box 4860...
-
Page 223: Transport Dimensions And Weights
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights Transport Dimensions and Weights 19.1 Lifting of engines Fig 19-1 Lifting of rigidly mounted in-line engines (4V83D0212c) Weights without flywheel [ton] [mm] [mm] [mm] Engine Lifting Transport Total Engine type device cradle weight W 6L50DF... - Page 224 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 19-2 Lifting of flexibly mounted in-line engines (4V83D0211c) Weights without flywheel [ton] [mm] [mm] [mm] Engine Fixing Lifting Transport Total Engine type rails device cradle weight W 6L50DF 8115 1600 5650 W 8L50DF 9950...
- Page 225 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights Fig 19-3 Lifting of rigidly mounted V-engines (4V83D0248C) Weights without flywheel [ton] X 1) X 2) Engine Lifting device Transport total weight Engine type [mm] [mm] [mm] cradle W 12V50DF 10380 10600 4530 W 16V50DF...
- Page 226 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 19-4 Lifting of flexibly mounted V-engines (4V83D0249C) Weights without flywheel [ton] X 1) X 2) Engine Lifting device Transport Total weight Engine type [mm] [mm] [mm] cradle W 12V50DF 10211 10601 4532 166.1...
-
Page 227: Engine Components
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights 19.2 Engine components Fig 19-5 Turbocharger (3V92L1224e) Weight, Weight, rotor Turbochar- Engine type com- block cart- plete ridge W 6L50DF NA 357 1874 1024 1460 W 6L50DF TPL 71 2003 1050 1957 W 8L50DF TPL 76... - Page 228 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Model Weight Engine type [mm] [mm] [mm] [kg] NA357 1650 W 6L50DF TPL71 1650 1105 W 8L50DF TPL71 1650 1105 W 9L50DF TPL71 1650 1105 NA357 1220 W 12V50DF TPL71 1220 W 16V50DF TPL71 1330...
- Page 229 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights Item Description Weight [kg] Piston Gudgeon pin Connecting rod, upper part Connecting rod, lower part Cylinder head 1250 Cylinder liner Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016 19-7...
- Page 230 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide Fig 19-8 Major spare parts (4V92L1477) Item Description Weight [kg] Injection pump Valve Injection valve Starting air valve Main bearing shell 19-8 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016...
- Page 231 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 19. Transport Dimensions and Weights Item Description Weight [kg] Main bearing screw Cylinder head screw Fig 19-9 Major spare parts (4V92L0931a) Item Description Weight [kg] Split gear wheel Camshaft gear wheel Bigger intermediate wheel Smaller intermediate wheel Wärtsilä...
- Page 232 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 233: Product Guide Attachments
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 20. Product Guide Attachments Product Guide Attachments This and other product guides can be accessed on the internet, from the Business Online Portal at www.wartsila.com. Product guides are available both in web and PDF format. Drawings are available in PDF and DXF format, and in near future also as 3D models. - Page 234 This page intentionally left blank...
-
Page 235: Annex
Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 21. ANNEX ANNEX 21.1 Unit conversion tables The tables below will help you to convert units used in this product guide to other units. Where the conversion factor is not accurate a suitable number of decimals have been used. Length conversion factors Mass conversion factors Convert from... -
Page 236: Collection Of Drawing Symbols Used In Drawings
21. ANNEX Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide 21.2 Collection of drawing symbols used in drawings Fig 21-1 List of symbols (DAAE000806c) 21-2 Wärtsilä 50DF Product Guide - a16 - 9 September 2016... - Page 240 Wärtsilä is a global leader in complete lifecycle power solutions for the marine and energy markets. By emphasising technological innovation and total efficiency, Wärtsilä maximises the environmental and economic performance of the vessels and power plants of its customers. Wärtsilä is listed on the NASDAQ OMX Helsinki, Finland. WÄRTSILÄ...








Need help?
Do you have a question about the WÄRTSILÄ 50DF and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers