Table of Contents
Advertisement
Available languages
Available languages
Note:Before sliding theworkpiece back, g ivethework-
piecea littlesideways shifttomoveit slightly awayfrom
thesawblade.
NEVER pickupanyshortcutoffscrappieces fromthe
tablewhilethesaw
is running. Wait until the saw blade
has come to a complete stop.
Figure
23=2
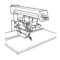
AUXILIARY FENCE
For added safety and convenience, the miter gauge can
be fitted with an auxiliary fence (E) if not already sup-
plied with one. If the auxiliary fence is not provided with
your saw, one can be purchased as an accessory or
one can be made from a dimensional piece of hard-
wood. This auxiliary fence can be fastened to the front
of the miter gauge by using two screws (not included)
through the slots (not shown) in the miter gauge body.
See figure 23.2.
Figure 23=3
F
CAUTION
When using the block as a cut-off gauge, it is very
important that the rear end of the block be positioned
so the workpiece is clear of the block before it enters
the blade. See figure 23-3.
Never use the fence as a cut-off gauge when crosscutting.
When cross-cutting a number of pieces to the same
length, a block of wood can be clamped to the fence
and used as a cut-off gauge as shown.
It is important
that this block of wood always be positioned in front of
the saw blade as shown.
Once the cut-off length is
determined, secure the fence and use the miter gauge
to feed the work into the blade. This block of wood
allows the cut-off piece to move freely along the table
surface without binding between the fence and the saw
table, thereby lessening the possibility of kickback and
injury to the operator.
See figure 23-3.
Note: This block allows the cut-off scrap piece to move
freely along the table surface without binding between
the fence and the blade, thereby lessening the possibil-
ity of kickback and injury to the operator.
2.
Once the cut-off length is determined, lock the
fence and slide the workpiece across the table
surface until it contacts the block. Use the miter
gauge (K) to feed the workpiece into the blade.
To avoid kickback when using the block (F) as a cut-off
gauge, it is very important that the rear end of the block
(G) be positioned so the workpiece (H) is clear of the
block before it enters the blade (I). Never use the fence
(J) as a cut-off gauge when crosscutting. See figure 23-3.
H
K
CUT-OFF GAUGE
1.
When cross-cutting a number of pieces to the same
length, clamp a block (F) of wood to the fence (J) to
use as a cut-off gauge. It is important that this block
of wood always be positioned in front of the saw
blade. See figure 23-3.
33
Hide quick links:
Advertisement
Table of Contents