Table of Contents
Troubleshooting

Summary of Contents for Miller Bobcat 250 NT
- Page 1 OM-4403 200 291E April 2002 Processes Stick (SMAW) Welding MIG (GMAW) Welding Flux Cored (FCAW) Welding Non-Critical TIG (GTAW) Welding Description Engine Driven Welding Generator Bobcat 250 NT Visit our website at www.MillerWelds.com...
- Page 2 We know you don’t have time to do it any other way. That’s why when Niels Miller first started building arc welders in 1929, he made sure his products offered long-lasting value and superior quality.
-
Page 3: Table Of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING ......1-1. Symbol Usage . - Page 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 9 – TROUBLESHOOTING ........... . . SECTION 10 –...
-
Page 5: Symbol Usage
SECTION 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING rom _nd_4/02 1-1. Symbol Usage Means Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards with this procedure! The possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols. This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! possible Y Marks a special safety message. -
Page 6: Engine Hazards
WELDING can cause fire or explosion. HOT PARTS can cause severe burns. D Allow cooling period before maintaining. Welding on closed containers, such as tanks, D Wear protective gloves and clothing when drums, or pipes, can cause them to blow up. Sparks working on a hot engine. -
Page 7: Additional Symbols For Installation, Operation, And Maintenance
READ INSTRUCTIONS. stopping engine. D Do not let low voltage and frequency caused by D Use only genuine MILLER replacement parts. low engine speed damage electric motors. D Perform engine maintenance and service D Do not connect 50 or 60 Hertz motors to the 100 Hertz receptacle according to this manual and the engine where applicable. -
Page 8: Principal Safety Standards
H.F. RADIATION can cause interference. ARC WELDING can cause interference. D High-frequency (H.F.) can interfere with radio D Electromagnetic energy can interfere with navigation, safety services, computers, and sensitive electronic equipment such as communications equipment. computers and computer-driven equipment D Have only qualified persons familiar with such as robots. -
Page 9: Signification Des Symboles
SECTION 1 – CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ – LIRE AVANT UTILISATION rom _nd_fre 11/98 1-1. Signification des symboles Signifie Mise en garde ! Soyez vigilant ! Cette procédure présente des risques de danger ! Ceux-ci sont identifiés par des symboles adjacents aux directives. Ce groupe de symboles signifie Mise en garde ! Soyez vigilant ! Il y a des Y Identifie un message de sécurité... -
Page 10: Dangers Existant En Relation Avec Le Moteur
LE SOUDAGE peut provoquer un in- DES PIÈCES CHAUDES peuvent cendie ou une explosion. provoquer des brûlures graves. D Prévoir une période de refroidissement avant d’effec- Le soudage effectué sur des conteneurs fermés tels que tuer des travaux d’entretien. des réservoirs, tambours ou des conduites peut provoquer D Porter des gants et des vêtements de protection pour leur éclatement. -
Page 11: Dangers Supplémentaires En Relation Avec L'installation, Le Fonctionnement
DES ORGANES MOBILES peuvent L’ACIDE DE LA BATTERIE peut pro- provoquer des blessures. voquer des brûlures dans les YEUX et sur la PEAU. D Ne pas approcher les mains des ventilateurs, cour- roies et autres pièces en mouvement. D Ne pas renverser la batterie. D Maintenir fermés et fixement en place les portes, D Remplacer une batterie endommagée. -
Page 12: Principales Normes De Sécurit
LE RAYONNEMENT HAUTE FRÉ- LE SOUDAGE À L’ARC risque de QUENCE (H.F.) risque de provoquer provoquer des interférences. des interférences. D L’énergie électromagnétique risque de provoquer des interférences pour l’équipement électronique D Le rayonnement haute fréquence (H.F.) peut sensible tel que les ordinateurs et l’équipement com- provoquer des interférences avec les équipements mandé... -
Page 13: Symbol Definitions
SECTION 2 – DEFINITIONS 2-1. Symbol Definitions Fast Fast/Slow Stop Engine Slow (Idle) (Run, Weld/Power) (Run/Idle) Read Operator’s Start Engine Amperes Volts Manual Engine Oil Fuel Battery (Engine) Engine Check Valve Do not switch while Engine Choke Work Connection Clearance welding Alternating Current Positive... -
Page 14: Dimensions, Weights, And Operating Angles
3-2. Dimensions, Weights, and Operating Angles Dimensions Height 33-1/2 in (851 mm) Width 18-3/4 in (476 mm) Y Do not exceed tilt angles or engine could Depth 46 in (1164 mm) be damaged or unit could tip. Y Do not move or operate unit where it could 18 in (457 mm) tip. - Page 15 3-4. Fuel Consumption (Onan-Powered Units) 206 148 3-5. Fuel Consumption (Kohler-Powered Units) 200 299 OM-4403 Page 11...
-
Page 16: Volt-Ampere Curves
3-6. Volt-Ampere Curves The volt-ampere curve shows the A. For CC/AC Mode minimum and maximum voltage and amperage output capabilities of the welding generator. Curves of all other settings fall between the curves shown. B. For CC/DC Mode C. For CV/DC Mode 200 296 / 200 297 / 200 298 OM-4403 Page 12... -
Page 17: Duty Cycle
3-7. Duty Cycle Duty cycle is the percentage of 10 minutes that unit can weld at rated load without overheating. Y Exceeding duty cycle can damage unit void warranty. Continuous Welding 100% Duty Cycle at 250 Amperes 200 293 SECTION 4 – INSTALLATION 4-1. -
Page 18: Engine Prestart Checks (Onan-Powered Units)
4-2. Engine Prestart Checks (Onan-Powered Units) Check all fluids daily. Engine must be cold and on a level surface. Unit is shipped with 10W30 engine oil. Full Follow run-in procedure in en- gine manual. This unit has a low oil pressure Gasoline shutdown switch. -
Page 19: Engine Prestart Checks (Kohler-Powered Units)
4-3. Engine Prestart Checks (Kohler-Powered Units) Check all fluids daily. Engine must be cold and on a level surface. Unit is shipped with 10W30 engine oil. Full Follow run-in procedure in en- gine manual. This unit has a low oil pressure shutdown switch. -
Page 20: Activating The Dry Charge Battery (If Applicable)
4-4. Activating The Dry Charge Battery (If Applicable) Remove battery from unit. Eye Protection – Safety Glasses Or Face Shield Rubber Gloves Vent Caps Sulfuric Acid Electrolyte (1.265 Specific Gravity) Well Fill each cell with electrolyte to bottom of well (maximum). Y Do not overfill battery cells. -
Page 21: Connecting The Battery
4-5. Connecting the Battery Y Connect negative (–) cable last. – Tools Needed: 3/8, 1/2 in Ref. 800 394-C / Ref. 200 017 / Ref. S-0756-D 4-6. Installing Exhaust Pipe Y Engine backfire can cause se- vere burns or other injuries. Do not point exhaust pipe toward control panel. -
Page 22: Connecting To Weld Output Terminals
4-7. Connecting to Weld Output Terminals See Section 5 for examples of typical weld connections and control settings. Work Weld Output Terminal Electrode Weld Output Terminal Connect work cable to Work terminal. Connect electrode holder cable or electrode weld cable to Electrode ter- minal for Stick and MIG welding. -
Page 23: Front Panel Controls
SECTION 5 – OPERATING THE WELDING GENERATOR 5-1. Front Panel Controls Shown with optional receptacle covers. Ref. 200 017 Engine Control Switch position. For best arc starts and when using weld Use switch to start engine, select speed, and and generator power together, use a low Engine Hour Meter stop engine. -
Page 24: Typical Stick Welding Connections And Control Settings
5-2. Typical Stick Welding Connections And Control Settings Y Stop engine. This section provides general guide- lines and may not suit all applications. The control panel shows the typical For best arc starts and best settings for welding with a 7018 (1/8 in) results using weld and generator electrode. -
Page 25: Typical Mig Welding Connections And Settings
5-3. Typical MIG Welding Connections And Settings A. Solid Wire Applications Y Stop engine. This section provides general guide- lines and may not suit all ap- plications. Typical Control Settings For .035 (ER70S-3) Solid Wire – Short Circuit Transfer The control panel shows the typical settings for welding with .035 (ER70S-3) solid wire. - Page 26 B. Self-Shielded Flux Core Wire Applications Y Stop engine. This section provides general guidelines and may not suit all applications. Typical Control Settings For .045 (71T-11) Self-Shielded Flux Core Wire The control panel shows the typi- cal settings for welding with .045 (71T-11) self-shielded flux core Note Coarse Range, wire.
-
Page 27: Typical Mig Connections And Settings Using Weld Control And Spoolgun
5-4. Typical MIG Connections And Settings Using Weld Control And Spoolgun Typical Settings For 4043 (.035) Tools Needed: Aluminum On 1/8 in Material: 3/4 in Note Coarse Range and Weld Process switch settings. Connect to unused Work contactor terminal. Plug and sensing lead not used in this application. -
Page 28: Standard Receptacles
SECTION 6 – OPERATING AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT 6-1. Standard Receptacles Y If unit does not have GFCI re- ceptacles, use GFCI-protected extension cord. Generator power decreases as weld current increases. Set Fine Control R1 at 10 for full generator power. 240 V 50 A AC Receptacle RC1 RC1 supplies 60 Hz single-phase power at weld/power speed. -
Page 29: Optional Generator Power Receptacles
6-2. Optional Generator Power Receptacles Y If unit does not have GFCI recep- tacles, use GFCI-protected exten- sion cord. Generator power decreases as weld current increases. Set Fine Control R1 at 10 for full genera- tor power. Combined output of all receptacles limited to 10 kVA/kW rating of the generator. -
Page 30: Wiring Optional 240 Volt Plug
6-3. Wiring Optional 240 Volt Plug The plug can be wired for a 240 V, 2-wire load or a 120/240V, 3-wire load. See circuit diagram. Plug Wired for 120/240 V, 3-Wire Load Current Available in Amperes When wired for 120 V loads, each 240 V Each 120 V Duplex duplex receptacle shares a load... - Page 31 50 h Clean tighten weld terminals. 100 h Change oil. See Clean cooling system. Section 7-5 and See Engine Manual. maintenance label. Service Clean cleaner element. tighten battery See Section 7-3. connections. 200 h Replace fuel Change oil filter. See filter.
-
Page 32: Maintenance Label (Onan-Powered Units)
7-2. Maintenance Label (Onan-Powered Units) OM-4403 Page 28... -
Page 33: Servicing Air Cleaner (Onan-Powered Units)
7-3. Servicing Air Cleaner (Onan-Powered Units) Y Stop engine. Y Do not run engine without air cleaner or with dirty element. Wrapper (Foam Element) Wash wrapper with soap and water solution. Allow wrapper to air dry completely. Spread 1 tablespoon SAE 30 oil evenly into wrapper. -
Page 34: Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, And Fuel Filter (Onan-Powered Units)
7-5. Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, and Fuel Filter (Onan-Powered Units) Y Stop engine and let cool. Oil Drain Valve 1/2 ID x 12 in Hose Oil Filter Change engine oil and filter accord- ing to engine owner’s manual. Y Close valve and valve cap before adding running engine. -
Page 35: Adjusting Engine Speed (Onan-Powered Units)
7-6. Adjusting Engine Speed (Onan-Powered Units) After tuning engine, check engine speeds with a tachometer (see table). If necessary, adjust speeds as follows: ± 2200 100 rpm Start engine and run until warm. ± Remove wrapper to access speed 3700 50 rpm adjustments. -
Page 36: Servicing Optional Spark Arrestor (Onan-Powered Units)
7-7. Servicing Optional Spark Arrestor (Onan-Powered Units) Y Stop engine and let cool. Spark Arrestor Screen Clean and inspect screen. Replace spark arrestor if screen wires are broken or missing. Tools Needed: 1/4 in Ref. 801 682-A / Ref. 183 175–A SECTION 8 –... - Page 37 100 h Change oil. See Section 8-4 Check air cleaner element. and maintenance label. See Section 8-3. Clean cooling system. See Clean and tighten battery Engine Manual. connections. 200 h Change oil filter. See Section Replace fuel filter. See 8-4 and maintenance label. Section 8-4.
-
Page 38: Servicing Air Cleaner (Kohler-Powered Units)
8-2. Maintenance Label (Kohler-Powered Units) 8-3. Servicing Air Cleaner (Kohler-Powered Units) Y Stop engine. Y Do not run engine without air cleaner or with dirty element. Wrapper (Foam Element) Wash wrapper with soap and water solution. Allow wrapper to air dry completely. -
Page 39: Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, And Fuel Filter (Kohler-Powered Units)
8-4. Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, and Fuel Filter (Kohler-Powered Units) Y Stop engine and let cool. Oil Drain Valve 1/2 ID x 12 in Hose Oil Filter Change engine oil and filter accord- ing to engine owner’s manual. Y Close valve and valve cap before adding running engine. -
Page 40: Adjusting Engine Speed (Kohler-Powered Units)
8-5. Adjusting Engine Speed (Kohler-Powered Units) After tuning engine, check engine speeds with a tachometer (see table). If necessary, adjust speeds as follows: ± 2200 50 rpm Start engine and run until warm. Turn Fine Control to 10. ± 3700 50 rpm Remove top cover to access speed adjustments. -
Page 41: Overload Protection (Kohler-Powered Units)
8-6. Overload Protection (Kohler-Powered Units) Y Stop engine. Disconnect negative (–) battery cable. Fuse F1 (See Parts List) F1 protects the weld excitation winding from overload. If F1 opens, weld output stops or is low. Fuse F2 (See Parts List) F2 protects the generator power excitation winding from overload. -
Page 42: Welding Troubleshooting
SECTION 9 – TROUBLESHOOTING 9-1. Welding Troubleshooting Trouble Remedy Low or no weld output; generator pow- Check control settings. er output okay at ac receptacles. Check weld connections. Check fuse F1, and replace if open (see Section 7-4 or 8-6). Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check brushes, slip rings, and integrated rectifiers SR2 and SR3. -
Page 43: Engine Troubleshooting
Trouble Remedy Low power output at ac receptacles. Check fuse F2, and replace if open (see Section 7-4 or 8-6). Increase Fine control R1 setting to max. High power output at ac receptacles. Check engine speed, and adjust if necessary (see Section 7-6 or 8-5). Erratic power output at ac receptacles. - Page 44 Trouble Remedy Unstable or sluggish engine speeds. Readjust throttle linkage if necessary. Check throttle solenoid TS1 for smooth operation. Tune-up engine according to engine manual. Engine does not return to idle speed. Remove weld and generator power loads. Check throttle linkage for smooth, non-binding operation. Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check idle module PC1, current transformer CT1, Engine Control switch S2, and throttle solenoid TS1.
- Page 45 Notes OM-4403 Page 41...
-
Page 46: Section 10 - Electrical Diagrams
SECTION 10 – ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS Figure 11-1. Circuit Diagram For Welding Generator OM-4403 Page 42... - Page 47 202 547-D OM-4403 Page 43...
-
Page 48: Grounding Generator To Truck Or Trailer Frame
SECTION 11 – GENERATOR POWER GUIDELINES 11-1. Selecting Equipment Generator Power Receptacles – Neutral Bonded To Frame 3-Prong Plug From Case Grounded Equipment 2-Prong Plug From Double Insulated Equipment Be sure equipment has this symbol and/or wording. gen_pwr 4/02 – Ref. ST-159 730 / ST-800 577 11-2. - Page 49 11-3. Grounding When Supplying Building Systems Equipment Grounding Terminal Grounding Cable GND/PE Use #10 AWG or larger insulated copper wire. Ground Device Y Ground generator to system earth ground if supplying power to a premises (home, shop, farm) wiring system. Use ground device as stated in electrical codes.
- Page 50 11-5. Approximate Power Requirements For Industrial Motors Industrial Motors Rating Starting Watts Running Watts Split Phase 1/8 HP 1/6 HP 1225 1/4 HP 1600 1/3 HP 2100 1/2 HP 3175 Capacitor Start-Induction Run 1/3 HP 2020 1/2 HP 3075 3/4 HP 4500 1400 1 HP...
- Page 51 11-7. Approximate Power Requirements For Contractor Equipment Contractor Rating Starting Watts Running Watts Hand Drill 1/4 in 3/8 in 1/2 in Circular Saw 6-1/2 in 7-1/4 in 8-1/4 in 1400 1400 Table Saw 9 in 4500 1500 10 in 6300 1800 Band Saw 14 in...
- Page 52 11-8. Power Required To Start Motor Motor Start Code AC MOTOR Running Amperage VOLTS AMPS Motor HP CODE Motor Voltage PHASE To find starting amperage: Step 1: Find code and use table to find kVA/HP. If code is not listed, multiply running amperage by six to find starting amperage.
- Page 53 11-10. Typical Connections To Supply Standby Power Y Have only qualified persons perform these connections Customer-supplied equipment is required if according to all applicable generator is to supply standby power during codes and safety practices. emergencies or power outages. Y Properly install and ground this equipment according to its Owner’s Manual and na- tioanl, state, and local codes.
- Page 54 11-11. Selecting Extension Cord (Use Shortest Cord Possible) Cord Lengths for 120 Volt Loads Y If unit does not have GFCI receptacles, use GFCI-protected extension cord. Maximum Allowable Cord Length in ft (m) for Conductor Size (AWG)* Current Load (Watts) (Amperes) 350 (106) 225 (68)
-
Page 55: Section 12 - Stick Welding (Smaw) Guidelines
SECTION 12 – STICK WELDING (SMAW) GUIDELINES 12-1. Stick Welding Procedure Y Weld current starts when electrode touches work- piece. Y Weld current can damage electronic parts in vehicles. Disconnect both battery cables before welding on a vehicle. Place work clamp as close to the weld as possible. - Page 56 12-2. Electrode and Amperage Selection Chart 3/32 6010 5/32 & 3/16 6011 7/32 6010 DEEP MIN. PREP, ROUGH 1/16 HIGH SPATTER 6011 DEEP 5/64 6013 EP,EN GENERAL 3/32 SMOOTH, EASY, 6013 7014 EP,EN FAST 5/32 3/16 LOW HYDROGEN, 7018 STRONG 7/32 FLAT SMOOTH, EASY,...
- Page 57 12-5. Positioning Electrode Holder ° ° ° ° End View of Work Angle Side View of Electrode Angle GROOVE WELDS ° ° ° ° End View of Work Angle Side View of Electrode Angle FILLET WELDS S-0060 12-6. Poor Weld Bead Characteristics Large Spatter Deposits Rough, Uneven Bead Slight Crater During Welding...
- Page 58 12-8. Conditions That Affect Weld Bead Shape NOTE Weld bead shape is affected by electrode angle, arc length, travel speed, and thickness of base metal. Correct Angle ° - ° Angle Too Large Angle Too Small Drag ELECTRODE ANGLE Spatter Normal Too Long Too Short...
- Page 59 12-10. Butt Joints Tack Welds Prevent edges of joint from drawing together ahead of electrode by tack welding the materials in position be- fore final weld. Square Groove Weld Good for materials up to 3/16 in (5 mm) thick. Single V-Groove Weld °...
- Page 60 12-13. Weld Test Vise Weld Joint Hammer Strike weld joint in direction shown. A good weld bends over but does not break. 2 To 3 in (51-76 mm) 2 To 3 in (51-76 mm) 1/4 in (6.4 mm) S-0057-B 12-14. Troubleshooting – Porosity Porosity –...
- Page 61 12-16. Troubleshooting – Incomplete Fusion Incomplete Fusion – failure of weld metal to fuse completely with base metal or a preceeding weld bead. Possible Causes Corrective Actions Insufficient heat input. Increase amperage. Select larger electrode and increase amperage. Improper welding technique. Place stringer bead in proper location(s) at joint during welding.
- Page 62 12-19. Troubleshooting – Burn-Through Burn-Through – weld metal melting completely through base metal resulting in holes where no metal remains. Possible Causes Corrective Actions Excessive heat input. Select lower amperage. Use smaller electrode. Increase and/or maintain steady travel speed. 12-20. Troubleshooting – Waviness Of Bead Waviness Of Bead –...
-
Page 63: Section 13 - Mig Welding (Gmaw) Guidelines
SECTION 13 – MIG WELDING (GMAW) GUIDELINES 13-1. Typical MIG Process Connections Using A Voltage-Sensing Wire Feeder Y Weld current can damage electronic parts in vehicles. Disconnect both battery cables before welding on a vehicle. Place work clamp as Constant close to the weld as possible. -
Page 64: Typical Mig Process Control Settings
13-3. Typical MIG Process Control Settings NOTE These settings are guidelines only. Material and wire type, joint design, fitup, position, shielding gas, etc. affect settings. Test welds to be sure they comply to specifications. Material thickness determines weld parameters. 1/8 or Convert Material .125 in Thickness to... -
Page 65: Holding And Positioning Welding Gun
13-4. Holding And Positioning Welding Gun NOTE Welding wire is energized when gun trigger is pressed. Before lowering helmet and pressing trigger, be sure wire is no more than 1/2 in (13 mm) past end of nozzle, and tip of wire is positioned correctly on seam. Hold Gun and Control Gun Trigger Workpiece... -
Page 66: Conditions That Affect Weld Bead Shape
13-5. Conditions That Affect Weld Bead Shape NOTE Weld bead shape depends on gun angle, direction of travel, electrode extension (stickout), travel speed, thickness of base metal, wire feed speed (weld current), and voltage. ° Push ° Perpendicular Drag GUN ANGLES AND WELD BEAD PROFILES Short Normal Long... -
Page 67: Gun Movement During Welding
13-6. Gun Movement During Welding NOTE Normally, a single stringer bead is satisfactory for most narrow groove weld joints; however, for wide groove weld joints or bridging across gaps, a weave bead or multiple stringer beads works better. Stringer Bead – Steady Movement Along Seam Weave Bead –... -
Page 68: Troubleshooting - Excessive Spatter
13-9. Troubleshooting – Excessive Spatter Excessive Spatter – scattering of molten metal particles that cool to solid form near weld bead. S-0636 Possible Causes Corrective Actions Wire feed speed too high. Select lower wire feed speed. Voltage too high. Select lower voltage range. Electrode extension (stickout) too long. -
Page 69: Troubleshooting - Lack Of Penetration
13-12. Troubleshooting – Lack Of Penetration Lack Of Penetration – shallow fusion between weld metal and base metal. Lack of Penetration Good Penetration S-0638 Possible Causes Corrective Actions Improper joint preparation. Material too thick. Joint preparation and design must provide access to bottom of groove while maintaining proper welding wire extension and arc characteristics. -
Page 70: Troubleshooting - Waviness Of Bead
13-15. Troubleshooting – Waviness Of Bead Waviness Of Bead – weld metal that is not parallel and does not cover joint formed by base metal. S-0641 Possible Causes Corrective Actions Welding wire extends too far out of nozzle. Be sure welding wire extends not more than 1/2 in (13 mm) beyond nozzle. Unsteady hand. -
Page 71: Common Mig Shielding Gases
13-17. Common MIG Shielding Gases This is a general chart for common gases and where they are used. Many different combinations (mixtures) of shielding gases have been developed over the years. The most commonly used shielding gases are listed in the following table. -
Page 72: Section 14 - Parts List
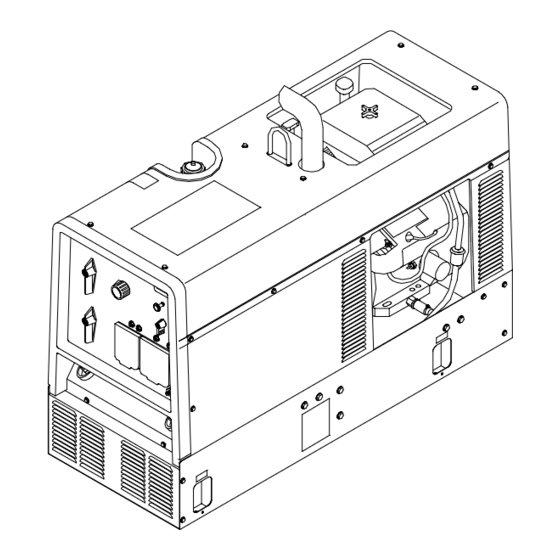
SECTION 14 – PARTS LIST Hardware is common and not available unless listed. Figure 14-1. Main Assembly (Onan OHV Engine Shown) 802 920-D OM-4403 Page 68... - Page 73 Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 14-1. Main Assembly ....181 881 Grommet, Neck Filler ..........
- Page 74 Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 14-1. Main Assembly (Continued) ....082 319 Cable, Cable, Bat Neg 17.750 (Battery To Engine Block) ......(Onan OHV &...
- Page 75 802 930 Figure 14-2. Generator Item Part Description Quantity Figure 14-2. Generator (Figure 14-1 Item 20) ..+202 986 Housing, Generator Front (Consisting Of) ........
- Page 76 ST-801 747-B Figure 14-3. Panel, Front w/Components Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 14-3. Panel, Front w/Components (Figure 14-1 Item 42) ....198 700 Switch, Polarity 5 Position With Leads And Jumpers .
- Page 77 Item Dia. Part Mkgs. Description Quantity Figure 14-3. Panel, Front w/Components (Figure 14-1 Item 42) (Continued) ....010 915 Washer, Flat .250 Id Brs .
- Page 79 Effective January 1, 2001 (Equipment with a serial number preface of “LB” or newer) This limited warranty supersedes all previous Miller warranties and is exclusive with no other Warranty Questions? guarantees or warranties expressed or implied. Call LIMITED WARRANTY – Subject to the terms and conditions APT, ZIPCUT &...
-
Page 80: Options And Accessories
Distributor Address City State For Service Call 1-800-4-A-Miller or see our website at www.MillerWelds.com to locate a DISTRIBUTOR or SERVICE AGENCY near you. Always provide Model Name and Serial/Style Number. Contact your Distributor for: Welding Supplies and Consumables Options and Accessories...






Need help?
Do you have a question about the Bobcat 250 NT and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers
i have a miller bobcat 250 welder it will not idle nown