Table of Contents
Advertisement
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for ECS 865PE-A
- Page 1 865PE-AL 865PE-A Rev. A+ System Board User’s Manual 77300333...
- Page 2 Copyright This publication contains information that is protected by copy- right. No part of it may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any transformation/adaptation without the prior written permission from the copyright holders. This publication is provided for informational purposes only.
-
Page 3: Fcc And Doc Statement On Class B
Battery: • Danger of explosion if battery incorrectly replaced. • Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommend by the manufacturer. • Dispose of used batteries according to the battery manufac- turer’s instructions. Joystick or MIDI port: • Do not use any joystick or MIDI device that requires more than 10A current at 5V DC. -
Page 4: System Board
The autorun screen (Main Board Utility CD) will appear. Click the “TOOLS” icon then click “Manual” on the main menu. System Board This user’s manual is for the 865PE-AL and 865PE-A system boards. The only difference between these boards is the 865PE-AL system board supports onboard LAN. -
Page 5: Table Of Contents
Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Introduction 1.1 Features and Specifications................. 1.2 Hyper-Threading Technology Functionality Requirements... 1.3 Package Checklist......................Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation System Board Layout .................... System Memory......................CPU.............................. Jumper Settings....................... Rear Panel I/O Ports....................I/O Connectors......................Chapter 3 - BIOS Setup 3.1 Award BIOS Setup Utility.................. - Page 6 Introduction Chapter 4 - Supported Softwares 4.1 Desktop Management Interface..............4.2 Drivers, Utilities and Software Applications........ 4.3 3D Audio Configuration..................4.4 Installation Notes......................Appendix A - Enabling the Hyper-Threading T echnology A.1 Enabling the Hyper-Threading Technology........Appendix B - System Error Messages B.1 POST Beep........................
-
Page 7: Features And Specifications
Introduction Chapter 1 - Introduction 1.1 Features and Specifications 1.1.1 Features Chipset • Intel 865PE chipset ® ® Intel 865PE Memory Controller Hub (MCH) ® Intel 82801EB I/O Controller Hub (ICH5) Processor The system board is equipped with Socket 478 for installing one of the following supported processors. - Page 8 Introduction Density 128 Mbit 256 Mbit 512 Mbit Density Width SS/DS SS/DS SS/DS SS/DS SS/DS Single/Double SS/DS 128/256MB 64MB/NA 256/512MB 128MB/NA 512/1024MB 256MB/NA 184-pin DDR Expansion Slots • 1 AGP slot • 5 PCI slots AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) • Supports AGP 3.0 (AGP 4x and 8x) and AGP 2.0 (AGP 1x and 4x) spec.
- Page 9 Introduction S/PDIF S/PDIF is a standard audio file transfer format that transfers digital audio signals to a device without having to be converted first to an analog format. This prevents the quality of the audio signal from degrading whenever it is converted to analog. S/PDIF is usu- ally found on digital audio equipment such as a DAT machine or audio processing device.
- Page 10 Introduction PCI Bus Master IDE Controller • Two PCI IDE interfaces support up to four IDE devices • Supports ATA/33, ATA/66 and ATA/100 hard drives • PIO Mode 4 Enhanced IDE (data transfer rate up to 14MB/ sec.) • Bus mastering reduces CPU utilization during disk transfer •...
- Page 11 Introduction BIOS • Award BIOS, Windows 98SE/2000/ME/XP Plug and Play ® compatible • Genie BIOS provides: CPU/DRAM overclocking AGP/PCI/SATA overclocking CPU/DIMM/AGP overvoltage • Supports SCSI sequential boot-up • Flash EPROM for easy BIOS upgrades • Supports DMI 2.0 function • 4Mbit flash memory Desktop Management Interface (DMI) The system board comes with a DMI 2.0 built into the BIOS.
-
Page 12: System Health Monitor Functions
Introduction I/O Connectors • 2 connectors for 4 additional external USB 2.0/1.1 ports • 1 connector for 1 external IEEE 1394 port • 1 front audio connector for external line-out and mic-in jacks • 1 connector for an external game/MIDI port •... - Page 13 Introduction 1.1.3 Intelligence Automatic Chassis/2nd Fan Off The chassis fan and 2nd fan will automatically turn off once the system enters the Suspend mode. Dual Function Power Button Depending on the setting in the “Soft-Off By PWR-BTTN” field of the Power Management Setup, this switch will allow the system to enter the Soft-Off or Suspend mode.
- Page 14 Introduction Wake-On-PS/2 Keyboard/Wake-On-Mouse This function allows you to use the PS/2 keyboard or PS/2 mouse to power-on the system. Important: The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support ≥ 720mA. Wake-On-USB Keyboard This function allows you to use a USB keyboard to wake up a system from the S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) state.
-
Page 15: Hyper-Threading Technology Functionality Requirements
Introduction system is capable of storing all programs and data files during the entire operating session into RAM (Random Access Memory) when it powers-off. The operating session will resume exactly where you left off the next time you power-on the system. Important: The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support ≥... -
Page 16: Package Checklist
Introduction 1.3 Package Checklist The system board package contains the following items: The system board A user’s manual One IDE cable for ATA/33, ATA/66 or ATA/100 IDE drives One 34-pin floppy disk drive cable One Serial ATA data cable One I/O shield One “Mainboard Utility”... -
Page 17: Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
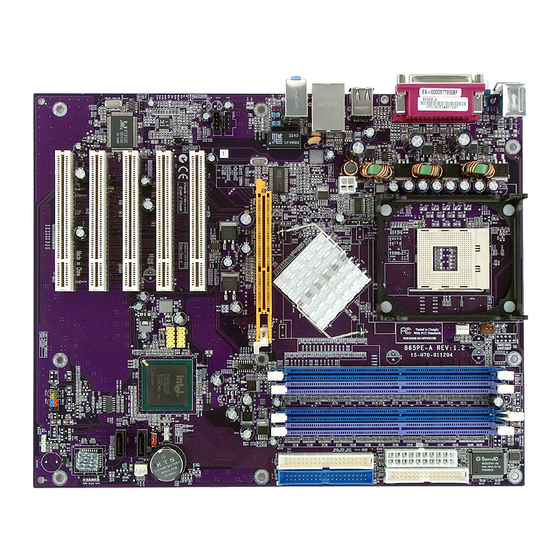
Hardware Installation Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation 2.1 System Board Layout 865PE-AL (Supports onboard LAN) - Page 18 Hardware Installation 865PE-A Note: The illustrations on the following pages are based on the system board that supports onboard LAN.
-
Page 19: System Memory
Hardware Installation Warning: Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage your system board, proces- sor, disk drives, add-in boards, and other components. Perform the upgrade instruction procedures described at an ESD workstation only. If such a station is not available, you can provide some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal part of the system chassis. - Page 20 Hardware Installation The system board supports the following memory interface. Single Channel (SC) Data will be accessed in chunks of 64 bits (8B) from the memory channels. Virtual Single Channel (VSC) If both channels are populated with different memory configura- tions, the MCH defaults to Virtual Single Channel.
- Page 21 Hardware Installation The table below lists the various optimal operating modes that should be configured for the memory channel operation. DDR 3 DDR 4 Config DDR 1 DDR 2 No memory Single channel A Single channel A Single channel A Single channel B Single channel B Single channel B...
-
Page 22: Installing The Dim Module
Hardware Installation 2.2.1 Installing the DIM Module A DIM module simply snaps into a DIMM socket on the system board. Pin 1 of the DIM module must correspond with Pin 1 of the socket. Notch Pin 1 1. Pull the “tabs” which are at the ends of the socket to the side. -
Page 23: Cpu
Hardware Installation 2.3 CPU 2.3.1 Overview The system board is equipped with a surface mount 478-pin CPU socket. This socket is exclusively designed for installing an Intel processor. 2.3.2 Installing the CPU 1. Locate Socket 478 on the system board. 2. - Page 24 Hardware Installation 3. Position the CPU above the socket then align the gold mark on the corner of the CPU (designated as pin 1) with pin 1 of the socket. Important: Handle the CPU by its edges and avoid touching the pins. Gold mark Pin 1 4.
-
Page 25: Installing The Fan And Heat Sink
Hardware Installation 5. Once the CPU is in place, push down the lever to lock the socket. The lever should click on the side tab to indicate that the CPU is completely secured in the socket. 2.3.3 Installing the Fan and Heat Sink The CPU must be kept cool by using a CPU fan with heatsink. - Page 26 Hardware Installation 1. The system board comes with the retention module base al- ready installed. Retention Retention hole hole Retention Retention hole hole Retention module base 2. Position the fan / heat sink and retention mechanism assembly on the CPU, then align and snap the retention legs’ hooks to the retention holes at the 4 corners of the retention module base.
- Page 27 Hardware Installation 3. The retention levers at this time remains unlocked as shown in the illustration below. Retention lever Retention lever 4. Move the retention levers to their opposite directions then push them down. This will secure the fan / heat sink and re- tention mechanism assembly to the retention module base.
-
Page 28: Jumper Settings
Hardware Installation 2.4 Jumper Settings 2.4.1 Jumper Settings for Clearing CMOS Data 1-2 On: Normal 2-3 On: (default) Clear CMOS Data If you encounter the following, a) CMOS data becomes corrupted. b) You forgot the supervisor or user password. c) You are unable to boot-up the computer system because the proc- essor’s ratio/clock was incorrectly set in the BIOS. - Page 29 Hardware Installation 4. After powering-on the system, press <Del> to enter the main menu of the BIOS. 5. Select the Genie Bios Setting submenu and press <Enter>. 6. Set the “CPU Clock” or “CPU Clock Ratio” field to its default setting or an appropriate bus clock or frequency ratio.
- Page 30 Hardware Installation 2.4.2 Jumper Settings for Selecting the PS/2 Keyboard/ Mouse Power 2-3 On: 5VSB 1-2 On: VCC (default) This jumper is used to select the power of the PS/2 keyboard and/or PS/2 mouse ports. Selecting 5VSB will allow you to use the Wake-On-PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse function.
-
Page 31: Jumper Settings For Selecting The Usb Power
Hardware Installation 2.4.3 Jumper Settings for Selecting the USB Power USB 1-4 (JP1) 2-3 On: 5VSB 1-2 On: VCC (default) USB 5-8 (JP4) 1-2 On: VCC 2-3 On: 5VSB (default) These jumpers are used to select the power of the USB ports. Selecting 5VSB will allow you to use the Wake-On-USB Key- board function. -
Page 32: Rear Panel I/O Ports
Hardware Installation 2.5 Rear Panel I/O Ports RJ45 Mic-in PS/2 IEEE Parallel Line-in Mouse 1394 Center/Bass Rear out PS/2 S/PDIF-in USB 1-2 USB 3-4 S/PDIF-out Line-out The rear panel I/O ports consist of the following: • PS/2 mouse port • PS/2 keyboard port •... - Page 33 Hardware Installation 2.5.1 PS/2 Mouse and PS/2 Keyboard Ports PS/2 Mouse PS/2 Keyboard The system board is equipped with an onboard PS/2 mouse (Green) and PS/2 keyboard (Purple) ports - both at location CN1 of the system board. The PS/2 mouse port uses IRQ12. If a mouse is not connected to this port, the system will reserve IRQ12 for other expansion cards.
- Page 34 Hardware Installation • BIOS Setting: “Keyboard/Mouse Power On” in the Power Management Setup submenu of the BIOS must be set accordingly. Refer to chapter 3 for more information. Important: The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support ≥ 720mA.
- Page 35 Hardware Installation 2.5.2 Serial Port The system board is equipped with an onboard serial port (Teal/ Turquoise) at location CN4 of the system board. It is a RS-232C asynchronous communication por t with 16C550A-compatible UART that can be used with a modem, serial printer, remote display terminal or other serial devices.
- Page 36 Hardware Installation 2.5.3 Parallel Port Parallel The system board has a standard parallel port (Burgundy) at lo- cation CN9 for interfacing your PC to a parallel printer. It sup- ports SPP, ECP and EPP. Setting Function Allows normal speed operation (Standard Parallel Port) but in one direction only.
- Page 37 Hardware Installation 2.5.4 S/PDIF-in/out Jacks S/PDIF-in S/PDIF-out SPDIF out SPDIF in The system board is equipped with an onboard S/PDIF-in RCA jack (red) and a S/PDIF-out RCA jack (yellow) at locations CN5 and CN6 of the system board. The S/PDIF connector at location J4 is for optical S/PDIF cable connection.
- Page 38 Hardware Installation 2.5.5 IEEE 1394 1394_1 1394_2 The system board is equipped with an onboard IEEE 1394 port at location CN7 of the system board. It is also equipped with a IEEE 1394 connector at location J9 (1394_2) for connecting an additional 1394 port. The 1394 port may be mounted on a card-edge bracket.
- Page 39 Hardware Installation 2.5.6 RJ45 Fast-Ethernet Port RJ45 LAN The system board is equipped with an onboard RJ45 fast- ethernet LAN port at location CN8 of the system board. It al- lows the system board to connect to a local area network by means of a network hub.
-
Page 40: Universal Serial Bus Ports
Hardware Installation 2.5.7 Universal Serial Bus Ports USB 2 USB 1 USB 4 USB 3 USB 5-6 USB 7-8 Four onboard USB 2.0/1.1 ports (Black) are at locations CN7 (USB 1-2) and CN8 (USB 3-4) of the system board. J10 (USB 5-6) and J11 (USB 7-8) connectors allow you to con- nect 4 additional USB 2.0/1.1 por ts. - Page 41 Hardware Installation Wake-On-USB Keyboard The Wake-On-USB Keyboard function allows you to use a USB keyboard to wake up a system from the S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) state. To use this function: • Jumper Setting: JP1 and JP4 must be set to “2-3 On: 5VSB”. Refer to “Jumper Settings for Selecting the USB Power”...
- Page 42 Hardware Installation 2.5.8 Audio Mic-in Line-in Line-out Center/Bass Rear out Front audio Mic-in, Line-in and Line-out The mic-in, line-in and line-out jacks are at location CN2 of the system board. A jack is a one-hole connecting interface for insert- ing a plug. •...
- Page 43 Hardware Installation • Line-out Jack (Lime) This jack is used to connect external speakers for audio output from the system board. Using this jack disables the front au- dio’s line-out function. Center/Bass and Rear Out Jacks Center/Bass and Rear Out Jacks (CN3) support 4 audio output signals: center channel, subwoofer, rear right channel and rear left channel.
- Page 44 Hardware Installation Driver Installation Install the “Audio Drivers” contained in the provided CD. The 3D Audio Configuration software, which is an audio panel for setting basic audio configurations, will at the same time be installed into your system. The application program will allow you to configure 2-channel, 4-channel and 6-channel audio modes as well as configure the audio effects.
-
Page 45: I/O Connectors
Hardware Installation 2.6 I/O Connectors 2.6.1 Game Port The system board is equipped with a 15-pin connector at loca- tion J7 for connecting an external game/MIDI port. The game port may be mounted on a card-edge bracket. Install the card- edge bracket to the system chassis then connect the game/MIDI port cable to connector J7. -
Page 46: Internal Audio Connectors
Hardware Installation 2.6.2 Internal Audio Connectors Ground Ground Left audio Right audio channel channel CD-in Ground Ground Left audio Right audio channel channel AUX-in The CD-in (J5) and AUX-in (J6) connectors are used to receive audio from a CD-ROM drive, TV tuner or MPEG card. -
Page 47: Floppy Disk Drive Connector
Hardware Installation 2.6.3 Floppy Disk Drive Connector The system board is equipped with a shrouded floppy disk drive connector that supports two standard floppy disk drives. To pre- vent improper floppy cable installation, the shrouded floppy disk header has a keying mechanism. The 34-pin connector on the floppy cable can be placed into the header only if pin 1 of the connector is aligned with pin 1 of the header. -
Page 48: Serial Ata Connectors
Hardware Installation 2.6.4 Serial ATA Connectors SATA 2 SATA 1 The system board is equipped with 2 SATA connectors at loca- tions J16 (SATA 2) and J17 (SATA 1) for connecting serial ATA devices. Connect one end of the SATA cable to a SATA connec- tor and the other end to your serial ATA device. -
Page 49: Ide Disk Drive Connector
Hardware Installation 2.6.5 IDE Disk Drive Connector IDE 2 IDE 1 IDE 2 IDE 1 The system board is equipped with two shrouded PCI IDE head- ers that will interface four Enhanced IDE (Integrated Drive Elec- tronics) disk drives. To prevent improper IDE cable installation, each shrouded PCI IDE header has a keying mechanism. - Page 50 Hardware Installation Note: Refer to your disk drive user’s manual for information about selecting proper drive switch settings. Adding a Second IDE Disk Drive When using two IDE drives, one must be set as the master and the other as the slave. Follow the instructions provided by the drive manufacturer for setting the jumpers and/or switches on the drives.
-
Page 51: Irda Connector
Hardware Installation 2.6.6 IrDA Connector IRRX N. C. Ground IRTX Connect your IrDA cable to connector J2 on the system board. Note: The sequence of the pin functions on some IrDA cable may be reversed from the pin function defined on the system board. Make sure to connect the cable to the IrDA connector according to their pin functions. -
Page 52: Cpu Fan Connector
Hardware Installation 2.6.7 CPU Fan Connector Sense Power Ground The CPU must be kept cool by using a fan with heatsink. Con- nect the CPU fan to the 3-pin fan connector at location J13 of the system board. The system is capable of monitoring the speed of the CPU fan. - Page 53 Hardware Installation 2.6.8 Chassis Fan and 2nd Fan Connectors Sense Power On/Off 2nd fan Sense Power On/Off Chassis fan The chassis fan connector (J22) and 2nd fan connector (J14) are used to connect cooling fans. The cooling fans will provide ad- equate airflow throughout the chassis to prevent overheating the CPU and system board components.
- Page 54 Hardware Installation 2.6.9 Wake-On-LAN Connector Ground +5VSB Your LAN card package should include a cable. Connect one end of the cable to the wakeup header on the card and the other end to location J8 on the system board. The network will detect Magic Packet and assert a wakeup signal to power-up the system.
- Page 55 Hardware Installation 2.6.10 Chassis Open Alarm Connector Chassis signal Ground The system board supports the chassis intrusion detection func- tion. To use this function, connect the chassis intrusion sensor cable from the chassis to J3. Whenever a chassis component has been removed, the sensor sends signal to J3 alerting you of a chassis intrusion event.
- Page 56 Hardware Installation 2.6.11 DIMM Standby Power LED DIMM Standby Power LED This DIMM Standby Power LED will turn red when the system’s power is on or when it is in the Suspend state (Power On Sus- pend or Suspend to RAM). It will not light when the system is in the Soft-Off state.
-
Page 57: Power Connectors
Hardware Installation 2.6.12 Power Connectors 3.3V 3.3V -12V 3.3V Ground Ground PS-ON Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground PW-OK 5VSB +12V +12V Ground Ground +12V We recommend that you use a power supply that complies with the ATX12V Power Supply Design Guide Version 1.1. An ATX12V power supply has a standard 20-pin ATX main power connector and a 4-pin +12V power connector that must be inserted onto CN11 and CN10 connectors respectively. -
Page 58: Front Panel Connectors
Hardware Installation 2.6.13 Front Panel Connectors RESET SPEAKER HD-LED PWR-LED ATX-SW HD-LED: Primary/Secondary IDE LED This LED will light when the hard drive is being accessed. RESET: Reset Switch This switch allows you to reboot without having to power off the system thus prolonging the life of the power supply or sys- tem. - Page 59 Hardware Installation PWR-LED: Power/Standby LED When the system’s power is on, this LED will light. When the system is in the S1 (POS - Power On Suspend) or S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) state, it will blink every second. Note: If a system did not boot-up and the Power/Standby LED did not light after it was powered-on, it may indicate that the CPU...
-
Page 60: Chapter 3 - Bios Setup
BIOS Setup Chapter 3 - BIOS Setup 3.1 Award BIOS Setup Utility The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is a program that takes care of the basic level of communication between the processor and peripherals. In addition, the BIOS also contains codes for vari- ous advanced features found in this system board. -
Page 61: Standard Cmos Features
BIOS Setup 3.1.1 Standard CMOS Features Use the arrow keys to highlight “Standard CMOS Features” and press <Enter>. A screen similar to the one below will appear. The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one. - Page 62 BIOS Setup 3.1.1.3 IDE Channel 0 Master, IDE Channel 0 Slave, IDE Channel 1 Master and IDE Channel 1 Slave Move the cursor to the “IDE Channel 0 Master”, “IDE Channel 0 Slave”, “IDE Channel 1 Master” or “IDE Channel 1 Slave” field, then press <Enter>.
- Page 63 BIOS Setup Capacity Displays the approximate capacity of the disk drive. Usually the size is slightly greater than the size of a formatted disk given by a disk checking program. Cylinder This field displays the number of cylinders. Head This field displays the number of read/write heads. Precomp This field displays the number of cylinders at which to change the write timing.
- Page 64 BIOS Setup 3.1.1.5 Video This field selects the type of video adapter used for the primary system monitor. Although secondary monitors are supported, you do not have to select the type. The default setting is EGA/VGA. EGA/VGA Enhanced Graphics Adapter/Video Graphics Array. For EGA, VGA, SVGA and PGA monitor adapters.
- Page 65 BIOS Setup 3.1.1.8 Extended Memory Displays the amount of extended memory detected during boot- 3.1.1.9 Total Memory Displays the total memory available in the system.
-
Page 66: Advanced Bios Features
BIOS Setup 3.1.2 Advanced BIOS Features The Advanced BIOS Features allows you to configure your sys- tem for basic operation. Some entries are defaults required by the system board, while others, if enabled, will improve the per- formance of your system or let you set some features according to your preference. - Page 67 BIOS Setup ® ® 3.1.2.3 Hyper-Threading Technology (for Intel Pentium 4 Processor with Hyper-Threading Technology only) ® This field is used to enable the functionality of the Intel ® Pentium 4 Processor with Hyper-Threading Technology and will appear only when using this processor. 3.1.2.4 Quick Power On Self Test This field speeds up Power On Self Test (POST) whenever the system is powered on.
- Page 68 BIOS Setup 3.1.2.8 Swap Floppy Drive When this field is enabled and the system is booting from the floppy drive, the system will boot from drive B instead of drive A. When this field is disabled and the system is booting from the floppy drive, the system will boot from drive A.
- Page 69 BIOS Setup 3.1.2.12 Typematic Rate Setting Disabled Continually holding down a key on your keyboard will cause the BIOS to report that the key is down. Enabled The BIOS will not only report that the key is down, but will first wait for a moment, and, if the key is still down, it will begin to report that the key has been depressed repeatedly.
- Page 70 BIOS Setup 3.1.2.17 MPS Version Control for OS This field is used to select the MPS version that the system board is using. 3.1.2.18 OS Select for DRAM > 64MB Select the “OS2” option only if the system that is running an OS/2 operating system has greater than 64MB RAM.
-
Page 71: Advanced Chipset Features
BIOS Setup 3.1.3 Advanced Chipset Features The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one. This section gives you functions to configure the system based on the specific features of the chipset. The chipset manages bus speeds and access to system memory resources. - Page 72 BIOS Setup If you selected “Fast” or “Turbo”: • Make sure to use DDR400. • It may cause instability to the system. If this happens, set this field to “User Define”. • The “Chipset Enhancement” to “Memor y Frequency For” fields are not configurable.
- Page 73 BIOS Setup 3.1.3.7 DRAM RAS# Precharge This field controls RAS# precharge (in local memory clocks). 3.1.3.8 Memory Frequency For This field is used to select the memory clock speed of the DIMM. DDR333 will run at 320MHz memory frequency when used with 800MHz FSB CPU.
- Page 74 BIOS Setup 3.1.3.12 Delay Prior To Thermal This field is used to select the time that would force the CPU to a 50% duty cycle when it exceeds its maximum operating tem- perature therefore protecting the CPU and the system board from overheating to ensure a safe computing environment..
-
Page 75: Integrated Peripherals
BIOS Setup 3.1.4 Integrated Peripherals The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one. 3.1.4.1 OnChip IDE Device Move the cursor to this field and press <Enter>. The following screen will appear. The settings on the screen are for reference only. - Page 76 BIOS Setup IDE HDD Block Mode Enabled The IDE HDD uses the block mode. The system BIOS will check the hard disk drive for the maxi- mum block size the system can transfer. The block size will depend on the type of hard disk drive. Disabled The IDE HDD uses the standard mode.
- Page 77 BIOS Setup IDE Primary Master/Slave UDMA and IDE Secondary Master/ Slave UDMA These fields allow you to set the Ultra DMA in use. When Auto is selected, the BIOS will select the best available option after checking your hard drive or CD-ROM. Auto The BIOS will automatically detect the settings for you.
- Page 78 BIOS Setup Serial ATA Port0 Mode and Serial ATA Port1 Mode These fields are used to select the master/slave mode of the serial ATA drives. Make sure they do not conflict with the settings of the IDE hard drives.
- Page 79 BIOS Setup 3.1.4.2 Onboard Device Move the cursor to this field and press <Enter>. The following screen will appear. The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one. USB Controller Enabled Enables the onboard USB.
- Page 80 BIOS Setup Onboard LAN Control This field is used to enable or disable the onboard LAN control- ler. Onboard 1394 Control This field is used to enable or disable the onboard 1394 control- ler.
- Page 81 BIOS Setup 3.1.4.3 Super IO Device Move the cursor to this field and press <Enter>. The following screen will appear. The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one. KBC Input Clock This field is used to select the input clock of your keyboard.
- Page 82 BIOS Setup IR Mode Select This field is used to select the type of IrDA standard supported by your IrDA device. For better transmission of data, your IrDA peripheral device must be within a 30 angle and within a dis- tance of 1 meter.
- Page 83 BIOS Setup EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) Allows bidirectional parallel por t operation at maximum speed. If you selected EPP, the “EPP Mode Select” field is configurable. If you selected ECP, the “ECP Mode Use DMA” field is configurable. If you selected ECP+EPP, both “EPP Mode Select” and “ECP Mode Use DMA”...
-
Page 84: Power Management Setup
BIOS Setup 3.1.5 Power Management Setup The Power Management Setup allows you to configure your sys- tem to most effectively save energy. The screen above list all the fields available in the Power Management Setup submenu, for ease of reference in this manual. In the actual CMOS setup, you have to use the scroll bar to view the fields. - Page 85 BIOS Setup 3.1.5.3 Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume When this field is set to Auto, the system will initialize the VGA BIOS when it wakes up from the S3 state. This can be configured only if the “ACPI Suspend Type” field is set to “S3(STR)”. 3.1.5.4 Power Management This field allows you to select the type (or degree) of power saving by changing the length of idle time that elapses before the...
- Page 86 BIOS Setup 3.1.5.8 HDD Power Down This is selectable only when the Power Management field is set to User Define. When the system enters the HDD Power Down mode according to the power saving time selected, the hard disk drive will be powered down while all other devices remain ac- tive.
- Page 87 BIOS Setup 3.1.5.12 Resume On LAN If you are using a LAN card that supports the remote wake up function, set this field to Enabled. The will allow the network to remotely wake up a Soft Power Down (Soft-Off) PC. However, if your system is in the Suspend mode, you can wake up the sys- tem only through an IRQ or DMA interrupt.
- Page 88 BIOS Setup 3.1.5.16 Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm This is used to set the time you would like the system to power- on. If you want the system to power-on everyday as set in the “Date (of Month) Alarm” field, the time set in this field must be later than the time of the RTC set in the Standard CMOS Fea- tures submenu.
- Page 89 BIOS Setup 3.1.5.19 KB Power On Hot Key This field is used to select a function key that you would like to use to power-on the system. 3.1.5.20 PWR Lost Resume State Keep Off When power returns after an AC power failure, the system’s power is off.
-
Page 90: Pnp/Pci Configurations
BIOS Setup 3.1.6 PnP/PCI Configurations This section describes configuring the PCI bus system. It covers some very technical items and it is strongly recommended that only experienced users should make any changes to the default settings. The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one. - Page 91 BIOS Setup 3.1.6.3 IRQ Resources Move the cursor to this field and press <Enter>. This field is used to set each system interrupt to either Reserved or PCI Device. The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one.
-
Page 92: Pc Health Status
BIOS Setup 3.1.7 PC Health Status The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one. 3.1.7.1 Current System Temperature, Current CPU Temperature, Cur- rent Chassis Fan Speed, Current CPU Fan Speed and Current Second Fan Speed These fields show the internal temperature of the system, current temperature of the CPU and the current fan speed of the chassis,... - Page 93 BIOS Setup 3.1.7.4 Shutdown Temperature You can prevent the system from overheating by selecting a tem- perature in this field. If the system detected that its temperature exceeded the one set in this field, it will automatically shutdown. This function will work only when you enable this function in the Hardware Monitor utility.
-
Page 94: Genie Bios Setting
BIOS Setup 3.1.8 Genie BIOS Setting The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one. 3.1.8.1 Super Patch Enabled Enables the Super Patch feature but will work ONLY when using 800MHz FSB and DDR400. Make sure to use this CPU/DIMM combination to boost system performance. - Page 95 BIOS Setup 3.1.8.4 CPU Clock Now Is This field will show the CPU clock based on the settings in the “CPU Clock” and “CPU Clock Ratio” fields. 3.1.8.5 AGP/PCI/SATA Clock This field is used to select the bus clock of the AGP, PCI and SATA.
- Page 96 BIOS Setup 3.1.8.10 DIMM Voltage Control This field allows you to manually select higher voltage supplied to the DRAM. If you want to use the DRAM’s default voltage, leave this field in its default setting. Important: Although this function is supported, we do not recommend that you use a higher voltage because unstable current may be sup- plied to the system board causing damage.
-
Page 97: Cmos Reloaded
BIOS Setup 3.1.9 CMOS Reloaded The CMOS Reloaded submenu allows you to save different con- figurations and when needed, allows you to conveniently restore one of these previously saved configurations. Highlight CMOS Re- loaded in the main menu then press <Enter>. The settings on the screen are for reference only. - Page 98 BIOS Setup Restoring a Configuration To restore one of the previously saved configurations, move the cursor to “Load” of “User Define Config 1” then press <Enter>. The message below will appear. Renaming a Configuration The default name given in the “User Define Config 1” field is “Config 1”...
-
Page 99: Load Optimized Defaults
BIOS Setup 3.1.10 Load Optimized Defaults The “Load Optimized Defaults” option loads optimized settings from the BIOS ROM. Use the default values as standard values for your system. Highlight this option in the main menu and press <Enter>. Type <Y> and press <Enter> to load the Setup default values. -
Page 100: Set Supervisor Password
BIOS Setup 3.1.11 Set Supervisor Password If you want to protect your system and setup from unauthorized entry, set a supervisor’s password with the “System” option se- lected in the Advanced BIOS Features. If you want to protect access to setup only, but not your system, set a supervisor’s pass- word with the “Setup”... -
Page 101: Set User Password
BIOS Setup 3.1.12 Set User Password If you want another user to have access only to your system but not to setup, set a user’s password with the “System” option se- lected in the Advanced BIOS Features. If you want a user to en- ter a password when trying to access setup, set a user’s password with the “Setup”... -
Page 102: Save & Exit Setup
BIOS Setup 3.1.13 Save & Exit Setup When all the changes have been made, highlight “Save & Exit Setup” and press <Enter>. Type “Y” and press <Enter>. The modifications you have made will be written into the CMOS memory, and the system will reboot. -
Page 103: Exit Without Saving
BIOS Setup 3.1.14 Exit Without Saving When you do not want to save the changes you have made, highlight “Exit Without Saving” and press <Enter>. Type “Y” and press <Enter>. The system will reboot and you will once again see the initial diagnostics on the screen. If you wish to make any changes to the setup, press <Ctrl>... -
Page 104: Updating The Bios
BIOS Setup 3.2 Updating the BIOS To update the BIOS, you will need the new BIOS file and a flash utility, AWDFLASH.EXE. You can download them from DFI’s web site or contact technical support or your sales representative. 1. Save the new BIOS file along with the flash utility AWDFLASH.EXE to a floppy disk. - Page 105 BIOS Setup 6. The following will appear. Do You Want to Save BIOS (Y/N) This question refers to the current existing BIOS in your sys- tem. We recommend that you save the current BIOS and its flash utility; just in case you need to reinstall the BIOS. To save the current BIOS, press <Y>...
-
Page 106: Chapter 4 - Supported Softwares
Supported Software Chapter 4 - Supported Software 4.1 Desktop Management Interface (DMI) The system board comes with a DMI built into the BIOS. DMI, along with the appropriately networked software, is designed to make inventory, maintenance and troubleshooting of computer sys- tems easier. - Page 107 Supported Software 4.1.2 Using the DMI Utility Award DMI Configuration Utility Copyright Award Software Inc, 1996 [Edit DMI] [Add DMI] [Load DMI File] [Save DMI File] BIOS *** BIOS Auto Detect *** System Enclosure/Chassis Type : BIOS Information Processor Handle : 0000 Memory Controller Vendor Name : Memory Module...
- Page 108 Supported Software Add DMI 1. Use the ← or → arrow keys to select the Add DMI menu. 2. Highlight the item on the left screen that you would like to add by using the ↑ or ↓ arrow keys, then press <Enter>. 3.
-
Page 109: Drivers, Utilities And Software Applications
Supported Software 4.2 Drivers, Utilities and Software Applications The CD that came with the system board contains drivers, utili- ties and software applications required to enhance the perform- ance of the system board. Inser t the CD into a CD-ROM drive. The autorun screen (Mainboard Utility CD) will appear. -
Page 110: Intel Chipset Software Installation Utility
Supported Software 4.2.1 Intel Chipset Software Installation Utility The Intel Chipset Software Installation Utility is used for updating Windows 98SE/2000/ME/XP's INF files so that the Intel chipset can be recognized and configured properly in the system. To install the utility, please follow the steps below. 1. -
Page 111: Audio Drivers
Supported Software 4.2.2 Audio Drivers The audio drivers are supported in the following operating sys- tems: Windows 98 SE, Windows ME, Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000 and Windows To install the driver, please follow the steps below. 1. - Page 112 Supported Software 3. The following screen will appear. 4. Follow the prompts on the screen to complete installation. 5. Reboot the system for the driver to take effect. Note: The 3D Audio Configuration software, which is an audio panel for setting basic audio configurations, will at the same time be installed into your system.
- Page 113 Supported Software 4.2.3 Intel USB 2.0 Drivers If you are using a USB 2.0 device, you must install the USB 2.0 driver. The drivers are supported in the following operating sys- tems: Windows 98 SE, Windows ME and Windows 2000.
- Page 114 Supported Software Windows 2000 does not suppor t auto-installation of the USB 2.0 driver. When you click “Intel USB 2.0 Drivers”, the “readme” screen will appear. 3. Follow the installation instructions shown on the screen. 4. Reboot the system for the driver to take effect. Important: ®...
-
Page 115: Lan Drivers
Supported Software 4.2.4 LAN Drivers The LAN drivers suppor t autorun for the following operating systems: Windows 98 SE, Windows ME, Windows 2000 and Windows To install the driver, please follow the steps below. 1. On the left side of the autorun screen, click the “NETWORK” icon. -
Page 116: Hardware Monitor
Supported Software 4.2.5 Hardware Monitor The system board comes with the Hardware Monitor utility con- tained in the provided CD. This utility is capable of monitoring the system’s “health” conditions and allows you to manually set a range (Highest and Lowest Limit) to the items being monitored. If the settings/values are over or under the set range, a warning message will pop-up. - Page 117 Supported Software 4.2.6 McAfee VirusScan Online (English OS only) The McAfee VirusScan Online is the most reliable and conven- ient way of protecting your PC from computer viruses. When you install McAfee VirusScan Online, your computer is safe be- cause it automatically scans for viruses and checks for virus up- dates so that PC protection stays up-to-date.
- Page 118 Supported Software 4.2.7 Microsoft DirectX 9 To install, please follow the steps below. 1. On the left side of the autorun screen, click the “TOOLS” icon. 2. Click “Microsoft DirectX 9” on the main menu. The following screen will appear. 3.
-
Page 119: Audio Configuration
Supported Software 4.3 3D Audio Configuration When you install the audio driver, the 3D Audio Configuration software will at the same time be installed into your system. 3D Audio Configuration is an audio panel for setting basic audio con- figurations. It allows you to configure 2-channel, 4-channel and 6- channel audio modes as well as configure the audio effects. - Page 120 Supported Software Speaker Output When you open 3D Au- dio Configuration, the de- fault screen that appears is the Speaker Output. This where will configure analog output settings to speakers. S/PDIF This panel is used to configure S/PDIF output which provides a low-dis- tortion digital data transfer between audio devices.
- Page 121 Supported Software Microphone This panel is used to configure the microphone. Xear 3D Xear 3D is a sound tech- nology for 2-channel vir- tual surround, adjustable multi-channel sound field, innovative listening mode, amazing sound effects and 3D positional audio. It has 3 functional blocks: Virtual Speaker Shifter, Sound Ef- fect and Multi-channel Mu-...
-
Page 122: Installation Notes
Supported Software 4.4 Installation Notes 1. "Autorun" ONLY supports the Windows 98 SE, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Windows NT 4.0 and Windows operating systems. If after inserting the CD, "Autorun" did not automatically start (which is, the Main Board Utility CD screen did not appear), please go directly to the root directory of the CD and double-click "Setup". -
Page 123: Appendix A - Enabling The Hyper-Threading T Echnology
Enabling Hyper-Threading Technology Appendix A - Enabling Hyper-Threading Technology A.1 Enabling Hyper-Threading Technology To enable the functionality of the Hyper-Threading Technology, please follow the requirements and steps below. Basically, the following ® ® presumes that you have already installed an Intel Pentium Processor with Hyper-Threading Technology. - Page 124 Enabling Hyper-Threading Technology Click the General tab. The processor shown under Computer should resemble the one shown below. Now click the Hardware tab then click Device Manager. The items shown under Computer and Processors should resemble the ones shown below.
- Page 125 Enabling Hyper-Threading Technology Lastly, press the <Ctr l> <Alt> and <Del> keys simultaneously. The Windows Task Manager dialog box will appear. Click the Performance tab. The diagram under CPU Usage History should resemble the one shown below.
-
Page 126: Appendix B - System Error Messages
System Error Message Appendix B - System Error Message When the BIOS encounters an error that requires the user to correct something, either a beep code will sound or a message will be displayed in a box in the middle of the screen and the message, PRESS F1 TO CONTINUE, CTRL-ALT-ESC or DEL TO ENTER SETUP, will be shown in the information box at the bottom. - Page 127 System Error Message setting than indicated in Setup. Determine which setting is correct, either turn off the system and change the jumper or enter Setup and change the VIDEO selection. FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (80) Unable to reset floppy subsystem. FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (40) Floppy type mismatch.
-
Page 128: Appendix C - Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Appendix C - Troubleshooting C.1 Troubleshooting Checklist This chapter of the manual is designed to help you with problems that you may encounter with your personal computer. To efficiently troubleshoot your system, treat each problem individually. This is to ensure an accurate diagnosis of the problem in case a problem has multiple causes. -
Page 129: Power Supply
Troubleshooting The picture seems to be constantly moving. 1. The monitor has lost its vertical sync. Adjust the monitor’s vertical sync. 2. Move away any objects, such as another monitor or fan, that may be creating a magnetic field around the display. 3. -
Page 130: Hard Drive
Troubleshooting Hard Drive Hard disk failure. 1. Make sure the correct drive type for the hard disk drive has been entered in the BIOS. 2. If the system is configured with two hard drives, make sure the bootable (first) hard drive is configured as Master and the second hard drive is configured as Slave. - Page 131 Troubleshooting Serial Port The serial device (modem, printer) doesn’t output anything or is outputting garbled characters. 1. Make sure that the serial device’s power is turned on and that the device is on-line. 2. Verify that the device is plugged into the correct serial port on the rear of the computer.











Need help?
Do you have a question about the 865PE-A and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers