Jungheinrich EJD 220 Operating Instructions Manual
Jungheinrich ejd 220 multi-talented truck
Hide thumbs
Also See for EJD 220:
- Operating instructions manual (73 pages) ,
- Operating instructions manual (226 pages)
Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Advertisement
Chapters
Table of Contents
Troubleshooting

Subscribe to Our Youtube Channel
Summary of Contents for Jungheinrich EJD 220
- Page 1 EJD 220 01.10 - Operating instructions 51132781 11.14...
- Page 2 Declaration of Conformity Jungheinrich AG, Am Stadtrand 35, D-22047 Hamburg Manufacturer or agent acting in the European Union Type Option Serial no. Year of manufacture EJD 220 Additional information On behalf of Date G EU Conformity Declaration The undersigned hereby declare that the powered industrial truck described below in...
- Page 4 Foreword Notes on the operating instructions The present ORIGINAL OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS are designed to provide sufficient instruction for the safe operation of the industrial truck. The information is provided clearly and concisely. The chapters are arranged by letter and the pages are numbered continuously.
- Page 5 Copyright Copyright of these operating instructions remains with JUNGHEINRICH AG. Jungheinrich Aktiengesellschaft Am Stadtrand 35 22047 Hamburg - Germany Tel: +49 (0) 40/6948-0 www.jungheinrich.com...
-
Page 6: Table Of Contents
Contents Correct Use and Application ........... General....................Correct application................... Approved application conditions.............. Proprietor responsibilities ................ Adding attachments and/or optional equipment ........Truck Description ..............Application ....................Truck models and rated capacity............. Travel direction definition................. Assemblies and Functional Description........... Assembly Overview ................. Functional Description ................ - Page 7 Charging the battery ................Charging the battery with a stationary charger........Charging the battery with an on-board charger (o) ........ Battery removal and installation .............. Lateral battery removal................Operation ................Safety Regulations for the Operation of the Forklift Truck....... Displays and Controls................Battery discharge monitor................
- Page 8 Lubricants and Lubrication Schedule ............130 Handling consumables safely ..............130 Lubrication Schedule ................132 Consumables................... 133 Maintenance and repairs ................. 134 Preparing the truck for maintenance and repairs ........134 Lifting and jacking up the truck safely............135 Cleaning ....................136 Front cover disassembly................
- Page 10 Appendix JH Traction Battery Operating Instructions These operating instructions apply only to Jungheinrich battery models. If using another brand, refer to the manufacturer's operating instructions.
-
Page 12: A Correct Use And Application
A Correct Use and Application General The truck must be used, operated and serviced in accordance with the present instructions. All other types of use are beyond its scope of application and may result in damage to personnel, the industrial truck or property. Correct application NOTE The maximum load and load distance are indicated on the capacity plate and must... -
Page 13: Approved Application Conditions
Approved application conditions – Operation in industrial and commercial environments. – Permissible temperature range 5°C to 40°C. – Operation only on secure, level surfaces with sufficient capacity. – Do not exceed the permissible surface and spot load limits on the travel routes. –... -
Page 14: Proprietor Responsibilities
Proprietor responsibilities For the purposes of the present operating instructions the “operating company” is defined as any natural or legal person who either uses the industrial truck himself, or on whose behalf it is used. In special cases (e.g. leasing or renting) the proprietor is considered the person who, in accordance with existing contractual agreements between the owner and user of the industrial truck, is charged with operational duties. -
Page 16: B Truck Description
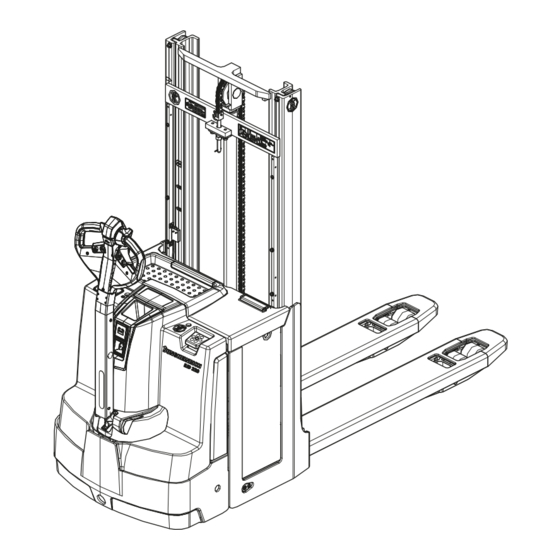
B Truck Description Application The EJD 220 is a three-wheel, electric tiller-operated pallet truck with a steered drive wheel and coupling unit It is designed to be used on level surfaces for lifting, stacking and transporting goods. For transportation, two pallets can be stacked on top of each other. Open bottom pallets or roll cages can be lifted. -
Page 17: Travel Direction Definition
Travel direction definition The following determinations have been made for travel direction specification: Item Travel direction Left Drive direction Load direction Right... -
Page 18: Assemblies And Functional Description
Assemblies and Functional Description Assembly Overview Item Component Item Component t Mast 13 t Charge display t Mast protection pane o CanDis o Protective grille 14 t Key switch (for cold store operation) t Battery cover o CanCode t Collision safety switch o ISM Access Module t Travel switch 15 t Support wheel... -
Page 19: Functional Description
Functional Description Safety mechanisms An enclosed, smooth truck geometry with rounded edges ensures safe handling of the truck. The wheels are surrounded by a solid skirt. The long tiller provides a maximum safety distance to the truck. When it is released and in hazardous situations, a gas strut forces the tiller up into the brake position. - Page 20 Hydraulic System Lifting and lowering are activated via the lift and lower buttons. Pressing the lifting button starts the pump unit, supplying hydraulic oil from the oil reservoir to the lift cylinder. With the two-stage Duplex mast (ZZ) (o) or three-stage telescopic mast (DZ) (o) a short, centre-mounted free lift cylinder initially lifts the load handler (free lift) without changing the overall height of the truck.
- Page 21 Mast The high strength steel sections are narrow, enabling excellent visibility of the load handler. The lift rails and the load handler run on permanently-lubricated and hence maintenance-free angled rollers. Load backrest (o) A load backrest is recommended as an additional protective mechanism to move low or small item loads above the mast protection frame or grille (o).
-
Page 22: Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications The technical specifications comply with the German "Industrial Truck Data Sheet" Guidelines. Technical modifications and additions reserved. Performance data EJD 220 Q Rated capacity 2000 Capacity for mast lift 1000 Capacity for support arm lift 2000 D Load centre distance Travel speed 6.0 / 6.0... -
Page 23: Dimensions
Dimensions... - Page 24 Model EJD 220 Load distance 1) Wheel base 1) 4) 1617 Lift 5) 1660 Initial lift h13 Lowered height h14 Tiller height in the travel position min./max. 711 / 1320 Length 4) 2022 Fork length including fork shank 4) b1/2 Overall width (drive)
-
Page 25: Weights
Weights Net weight incl. battery M/L 937 / 1032 Axle loading, laden 1120 / 1825 front/rear + battery 1160 / 1872 Axle loading, unladen 665 / 280 front/rear + battery 732 /300 Battery weight 220 / 288 Tyre type Tyre size, drive 230 x 65 Load section tyre size (single / tandem) 85 x 95 / 85 x 75... -
Page 26: En Norms
EN norms Noise emission level – EJD 220: 70 dB(A) in accordance with EN 12053 as harmonised with ISO 4871. The noise emission level is calculated in accordance with standard procedures and takes into account the noise level when travelling, lifting and when idle. The noise level is measured at the level of the driver's ear. -
Page 27: Conditions Of Use
Conditions of use Ambient temperature – operating at 5°C to 40°C Special equipment and authorisation are required if the truck is to be used continually in conditions of extreme temperature or condensing air humidity fluctuations. Electrical Requirements The manufacturer certifies compliance with the requirements for the design and manufacture of electrical equipment, according to EN 1175 "Industrial Truck Safety - Electrical Requirements", provided the truck is used according to its purpose. -
Page 28: Identification Points And Data Plates
Identification Points and Data Plates Warnings and notices such as capacity charts, strap points and data plates must be legible at all times. Replace if necessary. Indication Points X.XXXX.XX.XX XXXX XXXX 2000 kg 1600 100 mm Q max Q max... -
Page 29: Data Plate
Item Component Warning: “Do not step under the load handler” Attachment points for lifting by crane (with ZZ mast in the middle) Capacity plate Capacity Qmax Warning: "Do not reach through the mast" Serial number Warning: “No passengers” Model name Test plaque Data plate Cold store truck reference... - Page 30 Data plate The illustration shows the standard version for EU member states. The data plate may differ in other countries. Item Description Item Description Type Year of manufacture Serial number Load centre (mm) Rated capacity (kg) Output Battery voltage (V) Min./max.
-
Page 31: Truck Capacity Plate
Truck capacity plate Previous capacity plate -Nr. Serien-Nr. H mm D mm Current capacity plate SERIAL NO. The rating plate (22) indicates the maximum capacity Q (in kg) for a given load centre C (in mm) and corresponding lift height H (in mm) for the truck with a horizontal load. Example of how to calculate the maximum capacity: At a load centre distance C1 and a lift height H1, the maximum load capacity is Q1 The arrow shaped markings on the outer mast (43) and... -
Page 32: Wind Loads
Wind loads Wind forces can affect the stability of a truck when lifting, lowering and transporting loads with large surface areas. Light loads must be especially secured when they are subjected to wind forces. This will prevent the load from sliding or falling. Stop the truck in both cases. -
Page 33: Double Decker Mode Capacity Plate
Double Decker Mode Capacity Plate The double decker mode capacity plate (23) indicates the capacity Q kg of the truck while travelling: XXX kg 100 mm Q max Q max No transporting with a raised load. Max. capacity for horizontal transporting XXX kg with raised support arms without mast lift. -
Page 34: C Transport And Commissioning
C Transport and Commissioning Lifting by crane WARNING! All persons involved in loading by crane must be trained Incorrect crane loading procedures due to untrained personnel can cause the truck to fall. There is a risk of injury to personnel and a risk of material damage to the truck. Loading must only be performed by specialist personnel trained for this purpose. - Page 35 Lifting the truck by crane Requirements – Park the truck securely, see "Parking the truck securely" on page 63. – Remove any mast guards. Tools and Material Required – Lifting gear – Crane lifting gear Procedure • Secure the lifting slings to the strap points (21).
-
Page 36: Transport
Transport WARNING! Accidental movement during transport Improper fastening of the truck and mast during transport can result in serious accidents. Loading must only be performed by specialist personnel trained for this purpose. The specialist personnel must be instructed in securing loads on road vehicles and handling load securing devices. -
Page 37: Using The Truck For The First Time
Using the Truck for the First Time WARNING! The use of unsuitable energy sources can be hazardous Rectified AC current will damage the assemblies (controllers, sensors, motors etc.) of the electronic system. Unsuitable cable connections (too long, insufficient wire cross-section) to the battery (tow cables) can overheat, setting the truck and battery on fire. -
Page 38: D Battery - Servicing, Recharging, Replacement
D Battery - Servicing, Recharging, Replacement Safety Regulations Governing the Handling of Lead-Acid Batteries Maintenance personnel Batteries may only be charged, serviced or replaced by trained personnel. These operating instructions and the manufacturer’s instructions concerning batteries and charging stations must be observed when carrying out the work. Fire Protection Do not smoke and avoid naked flames when handling batteries. - Page 39 The use of unsuitable batteries that have not been approved for the truck by Jungheinrich, can lead to a deterioration of the braking characteristics of the truck during energy recovery, causing considerable damage to the electric controller and resulting in serious danger to the health and safety of individuals.
-
Page 40: Battery Types
Battery types Depending on the model, the truck will be supplied with different battery types. The following table shows which combinations are included as standard: Battery type Capacity (Ah) Min. weight Max. dimensions (kg) (mm) 24 volt battery 2 PzV 200 624X212X628 24 volt battery 2 PzS 250... -
Page 41: Exposing The Battery
Exposing the battery WARNING! An unsecured truck can cause accidents Parking the truck on an incline or with a raised load handler is dangerous and is strictly prohibited. Park the truck on a level surface. In special cases the truck may need to be secured with wedges. -
Page 42: Charging The Battery
Charging the battery WARNING! The gases produced during charging can cause explosions The battery gives off a mixture of oxygen and hydrogen (electrolytic gas) during charging. Gassing is a chemical process. This gas mixture is highly explosive and must not be ignited. Switch the charging station and truck off first before connecting/disconnecting the charging cable of the battery charging station to/from the battery connector. -
Page 43: Charging The Battery With A Stationary Charger
Charging the battery with a stationary charger Charging the battery Requirements – Expose the battery, see "Exposing the battery" on page 40. Procedure • Disconnect the battery connector (46) from the truck connector. • Connect the battery connector (46) to the charging cable (47) of the stationary charger. -
Page 44: Charging The Battery With An On-Board Charger (O)
The on-board charger consisting of a battery charger and battery controller must not be opened. If faulty, contact the manufacturer’s customer service department. The charger must only be used for batteries supplied by Jungheinrich or other approved batteries provided it has been adapted by the manufacturer's customer service department. - Page 45 4.2.1 Setting the charging characteristics (ELG 2430) The factory setting for trucks without a battery is the 0 position. A battery discharge indicator, a charge/discharge indicator, a CanDis or a bipolar LED can be attached to the connector (49). CAUTION! Remove the mains connector before setting the respective charging curve.
- Page 46 400 Ah Wet cell battery: PzM with pulse characteristic 180 - 400 Ah Jungheinrich 100 - 300 Ah NOTE All other switch positions (48) block the charger, and the battery is not charged. For PzM batteries with a capacity of less than 180 Ah set characteristic 1, beyond 180 Ah set characteristic 5.
- Page 47 4.2.2 Charging the battery Starting to charge with the on-board charger – ELG mains connection Mains supply: 230 V / 110 V (+10/-15%) Mains frequency: 50 Hz / 60 Hz The mains cable and mains connector (51) of the charger are contained in the battery compartment with their storage compartment (50) .
- Page 48 Completing battery charging, restoring the truck to operation NOTE If charging has been interrupted, the full battery capacity will not be available. Requirements – The battery is fully charged. Procedure • Remove the mains connector (51) from the mains socket and store it along with the cable in the storage compartment (50).
- Page 49 LED display (52) Green LED (charge status) Charging complete, battery full. (Charge interval, float or compensation charge). Flashes slowly Charging. Rapid flash Display at beginning of charge or after setting a new characteristic curve. Number of flash pulses corresponds to the characteristic curve set.
-
Page 50: Battery Removal And Installation
Battery removal and installation WARNING! Accident risk during battery removal and installation Due to the battery weight and acid there is a risk of trapping or scalding when the battery is removed and installed. Note the "Safety regulations for handling acid batteries" section in this chapter. Wear safety shoes when removing and installing the battery. -
Page 51: Lateral Battery Removal
Lateral battery removal CAUTION! Trapping hazard Trapping hazard when removing and installing the battery. When removing and installing the battery do not put your hands between the battery and the chassis. Removing the battery Requirements – Truck parked securely, see "Parking the truck securely"... - Page 52 CAUTION! Unsecured battery Unsecured batteries can slide out of the battery tray. After installing the battery make sure the battery lock (53) is in place to prevent it from sliding out. After installing the battery again, check all cables and plug connections for visible signs of damage.
-
Page 54: E Operation
E Operation Safety Regulations for the Operation of the Forklift Truck Driver authorisation The truck may only be used by suitably trained personnel, who have demonstrated to the proprietor or his representative that they can drive and handle loads and have been authorised to operate the truck by the proprietor or his representative. - Page 55 Hazardous area WARNING! Risk of accidents/injury in the hazardous area of the truck A hazardous area is defined as the area in which people are at risk due to travel or lifting operations of the truck, its load handler or the load. This also includes the area within reach of falling loads or lowering/falling operating equipment.
-
Page 56: Displays And Controls
Displays and Controls 13, 62 14, 63... - Page 57 Item Control /Display EJD 220 Function Slow travel button Pressing the slow travel button reduces the travel speed and acceleration. If the tiller is in the brake zone, pressing this button overrides the braking function and the truck can be operated at slow speed.
- Page 58 Item Control /Display EJD 220 Function Collision safety switch Safety feature – When applied the truck travels for approx. 3 seconds in the fork direction. The parking brake then applies. The truck remains switched off until the travel switch is returned to the neutral position.
-
Page 59: Battery Discharge Monitor
Battery discharge monitor The standard setting for the battery discharge indicator / discharge monitor is based on standard batteries. When using maintenance-free or special batteries, the display and cut-out points of the battery discharge monitor must be set by manufacturer's service department. If this adjustment is not made, the battery may become damaged due to deep discharge. -
Page 60: Battery Discharge Indicator
Battery discharge indicator When the truck has been released via the key switch, CanCode or ISM, the battery charge status is displayed. The LED colours (64) represent the following conditions: LED colour Charge status Green 40–100% Orange 30–40% Green/orange 20–30% flashes at 1 Hz 0–20% If the LED is red, the load can no longer be lifted. -
Page 61: Preparing The Truck For Operation
Preparing the Truck for Operation Checks and Operations to Be Performed Before Starting Daily Work WARNING! Damage and other truck or attachment (optional equipment) defects can result in accidents. If damage or other truck or attachment (optional equipment) defects are discovered during the following checks, the truck must be taken out of service until it has been repaired. -
Page 62: Preparing The Truck For Operation
Preparing the truck for operation Switching on the truck Requirements – For checks and operations to be performed before starting daily operation, see "Checks and Operations to Be Performed Before Starting Daily Work" on page 60. Procedure • Pull the Emergency Disconnect (19) to switch it on. •... -
Page 63: Checks And Operations To Be Carried Out When The Truck Is Operational
Checks and operations to be carried out when the truck is operational WARNING! Risk of accident due to damage to or other defects in the truck and optional features If damage or other truck or attachment (optional equipment) defects are discovered during the following checks, the truck must be taken out of service until it has been repaired. -
Page 64: Parking The Truck Securely
Parking the truck securely WARNING! An unsecured truck can cause accidents Do not park the truck on an incline. Do not park the truck without the brakes engaged or with a raised load handler. Park the truck on a level surface. In special cases the truck may need to be secured with wedges. -
Page 65: Industrial Truck Operation
Industrial Truck Operation Safety regulations for truck operation Travel routes and work areas Only use lanes and routes specifically designated for truck traffic. Unauthorised third parties must stay away from work areas. Loads must only be stored in places specially designated for this purpose. The truck must only be operated in work areas with sufficient lighting to avoid danger to personnel and materials. - Page 66 Negotiating slopes and inclines Negotiating slopes and inclines up to 15 % is only permitted when they are recognised lanes. The slopes and inclines must be clean, have a non-slip surface, and negotiating them safely must be within the technical specifications of the truck. The truck must always be driven with the load facing uphill.
-
Page 67: Emergency Disconnect
Emergency Disconnect CAUTION! Applying maximum braking can result in accidents Applying the Emergency Disconnect switch during travel will cause the truck to decelerate to a halt at maximum force. This may cause the load to slide off the load handler. There is a higher risk of accidents and injury. Do not use the Emergency Disconnect switch as a service brake. - Page 68 Press the Emergency Disconnect switch Procedure • Press the Emergency Disconnect (19). All electrical functions are deactivated. The truck brakes to a halt. Press the Emergency Disconnect switch on in emergencies. Releasing the Emergency Disconnect switch Procedure • Pull the Emergency Disconnect switch (19) to unlock it. All electrical functions are enabled and the truck is operational again (provided the truck was operational before the Emergency Disconnect was pressed).
-
Page 69: Automatic Braking
Automatic braking When the tiller is released, it returns automatically to the upper brake zone (B) and the brakes are applied automatically. WARNING! Risk of collision due to a defective tiller Operating the truck with a defective tiller can lead to collisions with persons or objects. If the tiller returns to the brake position slowly or not at all, the truck must be taken out of service until the cause of this fault is be rectified. -
Page 70: Travel
Travel WARNING! Collision hazard when operating the truck Collisions with personnel and equipment can result if the truck is operated with open panels. Do not operate the truck unless the panels and covers are closed and properly locked. When travelling through swing doors etc. make sure that the doors do not activate the collision safety button. - Page 71 oReduced speed when the load handler is fully loweredI When the load handler is fully lowered the truck can only travel at reduced speed. The load handler must be raised in order to use the maximum available speed.
- Page 72 4.4.1 Changing direction during travel CAUTION! Danger when changing direction during travel Changing direction during travel causes the truck to decelerate sharply. When the truck changes direction, it can start travelling at high speed in the opposite direction unless the travel switch is released in time. After setting off in the opposite direction, apply the travel switch gently or not at all.
-
Page 73: Slow Travel
Slow travel CAUTION! Risk of accident if the service brake is deactivated Particular care and attention is required by the operator during slow travel. The service brake is deactivated during slow travel and is only reactivated after the "slow travel" button is released. In hazardous situations brake by immediately releasing the "slow travel"... -
Page 74: Brakes
Brakes WARNING! Accident risk while braking The truck’s braking response depends largely on the floor condition and the type of surface. The truck’s braking distance increases when the ground is wet or dirty. The operator must be aware of floor conditions and take them into account when braking. - Page 75 The truck brakes regeneratively until it starts to move in the opposite direction. 4.7.5 Parking brake The mechanical brake applies automatically when the truck comes to rest.
-
Page 76: Load Handler Raise/Lower
Load handler raise/lower WARNING! Accident risk when lifting and lowering Other people can be injured in the truck's hazardous area. The hazardous area is defined as the area in which people are at risk from the movement of the truck including the load handler, etc. This also includes areas which can be reached by falling loads, operating equipment, etc. - Page 77 4.8.1 Raising the load handler Requirements – Prepare the truck for operation, see page 61. Procedure • Press the “Raise load handler” button (56) until you reach the desired lift height. NOTE Risk of material damage to the hydraulic unit When you have reached the mechanical stops of the load handler, do not press the "Raise load handler"...
- Page 78 4.8.2 Lowering the load handler Requirements – Prepare the truck for operation, see "Preparing the truck for operation" on page 61. Procedure • Press the “Lower load handler” button (58) until you reach the desired lift height. The lift/lower speed can be infinitely controlled via the movement of the button (approx.
-
Page 79: Lifting, Transporting And Depositing Loads
Lifting, transporting and depositing loads WARNING! Unsecured and incorrectly positioned loads can cause accidents. Before lifting a load unit, the driver must make sure that it has been correctly palletised and does not exceed the truck’s capacity. Instruct other people to move out of the hazardous area of the truck. Stop working with the truck if people do not leave the hazardous area. - Page 80 4.9.1 Raising a load Requirements – Load correctly palletised. – Load weight matches the truck's capacity. – Load handler evenly loaded for heavy loads. Procedure • Drive the truck carefully up to the pallet. • Drive the load handler slowly into the pallet until the pallet is against the back of the load handler (see graphic to the right).
- Page 81 4.9.2 Transporting loads Requirements – Load raised correctly. – Mast lowered for proper transport (approx. 150 - 500 mm above the ground). Do not travel with a raised load (>500 mm). In double decker mode: Load handler lowered as far as possible but without touching the lower load, see page 84.
- Page 82 4.9.3 Depositing a load CAUTION! Loads must not be set down on transport or escape routes, in front of safety installations or factory equipment that must be accessible at all times. Requirements – Storage location suitable for storing the load. Procedure •...
- Page 83 4.9.4 Lifting two palletised loads CAUTION! Risk to operational stability In order not to jeopardize the operational stability, pay attention to the weight when transporting two pallets so that the truck does not tip over. In order not to jeopardize the operational stability, the heavier pallet should always be transported underneath.
- Page 84 The additional pallet stop allows double pallets to be stacked without the subsequent need to align the pallets on top of each other.
- Page 85 4.9.5 Transporting two palletised loads above each other CAUTION! Risk to operational stability In order not to jeopardize the operational stability, pay attention to the weight when transporting two pallets so that the truck does not tip over. In order not to jeopardize the operational stability, the heavier pallet should always be transported underneath.
- Page 86 4.9.6 Lowering two palletised loads in turn CAUTION! Loads must not be deposited on travel or escape routes, in front of safety mechanisms or plant equipment that must be accessible at all times. Requirements – Storage location suitable for storing the load. Procedure •...
-
Page 87: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting This chapter enables the operator to localize and rectify basic faults or the results of incorrect operation himself. When trying to locate a fault, proceed in the order shown in the remedy table. If, after carrying out the following remedial action, the truck cannot be restored to operation or if a fault in the electronics system is displayed with a corresponding error code, contact the manufacturer’s service department. -
Page 88: Truck Does Not Start
Truck does not start Possible cause Remedy Battery connector not plugged in Check the battery connector and insert if necessary Emergency Disconnect pressed Release the Emergency Disconnect switch, see page 66 Key switch set to O Set the key switch to “I” Battery charge too low Check battery charge, charge the battery as required... -
Page 89: Load Cannot Be Lifted
Load cannot be lifted Possible Cause Remedy Truck not operational Carry out all measures listed under “Truck does not start” Hydraulic oil level too low Check the hydraulic oil level, see page 140 Battery discharge monitor has switched Charge the battery, see page 41 Faulty fuse Check the fuses, see page 143 Excessive load... -
Page 90: Operating The Truck Without Its Own Drive System
Operating the truck without its own drive system With the right optional equipment (o) it is possible to switch the truck to emergency operation via the GF60 service key: The brakes are released electrically and the truck can move without its own drive system, see "Emergency operation with service key GF60"... - Page 91 Activating the brake Procedure • Use wedges to prevent the truck from moving. • Remove the two M5x16 screws (69) from the brake (70). CAUTION! Open covers can cause injury and accidents The covers (battery cover, side panels, drive compartment cover etc.) must be closed during operation.
-
Page 92: Load Handler Emergency Lowering
Load handler emergency lowering WARNING! Lowering the mast can result in injuries Instruct other people to move out of the hazardous area of the truck during emergency lowering. Never stand underneath a raised load handler. If a second person is used to lower the load handler via the emergency lowering device, this person must consult with the operator. -
Page 93: Optional Equipment
Optional equipment Emergency operation with service key GF60 WARNING! Accidental truck movement When the brakes are de-activated the truck must be parked on a level surface, since the brakes are no longer effective. Do not release the brake on slopes or inclines. Do not park the truck with the brake released. - Page 94 Parking the truck Procedure • Turn the service key to the 0 position and remove the key. After switching back from level 2 to level 1, the lock bar returns to its original position. The brake is now activated again. WARNING! Only return the truck to service when you have identified and rectified the fault.
-
Page 95: Cancode Keypad (O)
CanCode Keypad (o) 8.2.1 Code lock The code lock allows a user or group of users to assign an individual user code. Travel programs can also be assigned to the individual user codes. The user code is configured with a master code and is described in the following sections in this chapter. - Page 96 The keypad consists of 10 digit keys, a Set key (76) and a o key (78). Digit keys The digit keys are used to enter the user or master code and select the travel program. The green LEDs of the digit keys 1, 2 and 3 (73, 74, 75) show the travel program setting.
- Page 97 8.2.2 Preparing the truck for operation with the keypad (CanCode) Preparing the truck for operation by entering a valid operator code Procedure • Pull the Emergency Disconnect to unlock it, see "Emergency Disconnect" on page 66. The LED (77) lights up red. •...
- Page 98 8.2.4 Changing the master code To change the length of the master code you must follow the procedure in "Choose length of the new master code (4-6 digit) and add user codes", see "Choose length of the new master code (4-6 digit) and add user codes" on page 106. If there are still user codes stored in the code lock, the master code to be changed must be the same length as the saved user codes.
- Page 99 Error displays changing the master code For the following events the LED (77) flashes red: Cause Remedy – New master code is already – Switch off the truck, see "Switching off the truck occupied by a user code with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. –...
- Page 100 8.2.5 Add operator code Requirements – To prepare the truck for operation, see "Preparing the truck for operation with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. Procedure • Press the O key (78). • Enter the valid master code with the digit keys. When you enter the valid master code the LED (77) flashes green.
- Page 101 Error displays adding a user code For the following events the LED (77) flashes red: Cause Remedy – The user code entered is not – Switch off the truck, see "Switching off the truck the same length as the with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. master code –...
- Page 102 8.2.6 Change operator code Requirements – To prepare the truck for operation, see "Preparing the truck for operation with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. Procedure • Press the O key (78). • Enter the valid master code with the digit keys. When you enter the valid master code the LED (77) flashes green.
- Page 103 Error displays changing a user code For the following events the LED (77) flashes red: Cause Remedy – The user code entered is not – Switch off the truck, see "Switching off the truck the same length as the with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. master code –...
- Page 104 8.2.7 Delete individual user codes Requirements – To prepare the truck for operation, see "Preparing the truck for operation with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. Procedure • Press the O key (78). • Enter the valid master code with the digit keys. When you enter the valid master code the LED (77) flashes green.
- Page 105 Error displays deleting individual user codes For the following events the LED (77) flashes red: Cause Remedy – The user code entered is not – Switch off the truck, see "Switching off the truck the same length as the with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. master code –...
- Page 106 8.2.8 Delete all user codes, Requirements – To prepare the truck for operation, see "Preparing truck operation with keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. Procedure • Press the O key (78). • Enter the valid master code with the digit keys. When you enter the valid master code the LED (77) flashes green.
- Page 107 8.2.9 Choose length of the new master code (4-6 digit) and add user codes The master code is factory set to a four-digit entry: If necessary, the four-digit master code can be changed to a five or six-digit entry. Before the master code length can be changed, all user codes must be deleted.
- Page 108 8.2.10 Setting the automatic truck cutout (timeframe) Requirements – To prepare the truck for operation, see "Preparing the truck for operation with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. Procedure • Press the O key (78). • Enter the valid master code with the digit keys. When you enter the correct master code the LED (77) flashes green.
- Page 109 Cause Remedy – Cutout time entered is out of – Switch off the truck, see "Switching off the truck range with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. – Enter the time again while making sure it is within range. Fixed cutout time (o) An automatic truck cutout is factory-set.
- Page 110 8.2.11 Assigning the travel program The travel programs are fixed to the user code and can be released or blocked with a configuration code. The configuration code can also be used to assign a starting travel program to each user code. The starting travel program is the travel program that is activated when the truck is switched on and is displayed by the (73,74,75) LEDs.
- Page 111 Specifying a configuration code: Setting Description – Travel program 1 is blocked for the user code selected 1st digit – Travel program 1 is enabled for the user code selected – Travel program 2 is blocked for the user code selected 2nd digit –...
- Page 112 Adapting the travel program configuration to the user code Procedure • Press the O key (78). • Enter the valid master code with the digit keys. When you enter the valid master code the green LED (77) flashes green. • Enter the parameters 0-2-4 with the digit keys. •...
- Page 113 Error displays configuring the travel programs For the following events the LED (77) flashes red: Cause Remedy – Blocked travel program – Switch off the truck, see "Switching off the truck defined as start travel with the keypad (CanCode)" on page 96. program –...
-
Page 114: Setting The Truck Parameters With Cancode
Setting the truck parameters with CanCode CAUTION! Faulty entry Without CanDis only CanCode internal parameters can be changed. Traction controller parameters can only be changed with CanDis, without CanDis the settings must be performed by the manufacturer's service department. CAUTION! Altering settings for the travel, steering and hydraulic functions can result in accidents Increasing or decreasing the settings for travel, steering and hydraulic functions can... - Page 115 The truck is now in travel mode and can be checked. To continue setting, confirm with the Set key (76) again. Saving travel parameters Requirements – Enter all parameters. Procedure • Run "SaveParameters" by pressing 1-2-3-Set. • Confirm with the O key (78).
-
Page 116: Parameters
Parameters Travel program 1 Function Setting Standard Comments Setting Setting 0256 Acceleration 0 - 9 (0.2 – 2.0 m/s (0,4 m/s 0260 Coasting brake 0 - 19 (0.2 – 3,3 m/s (0,5 m/s 0262 Reversing brake 0 - 9 (0.19-1.54 m/s (0,75 m/s 0264 Maximum speed in drive 24 - 60... - Page 117 Common parameters Function Setting Standard Comments Setting Setting 0267 Slow travel speed in drive 16 - 34 depending on travel direction (1,6 - 3,4 km/h) (2,0 km/h) switch 0267 Slow travel speed in fork 16 - 34 depending on travel direction (1,6 - 3,4 km/h) (2,0 km/h)
- Page 118 Battery parameter Function Range Standard Comments setting 1377 Battery type 0 - 5 0 = Normal (wet) (normal / high 1 = High performance performance / dry) (wet) 2 = Dry (maintenance-free) 3 = US "Flat Plate" type 4 = US "Pallet Pro" type 5 = US "Tubular Plate"...
- Page 119 Hydraulic function lock settings Function Range Standard Comments setting 2338 Lift Lower 0 - 15 0 = Lifting and lowering always released 1 = Lifting only with authorisation 2 = Lifting only when stationary 3 = Lifting only with authorisation and only when stationary 4 = Lowering only when stationary 5 = Lifting and lowering only with...
- Page 120 Function Range Standard Comments setting 2338 Lift Lower 0 - 15 13 = Lifting and lowering only with authorisation, lowering only when stationary 14 = Lifting and lowering only when stationary, lowering only with authorisation 15 = Lifting and lowering only with authorisation and only when stationary 1.
-
Page 121: Setting The Battery Parameters With Cancode
Setting the Battery Parameters with CanCode WARNING! Altering parameters cause accidents Altering settings cause accidents. This requires greater attention on the part of the operator The following example shows the parameter setting for the battery type (parameter 1377) to "dry - maintenance-free". - Page 122 Testing an altered parameter Requirements – The parameter is now saved. Procedure • Press the O key (78). • Enter the master code. • Enter the four-digit parameter number "1377" and confirm with the Set key. • Enter sub index "2" and confirm with the Set key. The parameter with subindex are displayed alternately with the current reading.
-
Page 123: Candis Display Instrument (O)
CanDis Display Instrument (o) The instrument indicates: Battery charge display (on board charger only) LED bars for battery charge status "Warning" symbol (yellow), Battery charge recommended "Stop" symbol (red); lift cutout, Battery charge essential No symbol when battery type set to normal or enhanced performance wet cell battery "T"... -
Page 124: Ism Access Module (O)
8.6.1 Discharge monitor function The discharge limit has been reached when the "Stop" symbol (82) lights up. When the discharge monitor function is activated lifting operations are disabled. Travel and lowering are still possible. Lifting is only enabled again when the battery is 70% charged. -
Page 126: F Industrial Truck Maintenance
F Industrial Truck Maintenance Operational Safety and Environmental Protection The checks and servicing operations contained in this chapter must be performed in accordance with the maintenance checklist service intervals. WARNING! Risk of accidents and component damage Any modification to the truck, in particular the safety mechanisms, is prohibited. Exception: Operating companies should only make changes or have changes made to powered industrial trucks if the truck manufacturer is no longer operating in the field and there is no successor to the business;... -
Page 127: Maintenance Safety Regulations
Maintenance Safety Regulations Maintenance and repair personnel The manufacturer has a service department specially trained for these tasks. A maintenance contract with the manufacturer will ensure trouble-free operation. Truck maintenance and repair work must only be carried out by specially trained personnel. -
Page 128: Working On The Electrical System
Working on the electrical system WARNING! Electrical current can cause accidents Make sure the electrical system is voltage-free before starting work on it. The capacitors in the controller must be completely discharged. The capacitors are completely discharged after approximately 10 minutes. Before starting maintenance on the electrical system: Only suitably trained electricians may operate on the truck's electrical system. -
Page 129: Hydraulic System
Hydraulic system WARNING! Leaky hydraulic systems can result in accidents Hydraulic oil can escape from leaky and faulty hydraulic systems. Report any defects immediately to your supervisor. Mark defective truck and take out of service. Do not return the industrial truck to service until you have identified and rectified the fault. -
Page 130: Lift Chains
Lift Chains WARNING! Non-lubricated and incorrectly cleaned lift chains can cause accidents Lift chains are safety-critical parts. They must not contain any serious contamination. Lift chains and pivot pins must always be clean and well lubricated. Lift chains should only be cleaned with paraffin derivatives e.g. petroleum or diesel fuels. -
Page 131: Lubricants And Lubrication Schedule
Lubricants and Lubrication Schedule Handling consumables safely Handling consumables Consumables must always be handled correctly. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions. WARNING! Improper handling is hazardous to health, life and the environment Consumables can be flammable. Keep consumables away from hot components and naked flames. Always keep consumables in prescribed containers. - Page 132 WARNING! Improper handling of oils can be hazardous Oils (chain spray / hydraulic oil) are flammable and poisonous. Dispose of used oils in accordance with regulations. Store used oil safely until it can be disposed of in accordance with regulations. Do not spill oil.
-
Page 133: Lubrication Schedule
Lubrication Schedule 0,55 l g Contact surfaces k Cold Store Application s Grease nipple a Transmission oil drain plug c Hydraulic oil drain plug Hydraulic oil filler neck b Transmission oil filler neck Transmission oil overflow and dipstick 1 Compound ratio for cold store usage 1:1... -
Page 134: Consumables
The Jungheinrich hydraulic oil can only be obtained from the Jungheinrich service department. The use of named alternative hydraulic oils is not prohibited but may lead to a decline in functionality. The Jungheinrich hydraulic oil may be mixed with one of the named alternative hydraulic oils. -
Page 135: Maintenance And Repairs
Maintenance and repairs Preparing the truck for maintenance and repairs All necessary safety measures must be taken to avoid accidents when carrying out maintenance and repairs. The following preparations must be made: Procedure • Park the truck securely, see "Parking the truck securely" on page 63. •... -
Page 136: Lifting And Jacking Up The Truck Safely
Lifting and jacking up the truck safely WARNING! Lifting and jacking up the truck safely In order to raise the truck, the lifting gear must only be secured to the points specially provided for this purpose. You may only work under a raised load handler if it has been secured with a sufficiently strong chain or the fastening bolt. -
Page 137: Cleaning
Cleaning 4.3.1 Cleaning the truck CAUTION! Fire hazard Do not use flammable liquids to clean the industrial truck. Disconnect the battery before starting cleaning work. Carry out all necessary safety measures to prevent sparking before cleaning (e.g. by short-circuiting). CAUTION! Risk of component damage when cleaning the truck Cleaning with a pressure washer can result in malfunctions due to humidity. - Page 138 Cleaning the truck Requirements – Prepare the truck for maintenance and repairs (see "Preparing the truck for maintenance and repairs" on page 134). Tools and Material Required – Water-based solvents – Sponge or cloth Procedure • Clean the surface of the truck with water-based solvents and water. Use a sponge or cloth to clean.
- Page 139 4.3.2 Cleaning the electrical system assemblies CAUTION! Risk of electrical system damage Cleaning the assemblies (controllers, sensors, motors etc.) of the electronic system with water can damage the electrical system. Do not clean the electrical system with water. Clean the electrical system with weak suction or compressed air (use a compressor with a water trap) and not a conductive, anti-static brush.
-
Page 140: Front Cover Disassembly
Front cover disassembly Disassembling the panel Procedure • Remove the two screws (85). • Carefully lift off the front panel (67). The front panel is now disassembled. Assembly is the reverse order. Drive panel disassembly and assembly The drive panel consists of two halves (68 and 86). Drive panel disassembly Tools and Material Required –... -
Page 141: Checking The Hydraulic Oil Level
Checking the hydraulic oil level Check oil level Requirements – Lower the load handler. – Prepare the truck for maintenance and repairs, see "Preparing the truck for maintenance and repairs" on page 134. Procedure • Lift off the front panel, see "Front cover disassembly" on page 139 •... -
Page 142: Check The Gear Oil Level
Check the gear oil level Check the gear oil level Requirements – Park the truck securely, see "Parking the truck securely" on page 63. Tools and Material Required – Oil sump Procedure • Place the oil sump underneath the transmission •... -
Page 143: Tightening The Wheel Nuts
Tightening the wheel nuts The wheel nuts on the drive wheel must be retightened in accordance with the maintenance intervals indicated in the maintenance checklist, see "Servicing and Inspection" on page 148. Tightening the wheel nuts Requirements – Prepare the truck for maintenance and repairs, see "Preparing the truck for maintenance and repairs"... -
Page 144: Checking Electrical Fuses
Procedure • Check the fuse ratings against the table and replace if necessary. The fuses are now checked. Item Component To protect EJD 220 Discharge indicator control fuse Electronic system control fuse 10 A Solenoid / magnetic brake control fuse... -
Page 145: 4.10 Restoring The Truck To Service After Maintenance And Repairs
4.10 Restoring the truck to service after maintenance and repairs Procedure • Thoroughly clean the truck, see page 136. • Lubricate the truck according to the lubrication diagram, see page 132. • Clean the battery, grease the terminals and connect the battery. •... -
Page 146: Decommissioning The Industrial Truck
Decommissioning the Industrial Truck If the truck is to be out of service for more than a month, it must be stored in a frost- free and dry room. All necessary measures must be taken before, during and after decommissioning as described hereafter. When the truck is out of service it must be jacked up so that all the wheels are clear of the ground. -
Page 147: Restoring The Truck To Service After Decommissioning
Restoring the truck to service after decommissioning Procedure • Thoroughly clean the truck, see "Cleaning" on page 136. • Lubricate the truck according to the lubrication schedule, see "Lubrication Schedule" on page 132. • Clean the battery, grease the terminals and connect the battery. •... -
Page 148: Safety Tests To Be Performed At Intervals And After Unusual Incidents
Safety tests to be performed at intervals and after unusual incidents The truck must be inspected at least annually (refer to national regulations) or after any unusual event by a qualified inspector. The manufacturer offers a safety inspection service which is performed by personnel specifically trained for this purpose. -
Page 149: Servicing And Inspection
Servicing and Inspection WARNING! Lack of maintenance can result in accidents Failure to perform regular servicing can lead to truck failure and poses a potential hazard to personnel and equipment. Thorough and expert servicing is one of the most important requirements for the safe operation of the industrial truck. -
Page 150: Maintenance Checklist
Maintenance checklist 10.1 Operating company 10.1.1 Standard equipment Brakes W A B C Test brakes. Electrical System W A B C Test warning and safety devices in accordance with operating instructions. Test displays and controls. Test Emergency Disconnect switch. Power Supply W A B C Check battery cable connections are secure, grease terminals if necessary. - Page 151 10.1.2 Optional equipment Electrolyte recirculation Power Supply W A B C Check hose connections and test the pump.
-
Page 152: 10.2 Customer Service
10.2 Customer Service 10.2.1 Standard equipment Brakes W A B C Test brakes. Check the air gap of the magnetic brake. Electrical System W A B C Check cables and motor mounting are secure. Test warning and safety devices in accordance with operating instructions. - Page 153 Chassis and Superstructure W A B C Check chassis and screw connections for damage. Check doors and/or covers. Check labels are legible and complete. Check mast attachment / mounting. Check mast protection pane / mast grille for damage. Hydraulic operations W A B C Test "hydraulic"...
- Page 154 10.2.2 Optional equipment Aquamatik Power Supply W A B C Test Aquamatik plug, hose connections and float and check for leaks. Test flow indicator and check for leaks. Battery refill system Power Supply W A B C Test battery refill system and check for leaks. Data recorder Electrical System W A B C...
- Page 155 Access module Electrical System W A B C Test access module, check for damage and make sure it is secure. Issued on: 27.05.2013 08:24:37...
- Page 156 A Traction Battery Appendix Contents Traction Battery Appendix............Correct Use and Application..............Data plate ....................Safety Instructions, Warning Indications and other Notes....... Lead acid batteries with armour plated cells and liquid electrolyte..Description....................Operation....................Servicing lead-acid batteries with armour plated cells......PzV and PzV-BS lead-acid batteries with sealed armour plated cells..
-
Page 157: Correct Use And Application
Correct Use and Application Failure to observe the operating instructions, carrying out repairs with non-original spare parts, tampering with the battery or using electrolyte additives will invalidate the warranty. Observe the instructions for maintaining the safety rating during operation for batteries in accordance with Ex I and Ex II (see relevant certification). -
Page 158: Safety Instructions, Warning Indications And Other Notes
Safety Instructions, Warning Indications and other Notes Used batteries must be treated as hazardous waste. These batteries are marked with the recycling symbol and the sign showing a crossed-out rubbish bin, and should not be disposed of with ordinary household waste. waste. -
Page 159: Lead Acid Batteries With Armour Plated Cells And Liquid Electrolyte
Lead acid batteries with armour plated cells and liquid electrolyte Description Jungheinrich traction batteries are lead acid batteries with armour plated cells and liquid electrolyte. The names of the traction batteries are PzS, PzB, PzS Lib and PzM. Electrolyte The rated density of the electrolyte assumes a temperature of 30°C and the rated electrolyte level is fully charged. -
Page 160: Operation
Operation 4.2.1 Commissioning unfilled batteries The operations required must be carried out by the manufacturer's customer service department or a customer service organisation authorised by the manufacturer. 4.2.2 Commissioning filled and charged batteries Checks and operations to be performed before starting daily work Procedure •... - Page 161 4.2.4 Charging the battery WARNING! The gases produced during charging can cause explosions The battery gives off a mixture of oxygen and hydrogen (electrolytic gas) during charging. Gassing is a chemical process. This gas mixture is highly explosive and must not be ignited. Always disconnect the charger and truck before connecting or disconnecting the charger and battery.
- Page 162 The electrolyte temperature rises by approx. 10 K during charging. Charging should therefore only begin when the electrolyte temperature is below 45°C. The electrolyte temperature of batteries must be at least +10°C before charging. Otherwise the battery will not charge correctly. Below 10°C the battery is insufficiently charged with standard charging systems.
-
Page 163: Servicing Lead-Acid Batteries With Armour Plated Cells
Servicing lead-acid batteries with armour plated cells Water quality The quality of the water used to fill up electrolyte must correspond to purified or distilled water. Purified water can be produced through distillation or ion exchangers and is then suitable for the production of electrolyte. 4.3.1 Daily –... -
Page 164: Pzv And Pzv-Bs Lead-Acid Batteries With Sealed Armour Plated Cells
PzV and PzV-BS lead-acid batteries with sealed armour plated cells Description PzV batteries are sealed batteries with fixed electrolytes, to which no water can be added over the entire lifespan of the battery. Relief valves are used as plugs which are destroyed when opened. -
Page 165: Operation
Operation 5.2.1 Commissioning Checks and operations to be performed before starting daily work Procedure • Make sure the battery is in physically good condition. • Make sure the terminals are correct (positive to positive and negative to negative) and check that contacts on the battery terminal conducting system are secure. •... - Page 166 NOTE Charging the battery incorrectly can result in material damage. Incorrect battery charging can result in overloading of the electric wires and contacts, hazardous gas formation and electrolyte leakage from the cells. Always charge the battery with DC current. All DIN 41773 charging procedures are permitted in the format approved by the manufacturer.
- Page 167 Charging the battery Requirements – Electrolyte temperature between +15°C and 35°C Procedure • Open or take off the tray lid or covers from the battery compartment. • Connect the battery to the switched off charger, ensuring the terminals are connect (positive to positive and negative to negative).
-
Page 168: Servicing Pzv And Pzv-Bs Lead-Acid Batteries With Sealed Armour Plated Cells
Servicing PzV and PzV-BS lead-acid batteries with sealed armour plated cells Do not add water! 5.3.1 Daily – Charge the battery after each discharge. 5.3.2 Weekly – Visually inspect for dirt and physical damage. 5.3.3 Every three months – Measure and record the overall voltage. –... -
Page 169: Aquamatik Water Replenishment System
Aquamatik water replenishment system Water replenishment system design > 3 m Water container Tap connection with ball cock Flow indicator Shut-off cock Locking coupling Battery lock connector... -
Page 170: Functional Description
Functional Description The Aquamatik water replenishment system is used to adjust the rated electrolyte level automatically on traction batteries for industrial trucks. The battery cells are interconnected through hoses and are attached to the water supply (e.g. water container) through a plug connection. When the shut-off cock is opened all the cells are filled with water. -
Page 171: Filling Time
Filling time The filling time for a battery depends on the electrolyte level, the ambient temperature and the filling pressure. Filling ends automatically. The water supply line must be disconnected from the battery when the water has been filled. Water quality The quality of the water used to fill up electrolyte must correspond to purified or distilled water. -
Page 172: Cleaning Measures
Cleaning measures The plug systems must only be cleaned with purified water in accordance with DIN 43530-4. No parts of the plugs must come into contact with solvent-based materials or soap. 6.10 Service mobile vehicle Mobile water filling vehicle with pump and filling gun to fill individual cells. The immersion pump in the container generates the necessary filling pressure. -
Page 173: Electrolyte Circulation
Electrolyte circulation Functional Description Electrolyte circulation ensures the supply of air during charging to mix the electrolyte, thereby preventing any acid layer, shortening the charge time (charge factor approx. 1.07) and reducing the formation of gas during charging. The charger must be suitable for the battery and electrolyte circulation. - Page 174 NOTE If an installed electrolyte circulation system is seldom used or not used at all, or if the battery is subjected to severe temperature fluctuations, the electrolyte may flow back into the hose system. Attach a separate coupling system to the air inlet line, such as: locking coupling on the battery side and through-coupling on the air supply side.
-
Page 175: Cleaning Batteries
Cleaning batteries Batteries and trays must be cleaned in order to – maintain cell insulation and protect cells from ground or external conductive parts. – Avoid damage from corrosion and stray currents. – Avoid excessive and varying automatic discharge of the individual cells or block batteries due to stray currents. - Page 176 Cleaning the battery with a high pressure cleaner Requirements – Cell connectors tight, plugged in securely – Cell plugs closed Procedure • Follow the high pressure cleaner's user instructions. • Do not use any cleaning additives. • Observe the permissible cleaning device temperature setting of 140°C. This generally ensures that the temperature does not exceed 60°C at a distance of 30cm behind the outlet nozzle.
-
Page 177: Storing The Battery
Storing the battery NOTE The battery should not be stored for longer than 3 months without charging as otherwise it will no longer be functional. If the battery is to be taken out of service for a long period, it should be stored fully charged in a dry room protected from frost.












Need help?
Do you have a question about the EJD 220 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers