Advertisement
Table of Contents
- 1 Table of Contents
- 2 General View
- 3 Warning and Safety Information
- 4 Installing and Maintaining Electrodes
- 5 Standardizing for Ph Measurement
- 6 Using Setup
- 7 Standardizing for Millivolt Measurement
- 8 Understanding Ph Theory
- 9 Temperature Compensation
- 10 Measuring Ph
- 11 Troubleshooting
- 12 Meter Specifications
- 13 Accessories
- Download this manual
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for Sartorius PB-11
- Page 1 Operation Manual Sartorius Basic Meter PB-11 98648-012-08...
-
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Contents General View Warning and Safety Information Installing and Maintaining Electrodes Standardizing for pH Measurement Using Setup Standardizing for Millivolt Measurement Understanding pH Theory Temperature Compensation Measuring pH Troubleshooting Meter Specifications Accessories C Declaration of Conformity... -
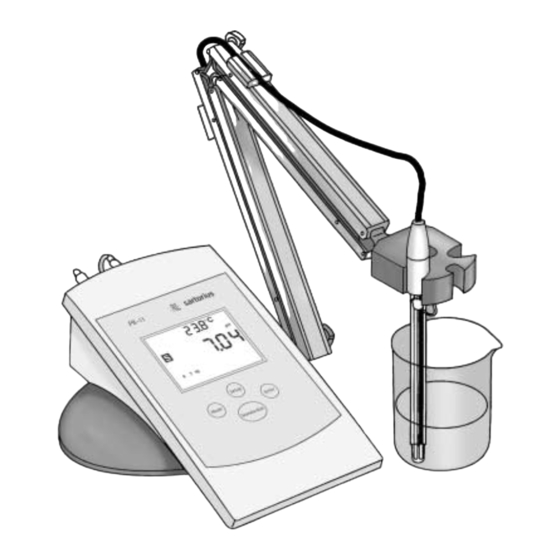
Page 4: General View
General View Front View Setup button: Press to clear buffers, review electrode calibration or select new autorecognized buffers Mode button: Press to toggle between pH and mV mode Standardize button: Press to enter each buffer Enter button: Press to select menu item options Measuring icon Temperature... - Page 5 Rear View Power cable connector Reference electrode connector (used with separate reference electrodes) BNC electrode connector Temperature compensation probe connector AC adapter Connecting to a Power Source...
-
Page 6: Warning And Safety Information
Warning and Safety Information For safety and operating reasons, only authorized service technicians may open the Basic Meter PB-11 housing. Therefore, only authorized technicians may repair or perform maintenance on this pH meter. Any tampering with the pH meter or negligent or intentional damage to this equipment will void any warranty claims against the manufacturer. -
Page 7: Installing And Maintaining Electrodes
Installing and Maintaining Electrodes 1. Remove the protective end cover from the electrode. 2. Before first use of your electrode, or whenever the electrode is dry, soak overnight in a standard solution or KCI solution. 3. Remove the shorting cap on the pH meter connector. Install the electrode by plugging the BNC and ATC connectors into the jacks on the rear panel. - Page 8 4. Option: Install an ion selective electrode by removing the BNC shorting cap and plugging the BNC connector (twist-lock) into the BNC jack. If a combination electrode is not available, plug the separate reference electrode into the ref pin. Reference Electrode 5.
-
Page 9: Standardizing For Ph Measurement
Standardizing for pH Measurement Because electrodes vary in their response, you must standardize (calibrate) your pH meter and electrode to compensate for electrode variation. The more frequently you standardize, the more accurate your measurements. Standardize daily, or more often, for accurate results. This pH meter allows automatic standardization using up to three buffers. - Page 10 3. Clear existing buffers when doing a new 2- or 3-point standardization. Use the Setup button. Also use the Setup button to select the individual sets of buffers. (See page 13.) [Standardize] 4. Press Standardize. The meter recognizes the buffer and flashes a buffer icon.
- Page 11 6. To enter a second buffer, place the electrode in [Standardize] the second buffer solution, stir, allow time for the electrode to stabilize, and press Standardize again. The meter recognizes the buffer and displays the first and second buffer values. 7.
- Page 12 10. After entering three buffers, the Standardizing icon goes out and the Measuring icon appears on the display to indicate that the meter returns to Measuring operation. Note: The meter continually adjusts for temperature. Therefore, buffers may vary slightly from the nominal values because of temperature.
-
Page 13: Using Setup
Using Setup The Setup button lets you clear all the standardiza- tion data that you have entered, review calibration information, or select the buffer set that you want. You can escape the setup mode at any time by pressing pH/mV. 1. - Page 14 4. Press Setup again to display a Set Buffers icon [Setup] and to display the first buffer set icons. 5. Press Enter to select the set of buffers shown on [Setup] or the display or Press Setup again to toggle between [Enter] the existing sets of buffers.
-
Page 15: Standardizing For Millivolt Measurement
Standardizing for Millivolt Measurement (Relative Millivolt) You will normally use millivolt measurements for determining ion concentration and for measuring redox potential (also called ORP, oxidation reduction potential). You will use an ion selective electrode (ISE), combined with a reference electrode, to measure ion concentration. - Page 16 2. Press Mode until your digital display indicates [Mode] mV mode. 3. Press Standardize to enter an mV standard and [Standardize] read relative mV. 4. When the signal becomes stable, or when you press Enter, the current absolute mV value (offset) becomes zero relative millivolts.
- Page 17 5. To clear an mV offset and return to absolute [Setup] millivolt mode, press Setup. The meter displays a flashing Clear icon, and shows the current relative millivolt offset. 6. To clear the previous mV offset, press Enter. [Enter] You then return to absolute mV mode.
-
Page 18: Understanding Ph Theory
Understanding pH Theory Defining pH By using a pH meter, you can determine The measurement of pH plays an important exact pH levels of solutions. For example, rather than say that lemon juice is quite role in identifying and controlling acidity and alkalinity levels for industry and acidic, you can say that lemon juice has research. -
Page 19: Temperature Compensation
Temperature Compensation !Note: Automatic temperature compensation only functions properly if a temperature probe is connected. Temperature compensation influences the results in two different ways: 1. pH values of the buffers change as a function of temperature. Each buffer varies as a function of the tempera- ture of the respective solution. -
Page 20: Measuring Ph
Measuring pH To measure pH with a conven- tional glass pH electrode, the meter uses a pH-sensing glass bulb that is sensitive to hydrogen ions. The potential developed at the glass membrane is directly related to the pH of the solution. The glass electrode is paired with a reference electrode which completes the electrical... -
Page 21: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting 1. If the signal from the electrode is out of range, the display will show “——”. This may happen when the electrode is not immersed in a solution. 2. The meter will display Error when it detects an error in electrode response. During standardization, the message indicates that the electrode is less than 90% or more than 105% of the correct response. - Page 22 Electrode Test 4. To test the pH electrode, place it in a good pH 7 buffer. Press pH/mV to use the mV pH=7 0 ± 30 mV mode, and note the millivolt reading. Repeat for either a pH 4 or pH 10 buffer. pH=4 169 to 186 mV The electrode signals must be within the...
-
Page 23: Meter Specifications
Meter Specifications –2.00 bis +20.00 Readability 0.01 Accuracy ± 0.01 –1800.0 to 1800.0 mV Readability 0.1 mV Accuracy ± 0.2 mV (0.05% if <– 400 mV/>+ 400 mV) Temperature range –5.0 to +105.0°C Readability 0.1°C Accuracy ± 0.2°C Calibration points Maximum 3 buffers Automatic buffer recognition 16 buffers 2;... -
Page 24: Accessories
Accessories Order No. pH combination electrodes: – Plastic body with built-in temperature sensor, KCI liquid-filled PY-P10 – Glass body with built-in temperature sensor KCI liquid-filled, platinum junction PY-P11 – Plastic body with built-in temperature sensor, gel-filled PY-P12 PY-P20 – Plastic body, gel-filled –... - Page 28 Sartorius AG Weender Landstrasse 94–108 37075 Goettingen, Germany Phone +49.551.308.0 Fax +49.551.308.3289 www.sartorius.com Copyright by Sartorius AG, Goettingen, Germany. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reprinted or translated in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Sartorius AG.















Need help?
Do you have a question about the PB-11 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers