Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Rated Welding
Amperage
Output
Range
280 A, 31 V DC,
35% Duty Cycle
250 A, 30 V DC,
20 – 280
60% Duty Cycle
225 A, 29 V DC,
100% Duty Cycle
cover_om 4/95 – Ref. ST-158 934-B
OWNER'S
MANUAL
Metro 300DXQ
CC/DC Welding Generator For SMAW And GTAW Welding
Maximum
Open-Circu
Auxiliary
it Voltage
Power Rating
DC
Single-Phase/
3-Phase,
61
7/10 kVA/kW,
32/15 A,
(Average)
220/380 V AC,
50 Hz
1996 MILLER Electric Mfg. Co.
October 1996
Form: OM-156 368D
Effective With Serial No. KG212352
Fuel
Engine
Capacity
Ruggerini RD211
Air-Cooled,
11.8 US gal
Two-Cylinder, 20
(44.6 L)
HP Diesel Engine
Sound
IP Rating
Power
98 Lwa
23
PRINTED IN USA
Advertisement
Table of Contents
Troubleshooting

Summary of Contents for Miller Metro 300DXQ
- Page 1 60% Duty Cycle 32/15 A, Two-Cylinder, 20 (44.6 L) (Average) HP Diesel Engine 220/380 V AC, 225 A, 29 V DC, 50 Hz 100% Duty Cycle 1996 MILLER Electric Mfg. Co. cover_om 4/95 – Ref. ST-158 934-B PRINTED IN USA...
- Page 3 Declaration of Conformity for European Community (CE) Products NOTE This information is provided for units with CE certification (see rating label on unit). Miller Electric Mfg. Co. Manufacturer’s Name: 1635 W. Spencer Street Manufacturer’s Address: Appleton, WI 54914 USA METRO 300DXQ...
-
Page 5: Table Of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR ARC WELDING ....... . . 1-1. -
Page 7: Symbol Usage
SECTION 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING rom _nd_5/97 1-1. Symbol Usage Means Warning! Watch Out! There are possible haz- ards with this procedure! The possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols. This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! possible ELEC- Marks a special safety message. -
Page 8: Section 1 - Safety Precautions For Arc Welding
WELDING can cause fire or explosion. HOT PARTS can cause severe burns. Allow cooling period before maintaining. Welding on closed containers, such as tanks, drums, or pipes, can cause them to blow up. Sparks Wear protective gloves and clothing when can fly off from the welding arc. - Page 9 MOVING PARTS can cause injury. BATTERY ACID can BURN SKIN and EYES. Do not tip battery. Keep away from fans, belts, and rotors. Replace damaged battery. Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards closed and securely in place. Flush eyes and skin immediately with water. Stop engine before installing or connecting unit.
-
Page 10: Additional Installation, Operation, And Maintenance Hazards
READ INSTRUCTIONS. electromagnetically compatible. To reduce possible interference, keep weld cables as short as Use only genuine MILLER replacement parts. possible, close together, and down low, such as on the floor. Perform engine maintenance and service ac- Locate welding operation 100 meters from any sensitive elec- cording to this manual and the engine manual. -
Page 11: Section 2 - Definitions
SECTION 2 – DEFINITIONS 2-1. Warning Label Definitions Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards as shown by the symbols. Become trained and read the in- structions before working on the machine or welding. Electric shock from welding electrode or wiring can kill. 1.1 Wear dry insulating gloves. - Page 12 Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards as shown by the symbols. Do not smoke and keep matches and flames away from battery. Sparks can cause battery gases to explode. Battery explosion can blind and injure. Wear a face shield. Battery acid can burn skin.
- Page 13 Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards as shown by the symbols. Hot muffler and exhaust pipes can cause severe burns. Do not touch hot muffler or pipes. S-176 230 3/96 Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards as shown by the symbols. Engine fuel plus flames or sparks can cause fire.
- Page 14 Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards as shown by the symbols. Falling equipment can cause serious injury and damage. Use lifting eye to lift or move unit only. proper equipment when lifting. Do not use lifting eye to lift and support unit and trailer or other heavy devices or accessories.
-
Page 15: Manufacturer's Rating Label For Ce Products
Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards as shown by the symbols. Ether will damage engine. Do not use ether as a starting aid. Read Owner’s Manual. Use glow plugs for 10–25 seconds to aid starting in cold weather. 10 – 25 s S-176 109 3/96 2-2. -
Page 16: Symbols And Definitions
2-3. Symbols And Definitions Fast Fast/Slow Stop Engine Slow (Idle) (Run, Weld/Power) (Run/Idle) Start Engine Glow Plug Temperature Fuel Engine Oil Remote 14 Panel/Local Check Injectors/ Check Valve Battery (Engine) Volts Pump Clearance Shielded Metal Arc Gas Tungsten Arc Amperes Arc Force (DIG) Welding (SMAW) Welding (TIG) -
Page 17: Section 3 - Installation
SECTION 3 – INSTALLATION 3-1. Installing Welding Generator Movement Airflow Clearance Location 18 in (460 mm) 18 in (460 mm) 18 in (460 mm) 18 in 18 in (460 mm) (460 mm) Grounding Generator Base Metal Vehicle Frame Equipment Grounding GND/PE Terminal Grounding Cable... -
Page 18: Fuel Consumption
3-3. Fuel Consumption SA-175 807 OM-156 368 Page 12... -
Page 19: Activating The Dry Charge Battery
3-4. Activating The Dry Charge Battery Remove battery from unit. Eye Protection – Safety Glasses Or Face Shield Rubber Gloves Vent Caps Sulfuric Acid Electrolyte (1.265 Specific Gravity) Well Fill each cell with electrolyte to bot- tom of well (maximum). Do not overfill battery cells. -
Page 20: Connecting Battery And Installing Exhaust Pipe
3-5. Connecting Battery And Installing Exhaust Pipe Stop engine. Installation of exhaust pipe is optional. Connect (–) cable last. – Tools Needed: 7/16, 1/2 in ST-801 079-A / Ref. ST-175 920-B 3-6. Engine Prestart Checks Check all fluids daily. Unit must be cold and on a level surface. -
Page 21: Weld Output Terminals And Selecting Cable Sizes
3-7. Weld Output Terminals And Selecting Cable Sizes ARC WELDING can cause Electromagnetic Interference. To reduce possible interference, keep weld cables as short as possible, close together, and down low, such as on the floor. Locate welding operation 100 meters from any sensitive electronic equipment. Be sure this welding machine is installed and grounded according to this manual. -
Page 22: Section 4 - Operating The Welding Generator
SECTION 4 – OPERATING THE WELDING GENERATOR 4-1. Front Panel Controls Using Idle Lock Switch 2100 rpm Using Glow Plug 70 F (21 C) 10 s 32 F (0 C) 2100 rpm 20 s –4 F (–20 C) 2100 rpm (No Load) 3200 rpm (Load) -
Page 23: Duty Cycle And Overheating
4-2. Duty Cycle And Overheating Duty Cycle is percentage of 10 minutes that unit can weld at rated load without overheating. Exceeding duty cycle can damage unit and void war- ranty. 35% Duty Cycle At 280 Amperes 60% Duty Cycle At 250 Amperes 3-1/2 Minutes Welding Minutes 6-1/2 Minutes Resting... -
Page 24: Section 5 - Operating Auxiliary Equipment
SECTION 5 – OPERATING AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT 5-1. Auxiliary Power Receptacles ∼ ∼ 50 Hz 50 Hz 380 V 220 V 280 A 0 kVA 0.7 kVA 3.2 A 250 A 1.5 kVA 2.3 A 3.0 kVA 13.6 A 200 A 3.8 kVA 5.8 A 6.0 kVA... -
Page 25: Section 6 - Maintenance & Troubleshooting
SECTION 6 – MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING 6-1. Routine Maintenance Stop engine before maintaining. See also Engine Manual and Mainte- Recycle engine nance Label. Service engine more often fluids. during severe conditions. Check Fluid Wipe Up Levels. Spills. See Section 3-6. 50 h Clean And Check Air Filter... -
Page 26: Maintenance Label
6-2. Maintenance Label OM-156 368 Page 20... -
Page 27: Changing Engine Oil And Oil Filter
6-3. Changing Engine Oil And Oil Filter Stop engine. See engine manual for oil/filter change procedure. Drain oil while engine is warm. Oil Fill Caps (Use Either Cap) Oil Drain Valve Close oil drain valve and cap before adding oil and run- ning engine. -
Page 28: Changing Fuel Filters
6-4. Changing Fuel Filters Stop engine and let cool. Secondary Fuel Filter Remove filter. Apply thin film of oil to gasket on new filter. Install filter. Primary Fuel Filter Fuel Line Remove filter. Inspect all fuel lines and replace if cracked or worn. Install new filter and clamps. -
Page 29: Adjusting Engine Speed
6-6. Adjusting Engine Speed After tuning engine, check engine speeds with a tachometer (see table for no load speeds). If neces- sary, adjust speeds as follows: Start engine and run until warm. Idle Speed Adjustment Turn Engine Control switch to Run/ Idle position. -
Page 30: Overload Protection
6-7. Overload Protection Stop engine. If checking fuse, disconnect battery negative (–) cable. If fuse or breaker continues to open, contact Factory Autho- rized Service Agent. Weld And Auxiliary Power Cir- cuits Fuse F2 F2 protects battery excitation cir- cuit. If F2 opens, weld and auxiliary output stops. -
Page 31: Servicing Optional Spark Arrestor
6-8. Servicing Optional Spark Arrestor Stop engine and let cool. Spark Arrestor Cleanout Plug Remove plug and remove any dirt covering cleanout hole. Exhaust Pipe Start engine and run at idle speed to blow out cleanout hole. If nothing blows out of hole, briefly cover end of exhaust pipe with fireproof mate- rial. - Page 32 Trouble Remedy High weld output. Check and adjust engine speed (see Section 6-6). Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check main rectifier. Erratic weld output. Clean and tighten weld output connections inside and outside unit. Use dry, properly-stored electrodes. Be sure connection to work piece is clean and tight. Remove excessive coils from weld cables.
- Page 33 Trouble Remedy Engine starts, but stops when Engine Check oil level. Engine stops if oil pressure gets too low (see Section 3-6). Control switch is released. High Or Low Engine Speed. Check and adjust engine speed (see Section 6-6). Engine does not return to idle speed. Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check throttle solenoid TS1, relay CR4, and idle control module.
- Page 34 NOTES OM-156 368 Page 28...
-
Page 35: Section 7 - Electrical Diagram
SECTION 7 – ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM Figure 7-1. Circuit Diagram For Welding Generator OM-156 368 Page 29... - Page 36 SD-182 024 OM-156 368 Page 30...
-
Page 37: Section 8 - Run-In Procedure
SECTION 8 – RUN-IN PROCEDURE run_in2 6/96 8-1. Wetstacking Heavy loading during first 50 hours will damage en- gine. Keep load less than 225A (weld) or 7 kVA (power) for first 50 hours. Do not idle engine longer than necessary. Piston rings seat faster if engine runs at weld/ power rpm, and the welding generator is kept loaded dur-... -
Page 38: Run-In Procedure Using Load Bank
8-2. Run-In Procedure Using Load Bank Stop engine. Do not touch hot exhaust pipe, engine parts, or load bank/grid. Keep exhaust and pipe away from flammables. Load Bank Turn all load bank switches Off. If needed, connect load bank to 115 volts ac wall receptacle or genera- tor auxiliary power receptacle. -
Page 39: Run-In Procedure Using Resistance Grid
8-3. Run-In Procedure Using Resistance Grid Stop engine. Do not touch hot exhaust pipe, engine parts, or load bank/ grid. Keep exhaust and pipe away from flammables. Resistance Grid Use grid sized for generator rated output. Turn Off grid. Welding Generator Set Amperage control at min. -
Page 40: Section 9 - Auxiliary Power Guidelines
SECTION 9 – AUXILIARY POWER GUIDELINES 9-1. Selecting Equipment Auxiliary Power Receptacles – Neutral Bonded To Frame 3-Prong Plug From Case Grounded Equipment 2-Prong Plug From Double Insulated Equipment Be sure equipment has this symbol and/or wording. aux_pwr 12/96 – Ref. ST-159 730 / ST-800 577 9-2. - Page 41 9-3. Grounding When Supplying Building Systems Equipment Grounding Terminal Grounding Cable GND/PE Use #10 AWG or larger insulated copper wire. Ground Device Ground generator to system earth ground if supplying power to a premises (home, shop, farm) wiring system. Use ground device as stated in electrical codes.
- Page 42 9-5. Approximate Power Requirements For Industrial Motors Industrial Motors Rating Starting Watts Running Watts Split Phase 1/8 HP 1/6 HP 1225 1/4 HP 1600 1/3 HP 2100 1/2 HP 3175 Capacitor Start-Induction Run 1/3 HP 2020 1/2 HP 3075 3/4 HP 4500 1400 1 HP...
- Page 43 9-7. Approximate Power Requirements For Contractor Equipment Contractor Rating Starting Watts Running Watts Hand Drill 1/4 in 3/8 in 1/2 in Circular Saw 6-1/2 in 7-1/4 in 8-1/4 in 1400 1400 Table Saw 9 in 4500 1500 10 in 6300 1800 Band Saw 14 in...
- Page 44 9-8. Power Required To Start Motor Motor Start Code AC MOTOR Running Amperage VOLTS AMPS Motor HP CODE Motor Voltage PHASE To find starting amperage: Step 1: Find code and use table to find kVA/HP. If code is not listed, multiply running amperage by six to find starting amperage.
- Page 45 9-10. Typical Connections To Supply Standby Power Power Company Service Meter Main and Branch Overcurrent Protection Double-Pole, Double-Throw Transfer Switch Obtain and install correct switch. Switch rating must be same as or Customer-supplied equipment is required if greater than the branch overcur- generator is to supply standby power during rent protection.
- Page 46 9-11. Selecting Extension Cord (Use Shortest Cord Possible) Cord Lengths for 120 Volt Loads If unit does not have GFCI receptacles, use GFCI-protected extension cord. Maximum Allowable Cord Length in ft (m) for Conductor Size (AWG)* Current Load (Watts) (Amperes) 350 (106) 225 (68) 137 (42)
-
Page 47: Section 10 - Parts List
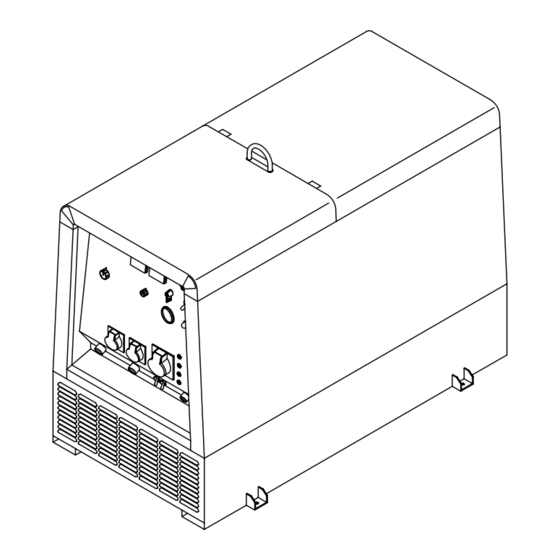
SECTION 10 – PARTS LIST 19 20 21 86 – Fig 10-4 91 – Fig 10-3 Figure 10-1. Main Assembly OM-156 368 Page 41... - Page 48 Fig 10-2 ST-801 286-C OM-156 368 Page 42...
- Page 49 Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 10-1. Main Assembly ....+163 828 . . . PANEL, side LH ..........
- Page 50 Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 10-1. Main Assembly (Continued) ....603 767 . . . CAP, weather No. 3 ..........
- Page 51 Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 10-1. Main Assembly (Continued) ... . 173 421 . . . CIRCUIT CARD, control main ........
- Page 52 Item Part Description Quantity Figure 10-2. Generator (Fig 10-1 Item 56) ... . . 166 770 STUD, stl .375-16 x 19.750 .........
- Page 53 Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 10-3. Panel, Front w/Components (Fig 10-1 Item 90) ..R4,5 ..072 623 POTENTIOMETER, CP plain rnd 1/T 2W 1K linear ....
- Page 54 Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 10-4. Control Box w/Components (Fig 10-1 Item 85) ..D1,5 ..135 184 . . . DIODE BOARD ...........














Need help?
Do you have a question about the Metro 300DXQ and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers