Summary of Contents for GE HEALTHCARE B40
- Page 1 GE Healthcare B40/B20 Patient Monitor User’s Reference Manual B40/B20 Patient Monitor English 2081504-001 E (Paper) © 2015 General Electric Company. All Rights Reserved.
- Page 3 B40/B20 Patient Monitor User's Reference Manual Related to software license VSP-C Monitoring functions 0459 Conformity according to the Council Directive 93/42/EEC concerning Medical Devices amended by 2007/47/EC. All specifications are subject to change without notice. Document no. 2081504-001 E October 22, 2015 GE Medical Systems Information Technologies, Inc.
- Page 4 Trademarks Listed below are GE Medical Systems Information Technologies and GE Healthcare Finland Oy trademarks used in this document. All other product and company names contained herein are the property of their respective owners.
-
Page 5: Table Of Contents
Indications for use: B40 ........ - Page 6 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Network................2-10 Symbols.
- Page 7 Alarms Overview ................5-1 Safety precautions.
- Page 8 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Changing the startup mode ..........6-8 Renaming a mode .
- Page 9 To create a snapshot manually: ..........7-13 To create automatic snapshots: .
- Page 10 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Recycling the monitor battery ..........9-5 Changing fuses .
- Page 11 Pacemaker detection Safety precautions............. . . 11-12 Warnings.
- Page 12 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Cautions ..............13-2 Overview .
- Page 13 Safety precautions..............15-1 Warnings.
- Page 14 B40/B20 Patient Monitor O2 setup menu ............17-10 Agent/N O Setup menu .
- Page 15 Preparing the patient and placing the electrodes ........18-6 Preparing the patient .
- Page 16 B40/B20 Patient Monitor...
-
Page 17: Introduction
1 Introduction... -
Page 19: About This Device
Introduction 1 Introduction About this device Indications for use: B40 This device is a portable multi-parameter unit to be used for monitoring and recording of, and to generate alarms for, multiple physiological parameters of adult, pediatric, and neonatal patients in a hospital environment and during intra-hospital transport. -
Page 20: Responsibility Of The Manufacturer
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Responsibility of the manufacturer GE Medical Systems Information Technologies, Inc. is responsible for the effects on safety, reliability and performance of the equipment only if: • Assembly operations, extensions, readjustments, modifications, or repairs are carried out by persons authorized by GE. - Page 21 Introduction • The SpO2 Parameter controlled desaturation study conforms to ISO 14155:2011. • The TEMP parameter conforms to ISO 80601-2-56. • The gas parameter conforms to ISO 80601-2-55. • This Monitor conforms to particular safety standard for multifunction patient monitoring equipment to IEC 60601-2-49.
-
Page 22: About This Manual
B40/B20 Patient Monitor About this manual This User’s Reference Manual describes the functions offered by the B40 and B20 patient monitor running the software license VSP-C. As the monitor setup may vary, some menus, displays and functions described may not be available in the monitor you are using. -
Page 23: Related Documentation
Push the Trim Knob. Monitor naming conventions In this manual, the B40 Patient Monitor and B20 Patient Monitor are referred to as “the monitor” when a function or a feature applies to both. For describing monitor-specific issues, the monitors are referred to as B40 and B20 respectively. -
Page 24: Safety Precautions
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Safety precautions The following list contains all the general warnings and cautions you should know before starting to use the system. Warnings and cautions specific to parts of the system can be found in the relevant section. -
Page 25: Cautions
Introduction • DISCONNECTION FROM MAINS - When disconnecting the system from the power line, remove the plug from the wall outlet first. Then you may disconnect the power cord from the device. If you do not observe this sequence, there is a risk of coming into contact with line voltage by inserting metal objects, such as the pins of leadwires, into the sockets of the power cord by mistake. -
Page 26: Esd Precautionary Procedures
B40/B20 Patient Monitor • Medical electrical equipment needs special precautions regarding electromagnetic compatibility, EMC, and needs to be installed and put into service according to the EMC information provided in the "Technical Reference Manual" by qualified personnel. • Portable and mobile RF communications equipment can affect the medical electrical equipment. -
Page 27: System Description
2 System description... -
Page 29: Safety Precautions
System description 2 System description Safety precautions Warnings • All system devices must be connected to the same power supply circuit • EXCESSIVE LEAKAGE CURRENT - Do not use a multiple socket outlet or extension cord. • INTERFACING OTHER EQUIPMENT - Devices may only be interconnected with each other or to parts of the system when it has been determined by qualified biomedical personnel that there is no danger to the patient, the operator, or the environment as a result. -
Page 30: System Introduction
B40/B20 Patient Monitor System introduction NOTE: Your system may not include all these components. Consult your local representative for the available components. 1, 4 Figure 2-1 Patient monitor components Monitor frame E modules: The compatible acquisition modules Extension rack Software: VSP-C... -
Page 31: Frame Front View
System description Frame front view Figure 2-2 B40 front B20 front Transportation handle Alarm light The Trim knob Command board keys Battery compartment Guide rail for GCX mounting Mains power and battery LEDs On/Off key Hemo connectors (10) E module... -
Page 32: Frame Back View
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Frame back view Figure 2-3 B40 back B20 back Figure 2-4 I/O and connectors Receptacle for power cord Serial port Defibrillator connector Nurse call connector Network connector Equipotential connector Multi I/O connector NOTE: The Multi I/O with ports 2,3,4 are optional parts for customer. -
Page 33: Acquisition Modules
System description Acquisition modules B40 acquisition modules: • E-miniC • E-sCO, E-sCAiO • N-CAiO • E-Entropy B20 acquisition modules: • E-miniC • E-Entropy E-miniC module Figure 2-5 E-miniC Water trap Sample gas inlet Gas outlet... -
Page 34: E-Sco, E-Scaio Module
B40/B20 Patient Monitor E-sCO, E-sCAiO module D-fend Pro water trap Gas sample, sampling line connector on the water trap Water trap container Gas exhaust, connector for the gas exhaust line (sampling gas out) N-CAiO module D-fend Pro water trap Gas sample, sampling line connector on the water trap... -
Page 35: Entropy Module
System description Entropy module Module keys Entropy connector How to identify the Hemo connectors’ configuration The monitor provides different configurations for Hemo measurement. The user can identify Hemo connectors’ configuration from connectors and label. Hemo connectors’ type Basic feature Optional feature Identifier NIBP Temperature... -
Page 36: Keyboard
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Keyboard You can control monitoring through the keys on the Command Board. For more information, see section "Monitoring basic." Admit/ Monitor Print/ Airway Alarm NIBP NIBP Zero All Reset Discharge Setup Record Auto On/Off Take Pt.Data Alarms... -
Page 37: Batteries
System description Batteries The monitor can be run either on mains power or batteries. Battery operation is initiated when the power cord is disconnected or when the mains power is lost during monitoring. The monitor has two lithium-ion batteries at most, located in the battery compartment. They can be charged separately, and screen symbols and monitor frame LEDs indicate their charging level and possible failure, see "Battery indicators"... - Page 38 B40/B20 Patient Monitor • In CARESCAPE network, the monitor can: − communicate with GE CARESCAPE Central Station V1 − communicate with GE CARESCAPE pro CIC version 4.0.8, 4.1.1 and 5.1.0 − compatible with Aware Gateway Server V1.6 − compatible with CARESCAPE Gateway Server V1.
-
Page 39: Symbols
System description Symbols On the rear panel this symbol indicates the following warnings and cautions: Electric shock hazard. Do not open the cover or the back. Refer servicing to qualified personnel. For continued protection against fire hazard, replace the fuse only with one of the same type and rating. - Page 40 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Home. Return to the Normal Screen view. ON/OFF. Fuse. Replace the fuse only with one of the same type and rating. Gas inlet. Gas outlet. Degree of ingress protection. Degree of protection against harmful ingress of water:...
- Page 41 System description Atmospheric pressure limitations. Recycled materials or may be recycled. This symbol indicates that the waste of electrical and electronic equipment must not be disposed as unsorted municipal waste and must be collected separately. Please, contact an authorized representative of the manufacturer for information concerning the decommissioning of your equipment.
- Page 42 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Audio alarms off indicator - Displays in the upper left corner of the alarm area when physiological audible alarms are turned off. Audio alarms paused indicator - Indicates all audio alarms are paused and the amount of time remaining for the alarm pause period displays as a countdown timer.
-
Page 43: Technical Specification
Without extension module 312±5 mm (H) * 312±5 mm (W) * 158±5 mm (D) With extension module 312±5 mm (H) * 352±5 mm (W) * 178±5 mm (D) Weight B40 with extension module <=7 kg B20 with extension module <=6 kg Monitor environment Operating temperature Normal operation: +5 to +40°C (41 to 104°F) - Page 44 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Operating altitude 660 to 1060 mbar E-Entropy module environment Operating temperature 10 to 40°C (50 to 104°F) Non-operating -20 to 60°C (-4 to 140°F) temperature Operating humidity 10 to 90% noncondensing Non-operating humidity 10 to 90% noncondensing...
- Page 45 System description Defibrillator synchronization connector NOTE: In the defibrillator synchronization connector, Pin 1,2,3,4,7 are grounding. Synchronization pulse (Pin 5) Pulse width: 10 ms ±20% positive pulse Delay: < 35 ms (R-wave peak to leading edge of pulse) Amplitude: CMOS compatible 3.5 V min.
-
Page 46: Parameters Specifications
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Parameters specifications ECG specifications Leads available 3-lead configuration: I, II, III 5-lead configuration: I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF and VA QRS detection range 0.5 to 5mV QRS detection width (Q to 40 to 120 ms Defibrillation protection... - Page 47 System description Figure 4a halved ampli- 9.9 s (8.4 to 11.5 s) tude: Figure 4a 7.1 s (5.8 to 8.2 s) normal amplitude: Figure 4a 4.4 s (4.2 to 4.6 s) doubled amplitude: Figure 4b halved ampli- 7.0 s (6.1 to 7.5 s) tude: Figure 4b 5.8 s (4.5 to 7.4 s)
-
Page 48: Specifications
B40/B20 Patient Monitor GE TruSignal SpO specifications Measurement and display 1 to 100% range Calibrated against functional oxygen saturation. Measurement accuracy Adult/Pediatric without motion: ±2 digits (±3 digits with ear sensor) (100 to 70%): with motion: ±3 digits low perfusion: ±3 digits Neonatal without motion: ±3 digits... - Page 49 System description Table 1: Accuracy for sensors (Arms) * GE SpO Sensor Non motion Motion (70- Low perfusion Neonatal (70-100%) 100%) (70-100%)** (70-100%) TS-E-D, TS-E2-GE, TS-E4-GE ±3 digits unspecified unspecified unspecified TS-SE-3 ±2 digits unspecified unspecified ±3 digits TS-F-D, TS-F2-GE, TS-F4-GE, TS-SA-D, TS- ±2 digits unspecified ±3 digits...
- Page 50 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Nellcor SpO specifications Measurement range 1 to 100% Display range 0 to 100% Calibrated against functional oxygen saturation. Measurement accuracy Adult 100 to 70% ±2 digits 100 to 70% ±3 digits Low perfusion 100 to 70% ±2 digits...
- Page 51 System description Sensor Light Source Wavelength Infrared: 905 nm (nominal) Red: 660 nm (nominal) Power Dissipation Infrared: 22.5 mW (max) Red: 27.5 mW (max) This information may be useful to clinicians, such as those performing photodynamic therapy. NIBP Measurement technique Oscillometric with step deflation Supported modes Manual, automatic and stat...
-
Page 52: Pulse Rate
± 0.1°C without temperature sensor Display resolution ± 0.1°C at 25 to 45 °C with reusable probes Probe types supported Use only GE Healthcare recommend temperature YSI probes. Temperature self-check At start-up and then every 10 minutes Probe type time response... - Page 53 System description Airway gases Accuracy specifications apply in normal conditions after a 30 min warm-up period: Ambient temperature 18 to 28°C, within ±5°C of calibration Ambient pressure 660 to 1060 hPa, ±67 hPa of calibration Ambient humidity 20 to 80%, within ±20% RH of calibration Sampling rate •...
- Page 54 B40/B20 Patient Monitor measurement accuracy • E-miniC module 0 to 15 vol%: ± (0.2 vol% + 2% of reading) • 15 to 20 vol%: ± (0.7 vol% + 2% of reading) NOTE: Valid for respiration rate < 40 breaths/min at I:E ratio of 1:1.
- Page 55 System description Anesthetic agents specified Hal, Enf, Iso: 0 to 6 vol% measurement range Sev: 0 to 8 vol% Des: 0 to 20 vol% Anesthetic agents ± (0.15 vol% + 5% of reading) measurement accuracy Anesthetic agents display 0.01% for values between 0…1% resolution 0.1% for values equal or above 1% Anesthetic agents total system...
- Page 56 B40/B20 Patient Monitor • Disturbing gas and its effect Halotane (4%): increases CO (5 vol%) < 0.3 vol% • Isoflurane (5%): increases CO (5 vol%) < 0.4 vol% • Enflurane (5%): increases CO (5 vol%) < 0.4 vol% • Desflurane (24%): increases CO (5 vol%) <...
- Page 57 System description Entropy Display range • • 0 to 100 Response Entropy (RE) • • 0 to 91 State Entropy (SE) • • 0 to 100% Burst Supression Ratio (BSR) Display accuracy ±1 or ±1% Amplifier 1 MΩ @ 50 Hz input impedance Defibrillation protection 3000 V, 130 J...
- Page 58 B40/B20 Patient Monitor 2-30...
-
Page 59: Installation
3 Installation... -
Page 61: Safety Precautions
Open the top of the box and carefully unpack all components. Confirm that all components are undamaged. If any of the components is damaged, contact the shipper. Confirm that all components are included. If any of the components is missing, contact your GE Healthcare distributor. -
Page 62: Choosing Location
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Choosing location Environmental requirements • Install the patient monitor to a location that meets the specified environmental requirements of operating temperature, humidity and atmospheric pressure. • Set up the device in a location which affords sufficient ventilation. The ventilation openings of the device must not be obstructed. -
Page 63: Check Configuration
34) > Service (26-23-8) Enter to license control menu: SW Management > License Check and record the product license. If the configuration is difference with your order, contact GE Healthcare distributor. Connection to Network WARNING Do not use with iCentral software V5.0.3 and earlier. -
Page 64: To Connect The Network
B40/B20 Patient Monitor HL7 network • The HL7 Network shall be installed according to the "B40/B20 Patient Monitor HL7 reference manual" To connect the network MC and S/5 network Use the CAT-5 network cable to connect the monitor to the network. -
Page 65: Inserting And Removing The E Module
Installation Inserting and removing the E module To use the E module, your monitor need pre-configure the extension rack from manufacture. To insert module: Align the module with the insertion guides Push the module into the monitor frame until it clicks and stops. Pull the module outwards to insure the module is firmly seated. -
Page 66: Installation Checkout
It is recommended to be performed after monitor installation. Skip the tests that are not applicable for the installed monitor. These instructions include a “B. Installation and checkout form, B40/B20” to be filled in when performing the procedures. Recommended tools NOTE: Use only properly maintained, calibrated and traceable measurement equipment for the specified calibrations and adjustments to ensure accuracy. -
Page 67: Functional Inspection
Installation • Verify that the modules are properly connected and locked in place. • Verify that the battery lid is properly locked. The cleaning precautions, cleaning requirements, cleaning procedures, and recommended cleaning solutions for the monitor are described in the "9. - Page 68 B40/B20 Patient Monitor • : After connecting SpO cable and sensor, SpO sensor will be lit. • Temperature: After connecting Temp cable and sensor, ‘Performing temp test:’ will display in Temp Digital Field for several seconds. • IBP: After connecting IBP cable and transducer, ‘InvBP’s not Zeroed’ will display in Message Field.
-
Page 69: Monitoring Basic
4 Monitoring basic... -
Page 71: Using Menus
Monitoring basic 4 Monitoring basic Using menus A menu is a list of functions or commands displayed on the monitor screen. To display a menu, press one of the Command Board keys. Figure 4-1 Example of a menu Menu header List of menu selections Indicates the present selection Adjustment window with other options... - Page 72 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Select items in the menus with the Trim Knob. For example, to change what is displayed in the ECG display: Select the desired function by pressing the menu key. Turn the Trim Knob to move the highlight down in the menu to the desired selection.
- Page 73 Monitoring basic Push the Trim Knob to enter an adjustment window or a submenu Turn the Trim Knob to choose the desired option or selection in the window. Push the Trim Knob to confirm the selection. Normal Screen Press the key to return to normal monitoring display.
-
Page 74: Starting And Ending
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Starting and ending Warnings • Always make sure that appropriate mode is chosen and necessary alarm limits are active according to the patient’s clinical condition. • Connect only one patient to the monitor at a time. Preparations Check that the monitor, accessories and monitor parts are clean and intact. -
Page 75: Admitting A Patient
Monitoring basic Admitting a patient Monitoring of a new patient is started by admitting the patient. After the patient has been admitted, you can start monitoring and trend gathering. To admit the patient: Admit/Discharge Press the key and select Admit Patient Choose the Patient Type (The option A/P means Adult/Pediatric, the option NEO means Neonatal). -
Page 76: Loading Previous Data
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Loading previous data If the patient has already been admitted on the same monitor and this monitor has been restarted, the Contin. Previous will be appeared. Admit/ Discharge Contin. Previous Select this to load the most recent patient trends from the monitor memory when less than 15 minutes has elapsed from the turn-off. -
Page 77: Discharging The Patient
Monitoring basic Discharging the patient When you end monitoring, discharge the patient. The monitor erases screen layout, trend data and alarm and parameter settings that were active during monitoring, and returns to the starting mode and its settings. Admit/Discharge Press the key. -
Page 78: Demo Mode
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Demo Mode The Demo Mode is designed for training and demo of operation before use. Under Demo Mode, the monitor displays the main vital signs values and waveforms. No need accessories, central station or any other peripheral equipment connect to the monitor while in Demo Mode. -
Page 79: Alarms
5 Alarms... -
Page 81: Overview
Alarms 5 Alarms Overview When an alarm for the monitored parameter becomes active: Figure 5-1 View of alarms Alarm messages appear in the message field in the order of priority. The measurement value flashes. The color (red, yellow) indicates the alarm category (high priority, medium priority). -
Page 82: Safety Precautions
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Safety precautions Warnings • Verify alarm processing is active and no arrhythmia occurred during power interruption. • Latched alarms are not retained through monitor reset if alarm condition is been removed. • Do not rely on secondary alarm system for receipt of alarm signal. -
Page 83: Alarm Indications
Alarms Alarm indications • When the monitor is turned on, you will hear a beep: this tells you that the alarm audio signal is working. Also the alarm light are lit up in red, yellow and cyan. You can also check Alarms Setup - Alarm Volume the functioning of the audio signal through •... -
Page 84: Alarm Priority
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Table 5-1 Alarm categories Signal Priority level High Medium Informational Alarms in Message Solid red background Yellow boundary, blue- Cyan boundary, blue- Blue-gray Field gray background gray background background field Alarm reset in Solid red background Yellow boundary, blue-... -
Page 85: Alarm Light
Alarms Alarm light In addition to the audible, the monitor has an alarm light, located in the top of the monitor. The alarm light flashes red, yellow and cyan according to the currently active highest priority alarm. The brightness of the light is fixed. Alarm activation Physiological alarms have individual activation criteria as shown in the table. -
Page 86: Alarms Setup Menu
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Alarms Setup menu You can view and adjust patient alarm limits in the Alarms Setup menu. Alarms ALARM LIMITS AND 10 MIN TRENDS: Alarms Setup Setup Exit Adjust Limits Auto Limits NIBP CVP Sp 2 CO2 Lat. - Page 87 Alarms NOTE: Audible alarms cannot be totally silenced with the Alarm Volume function. Alarm Light This is a grey option menu. The brightness of the alarm light is fixed, can’t be adjusted. Audio ON/OFF Opens a menu to select Silence Apnea, Silence ECG, Silence Apn & ECG or Silence All. NOTE: The silencing selections, except the Activate Alarms, are available only if alarm silencing has been enabled by selecting Monitor Setup - Install/Service (password) - Installation - Alarm Options - Show Audio ON/OFF - Yes.
-
Page 88: Adjusting Alarm Limits
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Adjusting alarm limits Adjusting limits Alarms Setup Press the key. Select Adjust Limits. Turn the Trim knob to selest the specific alarm to be configured. Choose the highlight measurement. If the desired measurement is not displayed in the window, select Next Page. -
Page 89: Alarm Off/On
Alarms Alarm off/on Alarms Setup Press the key. Select Adjust Limits. Select the measurement. If the desired measurement is not displayed, select Next Page. Push the Trim Knob. An adjustment window is displayed. In the adjustment window, turn the Trim Knob to change the selection OFF or ON. Select X Alarm in parameter’s menu and push the Trim Knob to change the selection OFF or ON. -
Page 90: Audio Off: Silencing Audible Alarms Permanently
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Audio off: silencing audible alarms permanently When audible alarms are turned off: • All audible alarms are turned off except for specific alarms configured to break through the audio off setting. • The audio off bell icon displays in the upper left corner of the display screen. -
Page 91: Audio On
Alarms Audio on Alarms Setup Press the key. Select Audio ON/OFF menu. Select Activate Alarms to turn on audible alarms. Audio paused or Alarm reset: silencing audible alarms temporarily NOTES: • When monitor’s remote control is set to active and the related feature has been enabled in the Central configuration. - Page 92 B40/B20 Patient Monitor • NIBP Dia high • NIBP Sys high • NIBP Mean high • NIBP Dia low • NIBP Sys low • NIBP Mean low − Technical alarms: • Leads off • Entropy cable off • Entropy sensor off •...
-
Page 93: Other Adjustable Features
Alarms Other adjustable features NOTE: This section describes the rest of the adjustable features regarding the alarms. You can adjust each feature if you know the required password for entering the Install/Service menu. If you wish to adjust the settings, we recommend that you contact the person responsible for the entire configuration. -
Page 94: Enabling Or Disabling Alarm Audio On/Off
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Enabling or disabling alarm audio ON/OFF With this selection, you can determine whether the audible alarms can be turned off or not. Monitor Setup Press the key. Select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Installation - Alarm Options. -
Page 95: Latching Alarms
Alarms Latching alarms If the Latching Alarms selection is active, the alarm messages stay on the screen even if the initial alarm condition goes away. This enables unattended monitoring. You will also hear a reminder beep every 10 seconds. To clear the message field of the no longer active alarm messages and to clear the beep: •... -
Page 96: Enabling Or Disabling Breakthrough Alarms
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Enabling or disabling breakthrough alarms The breakthrough alarms feature allows some alarms to “break through” (interrupt) an All Alarms Audio Off or a 2 minute alarm audio pause condition. See the “Default configuration worksheet” delivered with the monitor for details of which alarms and conditions are enable for breakthrough feature. -
Page 97: Changing Minimum Alarm Volume
Alarms Changing minimum alarm volume Monitor Setup Press the key. Select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Installation - Alarm Options. Select Min Alarm Volume and adjust the minimum alarm volume with the Trim Knob. Monitor Setup The default setting will be 5. 5-17... -
Page 98: Changing Reminder Volume
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Changing reminder volume Monitor Setup Press the key. Select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Installation - Alarm Options. Select Reminder Volume and adjust the alarm reminder volume with the Trim Knob. Monitor Setup The default setting will be 5. -
Page 99: Changing The Tone Pattern
Alarms Changing the tone pattern The monitor has four choices of alarming tone patterns: ISO, ISO2, General and IEC. To change the tone pattern: Monitor Setup Press the key. Select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Installation - Alarm Options. Select Alarm Tones and ISO, ISO2, IEC or General. -
Page 100: Enabling Or Disabling The Alarm Remote Control
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Enabling or disabling the alarm remote control The bedside monitor’s alarm can be remote controlled by central station: adjust alarm settings, alarm reset by CIC, alarm audio pause and silence all by iCentral. To enable the alarm remote control:... - Page 101 Alarms NurseCall With this selection, you can determine whether the NurseCall can be turned open according to NruseCall system electrical level in the hospital. Monitor Setup Press the key. Select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Installation - Alarm Options. Select NurseCall - NO.
- Page 102 B40/B20 Patient Monitor 5-22...
-
Page 103: Monitor Setup
6 Monitor setup... -
Page 105: Warnings
Monitor setup 6 Monitor setup Warnings • Operator should check the preset in use before use on each patient. • A hazard can exist when using differing presets on like devices in a common area. For instance, two beside monitors used in an ICU with different presets may present a hazard. Overview The monitor has numerous setup options for screen, parameters, alarms, etc. -
Page 106: Setting Time And Date
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Setting time and date The time is shown in the upper right corner of the screen. Turning off the monitor does not affect the clock. Monitor Setup Press and select Time and date. Monitor Setup Turn and push the Trim Knob to set the time and date: −... -
Page 107: Changing Monitor Installation Settings
Monitor setup Changing monitor installation settings Enter to following menu to setup settings: Monitor Setup - Install/Service (Enter password) - Installation Monitor Install / Service Setup Installation Units Alarm Options Printer Monitor Settings Previous Menu Set unit of height, weight and blood pressure. -
Page 108: Changing Alarm Options
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Changing alarm options Monitor Setup Press the key, select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Installation - Alarm Options. Monitor Setup • Show limits: YES(default) is show alarm limits in digit fields. • Show Audio ON/OFF: YES is enable alarm silence options in the Audio ON/OFF menu in Alarms Setup. -
Page 109: Changing Printer Settings
Monitor Setup Press the key. Select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Installation - Monitor Settings - Parameter Settings • CO2 Numbers: Set humidity compensation type Dry (default), Wet. • MAC Type (B40 only): Set MAC type MAC or MACage... -
Page 110: Setting Time Zone
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Setting time zone Time Zone menu is enable only when monitor is not connected to network and discharge paitent/haven’t admitted patient. Monitor Setup Press key. Select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Time Zone Monitor Setup •... -
Page 111: Changing The User Modes
Monitor setup Changing the user modes You can change the settings in each user mode to suit your specific needs. User modes are predefined combinations of settings that include both general and measurement specific settings. A user mode defines, for example, what is displayed on the screen and in the trends. General settings can be changed in the Monitor Setup menu, other settings in the parameter setup menus. -
Page 112: Changing The Startup Mode
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Changing the startup mode The monitor always starts in startup mode. The startup mode is one of the user modes, and it is chosen during configuration. To change the startup mode permanently. Monitor Setup Select - Install/Service - Save Modes. Enter the password. -
Page 113: Changing The Normal Screen Layout
Monitor setup Admit/ Discharge The selected mode is marked with a circle. You can return to the previous mode by selecting Return to X. During monitoring, you can make additional changes to the mode settings and, to make the changes permanent, save them through the Save Modes menu. Changing the Normal Screen layout At startup, the screen is arranged according to the startup mode definitions. -
Page 114: Modifying Waveform Fields
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Modifying waveform fields Up to six waveforms can be displayed on the central of the monitor at a time, with the related numerical filed on the right. The fields are numbered from up to down. Figure 6-2... -
Page 115: Modifying Digit Fields
Monitor setup Modifying digit fields Patient data may be displayed in up to four digit fields, located in the lower part of the screen. The fields are numbered from left to right. Figure 6-3 Digit field You may change the contents of each field, or turn them off individually. Before modifying the digit fields remember to check that the desired parameter module is plugged in. -
Page 116: Modifying Split Screen
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Modifying split screen You can split Normal Screen so that one part continuously displays trend data. To select a split screen view: Monitor Setup Press the key. Select Screen Setup. Select Split Screen and choose from the options: Trend or None. -
Page 117: Other Adjustable Screen Features
Monitor setup Other adjustable screen features Changing sweep speeds You can change the speed of the waveforms on the screen. The selections are Fast (6.25 mm/s) and Slow (0.625 mm/s). For hemodynamic parameters, the selections are 12.5, 25 and 50 mm/ s. -
Page 118: Changing The Recorder And Printer Settings
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Changing the recorder and printer settings Recorder settings Print/Record Press Select Record Waveforms. Print/ Record • Select Waveform 1 and select a parameter or select OFF. Then select Waveform 2 and Waveform 3 and their parameters. You can record up to three waveforms simultaneously. -
Page 119: Printer Settings
Monitor setup Select Record Trends. Print/ Record & Print Record Record Trends Record Numerical Trend Resolution 5 min Num. Trend Type Record Graphical IBP1 Graphic Trend 1 IBP2 Graphic Trend 2 IBP1 NIBP Previous Menu SpO2 Pleth -More- Change graphical trend recorded in upper field. -
Page 120: Configuring Trends And Snapshot
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Configuring trends and snapshot Monitor Install/Service Setup Trends & Snapshot Default Trend Graph Graphical Trends Snapshot Previous Menu Change default trend type: graphical or numerical. Changing default trend You can select graphical or numerical trends to be displayed by default:... -
Page 121: Configuring Snapshots
Monitor setup Configuring snapshots You can change the snapshot settings: Press Monitor Setup key. Select Install/Service and enter the password. Select Trends & Snapshot - Snapshot • Field 1 – Field 6: Select to display waveform, graphical trend or numerical trend. Field 1-5 can be displayed on screen and Field 6 can be printed. -
Page 122: Using Network
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Using Network Use the CAT-5 network cable to connect the monitor to the network. Make sure that the power is switched off. Connect one RJ-45 connector to the network port at the back of the monitor. Connect the other RJ-45 connector to the corresponding port on the wallbox. -
Page 123: Trends
7 Trends... -
Page 125: Safety Precautions
Trends and OCRG 7 Trends and OCRG Safety precautions Caution • Snapshot waveforms are in some cases drawn from compressed data that may not allow perfect reconstruction. Verify diagnostic waveform measurements with the waveform data from realtime graph strips. Overview The monitor displays two types of trend data: graphical and numerical. -
Page 126: Most Common Tasks
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Most common tasks • Displaying trends and activating Pt.Data & Trends Press the key and select Trends. the Trends menu The most recently displayed trend (graphical or numerical) is displayed together with the Trends menu. Scrolling time with trend cursor 1. -
Page 127: Minitrend View
Trends and OCRG Minitrend view Figure 7-1 Minitrend view You can split the Normal Screen page so that one fourth of the screen, on the left hand side, continuously shows graphical minitrends beside waveforms. Note that the split screen option is available only when the Normal Screen page shows waveforms. -
Page 128: Minitrend Length
B40/B20 Patient Monitor To select a split screen view: Monitor Setup Press the key. Select Screen Setup. Select Split Screen and Trend. Monitor Setup Minitrend length You can choose to view trend data from the last five minutes or the last 30 minute period. The five minute minitrend is updated every 10 seconds, the 30 minute minitrend is updated once every minute. -
Page 129: Graphical Trend View
Trends and OCRG Graphical trend view Figure 7-2 Graphical trend page Trends menu Measurement trend field Real time ECG Numeric value of a measurement at the trend cursor point Trend page number Snapshot point Time and marker field... -
Page 130: Symbols
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Symbols Trend bar, parameter scale to the left. The gap shows the blood pressure mean value. NIBP trend bar Dotted vertical line across the trend field indicates change, such as ST relearning or zeroing of an invasive blood pressure channel/ changing a label. -
Page 131: Graphical Trend Pages
Trends and OCRG Graphical trend pages Graphical trends contain: − Four pages − Six fields on each page Five fields are usually visible. The lowest (sixth) field is replaced by digit fields on the screen. All six fields are printed. Scale, label, unit and color of the parameter follow the real time waveform setting for each parameter. -
Page 132: Moving On Graphical Trend Pages
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Moving on graphical trend pages To see more parameters on other pages: • Select Scroll Pages in the Trends menu. Numeric measurement values for trended parameters are displayed next to the cursor. The cursor indicates the time when these values have been measured. To change the cursor location: In the Trends menu, select Cursor. -
Page 133: Numerical Trend View
Trends and OCRG Numerical trend view Figure 7-3 Numerical trend page Trend menu Page name and number Real time ECG Real time digit fields, if the Normal Screen shows waveforms... -
Page 134: Numerical Trend Pages
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Numerical trend pages Numerical trends contain: − four pages of maximum 72 hours trend information − real-time ECG on top of each page Resolution is five minutes. Moving between numerical trend pages • Use the Trim Knob to scroll the trend in vertical direction. -
Page 135: Factory Default Parameters
Trends and OCRG Factory default parameters You cannot change the contents of numerical trend fields. The parameter units follow the real time waveform settings of each parameter. Page 1: Vital parameters Mark Time SpO2 NIBP NIBP sys/dia mean sys/dia mean mean Page 2: Hemodynamics Mark... -
Page 136: Snapshots
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Snapshots A snapshot is a frozen frame of preconfigured waveforms or trends saved in the monitor memory. A snapshot can contain waveforms, numerical trends and graphical trends. You can take up to 10 snapshots. It is automatically numbered. When graphical trend view, snapshots mark “s”... -
Page 137: To Create A Snapshot Manually
Trends and OCRG To create a snapshot manually: • Take Snapshot Press the key. To create automatic snapshots: The monitor can automatically take snapshots on Brady, Tachy and Art sys/dia/mean high/low alarms if automatic snapshot creation is enabled. For enable this function, see "Configuring snapshots"... -
Page 138: Ocrg
B40/B20 Patient Monitor OCRG The monitor support 8 minutes OCRG (oxycardiorespirogram) function in the NEONATAL mode. The OCRG subsystem provides services to view and review specific high resolution trends, high resolution beatto- beat HR, high resolution beat-to-beat SpO2 and compressed respiration waveform - simultaneously in the same view. -
Page 139: Erasing Trend Data And Snapshot
Trends and OCRG Erasing trend data and snapshot Trends are erased when you discharge the patient. Admit/Discharge Press the key. Select Discharge. In the opened window, select Yes to erase the trends and to discharge the patient. Admit/ Discharge Showing alarm history •... - Page 140 B40/B20 Patient Monitor 7-16...
-
Page 141: Print And Record
8 Print and record... -
Page 143: Overview
Print and record 8 Print and record Overview You can manage recording and printing via the Print/Record menu. For recordings, you need a extension rack with recorder, and for printouts you need connect to network and a laser printer (PCL5 compatible, min. 2 MB memory). The monitor is connected to a laser printer via network. Recorder Recording The recorder:... -
Page 144: Recording Waveforms
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Recording waveforms You can record three waveforms to a local recorder as you set up. To start the recording, do one of the following: • Recorder Start/Stop Press the key, or Print/Record Press the key and select Record Waveforms - Record to Local To stop the recording: •... -
Page 145: Sample Of Waveform Recording
Print and record Sample of waveform recording Recorder speed Scale Selected waveform Date Time NOTE: Waveform scaling follows the displayed parameter scaling, when applicable. Selecting waveforms for recording You can select which waveforms and how many of them you want to record. Print/Record Press the key. -
Page 146: Changing The Paper Speed
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Changing the paper speed To see the waveforms more clearly or more generally, you can change the paper speed. The recorder speed can be 1, 6.25, 12.5, or 25 mm/second. Print/Record Press the key. Select Record Waveforms. -
Page 147: Controlling The Recording Time
Print and record Controlling the recording time You can adjust the recording time to be 30 seconds or continuous, which means that the recording continues until the recorder runs out of paper. Print/Record Press the key. Select Record Waveforms. Select Length and choose 30 s or Cont. The default setting for the recording time is 30 seconds. -
Page 148: Recording On Alarms
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Recording on alarms An automatic strip chart recording is activated when the following alarms reach the red level: Asystole, Tachy, Brady, Art Sys/Dia/Mean high, Art Sys/Dia/Mean low, V Fib, and V Tach. When recording is activated by alarms, the recording time is always 30 seconds and the delay always 12 seconds. -
Page 149: Recording Trends
Print and record Recording trends To record trends: Print/Record Press the key. Select Record Trends – Record Numerical or Record Graphical. Stop recording by selecting Stop Numerical or Stop Graphical. You can record numerical, graphical or tabular trends. Recording numerical trends Since the contents of the numerical trends are preconfigured, you cannot choose the parameters or change their order. -
Page 150: Tabular Trend Format
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Selecting the format for the recorded numerical trends You can select the format for the recorded numerical trend to be either Num. (vertical) or Tab. (horizontal): Print/Record Press the key and select Record Trends. Select Num Trend Type and Num. or Tab. -
Page 151: Inserting Recorder Paper
Print and record Inserting recorder paper To load paper in the reocrder: Open the recorder door by pressing the door latch. Remove the paper core. Place a new paper roll between the tabs of the paper holder. The paper should unroll from underneath the paper roll. -
Page 152: Printing
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Printing The monitor support the laser printer in S/5 network. The user can directly print the patient data from the laser printer when the monitor and printer are correctly configured on iCentral Server. The monitor don’t support the laser printer in CARESCAPE Unity network. The user can print the patient data from the CIC central station only. -
Page 153: Cleaning And Care
9 Cleaning and care... -
Page 155: Safety Precautions
Cleaning and care 9 Cleaning and care Safety precautions Warnings • Disconnect equipment from power line before cleaning • If liquid has accidentally entered the system or its parts, disconnect the power cord from the power supply and have the equipment serviced by authorized service personnel. •... -
Page 156: Cautions
B40/B20 Patient Monitor • Do not autoclave any part of the system with steam or sterilize with ethylene oxide. • Do not disinfect or open the water trap cartridge. Do not touch the water trap membrane. The hydrophobic membrane is damaged if any cleaning is attempted other than rinsing with water. -
Page 157: Regular Checks
Check that the red, yellow and cyan alarm lights are lit and the speaker gives an audible beep momentarily when the monitor starts up. Safety checks for software The GE Healthcare software design controls include performance of a risk analysis using methods consistent with ISO 14971 Medical devices - Application of risk management to medical devices. -
Page 158: Every Two Months
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Every two months • Change the water trap when the ‘Replace D-Fend’ message displays on the screen. • Perform gas calibration in continuous use, see “Calibrating” in Gas chapter for detail procedures. Every six months Gas calibration Perform gas calibration for airway gas monitoring according to the instructions in the relevant section. -
Page 159: Recycling The Monitor Battery
Cleaning and care Recycling the monitor battery When the battery no longer holds a charge, it should be replaced. Remove the old battery and follow your local recycling guidelines. Changing fuses Remove the power cord if used. Remove the fuse holder by pulling the holder out with screwdriver. If a fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the correct type and rating. -
Page 160: Pulse Oximetry Sensors
Allow the product to dry completely after cleaning. Pulse oximetry sensors The GE Healthcare pulse oximetry sensors are latex-free. Take possible patient allergies into account also when selecting the cleaning agent. Detach the sensor from the patient and the monitor. - Page 161 Cleaning and care flow is within 120 ± 20 ml/min for E-sCO, E-sCAiO and N-CAiO modules, 150 ± 25 ml/min for E-miniC). Follow local hospital’s regulations to dispose the accumulated fluids. • In anesthesia: Replace the water trap every two months or when the text 'Replace D- Fend' appears.
-
Page 162: Other Accessories
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Other accessories See the accessory package for instructions for how to clean and check them. Do not reuse single-use disposable accessories. -
Page 163: 10 Troubleshooting
10 Troubleshooting... -
Page 165: Overview
Troubleshooting 10 Troubleshooting Overview The troubleshooting section consists of two parts which together should help you resolve the most common monitoring problems. The parts are "Checklist" and "Messages". Checklist Check the following things before monitoring to ensure that you have remembered to make all essential preparations, and if any problems occur during monitoring. -
Page 166: Battery Indicators
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Battery indicators The messages, screen symbols and front panel LED indicators tell the user about the status of the batteries. For LED indicators, consult the table below and for messages, see section “Troubleshooting.” Table 10-1 Battery indicators... -
Page 167: Messages
Troubleshooting Messages Table 10-2 Messages Message Explanation What to do • Agent Mixture Mixture of halogenated agents is Check the ventilator and agent detected. vaporizer settings. • Alarm setup changed from Alarm limits or arrhythmia alarm Check the alarm limits and the Central priorities have been changed using arrhythmia alarm priorities;... - Page 168 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Message Explanation What to do • Check NIBP NIBP measurement affected by low Check the patient status. blood pressure and pulsation, or a • Check the measurement setup. change in patient's condition. • Check the cuff. •...
- Page 169 Troubleshooting Message Explanation What to do • Incompatible SpO2 Probe The SpO2 sensor is not compatible. Replace the sensor. See the “Supplies and accessories” manual • If the problem persists, contact authorized service personnel. • InvBP’s not zeroed One or both InvBP channels have not Zero the channel indicated or zero been zeroed.
- Page 170 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Message Explanation What to do • NIBP call service error NIBP error Contact authorized service personnel. • NIBP manual Autocycling mode is interrupted Check the NIBP setup and restart because of an air leak or loose cuff.
- Page 171 Troubleshooting Message Explanation What to do • Recorder: input voltage high, There are problems with the recorder Contact authorized service input voltage. Recorder: input voltage low personnel. • Recorder: thermal array There are problems with the recorder Contact authorized service overheat temperature.
- Page 172 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Message Explanation What to do • Temp sensor error Frame temperature sensor error. Contact authorized service personnel. • T1 temperature error Hardware failure or unsuccessful Check the probe whether is set to calibration. T2 temperature error 400.
-
Page 173: Advanced Ecg Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Advanced ECG troubleshooting Symptom Possible cause and solution • ECG signal is noisy or no Ensure that the patient is not shivering. Incorrect ECG filter. QRS is detected • Check the filter through - ECG Setup - Filter. Poor electrode quality or wrong positioning. •... -
Page 174: Advanced Arrhythmia Troubleshooting
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Why is the monitor calling The monitoring system may be detecting a wider QRS complex or artifact in V Tach when the patient some of the analyzed ECG waveforms. In addition, the V leads may be is not in V Tach? exhibiting polarity changes, which may occasionally cause an inaccurate call. -
Page 175: Advanced Impedance Respiration Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Advanced impedance respiration troubleshooting Symptom Possible cause and solution • Respiration measurement Check the electrode quality and positioning. fails • Adjust the detection limits. During ventilator-supported breathing, the respiration calculation may count only ventilator-produced inspirations and expirations. • Other electrical devices may interfere with the measurement. Why does the waveform If the detection sensitivity threshold is set too high, shallow breaths will not be have a combination of... - Page 176 B40/B20 Patient Monitor What does electrosurgical Electrosurgical interference is most obvious on the displayed waveform. It is interference look like and a very spiky, erratic looking waveform caused by the electrosurgical unit’s how can it be minimized? overwhelming interference. It can result in grossly inaccurate pulse oximeter results.
-
Page 177: Advanced Nibp Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Advanced NIBP troubleshooting Symptom Possible cause and solution • NIBP measurement does Check that cuff tubings are not bent, stretched, compressed or loose. not work or values seem • Prevent motion artifacts. unstable • Use cuffs of correct size. Why does the mean The following conditions may cause the mean value to display in the NIBP value display while the... -
Page 178: Advanced Invbp Troubleshooting
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Advanced InvBP troubleshooting Symptom Possible cause and solution • InvBP readings seem Make sure there are no air bubbles in the transducer system. Flush and unstable zero. • Place the transducer on the patient’s mid-heart level and zero. -
Page 179: Advanced Airway Gas Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Advanced airway gas troubleshooting Symptom Possible cause and solution • Airway gas values are too Check the sampling line and connectors for leakage. Why can we see dips in The dips seen in the capnogram during expiration are related to the sidestream the capnogram during gas sampling, the continuous gas flow to the Y-piece, and patient’s cardiac expiration? -
Page 180: Other Situations
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Other situations The following table lists some other situations that may occur during monitoring and possible explanations. Table 10-1 Other operation problems Symptom Possible cause and solution • Printing is not Print/Record Printer selection is None; change it through... -
Page 181: 11 Ecg
11 ECG... -
Page 183: Safety Precautions
11 ECG Safety precautions Warnings • Make sure that the leadwire set clips or snaps do not touch any electrically conductive material including earth. • Whenever patient defibrillation is a possibility, use non-polarizing (silver/silver chloride construction) electrodes for ECG monitoring •... -
Page 184: Overview
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Overview The electrocardiography, ECG, reflects the electrical activity generated by the heart muscle. ECG monitoring is used for a heart rate measurement, for arrhythmia analysis and for detecting pacemaker function and myocardial ischemia. In Normal Screen, when measuring 5-lead ECG, you can simultaneously monitor the waveforms of up to three different ECG leads. -
Page 185: Displaying Ecg And Heart Rate
Displaying ECG and heart rate Figure 11-2 Display of ECG and HR ECG1 is displayed first ECG2 is displayed below ECG1 ECG3 is displayed below ECG2 Selected lead label ECG gain bar (1 mV reference) Heart rate (HR) label Heart rate/pulse rate source (ECG/Art/ABP/Pleth) HR/PR value Heart beat detector is flashing with every detected heart beat (10) ST values are always displayed next to ECG2... -
Page 186: Preparing The Patient And Placing The Electrodes
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Preparing the patient and placing the electrodes Preparing the patient • Prepare the skin properly to ensure optimal signal quality. • Shave any hair from the electrode site. Gently rub the skin surface to increase capillary blood flow and remove dead skin cells and oil. -
Page 187: Lead Measurement
ECG connector ECG trunk cable, or 3-lead ECG cable with integrated leadwires 3 or 5 leadwire set NOTE: For a comprehensive list of accessories, see the “Supplies and Accessories“ catalog. Lead measurement The following table lists the electrodes needed to measure different ECG leads: Lead Electrodes needed R/RA, L/LA + F/LL or N/RL... -
Page 188: Setup Ecg Waveform View
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Setup ECG waveform view • To change the number of ECG waveforms in Normal Screen: Monitor Setup - Screen Setup - Waveform Fields Choose the ECG waveforms to display. • To change the waveform sweep speed: Monitor Setup - Sweep Speeds - Hemodynamics Choose the waveform sweep speed. -
Page 189: Adjusting The Ecg Size
Adjusting the ECG size Increasing or decreasing the ECG gain affects the size of the 1 mV bar at the left end of the ECG waveform and the size of the ECG waveform accordingly. ECG Setup menu For advanced ECG setup, please go the sub menu: - ECG Setup ECG Setup Beat Sound Volume... - Page 190 B40/B20 Patient Monitor When Pleth is monitored, the monitor provides a variable pulse beep, so that the tone of the pulse beep rises with increasing oxygen saturation and falls with decreasing saturation. This affects also the ECG tone. HR Source Selects the heart rate source (AUTO, ECG, ART, ABP, UAC or Pleth).
-
Page 191: Setting Heart Rate Alarm Limits
Setting heart rate alarm limits To set the heart rate alarm limits: Press the key. Select ECG Alarms. Select Adjust Limits. Alarms Setup You can also adjust the limits through - Adjust Limits. For detailed instructions, see section "Alarms." ADJUST ALARM LIMITS: Adjust Limits HR Alarm PVC Alarm... -
Page 192: Setting Pvc Alarm Limits
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Setting PVC alarm limits To set the PVC alarm limits: Press the key. Select ECG Alarms. Select PVC Alarm - ON. Select Adjust Limits. Alarms Setup You can also adjust the limits through - Adjust Limits. For detailed instructions, see section "Alarms."... -
Page 193: Ecg Printout Type
ECG printout type "Changing printer settings" page 6-5. NOTE: To adjust this feature, you need a password. If you wish to adjust the settings of the features, we recommend that you contact the person responsible for the entire configuration. Checklist Check that: •... -
Page 194: Pacemaker Detection
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Pacemaker detection Safety precautions Warnings • Do not diagnostically interpret pacemaker spike size and shape. • A pacemaker pulse can be counted as a QRS during asystole in either pace mode. Keep pacemaker patients under close observation. -
Page 195: Monitoring Pacemaker Patients
Monitoring pacemaker patients The monitor can detect and reject pacemaker. To display the pacing spike of cardiac pacemaker: Press ECG key. Select ECG Setup - Pacemaker, choose following opitions: • Hide = The pacing spike is filtered away from ECG data. •... -
Page 196: Arrhythmia Detection
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Arrhythmia detection Safety precautions Warnings • LOSS OR DETERIORATION OF ARRHYTHMIA DETECTION -Automated arrhythmia analysis programs may incorrectly identify the presence or absence of an arrhythmia. A physician must therefore interpret the arrhythmia information in conjunction with other clinical findings. -
Page 197: About The Arrhythmia Detection
for several minutes after the learning phase to allow the algorithm to reach optimal detection performance. About the arrhythmia detection When an ECG signal is detected at the start of monitoring, the arrhythmia detection algorithm begins acquiring and analyzing QRS complexes in the leads used for arrhythmia detection. This phase is known as learning. -
Page 198: Adjusting Arrhythmia Alarm Settings
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Adjusting arrhythmia alarm settings In the adjustment menu, the priority for all alarms are always red (high priority). You can turn and push the Trim Knob to set arrhythmia alarm to create snapshot. Press Select ECG Alarms - Arrh. Alarms. -
Page 199: Description Of The Arrhythmia Algorithm
Description of the arrhythmia algorithm When an ECG signal is detected at the start of monitoring, the arrhythmia detection algorithm begins acquiring and analyzing QRS complexes in the leads used for arrhythmia detection. This phase is known as learning. Once learning is complete, the dominant QRS complex is stored as a reference template. -
Page 200: St Detection
B40/B20 Patient Monitor ST detection Overview The ST value, analyzed by the monitor, shows the difference of electrical activity between ISO and ST points. Myocardial ischemia appears in the ECG as an ST segment deviation from the isoelectric line (ISO point). The ST segment generally rises above the PQ isoelectric line in the presence of transmural ischemia and is pressed below the isoelectric line in the subendocardial ischemia. -
Page 201: Monitoring The St Segment
Monitoring the ST segment The monitor analyzes ST for all measured leads and gives ST trends separately for each lead. Numerical ST data is shown to the right of the second real-time ECG waveform field. Monitor Setup You can also select numerical ST data to the lower digit field. Press the key and select Screen Setup - Digit Fields. -
Page 202: Setting The St Measurement Points
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Setting the ST measurement points Automatic setting of the J, ST and ISO points The ST algorithm automatically searches for the J and ISO points. The distance between the ST and J point is set according to the heart rate: −... -
Page 203: Setting St Alarm Limits
Setting ST alarm limits To set the ST alarm limits: Press the key. Select ECG Alarms. Select ST Alarms. Select Adjust Limits. Alarms Setup You can also adjust the limits through - Adjust Limits. ADJUST ALARM LIMITS: Adjust Limits Lat. Alarm Inf. -
Page 204: Description Of The St Segment Measurement Algorithm
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Description of the ST segment measurement algorithm The ST segment begins at the point where the QRS ends (J point). Diagnostic criteria of ST segment changes are measured at 60 ms after the J point. For monitoring purposes it is important to keep the measurement point fixed during monitoring to notice the ST changes on the respective trends. -
Page 205: Impedance Respiration
12 Impedance respiration... -
Page 207: Safety Precautions
Impedance respiration 12 Impedance respiration Safety precautions Warnings • Make sure that the leadwire set clips or snaps do not touch any electrically conductive material including earth. • The monitor may not detect all episodes of inadequate breathing, nor does it distinguish between central, obstructive and mixed apnea events. -
Page 208: Overview
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Overview Impedance respiration is measured across the thorax. When the patient is breathing or is ventilated, the volume of air changes in the lungs, resulting in impedance changes between the electrodes Respiration rate is calculated from these impedance changes, and a respiration waveform is displayed on the monitor screen. -
Page 209: Respiration Rate Source
Impedance respiration Respiration rate source Respiration rate is calculated automatically when ECG or CO is measured unless the respiration measurement is turned off. When CO is measured, the respiration rate is automatically calculated from CO Silence Respiration rate calculation switches back to impedance respiration if you press the Alarms key during an Apnea alarm. -
Page 210: Patient Connections
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Patient connections The setup is the same as for the ECG measurement. For more information, see section “ECG.” R=RED (IEC) L=YELLOW (IEC) R=RED (IEC) L=YELLOW (IEC) RA=WHITE (AAMI) LA=BLACK (AAMI) RA=WHITE (AAMI) LA=BLACK (AAMI) LEAD I R/RA... -
Page 211: Activating Measurement
Impedance respiration Activating measurement Select respiration in a waveform or a digit field, otherwise the respiration information is not included in the trends and the alarms are not operative. Monitor Setup - Screen Setup - Waveform Fields or Digit Fields, Or Others - Resp Setup - Screen Setup - Waveform Fields or Digit Fields Refer to... -
Page 212: Improving Waveform Readability
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Improving waveform readability To improve readability, increase the waveform size. Others Press the key. Select Resp Setup. Select Size and adjust the waveform size. Others The bar on the left side of the waveform always indicates a 1 Ω reference. -
Page 213: Correcting The Respiration Number
Impedance respiration Correcting the respiration number Normally, we recommend the use of the AUTO detection limit. However, in some specific cases you may wish to adjust the limits manually. − When the respirations are weak, you can manually adjust the detection limits (measurement sensitivity) closer to each other to ensure that all respirations are included in the RR value. -
Page 214: Turning Off The Measurement
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Turning off the measurement If the impedance respiration measurement signal interferes with other measurements, such as ECG, you can turn it off. Others Press the key. Select Resp Setup. Select Measurement OFF. Others Checklist Check that: •... -
Page 215: 13 Pulse Oximetry
13 Pulse oximetry... -
Page 217: Safety Precautions
Pulse oximetry 13 Pulse oximetry Safety precautions Warnings • Allow sensor and cable to dry completely after cleaning. Moisture and dirt on the connector can affect the measurement accuracy. • To prevent erroneous readings, do not use physically damaged sensors, cables or modules. -
Page 218: Cautions
B40/B20 Patient Monitor • Change the sensor site immediately if there is evidence of blistering, skin erosion, or ischemic skin necrosis (such as skin discoloration or reddening). Otherwise, change the site every four hours. • A pulse oximeter should not be used as an apnea monitor. -
Page 219: Overview
Pulse oximetry Overview Oxygen saturation SpO is the percentage of saturated hemoglobin compared to total hemoglobin measured by a two wavelength pulse oximeter (also called functional or In Vivo oxygen saturation. The SpO value is measured by light absorption technique: Red and infrared light is emitted from the emitter side of the sensor. -
Page 220: Display Of Pulse Oximetry
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Display of pulse oximetry Figure 13-2 Display of SpO value and pleth waveform Scale of plethysmogram Label Oxygen saturation (SpO ) value Pulse oximetry message field Patient connections Figure 13-3 Pulse oximetry setup Compatible SpO measurement capability... -
Page 221: Connecting The Patient
Pulse oximetry NOTES: • GE sensors are latex-free. • Use dry and clean sensors only. • Do not use damaged sensors. • Check that you are not re-using a disposable sensor or other disposable accessories. • For a comprehensive list of accessories, see the "Supplies and Accessories" catalog delivered with the monitor. -
Page 222: Pulse Oximetry Menu
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Pulse oximetry menu Pulse Oximetry Pulse Oximetry Averaging Pleth Scale SpO2 Response Normal Pleth Scale Sensitivity Maximum Beat Sound Volume HR Source Beat Sound Volume AUTO SpO2 Alarm HR Source AUTO Screen Setup SpO2 Alarm Normal Screen... -
Page 223: Data Update And Averaging
Pulse oximetry Sensitivity (Masimo SpO configuration only) Adjusting the Masimo SpO sensor sensitivity level. − Use the Normal sensitivity setting for normal patient monitoring purposes. − Use the Maximum sensitivity setting for improved poor perfusion performance and for faster tracking of rapid SpO saturation changes. -
Page 224: During Monitoring
B40/B20 Patient Monitor During monitoring Patient condition or prolonged use may require changing the sensor site periodically. Check skin integrity, circulatory status and correct alignment and change sensor site at least every four hours. For patients with poor peripheral blood circulation or sensitive skin, change the site at intervals of 30 minutes to one hour. -
Page 225: Measurement Limitations
Pulse oximetry Measurement limitations • The monitors are designed to minimize the interference of electrosurgery. Under some circumstances electrosurgery may cause noise on the screen. Therefore, be careful in interpreting the results, especially the plethysmographic pulse waveform, during electrosurgery. • The saturation values may be somewhat higher for smokers. -
Page 226: Spo2 Functional Testers
B40/B20 Patient Monitor • Electromagnetic interference (EMI) • Ventilator-induced pressure changes SpO2 functional testers Some models of commercially available bench-top functional testers and patient simulators can be used to verify proper functionality of pulse oximeter sensors, cables and monitors. While such devices may be useful for verifying that the pulse oximetry system is functional, they are incapable of providing the data required to properly evaluate the accuracy of the system’s SpO... - Page 227 Pulse oximetry Figure 13-4 Bland-Altman plot of TruSignal V2 with Oxy-F sensor. Population mean bias: 0.0, upper 95% limit of agreement: 2.2, lower 95% limit of agreement: -2.2, between subject variance: 10.2, Within-subject variance: 0.9. Figure 13-5 Bland-Altman plot of TruSignal V2 with Oxy-W sensor. Population mean bias: 1.1, upper 95% limit of agreement: 4.5, lower 95% limit of agreement: -2.3, between subject variance: 41.5, within-subject variance: 1.5.
- Page 228 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Figure 13-6 Bland-Altman plot of TruSignal V2 with Oxy-SE sensor. Population mean bias: 1.3, upper 95% limit of agreement: 4.2, lower 95% limit of agreement: -1.7, between subject variance: 29.2, within-subject variance: 1.2. Figure 13-7 Bland-Altman plot of TruSignal V2 with Oxy-AP sensor. Population mean bias: 1.3.
- Page 229 Pulse oximetry Figure 13-8 Bland-Altman plot of TruSignal V2 with Oxy-AF sensor. Population mean bias: 0.9, upper 95% limit of agreement: 3.8, lower 95% limit of agreement: -2.0, between subject variance: 10.7, within-subject variance: 1.7. Figure 13-9 Bland-Altman plot of TruSignal V2 with Oxy-E sensor. Population mean bias: 0.8, upper 95% limit of agreement: 3.9, lower 95% limit of agreement: -2.3, between subject variance: 20.8, within-subject variance: 1.7.
- Page 230 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Figure 13-10 Bland-Altman plot of TruSignal V2 with Oxy-AP sensor, motion conditions. Population mean bias: 0.8. Upper 95% limit of agreement: 5.0, lower 95% limit of agreement:-3.4. Between subject variance: 22.6, within-subject variance: 3.6. Figure 13-11 Bland-Altman plot of TruSignal V2 with Oxy-AF sensor, motion conditions.
-
Page 231: Checklist
Pulse oximetry Checklist Check that • Only one module with pulse oximetry measurement is inserted. • Correct SpO sensor is selected for each patient size. • The sensor is completely dry after cleaning. • Sensor or interconnect cable is plugged to the blue connector in the module. •... - Page 232 B40/B20 Patient Monitor 13-16...
-
Page 233: Non-Invasive Blood Pressure
14 Non-invasive blood pressure... -
Page 235: Safety Precautions
• GE Healthcare monitors are designed for use with dual-hose cuffs and tubing. The use of single-hose cuffs with dual hose tubing can result in unreliable and inaccurate NIBP data. •... -
Page 236: Overview
B40/B20 Patient Monitor • Periodically check patient limb circulation distal to the cuff. Check frequently when using Auto NIBP in one and two minute intervals. The one and two minute intervals are not recommended for extended periods of time. •... -
Page 237: Direct Function Keys
Non-invasive blood pressure Direct function keys There are two keys for starting NIBP on the Command Board: Starts and stops autocycling measurements. NIBP Auto ON/OFF NIBP Starts a single measurement, and cancels any measurement. Start/Cancel Displaying non-invasive blood pressure NIBP can be displayed in the digit field: Figure 14-2 NIBP digit field display Systolic and diastolic pressure value of non-invasive blood pressure Label... -
Page 238: Patient Connections
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Patient connections Figure 14-3 NIBP setup NIBP connector in monitor Cuff hose Cuff of correct size Place the arrow (4) over the brachial artery. Check that the index line (5) falls within the range markings on the cuff, and wrap the cuff around the upper arm. -
Page 239: Selecting A Cuff And A Cuff Hose
Non-invasive blood pressure Selecting a cuff and a cuff hose Two different cuff hoses with different cuff connections are available: − BLACK hose for adults and pediatric (corresponding inflation limits A/P including cuff identification. − LIGHT BLUE hose for neotatal (corresponding inflation limit NEO without cuff identification. -
Page 240: Nibp Setup Menu
B40/B20 Patient Monitor NIBP Setup menu NIBP NIBP NIBP Setup Ready Prompt Inflation Limits AUTO Previous Menu Adjust volume of sound indicating completion of NIBP measurement. Ready Prompt Ready prompt gives an audible tone when the NIBP measurement is ready. Adjust the volume of the beep tone from 1 (soft) to 10 (loud), or to 0 (OFF.) -
Page 241: Starting
Non-invasive blood pressure Starting Note that the measurement unit may be mmHg or kPa. The unit is selected during Monitor Setup configuration through - Install/Service - Installation - Units. You can start the NIBP measurement using either the direct function keys, or from the NIBP NIBP menu by pressing the key. -
Page 242: Autocycling
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Autocycling NIBP Auto On/Off key sets automatic NIBP measurement at selected intervals on and off. To automatically measure NIBP at set time intervals, you must first set the cycle time before setting the automatic measurements. You also can configure a custom auto mode to meet the need of your clinical situation. -
Page 243: Setting Custom Mode
Non-invasive blood pressure Setting custom mode You can set up to 4 separate steps for auto NIBP determinations by setting the time interval and how many times this interval is repeated. To set the custom mode: • NIBP Press the key. -
Page 244: Starting And Stopping A Single Manual Measurement
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Starting and stopping a single manual measurement To start the measurement, do one of the following: • NIBP Start/Cancel Press the key, or NIBP press the key and select Start Manual. To stop any NIBP measurement, do one of the following: •... -
Page 245: Principles Of Superstat Noninvasive Blood Pressure Determination
Non-invasive blood pressure Principles of SuperSTAT Noninvasive Blood Pressure Determination The oscillometric method of determining NIBP is accomplished by a sensitive transducer which measures cuff pressure and pressure oscillations within the cuff. For the first determination taken on a patient, the algorithm stores the pattern of the patient's oscillation size as a function of the pressure steps. -
Page 246: Systolic Search
B40/B20 Patient Monitor The operating cycle is composed of four parts: inflation time, deflation time, evaluation time, and wait time. Wait time, which varies from mode to mode, is affected by the cycle time (auto mode) or operator intervention (manual mode). The figure shows the basic operating cycle for an NIBP determination. -
Page 247: Automatic Nibp Double Check
Non-invasive blood pressure Automatic NIBP double check If the NIBP value exceeds the alarm limits, a low level alarm will be given and the auto measurement takes place, if the alarm situation persists, the alarm will be raise to yellow level. NIBP measurement limitations •... - Page 248 B40/B20 Patient Monitor 14-14...
-
Page 249: Invasive Blood Pressure
15 Invasive blood pressure... -
Page 251: Safety Precautions
Invasive blood pressure 15 Invasive blood pressure Safety precautions Warnings • All invasive procedures involve risks to the patient. Use aseptic technique. Follow catheter manufacturer's instructions. • Make sure that no part of the patient connections touches any electrically conductive material including earth. -
Page 252: Direct Function Keys
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Invasive pressures connector Figure 15-1 Invasive pressure measurement connector Direct function keys There is a key for zeroing IBP on the Command Board: Zeros all pressure transducers. Zero All NOTE: Selecting Zero ALL does not zero ICP. Zero it separately. -
Page 253: Display Of Invasive Blood Pressure
Invasive blood pressure Display of invasive blood pressure Figure 15-2 InvBP display Invasive blood pressure waveforms with zero and reference lines Selected pressure label Selected pressure scale Field for messages and alarm limit settings Systolic, diastolic and mean pressure values of invasive blood pressures You can have a combined display of all those waveforms that are selected on the screen. -
Page 254: Patient Connections
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Patient connections Connect the pressure transducer to the transducer adapter cable. Connect the cable to the red connector in the module, or to the dual invasive blood pressure adapter cable. NOTE: Invasive pressures need to be zeroed after reconnecting the pressure transducer or cable, and whenever the patient’s position is changed. -
Page 255: Zeroing Invasive Blood Pressure Transducers
Invasive blood pressure Zeroing invasive blood pressure transducers Prior to monitoring, zero transducers at the patient’s phlebostatic axis. Zeroing the pressure transducers is very important for accurate pressure measurements. To avoid inaccurate measurements, you must zero the pressure transducers: • Before measuring invasive blood pressures. -
Page 256: Invasive Pressures Menu
B40/B20 Patient Monitor • Invasive pressures need to be zeroed after reconnecting the pressure transducer or cable, and whenever the patient’s position is changed. If all channels have not been zeroed, the message ‘InvBP not zeroed’ appears. However, the alarms advance to yellow and red levels regardless of zeroing. -
Page 257: Determining Pressure Values Visually
Invasive blood pressure the heart rate calculation in a specified order: ECG (the lead with highest R-wave), pressure (Art), and plethysmographic pulse waveform. IBPX Alarm Alarms can be adjusted in this menu or in the Alarms Setup menu which opens by pressing the Alarms Setup key. -
Page 258: Cerebral Perfusion Pressure
B40/B20 Patient Monitor The labels are the following: IBP1, IBP2 Standard labels Arterial pressure Central venous pressure Pulmonary arterial pressure Right atrial pressure Right ventricular pressure Left atrial pressure First intracranial pressure Arterial blood pressure Umbilical artery catheters umbilical venous catheters Both Art and ABP labels are available for situations when two arterial lines are desired but you want to use different settings or alarm labels. -
Page 259: Adjusting Alarm Sources And Limits
Invasive blood pressure Adjusting alarm sources and limits You can adjust or turn off pressure alarm limits in the Alarms Setup/Adjust Limits menu. Enter Alarms Setup the menu by pressing the key. For each pressure channel you can choose as a source Sys (Systolic), Dia (Diastolic), Mean or Off. -
Page 260: Smart Invbp And Flushing
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Smart InvBP and flushing Flushing is performed to keep the lines open. It prevents blood from clotting and occluding the lines and measurements. Infusion that is used for flushing goes through the dome into the patient’s artery. -
Page 261: 16 Temperature
16 Temperature... -
Page 263: Safety Precautions
The signal from the probe is processed by the monitor and is displayed as measured numerics. As a measuring probe use only GE Healthcare temperature probes or defibrillator-proof YSI 400 series probes. You can measure, for example, esophageal, nasopharyngeal, rectal, and skin temperature. -
Page 264: Displaying Temperature
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Displaying temperature Figure 16-2 T1+T2 digit display Labels Temperature measurement value Calculated T2-T1 difference The other options are individual T1 and T2 readings in a digit field. Patient connections Figure 16-3 Temperature measurement setup Compatible temperature measurement capability... -
Page 265: Temp Setup Menu
Temperature • A temperature channel is deactivated when a temperature interface cable is detached from the monitor. Temp Setup menu Others T1, 2 Label Allows you to label each temperature measurement site. Unit Allows you to select the units to be either degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit. Allows you to adjust temperature alarm limits for two measurement sites, measured by T1 or T2. -
Page 266: Combining Different Temperatures
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Combining different temperatures The monitor displays the difference between different temperatures if they are displayed in the same digit field. differences (T2-T1,) are displayed in the temperature digit field if you choose them in the same digit field. For example, to display T1+T2:... -
Page 267: 17 Airway Gas
17 Airway gas... -
Page 269: Safety Precautions
Airway gas 17 Airway gas Safety precautions Warnings • Always check the airway adapter for a tight connection and proper operation before attaching it to the patient. • Remove the airway gas sampling line from the patient’s airway while nebulized medications are being delivered. -
Page 270: Cautions
B40/B20 Patient Monitor • When using the CARESCAPE respiratory modules and Airway Gas Option module with volume controlled ventilation at low tidal volumes, the specified gas withdrawal rate may significantly reduce the amount of gas delivered to the patient. •... -
Page 271: Overview
Airway gas Overview The E-miniC, CARESCAPE Respiratory Module (E-sCO and E-sCAiO modules) and Airway Gas Option (N-CAiO module) provide airway measurements. Letters in these module name stand for: C=CO and N O, O=patient O , A=anesthetic agents and i=agent identification The following table shows the airway gases for each acquisition module. -
Page 272: Display Of Gases
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Display of gases Figure 17-2 CO waveform display 30 minute trend for CO (selected in the Monitor Setup menu) Gas waveforms Message field for gases Gas label Digit field for ET and FI gas values Respiration rate... -
Page 273: Airway Gases Measurement Setup
Airway gas Figure 17-4 Anesthetic Agents waveform display 30 minute trend for Anesthetic Agent Primary agent gas waveform Message field for gases Primary agent gas label Digit field for ET and FI gas values Scale NOTE: When the measured anesthetic agent value is outside the specified measurement range, the numeric value is gray. -
Page 274: Carescape Respiratory Modules And Airway Gas Option To Patient Connection
B40/B20 Patient Monitor CARESCAPE Respiratory Modules and Airway Gas Option to patient connection E-sCO, E-sCAiO or N-CAiO module Gas sample, gas sampling line connector on the water trap Gas sampling line Gas sampling line connector on the airway adapter; place the connector upwards... -
Page 275: Patient Connections
Airway gas Patient connections Make sure that the water trap container is empty and properly attached. Connect the gas sampling line to the sampling line connector on the water trap. If CARESCAPE Respiratory Module or Airway Gas Option is used with N O or volatile agents, connect the sample gas outlet to gas scavenging. - Page 276 B40/B20 Patient Monitor Mask ventilation Mask Bacterial filter Airway adapter Sample line Infant ventilation Endotracheal tube Pediatric airway adapter Fresh gas inlet Sample line 17-8...
-
Page 277: Airway Gas Setup Menu
Airway gas Airway Gas setup menu setup menu Airway Scale Allows you to select the following scales: scale options for % scale options for kPa scale options for mmHg 0-6% 0 - 6 kPa 0 - 50 mmHg 0-10% 0 - 10 kPa 0 - 80 mmHg 0-15% 0 - 15 kPa... -
Page 278: O2 Setup Menu
B40/B20 Patient Monitor setup menu NOTE: B40 only. Airway Scale Allows you to select the O waveform scales. The scale selesctions for O waveform are: DIFF6, DIFF10, DIFF15, DIFF30,10-60% and 100%. Measuremnet Set O measurement and alarm on or off. -
Page 279: To Select The Mac Type
To select alarm sources, go to the CO2 Setup - CO2 Alarm, Resp Rate Alarm O2 Setup (B40 only) - O2 Alarm Agent/N2O Setup (B40 only) - Agent Alarm The selections are FI or ET as the high and low alarm limit. -
Page 280: Scavenging
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Scavenging When N O and volatile anesthetics are used, prevent operating room pollution by connecting the sample gas outlet (gas exhaust) of the module to the scavenging system. Follow local hospital’s regulations Scavenging through the ventilator reservoir Connect an exhaust line to the sample gas outlet (gas exhaust) on the module's front panel. -
Page 281: Calibrating
P/N: 755587, Calibration Gas, CO2, O2, Balance, 4 cans/pkg (with E-sCO module) US only NOTE: Use only the specified GE Healthcare calibration gas for the gas calibration to ensure measurement accuracy. Do not use any other calibration gases. Check the calibration gas container's labelling to ensure that the calibration gas has not expired. -
Page 282: Procedure
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Figure 17-6 Connecting sampling line to the gas valve and feeding gas Procedure NOTE: Gas calibration is not available during the first 5 minutes after the module is connected. For maximum accuracy, let the monitor to warm up for 30 minutes before starting calibration. - Page 283 Airway gas Normal Screen If the message ‘Zero error’ is displayed, press the key and repeat the calibration procedure. If the problem persists, contact authorized service personnel. The monitor performs autozeroing after start up. The autozeroing intervals are: 4 min, 15 min, 30 min and 60 minutes after start-up, thereafter every 60 minutes.
-
Page 284: Basics Of Airway Gases Measurement
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Basics of airway gases measurement Airway gases measurement description, CARESCAPE respiratory modules and Airway Gas Option With CARESCAPE Respiratory Modules and Airway Gas Option, you can measure and monitor gases being delivered to the patient and exhaled by the patient through the breathing circuit. -
Page 285: Automatic Agent Identification With E-Scaio, N-Caio Modules
Airway gas Automatic agent identification with E-sCAiO, N-CAiO modules The modules with agent identification option will automatically identify and select Isoflurane, Desflurane, Sevoflurane, Enflurane and Halothane. The E-sCAiO module is able to identify two agents simultaneously and displaying them as primary and secondary agents. The N-CAiO module is able to identify and display one agent. - Page 286 B40/B20 Patient Monitor − ISO21647:2004 + C1:2005, Medical electrical equipment - Particular requirements for the basic safety and essential performance of respiratory gas monitors. • References for MACage calculations: − Eger, E.I. II.: Age, minimum alveolar anesthetic concentration, and minimum alveolar anesthetic concentration-awake.
-
Page 287: Et Balance Gas
Airway gas ET balance gas You can obtain a calculated value for balance gas, EtBal. End-tidal balance gas is the percentage of gas concentration not measured by the gas sensors. It is displayed in digit field with the MAC value. An increased balance gas value may indicate the amount of nitrogen flushed out from the patient into the circuit. - Page 288 B40/B20 Patient Monitor EtCO2 value % EtCO2 value mmHg Indicates 4.5 to 5.5% 34 to 41 mmHg normocapnia < 4% < 30 mmHg hypocapnia > 6% > 45 mmHg hypercapnia Dips in capnogram The dips seen in the capnogram during expiration are related to the sidestream gas sampling, the continuous gas flow to the Y-piece, and patient’s cardiac contractions, which cause intra-...
-
Page 289: Oxygen Measurement Interpretation
Airway gas Oxygen measurement interpretation The CARESCAPE respiratory modules and Airway Gas Option oxygen measurement provides: • Inspired oxygen level, the actual inspired oxygen concentration • End-tidal oxygen level, the expired oxygen concentration • Inspiratory-expiratory oxygen difference reflects patient’s consumed oxygen volume- percentage from the administered gas mix •... -
Page 290: How To Prevent Effects Of Humidity
B40/B20 Patient Monitor How to prevent effects of humidity In anesthesia, the lower the fresh gas flow, the more rebreathed gas recirculates through the absorber and the more humidity and heat is produced through the chemical CO absorption process. •... -
Page 291: Airway Gases Calculations
Airway gas Airway gases calculations • MAC = where AA =primary agent, AA =secondary agent, x(AA) is Hal=0.75%, Enf=1.7%, Iso=1.15%, Sev=2.05%, Des=6.0% and N O=100%. • -0.00303age MACage (volatile agent) = (0.05T-0.85) A (1.32 x 10 where T=temperature, A=MAC atmN2O •... -
Page 292: Checklist
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Checklist Check that: • Water trap is locked into the module. • Water trap container is empty. • A new sampling line is used after each patient. • Sampling line is connected to the water trap. •... -
Page 293: 18 Entropy
18 Entropy... -
Page 295: Safety Precautions
Entropy 18 Entropy Safety precautions Warnings • Make sure that the electrodes, sensor and connectors do not touch any electrically conductive material, including earth . • DEFIBRILLATOR PRECAUTIONS - Patient signal inputs labeled with the CF and BF symbols with paddles are protected against damage resulting from defibrillation voltages. To ensure proper defibrillator protection, use only the recommended cables and leadwires. -
Page 296: Overview
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Overview Entropy is a non-invasive parameter suitable for adults and pediatric patient population older than two years of age. Entropy may be used as an aid in monitoring the effects of certain anesthetic agents on the patient’s central nervous system (CNS) during general anesthesia. Displaying and using clinical information from Response Entropy (RE) and State Entropy (SE) may allow the clinician to tailor the anesthetic according to the individual needs of a patient. -
Page 297: Entropy Measurement Description
Entropy Entropy measurement description EEG signals reflect the underlying state of brain activity. As a person falls asleep or is anesthetized, the brain function (activity) starts to decrease and becomes more orderly and regular. EEG changes from irregular to more regular patterns when anesthesia deepens. Similarly, frontal EMG quiets down as the deeper parts of the brain are increasingly saturated with anesthetics. -
Page 298: Burst Suppression Ratio (Bsr)
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Burst suppression ratio (BSR) BSR is defined as the percentage of time of suppressed (isoelectric, flatline) EEG periods during the last minute of observation. Emergence of burst suppression pattern may indicate very deep anesthesia, hypothermia or ischemia. -
Page 299: Displaying Eeg Waveform
Entropy Displaying EEG waveform Figure 18-2 Display of EEG waveform EEG waveform is displayed EEG waveform label EEG waveform scale Entropy label Response Entropy (RE) label Response Entropy (RE) value State Entropy (SE) label State Entropy (SE) value Burst suppression ratio (BSR) label (10) Burst suppression ratio (BSR) value (11) Burst suppression ratio (BSR) unit Entropy module keys... -
Page 300: Preparing The Patient And Placing The Electrodes
B40/B20 Patient Monitor active assessment of the effects of neuromuscular blockade agents on the neuromuscular junction. • Neuromuscular blocking agents administered in surgically appropriate doses are not known to affect the EEG, but are known to have an effect on the EMG. RE values may drop in response to NMBA administration, due to paralysis of facial muscles. -
Page 301: Entropy Setup Menu
Entropy Entropy Setup menu To enter the Entropy setup menu: Others Entr.EEG Scale Adjusts the setting of Entropy EEG waveform scale. The scale selesctions for Entropy EEG waveform are: 25 µV, 50 µV, 100 µV, 250 µV, 400 µV and 500 µV. Trend Length Adjusts the length of trend shown in the horizontal dight field. -
Page 302: Starting Sensor Check Manually
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Starting sensor check manually When the patient’s EEG pattern, RE and SE value change considerably, the monitor should start Entropy sensor checking manually. Other Press the key. Select Entropy Select Check Sensor . Others Setting RE and SE alarm limits... - Page 303 Entropy Alarms Setup You can also adjust the limits through - Adjust Limits . For detailed instructions, see section "Alarms." Others NOTE: • The default values for RE and SE alarm are off. Please set the alarm on by selecting RE Alarms .
-
Page 304: Entropy Measurement Limitations
B40/B20 Patient Monitor Entropy measurement limitations • Entropy measurement is not indicated for pediatric patients younger than two years old. • Entropy is not validated with patients undergoing sedation. • Unusual or excessive electrical interference is a potential cause for artifact. During extended periods of electrocautery there may not be any good EEG epochs, and Entropy values will not be displayed. -
Page 305: Abbreviations
Abbreviations Abbreviations /min beats per minute, breaths per minute °C Celsius degree °F Fahrenheit degree µg microgram arm (describing location) alveolar arterial a/AO arterio-alveolar PO ratio AaDO alveolo-arterial oxygen difference anesthetic agent AAMI Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation arterial blood gases arterial pressure Anesthesia Delivery Unit... - Page 306 Abbreviations bispectral index Blad bladder temperature Blood blood temperature (C.O. measurement) Body body temperature blood pressure Brady bradycardia body surface area burst suppression ratio B-to-B beat-to-beat BTPS body temperature and pressure, saturated gas calculated/derived value chest C(a-v)O arteriovenous oxygen content difference C.C.O.
- Page 307 Abbreviations compressed spectral array computer tomography (mixed) venous oxygen content central venous pressure decibel double burst stimulation (NMT) delete Delta, De delta frequency band depr. depression desflurane diastolic pressure Diagn diagnostic (ECG filter) DIFF difference S/5 Device Interfacing Solution oxygen delivery oxygen delivery index digital signal converter dynamic...
- Page 308 Abbreviations evoked potential electrostatic discharge esophageal temperature end-systolic volume ESVI end-systolic volume index ET, Et end-tidal concentration EtAA end-tidal anesthetic agent EtBal end-tidal balance gas EtCO end-tidal carbon dioxide end-tidal nitrous oxide end-tidal oxygen ET-tube, ETT endotracheal tube EVLW extravascular lung water EVLWI extravascular lung water index expiratory...
- Page 309 Abbreviations Hbtot total hemoglobin HCO3- bicarbonate Hemo hemodynamic Hemo Calcs hemodynamic calculations reduced hemoglobin heat and moisture exchanger HMEF heat and moisture exchanger with filter hectopascal heart rate HRdiff heart rate difference height hardware hertz International Electrotechnical Comission inspiratory-expiratory ratio IABP intra-aortic balloon pump inspiratory capacity...
- Page 310 Abbreviations laboratory local area network left atrial pressure lateral pound liquid crystal display left cardiac work light emitting diode LVEDP left ventricular end diastolic pressure LVEDV left ventricular end diastolic volume LVSW left ventricular stroke work LVSWI left ventricular stroke work index minimum alveolar concentration maximum mbar...
- Page 311 Abbreviations Naso nasopharyngeal temperature neonate network NIBP non-invasive blood pressure Ni-Cd nickel-cadmium Ni-MH nickel-metal hydride neuromuscular transmission nitric oxide NTPD normal temperature and pressure, dry gas Num. numerical oxygen oxygen extraction ratio oxygenated hemoglobin operation room oxygenation Oxy Calcs oxygenation calculations partial pressure pressure P(BTPS)
- Page 312 Abbreviations PEEPi intrinsic positive end expiratory pressure PEEPtot total positive end expiratory pressure (anesthesia) PgCO gastrointestinal carbon dioxide concentration arterial pH intramucosal pH (mixed) venous pH patient interface cable Pleth plethysmographic pulse waveform pacemaker PM non-capt. pacemaker non-capturing PM non-funct. pacemaker non-functioning Pmax maximum pressure...
- Page 313 Abbreviations Resp Rate respiration rate (total) (measured) radio frequency average (root mean square) power Room room temperature respiratory quotient respiration rate (total) (measured) rhythm residual volume RVEDV right ventricular end-diastolic volume RVESV right ventricular end-systolic volume right ventricular pressure RVSW right ventricular stroke work RVSWI right ventricular stroke work index...
- Page 314 Abbreviations (mixed) venous oxygen saturation systemic vascular resistance SVRI systemic vascular resistance index software stroke volume variation systolic pressure time (min) temperature tesla T(BTPS) temperature in BTPS conditions first stimulus as % of the reference value (NMT) T1, T2 temperature channel identification on module Tab.
- Page 315 Abbreviations CalcI calculated oxygen consumption index* oxygen consumption index volume V Run ventricular run V Tachy ventricular tachycardia WLAN wireless local area network weight extreme year years * with Fick equation A-11...
- Page 316 Abbreviations A-12...
- Page 317 Installation and checkout form, B40/B20 APPENDIX B: Installation and checkout form, B40/B20 Customer Service Service engineer Date Monitor license MAC Address: License key: Modules Gas module: Entropy module: OK = Test OK N.A. = Test not applicable Fail = Test failed...
- Page 318 B40/B20 Patient Monitor...
- Page 320 1 800 558 5120 (US only) Fax: + 86 21 3877 7451 Fax: + 49 761 45 43 - 233 Fax:+ 1 414 355 3790 GE Medical Systems Information Technologies, a General Electric Company, going to market as GE Healthcare www.gehealthcare.com 0459...
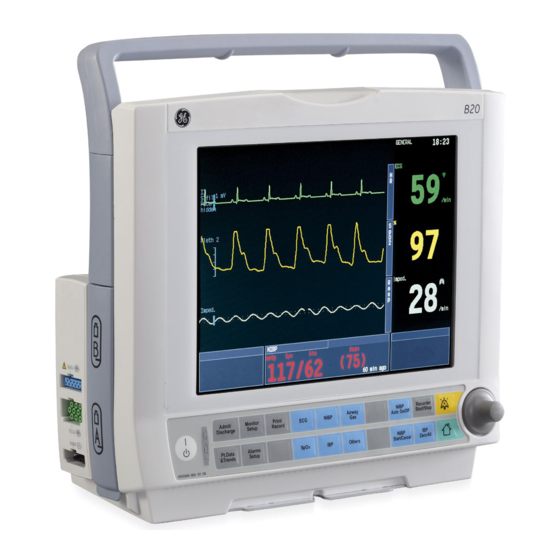










Need help?
Do you have a question about the B40 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers
Resp measurement is off how do I turn it on
To turn on the respiratory measurement feature on the GE Healthcare B40:
1. Press the "Others" key.
2. Select "Resp Setup."
3. Enable the measurement by choosing an option other than "Measurement OFF."
This activates the respiratory measurement feature.
This answer is automatically generated