Table of Contents
Advertisement
S7012
Version 1.1
Copyright
®
Copyright © 2009 MiTAC International Corporation. All rights reserved. TYAN
is a
registered trademark of MiTAC International Corporation.
Trademark
All registered and unregistered trademarks and company names contained in this
manual are property of their respective owners including, but not limited to the
following.
®
TYAN
is a trademark of MiTAC International Corporation.
®
Intel
Nehalem-EP Series and combinations thereof are trademarks of Intel
Corporation.
AMI, AMI BIOS are trademarks of AMI Technologies.
Microsoft, Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
SuSE is a trademark of Novell.
IBM, PC, AT, and PS/2 are trademarks of IBM Corporation.
Notice
Information contained in this document is furnished by MiTAC International
Corporation and has been reviewed for accuracy and reliability prior to printing.
MiTAC assumes no liability whatsoever, and disclaims any express or implied
warranty, relating to sale and/or use of TYAN products including liability or
warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose or merchantability. MiTAC
retains the right to make changes to product descriptions and/or specifications at
any time, without notice. In no event will MiTAC be held liable for any direct or
indirect, incidental or consequential damage, loss of use, loss of data or other
malady resulting from errors or inaccuracies of information contained in this
document.
1
http://www.tyan.com
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for TYAN TYAN S7012
- Page 1 In no event will MiTAC be held liable for any direct or indirect, incidental or consequential damage, loss of use, loss of data or other malady resulting from errors or inaccuracies of information contained in this document.
-
Page 2: Table Of Contents
Table of Contents Check the box contents! Chapter 1: Introduction Congratulations Hardware Specifications AST2050 Application Chapter 2: Board Installation Board Image Block Diagram Board Parts, Jumpers and Connectors Installing the Processor and Heatsink Thermal Interface Material Finishing Installing the Heatsink Tips on Installing Motherboard in Chassis Installing the Memory Attaching Drive Cables... -
Page 3: Check The Box Contents
Check the box contents! If any of these items are missing, please contact your vendor/dealer for replacement before continuing with the installation process. 1x S7012 motherboard 2 x mini SAS Cable (optional) 6 x Serial ATA Cable 1 x USB2.0 cable 1 x S7012 User’s Manual 1 x S7012 Quick Reference Guide 1 x I/O Shield Installation Guide... - Page 4 NOTE http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 5: Chapter 1: Introduction
All of this provides the S7012 the power and flexibility to meet the needs of nearly any server application. Remember to visit TYAN’s Website at http://www.tyan.com. There you can find information on all of TYAN’s products with FAQs, online manuals and BIOS... -
Page 6: Ast2050 Application
Input /Output RJ-45 Power Front Panel SATA Chipset Voltage System Monitoring Temperature Others Onboard Chipset AST2050 IPMI Server Feature Management AST2050 iKVM Feature Brand / ROM size BIOS Feature Form Factor Form Factor Board Dimension Operating OS supported list System... -
Page 7: Chapter 2: Board Installation
Chapter 2: Board Installation You are now ready to install your motherboard. The mounting hole pattern of the S7012 matches the SSI EEB specification. Before continuing with installation, confirm that your chassis supports an SSI EEB motherboard. How to install our products right… the first time The first thing you should do is reading this user’s manual. -
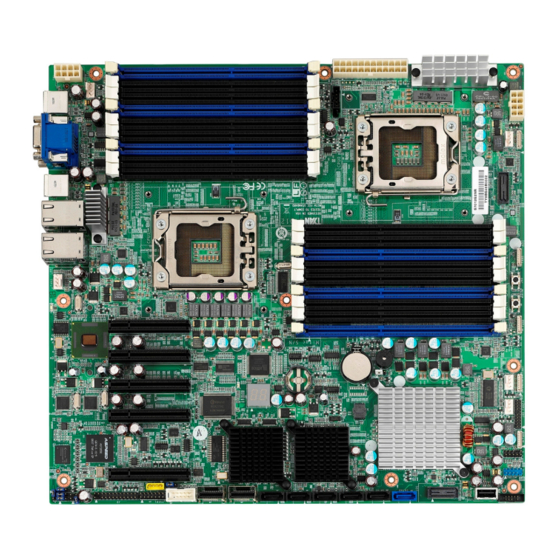
Page 8: Board Image
2.1- Board Image S7012 This picture is representative of the latest board revision available at the time of publishing. The board you receive may or may not look exactly like the above picture. http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 9: Block Diagram
2.2 - Block Diagram S7012 http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 10: Board Parts, Jumpers And Connectors
2.3 - Board Parts, Jumpers and Connectors This diagram is representative of the latest board revision available at the time of publishing. The board you receive may not look exactly like the above diagram. Jumper Legend OPEN - Jumper OFF, without jumper cover CLOSED –... - Page 11 Jumper/Connector J9 (TYFP1) USB3 J41/J42/J43/J44/J45 J2/J8/J36/J37/J38 J39/J40 JP1/JP2 Function Standard Front Panel Connector BMC I C Bus Header USB Front Panel Header (blue) COM2 Connector PSMI Connector Chassis Intrusion Header CPLD JTAG Header Type-A USB Connector ICH SGPIO Header Port 80 Header 8-pin 4056 Fan Connector (reserved for BB) 4-pin Fan Connector Reset Switch/Power Switch...
- Page 12 (From left to right) SATA5/SATA4/SATA3/SATA2/SATA1/SATA0 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 13 J18: COM2 Connector J15: PORT 80 Header J16: BMC I C Header J34: USB Front Panel Header (Blue) SATA0/1/2/3/4/5: Serial ATA Connector Signal Signal CLK_33M PLTRST Signal IPMB_DAT IPMB_CLK Signal USB D- USB D+ Connects to the Serial ATA ready drives via the Serial ATA cable.
- Page 14 J6: Chassis Intrusion Header Signal INTRUDER# http://www.tyan.com Signal...
- Page 15 J9 (TYFP1): Standard Front Panel Connector PIN1 PWRLED+ PIN2 +5VSB PIN9 HDLED- PIN10 PSI_BMC_R- PIN17 PIN18 SMBCLK NOTE1: +3.3V power rail is IDLED, WLED (Warning LED), LANLED NOTE2: +5V power rail is PWRLED, HDLED J24: PSMI Connector J2/J8/J36/J37/J38: 4-pin Fan Header PWM Control +12V Tachometer...
- Page 16 USB3 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 17 USB3: Type-A USB Connector J33: ICH SGPIO Header J35: CPLD JTAG Header JP3: Clear CMOS Jumper Normal (Default) Clear JP1/JP2: COM2 Switch Jumper Signal USB D+ Signal SMBCLK SMBDAT Signal JTAG_TCK JTAG_TDO JTAG_TMS JTAG_TDI Use this jumper when you forgot your system/setup password or need to clear system BIOS setting.
- Page 18 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 19 J7: BMC Reset Jumper J1: LSI 1068E Device ID Select Jumper J3: LSI 1068E Enable/Disable Jumper Pin 1-2 Open: Enable BMC(Default) Pin 1-2 Closed: Disable BMC Pin 1-2 Closed: LSI 1068E Device ID (Default) Pin 2-3 Closed: :LSI 1068E Device ID – Device ID bit [0] =0b1 Pin 1-2 Closed: Enable LSI 1068E (Default) Pin 2-3 Closed: Disable LSI 1068E...
-
Page 20: Installing The Processor And Heatsink
2.4 - Installing the Processor and Heat Sink Your S7012 supports the latest processor technologies from Intel TYAN website for latest processor support: Processor Installation (LGA1366 Socket) The processor should be installed carefully. Make sure you are wearing an antistatic strap and handle the processor as little as possible. - Page 21 Step 4: Close the CPU socket cover (A) and press the CPU socket lever down to secure the CPU (B). Take care when installing the processor as it has very fragile connector pins below the processor that can bend and break if inserted improperly.
- Page 22 CPU VRD/IOH Heat Dispersion Notice Install FAN INTO ChASSIS TO LET AIR FLOW IN!!! - To ensure that the board runs efficiently and does not overheat, make sure there is air flow around the CPU VRD/IOH (as shown) to help disperse the heat generated around the area.
-
Page 23: Thermal Interface Material
2.5 - Thermal Interface Material Note: Always check with the manufacturer of the heat sink & processor to ensure the Thermal Interface material is compatible with the processor & meets the manufacturer’s warranty requirements. There are two types of thermal interface materials designed for use with the processors. -
Page 24: Finishing Installing The Heatsink
2.6 - Finishing Installing the Heat Sink After you have finished installing the heat sink onto the processor and socket, attach the end wire of the fan (which should already be attached to the heat sink) to the motherboard. The following diagram illustrates how to connect fans onto the motherboard. -
Page 25: Tips On Installing Motherboard In Chassis
2.7 - Tips on Installing Motherboard in Chassis Before installing your motherboard, make sure your chassis has the necessary motherboard support studs installed. These studs are usually metal and are gold in color. Usually, the chassis manufacturer will pre-install the support studs. If you are unsure of stud placement, simply lay the motherboard inside the chassis and align the screw holes of the motherboard to the studs inside the case. -
Page 26: Installing The Memory
2.8 - Installing the Memory Before installing memory, ensure that the memory you have is compatible with the motherboard and processor. Check the TYAN Web site at: www.tyan.com for details of the type of memory recommended for your motherboard. The following diagram shows common types of DDR3 memory modules. Key points to note before installing memory: •... - Page 27 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 28 Memory Installation Procedure Follow these instructions to install memory modules into the S7012. 1. Press the locking levers in the direction shown in the following illustration. Align the memory module with the socket. The memory module is keyed to fit only one way in the socket.
-
Page 29: Attaching Drive Cables
2.9 - Attaching Drive Cables Attaching Serial ATA Cables The S7012 is also equipped with 6 Serial ATA (SATA) channels. Connections for these drives are also very simple. There is no need to set Master/Slave jumpers on SATA drives. TYAN has supplied six SATA cables. If you are in need of other cables or power adapters please contact your place of purchase. -
Page 30: Installing Add-In Cards
2.10 - Installing Add-In Cards Before installing add-in cards, it’s helpful to know if they are fully compatible with your motherboard. For this reason, we’ve provided the diagrams below, showing the slots that appear on your motherboard. 4 PCI-E x8 slots with PCI-E x8 signal 1 PCI-E x8 slot with PCI-E x4 signal Simply find the appropriate slot for your add-in card and insert the card firmly. -
Page 31: Installing I/O Shield
2.11 – Installing I/O Shield Before you connect external devices, look into your motherboard package and take out the I/O shield. Follow the following instructions to install the I/O shield to your rear panel. 1. Preparation flat-head screw driver x 1 long nose pliers x 1 protective gloves x 1 I/O shield x 1... -
Page 32: Connecting External Devices
2.12 - Connecting External Devices The following diagram will detail the rear port stack for this S7012 motherboard: VGA Port Serial Port USB x 2 NOTE: Peripheral devices can be plugged straight into any of these ports but software may be required to complete the installation. Onboard LAN LED Color Definition The three onboard Ethernet ports have green and yellow LEDs to indicate LAN status. -
Page 33: Installing The Power Supply
2.13 - Installing the Power Supply There are three power connectors on your S7012. - 24-pin (PW3) - 8-pin (PW1, PW4) 1 x 24-pin 12V Power Connector (PW2) 2 x 8-pin 12V Power Connector (PW1, PW3) NOTE: Please be aware that ATX 2.x, ATX12V and ATXGES power supplies may not be compatible with the board and can damage the motherboard and/or CPU(s). - Page 34 NOTE http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 35: Chapter 3: Bios Setup
Chapter 3: BIOS Setup About the BIOS The BIOS is the basic input/output system, the firmware on the motherboard that enables your hardware to interface with your software. The BIOS determines what a computer can do without accessing programs from a disk. The BIOS contains all the code required to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial communications, and a number of miscellaneous functions. - Page 36 Setup Basics The table below shows how to navigate in the setup program using the keyboard. <F1> <ESC> arrow keys ↑ or ↓ arrow keys <Tab> or <Shift-Tab> <Home> or <End> <PgUp> or <PgDn> <-> <+> <F8> <F9> <F10> <Enter> Getting Help Press [F1] to display a small help window that describes the appropriate keys to use and the possible selections for the highlighted item.
-
Page 37: Bios Main Menu
3.1 - BIOS Main Menu The Main BIOS Menu is the first screen that you can navigate. The Main BIOS setup menu screen has two main frames. The left frame displays all the options that can be configured. "Grayed-out" options cannot be configured, options in blue can be changed. -
Page 38: Advanced Menu
Section for Advanced AHCI Menu Item Configuration Configure/monitor the Menu Item Hardware Health IPMI configuration including Menu Item server monitoring and event log http://www.tyan.com Chipset Exit Options for CPU ← → Select Screen ↑↓ Select Item Enter Go to Sub Screen... - Page 39 Feature Advanced Settings Intel VT-d Configuration PCI Express Configuration Remote Access Configuration Trusted Computing Onboard Devices Configuration Option Configure Intel Menu Item Technology for Directed I/O (VT-d) support Menu Item Configure PCI Express Support Menu Item Configure Remote Access Configure settings related to Menu Item Trusted Computing Information Onboard Devices and PCI Add-...
-
Page 40: Cpu Configuration
3.2.1 CPU Configuration You can use this screen to view CPU Configuration Menu. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages. Main Advanced Configure advanced CPU settings... - Page 41 C1E Support Hardware Prefetcher Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch Max CPUID Value Limit ® Intel Virtualization Tech Execute-Disable Bit Capability ® Intel HT Technology Active Processor Cores A20M ® Intel SpeedStep Tech ® NOTE: Intel TurboMode Tech will appear when Intel [Enabled].
- Page 42 C3 State C6 State C State package limit setting C1 Auto Demotion C3 Auto Demotion ACPI C2 Nehalem C State action select ACPI C3 Disabled Enabled Nehalem C State action select Disabled Auto Selected option will program into C state package limit register. When enabled, CPU will Enabled conditionally demote C3/C6/C7...
-
Page 43: Ide Configuration Submenu
3.2.2 IDE Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to select options for the IDE Configuration Settings. Use the up and down <Arrow> keys to select an item. Use the <Plus> and <Minus> keys to change the value of the selected option. Main Advanced IDE Configuration... - Page 44 3.2.2.1 SATA0 Sub-Menu Main Advanced SATA0 Device: Not Detected Type LBA /Large Mode Block (Multi-Sector Transfer) PIO Mode DMA Mode S.M.A.R.T. 32 Bit Data Transfer Feature SATA0 Type LBA/Large Mode Block (Multi-Sector Transfer) PIO Mode DMA Mode S.M.A.R.T. 32Bit Data Transfer BIOS Setup Utility PCI/PnP Boot...
-
Page 45: Super Io Configuration Sub-Menu
3.2.3 Super IO Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to select options for the Super I/O settings. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option Main Advanced... -
Page 46: Usb Configuration Submenu
3.2.4 USB Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to view the USB Configuration Menu. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages. - Page 47 3.2.4.1 – USB Mass Storage Device Configuration Sub-Menu Main Advanced USB Mass Storage Device Configuration USB Mass Storage Reset Delay Device #1 Emulation Type Feature USB Mass Storage Device Configuration USB Mass Storage Reset Delay Device #1 Emulation Type BIOS Setup Utility PCI/PnP Boot Security...
-
Page 48: Acpi Configuration Sub-Menu
3.2.5 ACPI Configuration Sub-Menu Use this screen to select options for ACPI. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. A description of the selected item appears on the right side of the screen. -
Page 49: Advanced Acpi Configuration Sub-Menu
3.2.5.1 Advanced ACPI Configuration Sub-Menu Main Advanced Advanced ACPI Configuration ACPI Version Features ACPI APIC support AMI OEMB table Headless mode ACPI SRAT Table Feature Advanced ACPI Configuration ACPI Version Features ACPI APIC Support AMI OEMB table Headless mode ACPI SRAT Table BIOS Setup Utility PCI/PnP Boot... - Page 50 3.2.5.2 Chipset ACPI Configuration Sub-Menu Main Advanced South Bridge ACPI Configuration Energy Lake Feature ACPI APIC SCI IRQ High Performance Event Timer HPET Memory Address Feature Chipset ACPI Configuration Energy Lake Feature ACPI APIC SCI IRQ High Performance Event Timer HPET Memory Address BIOS Setup Utility PCI/PnP...
-
Page 51: Ahci Configuration Sub-Menu
3.2.6 AHCI Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to view the AHCI Configuration Menu. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages. - Page 52 3.2.6.1 AHCI Port0/Port1/Port2/Port3/Port4/Port5 Sub-Menu Main Advanced AHCI Port0 Device: Not Detected SATA Port0 S.M.A.R.T. Feature AHCI Port0 Configuration SATA Port0 S.M.A.R.T. BIOS Setup Utility PCI/PnP Boot Security [Auto] [Enabled] Option Auto Select the type of device connected to the system. Not Installed S.M.A.R.T (Self-Monitoring Enabled...
-
Page 53: Hardware Health Configuration Sub-Menu
3.2.7 Hardware Health Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to view the Hardware Health Configuration Settings. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages. - Page 54 3.2.7.1 Sensor Data Register Monitoring Sub-Menu Main Advanced NAME CPU0 (PECI) CPU1 (PECI) DIMM0 Area (RT3) PCI Area (RT2) CPU0 VCORE CPU1 VCORE 3.3V +12V VBAT Sys. 1 (CPU0) Sys. 2 (CPU1) Sys. 3 (Front 1) Sys. 4 (Front 2) Sys.
- Page 55 3.2.8 IPMI 2.0 Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to view the IPMI 2.0 Configuration Settings. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages.
- Page 56 3.2.8.1 View BMC System Event Log Sub-Menu Main Advanced Total Number of Entries: 260 SEL Entry Number SEL Record ID SEL Record Type Event Timestamp Generator ID Event Message Format Ver Event Sensor Type Event Sensor Number Event Dir Type Event Data Read only.
-
Page 57: Lan Configuration Sub-Menu
3.2.8.3 LAN Configuration Sub-Menu Main Advanced LAN Configuration Channel Number Status IP Address Configuration IPMI DHCP Current IP Address in BMC Current Subnet Mask in BMC Current MAC Address in BMC Feature LAN Configuration Channel Number Status IPMI DHCP Current IP Address in BMC Current Subnet Address in BMC Current MAC Mask in BMC BIOS Setup Utility... - Page 58 3.2.9 Intel VT-d Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to view the Intel VT-d Configuration Settings. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages.
-
Page 59: Pci Express Configuration Sub-Menu
3.2.10 PCI Express Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to configure the PCI Express Support. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages. -
Page 60: Remote Access Configuration Sub-Menu
You can use this screen to view the Remote Access Configuration Menu. This feature allows access to the Server remotely via serial port. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. - Page 61 Feature Configure Remote Access type and parameters Redirection After BIOS POST Terminal Type VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support Sredir Memory Display Delay Option Disable: Turns off the redirection Disabled after POST Boot Loader: Redirection is active during POST and during Boot Loader. Boot Loader Always: Redirection is always active.
-
Page 62: Trusted Computing Sub-Menu
3.2.12 Trusted Computing Sub-Menu You can use this screen to view the Trusted Computing Menu. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages. -
Page 63: Onboard Devices Configuration Sub-Menu
3.2.13 Onboard Devices Configuration Sub-Menu You can use this screen to view the Onboard Devices Configuration Menu. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. The settings are described on the following pages. -
Page 64: Pci Pnp Menu
3.3 - PCI PnP Menu You can use this screen to view PnP (Plug & Play) BIOS Configuration Menu. This menu allows the user to configure how the BIOS assigns resources & resolves conflicts. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. - Page 65 Allocate IRQ to PCI VGA Palette Snooping PCI IDE BusMaster Yes: assigns IRQ to PCI VGA card if card requests IRQ. This is the default setting and should not be changed unless the Disabled VGA card manufacturer requires Palette Snooping to be Enabled. Enabled: informs the PCI devices that an ISA graphics device is Enabled...
-
Page 66: Boot Menu
3.4 - Boot Menu You can display Boot Setup option by highlighting it using the Arrow ( / ) keys and pressing Enter. The settings are described on the following pages. Main Advanced Boot Settings Boot Settings Configuration Boot Device Priority Hard Disk Drives 3.4.1 Boot Settings Configuration Sub-Menu Use this screen to select options for the Boot Settings Configuration. - Page 67 Feature Boot Settings Configuration Quick Boot Quiet Boot Add On ROM Display Mode Bootup Num-Lock Wait for ‘F1’ If Error Hit ‘DEL’ Message Display Interrupt 19 Capture Endless Boot Option Enabled This option allows user bypass BIOS self test during POST. Disabled Disabled: displays normal POST Disabled...
-
Page 68: Boot Device Priority
3.4.2 Boot Device Priority Use this screen to select options for the Boot Device Priority. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. Main Advanced Boot Device Priority... -
Page 69: Hard Disk Drives
3.4.3 Hard Disk Drives Use this screen to select options for the Hard Disk Drives. Use the up and down arrow ( / ) keys to select an item. Use the Plus and Minus (+/-) keys to change the value of the selected option. Main Advanced Hard Disk Drives... -
Page 70: Security Menu
3.5 - Security Menu The system can be configured so that all users must enter a password every time the system boots or when BIOS Setup is entered, using either the Supervisor password or User password. The Supervisor and User passwords activate two different levels of password security. -
Page 71: Chipset Menu
3.6 - Chipset Menu This menu allows the user to customize functions of the Intel Chipsets. Select a menu by highlighting it using the Arrow ( / ) keys and pressing Enter. The settings are described on the following pages. Main Advanced Advanced Chipset Settings... -
Page 72: Cpu Bridge Configuration Sub-Menu
3.6.1 CPU Bridge Configuration Sub-Menu This menu gives options for customizing CPU Bridge Chipset settings. Select a menu by highlighting it using the Arrow ( / ) keys and pressing Enter. The settings are described on the following pages. Main Advanced CPU Bridge Chipset Configuration CPU Revision... -
Page 73: North Bridge Configuration Sub-Menu
3.6.2 North Bridge Configuration Sub-Menu This menu gives options for customizing North Bridge Chipset settings. Select a menu by highlighting it using the Arrow ( / ) keys and pressing Enter. The settings are described on the following pages. Main Advanced North Bridge Chipset Configuration NB Revision... -
Page 74: South Bridge Configuration Sub-Menu
3.6.3 South Bridge Configuration Sub-Menu This menu gives options for customizing South Bridge Chipset settings. Select a menu by highlighting it using the Arrow ( / ) keys and pressing Enter. The settings are described on the following pages. Main Advanced South Bridge Chipset Configuration SLP_S4# Min. - Page 75 3.6.4 ME Subsystem Configuration Sub-Menu This menu provides selection for ME subsystem configuration. Select a menu by highlighting it using the Arrow ( / ) keys and pressing Enter. The settings are described on the following pages. Main Advanced ME Subsystem Configuration ME-HECI Feature South Bridge Chipset Configuration...
-
Page 76: Exit Menu
3.7 - Exit Menu You can display an Exit BIOS Setup option by highlighting it Arrow ( / ) keys and pressing Enter. Main Advanced Exit Options Save Changes and Exit Discard Changes and Exit Discard Charges Load Optimal Defaults Load Failsafe Defaults Save Changes and Exit Use this option to exit setup utility and re-boot. -
Page 77: Chapter 4: Diagnostics
Chapter 4: Diagnostics NOTE: if you experience problems with setting up your system, always check the following things in the following order: Memory, Video, CPU By checking these items, you will most likely find out what the problem might have been when setting up your system. -
Page 78: Amibios Post Code
4.3 - AMIBIOS Post Code The POST code checkpoints are the largest set of checkpoints during the BIOS pre- boot process. The following table describes the type of checkpoints that may occur during the POST portion of the BIOS: Checkpoint Description Disable NMI, Parity, video for EGA, and DMA controllers. - Page 79 Checkpoint Description Initializes different devices through DIM. See DIM Code Checkpoints section of document for more information. Initializes DMAC-1 & DMAC-2. Initialize RTC date/time. Test for total memory installed in the system. Also, Check for DEL or ESC keys to limit memory test. Display total memory in the system. Mid POST initialization of chipset registers.
- Page 80 NOTE http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 81: Glossary
Glossary ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface): a power management specification that allows the operating system to control the amount of power distributed to the computer’s devices. Devices not in use can be turned off, reducing unnecessary power expenditure. AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): a PCI-based interface which was designed specifically for demands of 3D graphics applications. - Page 82 Bus: a data pathway. The term is used especially to refer to the connection between the processor and system memory, and between the processor and PCI or ISA local buses. Bus mastering: allows peripheral devices and IDEs to access the system memory without going through the CPU (similar to DMA channels).
- Page 83 Global timer: onboard hardware timer, such as the Real-Time Clock (RTC). Handshaking: a process where two devices initiate communications. One device, typically the server, sends a message to another device, typically a client, in order to request establishment of a communications channel. The two devices will then exchange messages back and forth in order to settle on a communications protocol.
- Page 84 I/O (Input/Output): the connection between your computer and another piece of hardware (mouse, keyboard, etc.) Initial Program Load (IPL): a feature built into BBS-compliant devices, describing those devices as capable of loading and executing an OS, as well as being able to provide control back to the BIOS if the loading attempt fails.
- Page 85 PM timers (Power Management timers): software timers that count down the number of seconds or minutes until the system times out and enters sleep, suspend, or doze mode. PnP (Plug-n-Play): a design standard that has become ascendant in the industry. Plug-n-Play devices require little set-up to use.
- Page 86 SSI (Server System Infrastructure): an industry initiative intended to provide ready-to-use design specifications for common server hardware elements (chassis, power supplies, and racks) to promote and support server industry growth. Standby mode: in this mode, the video and hard drives shut down; all other devices continue to operate normally.
-
Page 87: Technical Support
Technical Support If a problem arises with your system, you should turn to your dealer for help first. Your system has most likely been configured by them, and they should have the best idea of what hardware and software your system contains. Furthermore, if you purchased your system from a dealer near you, you can bring your system to them to have it serviced instead of attempting to do so yourself (which can have expensive consequences). - Page 88 radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try one or more of the following measures: Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna. Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver. Plug the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that of the receiver.













Need help?
Do you have a question about the TYAN S7012 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers