Advertisement
Quick Links
Shihlin Electric General Inverters
SC3 Series
User Manual
High price–performance ratio
SC3-021-0.2K~2.2K
SC3-023-0.2K~3.7K
SC3-043-0.4K~5.5K
SC3-043-7.5K/11KF~18.5K/22KF
SC3-043-22K
MANUAL GUIDE
DELIVERY CHECK
INVERTER
INTRODUCTION
BASIC OPERATION
PARAMETER
DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION AND
MAINTENANCE
APPENDIX
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Advertisement

Summary of Contents for Shihlin electric SC3-043-7.5K/11KF
- Page 1 Shihlin Electric General Inverters SC3 Series User Manual High price–performance ratio SC3-021-0.2K~2.2K SC3-023-0.2K~3.7K SC3-043-0.4K~5.5K SC3-043-7.5K/11KF~18.5K/22KF SC3-043-22K MANUAL GUIDE DELIVERY CHECK INVERTER INTRODUCTION BASIC OPERATION PARAMETER DESCRIPTION INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE APPENDIX...
- Page 3 Safety instructions 1. MANUAL GUIDE 1.1 Safety instructions Thank you for choosing Shihlin inverters SC3 series. This user manual introduces how to use the product correctly. Please read the user manual carefully before using the product. In addition, please use the product after understanding the safety instructions.
- Page 4 Table of contents 1.2 Table of contents User Manual .................................... 1 1. MANUAL GUIDE ................................1 1.1 Safety instructions ..............................1 1.2 Table of contents ..............................2 1.3 Definitions of terminologies ........................... 10 2. DELIVERY CHECK ................................11 2.1 Nameplate instruction ............................11 2.2 Type instruction ..............................
- Page 5 Table of contents 3.5.1 Transportation ..........................19 3.5.2 Stockpile............................19 3.5.3 Installation notice ..........................19 3.5.4 EMC installation instructions......................22 3.6 Peripheral devices ..............................23 3.6.1 System Wire Arrangement .......................23 3.6.2 No-fuse breaker and magnetic contactor ..................24 3.6.3 Regeneration brake resistor ......................25 3.7 Terminal wire arrangement ........................... 26 3.7.1 Main circuit Terminals ........................27 3.7.2 Main circuit wiring and terminal specification ..................28 3.7.3 Ground .............................29...
- Page 6 Table of contents 4.2.4 Operation flow chart for frequency setting ..................38 4.2.5 Operation flow chart for parameter setting ..................39 4.2.6 Operation flow chart for HELP mode ....................39 4.3 Basic operation steps for different modes ......................40 4.3.1 Basic operation steps for PU mode(00-16(P.79)=0 or 1) ............40 4.3.2 Basic operation steps for external mode (00-16(P.79)=0 or 2) .............40 4.3.3 Basic operation steps for JOG mode (00-16(P.79)=0 or 1) ............41 4.3.4 Basic operation steps for communication mode (00-16(P.79)=3) ..........41...
- Page 7 Table of contents 5.1.6 Built-in keypad set target frequency selection .................56 5.1.7 PWM carrier frequency ........................57 5.1.8 Stop operation selection ........................58 5.1.9 Forward/reverse rotate prevent function ..................59 5.1.10 Operation mode selection ......................59 5.1.11 Motor control mode selection ......................60 5.1.12 Motor types selection ........................60 5.1.13 50/60Hz switch selection .......................61 5.1.14 Parameter mode setting ........................61 5.2 Basic Parameter Group 01 ...........................
- Page 8 Table of contents 5.3 Analog input and output parameter group 02 ....................78 5.3.1 Proportional linkage gain .........................79 5.3.3 Terminal 3-5 signal selection and processing .................80 5.3.4 Inverter rated current display level ....................85 5.4 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 ......................86 5.4.1 Digital input terminals function selection ..................89 5.4.2 Digital output terminals function selection ..................93 5.4.3 Terminal logic selection ........................94...
- Page 9 Table of contents 5.7.6 Maintenance alarm function......................114 5.7.7 Short circuit to ground protection ....................114 5.7.9 Time record function ........................115 5.7.11 Fire mode ............................ 117 5.8 Communication parameter group 07 ......................... 119 5.8.1 Shihlin protocol and Modbus protocol ..................120 5.8.2 Communication EEPROM write selection ..................
- Page 10 Table of contents 5.10.11 Voltage stall action level ......................153 5.10.12 Reciprocating machine function ....................153 5.11 Advanced parameter group 11 ........................155 5.11.1 Slip compensation gain ....................... 155 5.11.2 Torque boost filter ........................155 5.11.3 Current filter ..........................155 5.12 Special Adjustment Parameter Group 13 .......................
- Page 11 Table of contents 6.2.6 Hi-pot test ............................164 7. Appendix ..................................165 7.1 Appendix 1 Parameter table ..........................165 7.1.1 Parameter in P sequence ......................165 7.1.2 Group mode ..........................181 7.2 Appendix 2 Alarm code list ..........................197 7.3 Appendix 3:Warning code list .......................... 201 7.4 Appendix 4:Troubles and solutions ........................
- Page 12 Definitions of terminologies 1.3 Definitions of terminologies Output frequency, target frequency, steady output frequency The actual output current frequency of inverter is called “output frequency.” The frequency set by user (via built-in keypad, multi-speed terminals, voltage signal, and current signal or ...
- Page 13 Hardware and Firmware version S/N : C3ANCAS18A0001 VER:0.180A Serial number IP20 Protection level Suzhou Shihlin Electric & Engineering Co.,Ltd. MADE IN CHINA 2.2 Type instruction SC3-043-7.5K/11KF - xy None: General model - xy : Customized or dedicated or region Suitable motor : 7.5K/11KF...
- Page 14 Electric specification 3. INVERTER INTRODUCTION 3.1 Electric specification 3.1.1 440V series three-phase Frame SC3-043-□□□K-xy 0.75 Rated output capacity (kVA) Rated output current (A) Applicable motor capacity (HP) Inverter Applicable motor capacity (kW) 0.75 Output Overload current rating 150% 60 seconds, 200% 1 seconds (inverse-time characteristics) Carrier frequency (kHz) 1~15kHz Maximum output voltage...
- Page 15 Electric specification 3.1.2 220V series three-phase Frame Model SC3-023-□□□K-xy 0.75 Rated output capacity (kVA) Rated output current (A) 17.5 Applicable motor capacity (HP) 0.25 Inverter Applicable motor capacity (kW) 0.75 Output Overload current rating 150% 60 seconds, 200% 1 seconds (inverse-time characteristics) Carrier frequency (kHz) 1~15kHz Maximum output voltage...
- Page 16 Electric specification 3.1.3 220V series single phase Frame Model SC3-021-□□□K-xy 0.75 Rated output capacity (kVA) Rated output current (A) Applicable motor capacity (HP) 0.25 Inverter Applicable motor capacity (kW) 0.75 Output Overload current rating 150% 60 seconds, 200% 1 seconds (inverse-time characteristics) Carrier frequency (kHz) 1~15kHz Maximum output voltage...
- Page 17 General specification 3.2 General specification Control method SVPWM,V/F control,General flux vector control Output frequency range 0~599Hz (*1) Within 100Hz, the resolution is 0.01Hz Frequency Digital setting Above 100Hz, the resolution is 0.1Hz. setting DC 0~5V or 4~20mA signal: 11 bit, resolution Analog setting DC 0~10V signal: 12 bit.
- Page 18 Appearance and dimensions 3.3 Appearance and dimensions 3.3.1 Frame A unit:mm Model SC3-021-0.2K SC3-021-0.4K SC3-021-0.75K SC3-023-0.2K SC3-023-0.4K 26.5 (tighten torque SC3-023-0.75K 20~25kgf.cm) SC3-023-1.5K SC3-043-0.4K SC3-043-0.75K SC3-043-1.5K INVERTER INTRODUCTION 16...
- Page 19 Appearance and dimensions 3.3.2 Frame B/C/D unit:mm Model SC3-021-1.5K SC3-021-2.2K SC3-023-2.2K SC3-023-3.7K 26.5 (tighten torque 20~25kgf.cm) SC3-043-2.2K SC3-043-3.7K SC3-043-5.5K SC3-043-7.5K/11KF (tighten torque 115.6 198.6 Note 1 20~25kgf.cm) SC3-043-11K/15KF SC3-043-15K/18.5KF (tighten torque SC3-043-18.5K/22KF 158.6 243.6 Note 1 20~25kgf.cm) SC3-043-22K Note1: Frame C and frame D do not have this feature, that is, they do not support DIN rail installation...
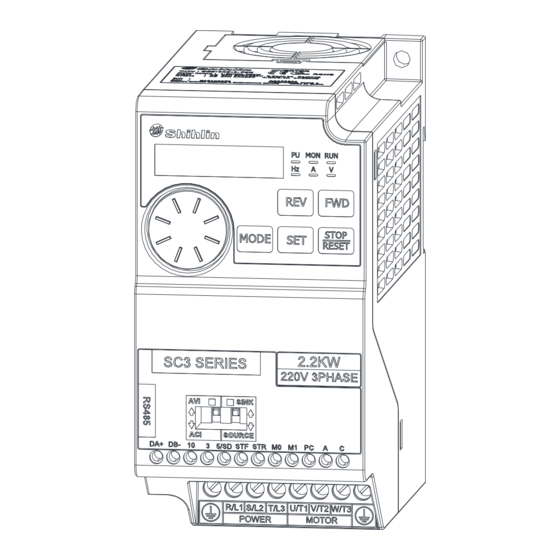
- Page 20 Name of each component 3.4 Name of each component 3.4.1 Frame A/B Fan lid Product nameplate Lower lid Upper lid External keypad connector Control circuit sticker Mounting holes 3.4.2 Frame C/D Fan lid Product nameplate foundation membrane switch knobne switch Upper lid External keypad connector Control circuit sticker...
- Page 21 Installation and wiring 3.5 Installation and wiring 3.5.1 Transportation Hold the body when carrying and don’t only hold the cover or any part of the inverter, otherwise it may drop down. 3.5.2 Stockpile The product must be placed in the packaging box before installation. In order to make the product conform to the scope of warranty of the company and facilitate maintenance in the future, please pay attention to the following matters when storing if the inverter will not be used temporarily: 1.
- Page 22 Installation and wiring Please install the inverter vertically in order not to reduce the heat dissipation effect: (a) Vertical installation (b) Horizontal installation (c) Transverse installation Please follow the installation restrictions shown below to ensure enough ventilation space for inverter cooling and wiring space: Arrangement of single or paralleling inverter:...
- Page 23 Installation and wiring Note:1. When installing inverters of different sizes in parallel, please align the upper positions of the inverters before installing. For easier replacement of the cooling fan. 2. When it is inevitable to arrange inverters vertically to minimize space,install guides since heat from the bottom inverters can increase the temperature on the top inverters, causing inverter failures.
- Page 24 Installation and wiring 3.5.4 EMC installation instructions Just as other electrical and electronic equipment, an inverter is the source of electromagnetic interference and an electromagnetic receiver when working with a power system. The amount of electromagnetic interference and noise is determined by the working principles of an inverter.
- Page 25 Peripheral devices 3.6 Peripheral devices 3.6.1 System Wire Arrangement please provide power Power specified in manual Molded case When power ON there circuit breaker might be huge inrush (MCCB) or Power current flows to inverter. earth leakage Refer to chapter 3.6.2 for current model selection.
- Page 26 Peripheral devices 3.6.2 No-fuse breaker and magnetic contactor Applicable no-fuse switch Applicable electromagnetic Inverter model Motor capacity Power source capacity (NFB/MCCB) type contactor (MC) type (Shihlin Electric) (Shihlin Electric) SC3-043-0.4K 440V 0.5HP 1.5kVA BM30SN3P3A S-P11 SC3-043-0.75K 440V 1HP 2.5kVA BM30SN3P5A S-P11 SC3-043-1.5K...
- Page 27 Peripheral devices 3.6.3 Regeneration brake resistor brake resistor Max. braking torque limit (10%ED,125%braking torque) Applicable Voltage motor (kW) Min. resistance Max. braking current Max. peak power Equivalent resistor specs (Ω) (kW) 150W 100Ω 220W 68.2Ω 220W 68.2Ω 370W 40.5Ω 220W 272.8Ω 370W 162.2Ω...
- Page 28 Terminal wire arrangement 3.7 Terminal wire arrangement ON:Defaut Screw OFF:Remove Screw SINK SOURCE Note: 1. SC3-043-0.4K~1.5K,SC3-023-0.2K~1.5K,SC3-021-0.2K~0.75K without +/P 、PR and N terminals; SC3-043-2.2K~5.5K,SC3-023-2.2K~3.7K,SC3-021-1.5K~2.2K without N terminals. 2.All series includes built-in RFI filters, in order to comply with CE regulations, please refer to related parts in this manual .
- Page 29 Terminal wire arrangement 3.7.1 Main circuit Terminals Description Main circuit terminals description R/L1-S/L2-T/L3 Connect to commercial power supply U/T1-V/T2-W/T3 Connect to three-phase induction motor. (+/P)-PR Connect to braking resistor (frame B built-in braking unit) Connect to ground Note: There’s no "+/P" and "PR" terminals in Frame A (no built-in braking unit). Terminal layout of the main circuit terminals ...
- Page 30 SC3-023-1.5K SC3-021-1.5K SC3-043-2.2K SC3-021-2.2K SC3-023-2.2K SC3-043-3.7K SC3-043-5.5K SC3-023-3.7K SC3-043-7.5K/11KF 9.5~10.5 SC3-043-11K/15KF SC3-043-15K/18.5KF 19~20 SC3-043-18.5K/22KF SC3-043-22K Note:1. Do not connect power wire to motor terminals (U/T1)(V/T2)(W/T3) on inverter, otherwise it will cause damage. 2. Do not add phase capacitor, surge absorber or magnetic contactor on the output side of the inverter.
- Page 31 Terminal wire arrangement 3.7.3 Ground For safety and to reduce noise, the grounding of the inverter must be well grounded. To avoid electric shocks and fire accident, the external metal ground wire of the equipment should be short and thick, and should be connected to specific grounding terminals on the inverter.
- Page 32 Terminal wire arrangement 3.7.5 Control circuit Control terminal name Terminal type Terminal name Function instructions Terminal specifications Input impedance:4.7 kΩ These 4 are multi-function control Digital signal Action current :5mA( when 24VDC) terminals, can switch between input Voltage range:10~28VDC SINK/SOURCE.
- Page 33 Terminal wire arrangement Inverter Inverter Sink input: Digital input control Sink input: Digital input control terminal connect terminal connect to SD directly to open collector PLC directly Inverter Sink input: Digital input control terminal connect to open collector PLC with exterior power supply If "Source Input”...
- Page 34 Terminal wire arrangement Inverter Source Input: Digital input control terminal connect to open emitter PLC with exterior power supply Arrangement of control terminal Wires connection For the control circuit wiring, strip off the sheath of a cable, and use it with a blade terminal. For a single wire, strip off the sheath of the wire and apply directly.
- Page 35 Terminal wire arrangement Note:1. Please Use a small flathead screwdriver (tip thickness: 0.6mm, width: 3.0mm). If a flathead screwdriver with a narrow tip is used, terminal block maybe damaged. 2. Tightening torque is 3.2~4.8 kgf.cm, too large tightening torque can cause screw slippage, too little tightening torque can cause a short circuit or malfunction.
- Page 36 Replacement procedure of fan 3.8 Replacement procedure of fan 3.8.1 Frame A/B 1. Press the hooks on both sides of the fan cover to 2. After disconnecting the fan connector, take out the fan, remove the fan cover, as shown in the figure below. as shown in the figure below.
- Page 37 Component name of keypad 4. BASIC OPERATION 4.1 Component name of keypad Operation parts Name Content PU: On when in PU/JOG operation mode, flickers in H1~H5 operation Operation mode indicator mode. Keypad status indicator MON:On to indicate keypad is in monitoring mode RUN indicator Flickers when running.
- Page 38 Operation modes of inverter 4.2 Operation modes of inverter Operation modes are related to signal source for the target frequency and signal source for motor starting. In Shihlin SC3 inverter there are nine kinds of operation modes: “PU mode( )”, “JOG mode( )”, “External mode(...
- Page 39 Operation modes of inverter 4.2.1 Flow chart for switching operation mode Note: 1. In “PU mode”, keypad screen displays and the indicator in will light up. 2. In “External mode”, keypad screen displays 3. In “Combined mode 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5”, the indicator in will flicker.
- Page 40 Operation modes of inverter 4.2.3 Operation flow chart for monitoring mode ●Take PU mode as an example: Note: 1. In “monitoring output frequency” mode, indicator in will light up, and the screen will display current output frequency. 2. In “monitoring optional value” mode, indicator in will light up, and the screen will display current optional value.
- Page 41 Operation modes of inverter 4.2.5 Operation flow chart for parameter setting Flicker Flicker Flicker Flicker 0 0- 0 0 0 0- 0 0 0 1- 0 0 0 1- 0 0 1 0- 0 0 0 1- 0 0 0 1- 1 0 0 1- 0 2 Flicker 0 1- 0 2...
- Page 42 Basic operation steps for different modes 4.3 Basic operation steps for different modes 4.3.1 Basic operation steps for PU mode(00-16(P.79)=0 or 1) Step Description • Switch operation mode to PU mode, and indicator in will light up. Note: 1. When 00-16(P.79) =0, the inverter will first be in external mode after power on or reset. 2.
- Page 43 Basic operation steps for different modes 4.3.3 Basic operation steps for JOG mode (00-16(P.79)=0 or 1) Step Description • Switch operation mode to JOG mode and indicator in will light up, the display shows Note: 1. For detailed operating procedures for the monitor mode, please refer to section 4.2 Operation modes of inverter. •...
- Page 44 Basic operation steps for different modes 4.3.6 Basic operation steps for combined mode 2 (00-16(P.79)=5) Step Description • In Combined Mode 2, indicator in will light up. Note: For selecting and switching the operation mode, please refer to section 4.2 Operation modes of inverter. •...
- Page 45 Basic operation steps for different modes 4.3.8 Basic operation steps for combined mode 4(00-16(P.79)=7) Step Description • In Combined Mode 4, indicator in will flicker. Note: 1. For detailed operation procedures for monitor mode, please refer to Section 4.2. Default priority from high to low: •...
- Page 46 Operation 4.4 Operation 4.4.1 Check and preparation before running Before running, the following shall be checked: 1. Check if the wiring is correct. Inverter output terminals (U/T1, V/T2, W/T3) cannot be connected to the power. Confirm that grounding terminal ( ) is well grounded.
- Page 47 Test run 4.4.3 Test run Check cables and abnormalities before the test run. After power on, the inverter is in external mode. 1. After power on, make sure no alarm on built-in keypad, make sure indicator is on. 2. Connect a switch between STF/SD and STR/SD. 3.
- Page 48 System parameter group 00 5. PARAMETER DESCRIPTION 5.1 System parameter group 00 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 00-00 P.90 Inverter model Read only 00-01 P.188 Firmware version Read only 0: Off 1: Clear alarm history (P.996=1) P.996 2: Reset inverter (P.997=1) Parameter 00-02...
- Page 49 System parameter group 00 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: Output AC voltage (V) 1: DC bus voltage. (V) 2: Inverter temperature rising accumulation rate (%) 3: Target pressure of the constant pressure system (%) 4: Feedback pressure of the constant pressure system (%) 5: Running frequency (Hz) 6: Electronic thermal accumulation rate (%) 7:Reserved...
- Page 50 System parameter group 00 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: Off 1: When 00-11(P.72)<5,Soft-PWM is on(only apply to V/F control) Soft-PWM carrier 00-12 P.31 2:When 00-11(P.72)>9, if the IGBT temperature is higher function selection than 60°c, carrier frequency will decrease automatically, when temperature go back to under 40°c, carrier frequency go back to 00-11(P.72) value 0: Idling brake...
- Page 51 System parameter group 00 5.1.1 Inverter information For checking inverter model, control board firmware version, etc. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 00-00 Inverter model Read only Read only P.90 00-01 Firmware version Read only Read only Inverter control board firmware version P.188 Inverter model ...
- Page 52 System parameter group 00 5.1.2 Parameter restoration Set parameters back to default. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Clear alarm history (P.996=1) Reset inverter (P.997=1) Parameter 00-02 Restore all parameters to default (P.998=1) restoration Restore some parameters to default 1 (P.999=1) Restore some parameters to default 2 (P.999=2) Restore some parameters to default 3 (P.999=3) Setting...
- Page 53 System parameter group 00 Group Name 00-21 P.300 Motor control mode selection 02-25 P.198 Terminal 3-5 minimum input current/ voltage 02-26 P.199 Terminal 3-5 maximum input current/ voltage 02-27 P.196 Percentage corresponds to terminal 3-5 minimum input current/ voltage 02-28 P.197 Percentage corresponds to terminal 3-5 maximum input current/ voltage 02-61...
- Page 54 System parameter group 00 5.1.3 Parameter protection It is used to select whether parameters can be written to prevent changing parameter values due to misoperation. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Parameters can be written only when the motor stops. Selection of Parameters cannot be written.
- Page 55 System parameter group 00 Most parameters cannot be written. (00-03(P.77)=“1”) Exception Parameters below can be written: Group Name 00-03 P.77 Selection of parameters write protection 00-16 P.79 Operation mode selection When running, most parameters can be written.(00-03(P.77)=“2” ) Exception When running, the parameters below cannot be written: Group...
- Page 56 System parameter group 00 Password all clear 1. Write the correct password in 00-04(P.294) to unlock the password protection; 2. Write 0 in 00-05(P.295), password will be all cleared. Note: If password is forgotten, enter the same incorrect password three times in 00-04(P.294), and the interval between two consecutive times is not more than 10s.
- Page 57 System parameter group 00 Note: 1. The “output frequency” here is the value after slip compensation. 2. The multi-function display function is implemented in the monitor voltage mode. For switching to monitor voltage mode, refer to section 4.2.3. 3. Digital terminal input state detail 4.
- Page 58 System parameter group 00 5.1.6 Built-in keypad set target frequency selection Select different frequency setting mode of the built-in keypad. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Use wheel on built-in keypad or external keypad to set XXX0 frequency XXX1 Use keypad knob on external keypad to set frequency X0XX Frequency change done and setting saves in 30 seconds...
- Page 59 System parameter group 00 5.1.7 PWM carrier frequency The motor sound can be changed by adjusting PWM carrier frequency properly. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 1~15kHz 11K/15KF and below mode 00-11 Carrier 5kHz 1~15 15K/18.5KF and above Heavy Duty P.72 frequency 1~10...
- Page 60 System parameter group 00 5.1.8 Stop operation selection Select the inverter stop method Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Idling brake 00-13 Idling brake / DC P.71 brake DC brake Press button and inverter stop running in PU and 00-14 function H2(combine mode 2) mode...
- Page 61 System parameter group 00 5.1.9 Forward/reverse rotate prevent function Set this parameter to limit the motor rotation to only one direction, and prevent reverse rotation fault resulting from the incorrect input of the start signal. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Forward/reverse rotation are both permitted.
- Page 62 System parameter group 00 5.1.11 Motor control mode selection Choose control mode for the AC motor Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 00-21 Motor control mode Induction motor V/F control P.300 selection Induction motor simple vector control Setting Motor control mode Induction motor V/F control: user can design proportion of V/F as required and can control multiple motors ...
- Page 63 System parameter group 00 5.1.13 50/60Hz switch selection Select between 50Hz or 60Hz according to different power source frequency or default motor frequency, this effects all frequency-related parameters. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Frequency related parameter default value is 60Hz. 00-24 50Hz/60Hz Frequency related parameter default value is 50Hz.
- Page 64 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2 Basic Parameter Group 01 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 01-00 Maximum frequency 0.00~01-02(P.18)Hz 120.00Hz 01-01 Minimum frequency 0~120.00Hz 0.00Hz High-speed maximum 01-02 P.18 01-00(P.1)~650.00Hz 120.00Hz frequency 50Hz system setting: 0~650.00Hz 50.00Hz 01-03 Base frequency 60Hz system setting: 0~650.00Hz 60.00Hz...
- Page 65 Basic Parameter Group 01 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0~650.00Hz 01-18 P.93 Frequency jump 2A 99999 99999:Off 0~650.00Hz 01-19 P.94 Frequency jump 2B 99999 99999:Off 0~650.00Hz 01-20 P.95 Frequency jump 3A 99999 99999:Off 0~650.00Hz 01-21 P.96 Frequency jump 3B 99999 99999:Off 0~360.00s/0~3600.0s...
- Page 66 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.1 Limiting the output frequency Output frequency can be limited. Fix the output frequency at the upper and lower limits. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 01-00 0.00~01-02 Maximum frequency 120.00Hz (P.18)Hz 01-01 Minimum frequency 0.00Hz 0~120.00Hz Output minimum frequency...
- Page 67 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.2 Base frequency, base voltage Use this function to adjust the inverter outputs (voltage, frequency) to match with the motor rating. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 01-03 50.00Hz 50Hz system(00-24(P.189)=1) Base frequency 0.00~650.00Hz 60.00Hz 60Hz system(00-24(P.189)=0)...
- Page 68 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.3 Acceleration/deceleration time setting Use this function to set motor acceleration/deceleration time. Setting Parameter Name Default Content Range Linear acceleration /deceleration curve 01-05 Acceleration/ deceleration S shape acceleration /deceleration curve 1 (Note 1) P.29 curve selection S shape acceleration /deceleration curve 2 (Note 2) S shape acceleration /deceleration curve 3 (Note 3) 5.00s...
- Page 69 Basic Parameter Group 01 S shape acceleration /deceleration curve 2(01-05(P.29)=2) An acceleration slope is formed by the combination of 01-06(P.7) and 01-09(P.20). A deceleration slope is formed by the combination of 01-07(P.8) and 01-09(P.20). When the target frequency varies, the acceleration increases S-shape according to the “acceleration slope”. The deceleration decreases S-shape according to the “deceleration slope”.
- Page 70 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.4 Torque boost V/F For an inverter controlled by V/F mode, when the motor starts up, the starting torque is usually insufficient since the output voltage of the inverter is low. In this case, the output voltage can be elevated by setting the torque boost 01-10(P.0) properly, and thus getting a better starting torque.
- Page 71 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.6 Load pattern selection V/F In V/F control, you can choose the best output characteristics for different applications and load. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content For constant torque loads (conveyor belt, etc.) For variable torque loads (fans and pumps, etc.) 01-12 Load pattern...
- Page 72 Basic Parameter Group 01 01-12(P.14)=4 01-12(P.14)=5 01-04 (P.19) 100% 01-35 (P.169) 01-33 (P.167) 01-31 (P.165) 01-29 01-10 (P.163) (P.0) 01-27 (P.99) Output frequency 01-10 01-34(P.168) (P.0) Output frequency (Hz) (Hz) 01-03 01-30(P.164) 01-26(P.98) 01-03(P.3) 01-28(P.162) 01-32(P.166) (P.3) Determine whether the curve is high starting torque or decreasing torque according to the value of the parameter set in the figure (Note When 01-12(P.14)=5, the value of A is 7.1% (Note 2) 01-12(P.14)=6,7,8...
- Page 73 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.7 JOG run The frequency and acceleration/deceleration time for JOG running can be set. JOG can be used for conveyor positioning, test run, etc. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 01-13 JOG frequency 5.00Hz 0~650.00Hz P.15 01-14 0~360.00s/...
- Page 74 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.8 Output frequency filter time This filter can reduce the impact when switching the frequency between high and low, and thus reduce the vibration of machine Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 01-15 Output frequency filter 0~31 P.28 time...
- Page 75 Basic Parameter Group 01 For example: assuming 01-16(P.91)=45 and 01-17(P.92)=50; If the target frequency ≤ 45Hz, then the steady output frequency = the target frequency. If 45Hz ≤ target frequency < 50Hz, then the steady output frequency = 45Hz. If the target frequency ≥...
- Page 76 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.10 Second function When given RT signal, these parameters will work. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 0~360.00s/0~3600.0s 01-08(P.21)=0 / 01-08(P.21)=1 01-22 Second acceleration 99999 P.44 time 99999 01-23 Second deceleration 0~360.00s/0~3600.0s 01-08(P.21)=0 / 01-08(P.21)=1 99999 P.45 time...
- Page 77 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.11 Middle frequency, output voltage of middle frequency V/F Parameters can be set when using special motors, especially to adjust motor torque. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 01-26 Middle frequency 1 3.00Hz 0~650.00Hz P.98 01-27 Output voltage 1 of 10.0%...
- Page 78 Basic Parameter Group 01 5.2.12 S pattern time It is used to set the acceleration time of S pattern acceleration/deceleration. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 01-36 S curve time at the beginning 0~25.00s/ 01-08(P.21)=0/ 0.20s P.255 of acceleration 0~250.0s 01-08(P.21)=1 0~25.00s/...
- Page 79 Basic Parameter Group 01 Example: when the parameters are in default value (60 Hz system), the actual acceleration time from stop state to 60Hz in accordance with S shape acceleration/deceleration curve 3 is as follows: 01-37 Acceleration/ (P.256) deceleration reference Frequency (01-09(P.20))...
- Page 80 Analog input and output parameter group 02 5.3 Analog input and output parameter group 02 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 02-06 P.185 Proportional linkage gain 0~100% 0: Off 2: Output frequency = basic frequency + auxiliary frequency (given by terminal 3-5) 02-07 P.240 Auxiliary frequency...
- Page 81 Analog input and output parameter group 02 5.3.1 Proportional linkage gain This function is used to multiply frequency command from external analog input terminal. When multiple inverters are running in proportion, it is effective to use this function to fine-tune the frequency command from master inverter to slave inverter.
- Page 82 Analog input and output parameter group 02 5.3.2 Auxiliary frequency Frequency can be adjusted and synthesized flexibly to meet the different control requirements in different scenarios. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Output frequency = basic frequency + auxiliary frequency (given by terminal 3-5) 02-07 Auxiliary frequency...
- Page 83 Analog input and output parameter group 02 Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 02-26 Terminal 3-5 maximum 10.00V 0~20.00mA/V P.199 input current/ voltage Percentage corresponds 02-27 to terminal 3-5 minimum 0.0% 0%~100.0% P.196 input current/ voltage Percentage corresponds 02-28 to terminal 3-5 maximum 100.0% 0%~100.0% P.197...
- Page 84 Analog input and output parameter group 02 02-28 (P.197) 02-27 (P.196) Terminal 3-5 signal B value A value Example 1.2: Set 02-27(P.196) and 02-28(P.197) value, then set 02-25(P.198) and 02-26(P.199). Figure is shown as follows: 02-28 (P.197) 02-27 (P.196) Terminal 3-5 signal 02-25 02-26 (P.198)...
- Page 85 Analog input and output parameter group 02 Example 2: This example is for users who need the motor to run at 10Hz when the potentiometer is turned to the left end. All frequencies above 10Hz can still be adjusted by the user freely. Max operation Parameter setting frequency...
- Page 86 Analog input and output parameter group 02 Max operation frequency Parameter setting : 60Hz 02-21(P.39) = 60.00Hz Max operation frequency 02-20(P.17) = 1 Select voltage signal 02-61( P.141) = 0 02-25(P.198)=1V,02-26( P.199) =10V Terminal 3-5 max/min positive voltage 02-27(P.196)=0%, 02-28(P.197) =100% Percentage corresponds to terminal 3-5 input voltage Voltage...
- Page 87 Analog input and output parameter group 02 Terminal 3-5 disconnect function If 02-24(P.184) = 0, after disconnection, inverter will slow down to 0Hz, and after reconnection, the inverter will accelerate to current given frequency. If 02-24(P.184) =1 after disconnection, the keypad will display “AErr” alarm, inverter will slow down to 0Hz and at the same time multi-function digital output terminal will set off an alarm;...
- Page 88 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 5.4 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: STF(Inverter runs forward) 1: STR(Inverter runs reverse) 2: RL(Multi-speed low speed) 3: RM(Multi-speed medium speed) 4: RH(Multi-speed high speed) 5: Reserved 6: External thermal relay actuate 7: MRS(Stops inverter output immediately)
- Page 89 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 37~38:Reserved 39: STF/STR +STOP (Use with RUN signal, when ON, motor runs reverse, when OFF, motor stops then runs forward.) 40: P_MRS (Stops inverter output immediately by pulse signal input) 41~42:Reserved Terminal...
- Page 90 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number Digital input terminal filter 03-17 P.157 0~2000 time 0: When power on digital terminals work directly Digital input terminal enable 03-18 P.158 1: When power on digital terminals work after when power on switch off then on Output frequency detection...
- Page 91 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 5.4.1 Digital input terminals function selection Use the following parameters to change the digital input terminal functions. Each terminal may choose any function between 0~45 (Note 1) Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content STF(Inverter runs forward) STR(Inverter runs reverse) RL(Multi-speed low speed)
- Page 92 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content STF/STR +STOP (Use with RUN signal, when ON, motor runs reverse, when OFF, motor stops then runs forward.) P_MRS (Stops inverter output immediately by pulse signal input) 41~42 Reserved 03-00 Terminal STF...
- Page 93 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 Two-wire control mode 2: command RUN(03-0X(P.8X)=28) Stop STF/STR(03-0X(P.8X)=29) Stop Forward Reverse Three-wire control mode 1 (with seal-in function): K0 is STOP, normal close. When trigger inverter will stop. K1 is forward and K2 is reverse, normal open. All K0 K1 K2 are edge trigger button. STF(03-0X(P.8X)=0) STR(03-0X(P.8X)=1) STOP(03-0X(P.8X)=31)
- Page 94 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 Set value : 45 Second frequency source mode When this terminal is on, target frequency is set by 00-17(P.97). Fire mode command 1(RUN command included) When in fire mode(06-84(P.207) = XXX1 or XXX2), if the terminal with related function is ON, the inverter goes into fire mode and starts compulsorily.
- Page 95 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 5.4.2 Digital output terminals function selection Detect some information that occurs during the operation of the inverter. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content RUN(Output when inverter running): Output signal when inverter run above starting frequency SU(Output when reach target frequency): Output signal when the output frequency reaches target frequency FU(Output when reach certain frequency): Output signal...
- Page 96 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 5.4.3 Terminal logic selection The function is bits-setting, if the bit shows 1, it means that the action of multi-function digital input terminal is negative logic; otherwise, it means that the action is positive logic. Parameter Name Default...
- Page 97 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 5.4.4 Digital output signal delay This parameter is used to delay and confirm the digital output signal. Delay time acts like confirmation time, which can prevent some unknown interference. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 03-16 Output signal delay...
- Page 98 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 5.4.6 Digital input terminal enable when power on Choose when power on if digital input terminal operates immediately. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content When power on digital terminals work directly 03-18 Digital input terminal When power on digital terminals work after switch off...
- Page 99 Digital input/ output parameter group 03 If 03-21(P.42)=30 and 03-22(P.43)=20, FU signal will output when forward rotation frequency exceeds 30Hz; and when reverse rotation frequency exceeds 20Hz, FU signal will also be output. If 03-21(P.42)=30 and 03-22(P.43)=99999 (default), FU signal will output when forward and reverse rotation ...
- Page 100 Multi-speed parameter group 04 5.5 Multi-speed parameter group 04 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 04-00 Speed 1 (high speed) 0~650.00Hz 60.00Hz 04-01 Speed 2 (medium speed) 0~650.00Hz 30.00Hz 04-02 Speed 3 (low speed) 0~650.00Hz 10.00Hz 0~650.00Hz 04-03 P.24 Speed 4 99999...
- Page 101 Multi-speed parameter group 04 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number Programmed operation mode 04-27 P.101 0~6000.0s 0.0s speed 1 operating time Programmed operation mode 04-28 P.102 0~6000.0s 0.0s speed 2 operating time Programmed operation mode 04-29 P.103 0~6000.0s 0.0s speed 3 operating time Programmed operation mode...
- Page 102 Multi-speed parameter group 04 5.5.1 16 steps speed With the combination of digital input terminal RL, RM, RH and REX, 16 steps speed can be selected (up to 16 speeds) Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 04-00 Speed 1 (high speed) 60.00Hz 0~650.00Hz 04-01...
- Page 103 Multi-speed parameter group 04 Speed Speed Speed (High speed) speed1 Speed Speed Speed Speed speed (Medium Speed speed) Speed 2 Speed Speed (Low speed) Speed 3 Speed Speed Time ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON ON When one of parameters 04-03~04-06(P.24~P.27), 04-08~04-14(P.143~P.149) value is 99999, the target ...
- Page 104 Multi-speed parameter group 04 5.5.2 Programmed operation mode The application of this parameter can be used as the operation process control for general small machinery, food processing machinery and washing equipment, which can replace some traditional relays, switches, timer and other control circuit, etc.
- Page 105 Multi-speed parameter group 04 Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 04-33 Programmed operation mode 0.0s 0~6000.0s P.107 speed 7 operating time 04-34 Programmed operation mode 0.0s 0~6000.0s P.108 speed 8 operating time 04-35 Programmed operation mode 0~600.00s/ 0.00s P.111 speed 1 Acc/Dec time 0~6000.0s 04-36 Programmed operation mode...
- Page 106 Multi-speed parameter group 04 When 04-16(P.121) is set to 0, there will be no cycle operation. When 04-17(P.122) is 1~8, it is the section that will cycle to after the first cycle. For example: When 04-17(P.122)=3, the cycle operation will start from speed 3 after the speed 1 to speed 8 operations have been completed.
- Page 107 Motor parameter group 05 5.6 Motor parameter group 05 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: Off 1: Induction motor specifications automatic measurement (Run motor to measure) Motor specifications 2: Induction motor specifications automatic 05-00 P.301 automatic measurement measurement (Don’t run motor to measure) 3: Induction motor specifications automatic measurement (Measure when operating)
- Page 108 Motor parameter group 05 Automatic induction motor parameters measurement includes the following steps: Check wiring (refer to 3.7 Terminal wire arrangement) Motor specs Setting (05-05(P.302)~05- 06(P.307)) 05-00(P.301) parameter setting? 1 、2 Press FWD/REV button, start tuning, keypad screen shows “TUN” Success? Failed, keypad screen Success, keypad screen...
- Page 109 Motor parameter group 05 5.6.2 Motor parameter Inverter has built-in standard parameters for motor. Modify the default values according to the actual situation to conform to the actual values as much as possible. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 05-01 Motor rated power 0.00kW...
- Page 110 Protection parameter group 06 5.7 Protection parameter group 06 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 06-00 Electronic thermal relay capacity 0~500.00A 0.00A 06-01 P.22 Stall prevention operation level 0~250.0% 150.0% 0~200.0% Stall prevention operation level 06-02 P.23 99999: Stall prevention operation level is the 99999 correction factor setting value of 06-01(P.22).
- Page 111 Protection parameter group 06 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number Total inverter operation time 0~1439 min 06-27 P.292 0min (minutes) Total inverter operation time 06-28 P.293 0~9999 day 0day (days) Total inverter power on time 06-29 P.296 0~1439 min 0min (minutes) 06-30...
- Page 112 Protection parameter group 06 5.7.1 Electronic thermal relay capacity “Electronic thermal relay” uses inverter computing power to simulate a thermal relay for preventing motor from overheating. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 06-00 Electronic thermal 0.00A 0~500.00A relay capacity Setting Electronic thermal relay capacity Please set the value of 06-00(P.9) as the rated current value of the motor at the rated frequency.
- Page 113 Protection parameter group 06 5.7.2 Current stalling protection In order to avoid the alarm and stop of the inverter due to overcurrent and overvoltage, the output current is monitored to automatically change the output frequency. It can realize stall prevention during acceleration and deceleration process or during electric regeneration, and make high response current limit valid.
- Page 114 Protection parameter group 06 5.7.3 Regenerative brake When performing frequent start and stop operation, regenerative brake usage rate can be increased by using the brake resistor or the brake unit. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 06-05 Regenerative brake Brake duty is fixed at 3%, parameter 06-06(P.70) will be off.
- Page 115 Protection parameter group 06 5.7.4 Over torque detection Output current detection function can be used for over torque detection. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 06-08 Over torque No over torque detection. 0.0% P.155 detection level 0.1~200% Over torque detection. 06-09 Over torque 1.0s...
- Page 116 Protection parameter group 06 5.7.5 Cooling fan working mode Control the start and stop conditions of the fan and the alarm output mode through parameter settings. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content When running turn on the fan, after stop for 30 seconds turn off the fan.
- Page 117 Protection parameter group 06 5.7.8 Input phase loss protection Turn on input phase failure protection Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 06-13 Input phase loss When input phase loss, built-in keypad shows IPF alarm and P.281 protection inverter stops Setting Input phase loss protection When 06-13(P.281)=1, input phase loss protection is on;...
- Page 118 Protection parameter group 06 5.7.10 Alarm query function This function provides users with information about latest 12 alarm codes. Setting Parameter Name Default Content Range 06-40 Alarm record code 0~12 P.288 query 06-40 (P.288) value 1~12 corresponds to 06-41(P.289)’s alarm E1~E12.
- Page 119 Protection parameter group 06 5.7.11 Fire mode Fire mode applies to the field of fire control Parameter Name Default Value Setting Range Content Invalid:Fire mode is forbidden( normal mode) XXX0 XXX1 Forward operation:The inverter runs forward in fire mode XXX2 Reverse operation:The inverter runs reversely in fire mode Manually exit fire mode 1:If the start fire mode terminal is...
- Page 120 Protection parameter group 06 5.When in fire mode, the inverter does not execute PID function. Any operating PID function is invalid automatically. 6.When in fire mode, the inverter does not execute the starting DC brake function. Any operating DC brake is invalid automatically when in fire mode.
- Page 121 Communication parameter group 07 5.8 Communication parameter group 07 Parameter Group Name Setting range Default Page number Communication protocol 0:Modbus protocol 07-00 P.33 selection 1:Shihlin protocol Inverter communication 07-01 P.36 0~254 station number 0:baud rate :4800bps 1:baud rate :9600bps 2:baud rate :19200bps Serial communication baud 07-02 P.32...
- Page 122 Communication parameter group 07 5.8.1 Shihlin protocol and Modbus protocol These protocols can link and communicate with upper controller through RS485 communication port of inverter for parameter setting, monitoring, etc. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 07-00 Communication Modbus protocol P.33 protocol selection Shihlin protocol...
- Page 123 Communication parameter group 07 Note:1. Maximum inverter connect number is determined by wiring method and impedance matching. Please set station number value to non-zero when using Modbus protocol. 2. If communication error times exceed set value of 07-08(P.52), and 07-10(P.153) is set to 0, OPT alarm will trigger.
- Page 124 Communication parameter group 07 Upper Data read out controller ② ① Inverter ⑤ Time ③ Inverter ④ Upper Data write in controller Please refer to the following table for descriptions of communication actions and communication data format type in the above steps: Frequency Parameter...
- Page 125 Communication parameter group 07 *1) Control code Signal ASCII code Content Signal ASCII Code Content NULL Acknowledge Start of Text Line Feed End of Text Carriage Return Enquiry Negative Acknowledge *2) Waiting time set from 0 to 15 with 10ms unit. Example: set value 5 --->50ms. *3) End symbol (CR, LF codes) When performing data communication from upper controller to inverter, CR and LF codes at the end of message will be automatically set according to upper controller mode.
- Page 126 Communication parameter group 07 Inverter station Code Data Check code Waiting time number 0 H0000 Sum Check H30 H30 H46 H41 H30 H30 H30 H30 H44 H37 Step 2: After receive and processing the data without error, inverter will send reply to upper controller in Format C: Inverter station number 0 H30 H30 Example 3.
- Page 127 Communication parameter group 07 Example 5. Write 600 into 01-28(P.162) (this parameter range is set from 0 to 599.00) Step 1~2 are the same as Step 1~2 of Example 3; Step 3: Upper controller requests inverter to write 600 in 01-28(P.162) in Format A: Inverter station Reference Data...
- Page 128 Communication parameter group 07 Message compensation: Format Start Function Data Error check Stop ① Address ② ③ ④ ASCII 0D 0A 8bit 8bit n×8bit 2×8bit >=10ms >=10ms Message Content Setting range: 0~254. 0 is for broadcast address, 1~254 for slave device (inverter) address. ①Address 07-01(P.36)is used to set the Slave device address when Master device sends information to the Slave information group...
- Page 129 Communication parameter group 07 Communication format: Data readout(H03) Mode Start Address*1) Function*2) Start address*3) Number of register*4) Check Stop ASCII 2char 2char 4char 4char 2char 0D 0A >=10ms 8bit 8bit 2byte 2byte 2byte >=10ms Normal response Mode Start Address*1) Function*2)...
- Page 130 Communication parameter group 07 Normal response Mode Start Address*1) Function*2) Start Address*3) Number of register *4) Check Stop ASCII 2char 2char 4char 4char 2char 0D 0A >=10ms 8bit 8bit 2byte 2byte 2byte >=10ms Message Content *1)Address Set the address for sending information *2)Function code *3)Start address Set as the start address for the register that needs to be written...
- Page 131 Communication parameter group 07 Message Content *1) Address Set the address for sending information *2) Function code Function code set by Master+H80 *3)Error code Set code in the following table Error code list: Source Code Meaning Remarks In query data sent by Master, the function code cannot be processed by slave illegal function code device.
- Page 132 Communication parameter group 07 Step 2: After receive and processing the data without error, inverter will send 01-28(P.162) to upper controller. Mode Start Address Function Number of data read Read data Check Stop ASCII H30 H31 H30 H33 H30 H32 H46 H46 H46 H46 H46 H43...
- Page 133 Communication parameter group 07 Communication command list Set the following command codes and data to perform various operation control, monitoring, etc. Shihlin protocol Modbus Modbus Item Data content and function description command code command code address H0000: Communication mode; Operation mode H0001: External mode;...
- Page 134 Communication parameter group 07 Shihlin protocol Modbus Modbus Item Data content and function description command code command code address Parameter 1.Please refer to the parameter table for data range H00~H63 and decimal point position read-out 2.Modbus address of each parameter in P P mode: parameter mode corresponds to hexadecimal value H0000~H018F...
- Page 135 Communication parameter group 07 Shihlin Modbus protocol Modbus Item Data content and function description command command address code code P parameter mode: H0000:P.0~P.99; H0001:P.100~P.199; Read H0002:P.200~P.299; Page H0003:P.300~P.399; change for Parameter group mode: parameter H0064:00-00~00-99; H006B:07-00~07-99 reading H0065:01-00~01-99; H006C:08-00~08-99 and writing H0066:02-00~02-99;...
- Page 136 Communication parameter group 07 Table for parameter recovery Data P parameter Communication p Table 1 Table 2 User registered Other P Error content operation parameter (Note 1) (Note 2) (Note 2) parameter parameter code H5A5A 00-02=4(P.999=1) o(Note 3) x(Note 4) H5566 00-02=5(P.999=2) H5959...
- Page 137 Communication parameter group 07 5.8.2 Communication EEPROM write selection Use this function if parameter settings are frequently written by communication Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content When writing parameters in communication mode, write in Communication 07-11 RAM and EEPROM EEPROM write-in P.34 When writing parameters through communication, only...
- Page 138 PID parameter group 08 5.9 PID parameter group 08 Parameter Group Name Setting range Default Page number 0: Off 2: Parameter 08-03(P.225) as target value, terminal 3-5 08-00 P.170 PID function selection current/voltage input as feedback source 3:Target value is set by multi-speed value, and feedback from terminal 3-5 current/voltage input PID feedback control 0: Negative feedback control.
- Page 139 PID parameter group 08 5.9.1 PID function selection Inverter can control flow, volume or pressure by PID control. By using parameter setting as target source, and with analog signal as feedback source, it forms a closed loop control system. Parameter Name Default...
- Page 140 PID parameter group 08 Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 08-10 Sleep detection 0.0% 0~100.0% P.178 deviation 08-11 Sleep detection 1.0s 0~255.0s P.179 duration time 08-12 Wake-up level 90.0% 0~200.0% P.180 08-13 Stop level 0~120.00Hz 40.00Hz P.181 When the deviation value accumulated by 50Hz 50.00Hz integral time, need to set an upper limit for...
- Page 141 PID parameter group 08 Needs to calibrate the feedback signal Adjust the feedback signal to a certain value, calculate the ratio of this value to the feedback range, and then write this ratio value to 08-18 (P.223); Re-adjust the feedback signal to another value and calculate the ratio of this value to the feedback range, and then write this ratio value to 08-19 (P.224).
- Page 142 PID parameter group 08 Example: 08-10(P.178)=5%, 08-11(P.179)=1.0s, 08-12(P.180)=90%, 08-13(P.181)=40Hz, 08 -15(P.183)=0.5Hz. When the feedback value is greater than 95% of the target feedback value and less than 105% of the target feedback value, it is in stable zone. In the stable zone, inverter reduces the output frequency based on 0.5 Hz per second.
- Page 143 PID parameter group 08 5.9.3 PID pressure range setting Set the range of PID target and feedback. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 08-43 PID pressure range 100.0 1.0~100.0 Set the range of PID target and feedback P.251 (Bar) setting Setting PID pressure range The setting of the PID target value can be %, bar, Kg, etc.
- Page 144 Application parameter group 10 5.10 Application parameter group 10 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number DC brake operating 10-00 P.10 0~120.00Hz 3.00Hz frequency 10-01 P.11 DC brake operating time 0~60.0s 0.5s 4.0% 7.5K/11KF and below model:0~30.0% 10-02 P.12 DC brake operating voltage 2.0% 11K/15KF and above model:0~30.0%...
- Page 145 Application parameter group 10 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: Off. 10-13 P.67 Auto reset times 1~10: If the alarm exceeds 10-13(P.67) times, inverter will not reset. 10-14 P.68 Auto reset waiting time 0~360.0s 6.0s 10-15 P.69 Auto reset times count Read only Forward and reverse rotation...
- Page 146 Application parameter group 10 5.10.1 DC injection brake When stopping the motor, apply DC voltage on motor to stop motor shaft from rotating, users can adjust the DC brake time and braking torque. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 10-00 DC brake operating 3.00Hz...
- Page 147 Application parameter group 10 5.10.2 Zero-speed control Zero-speed function selection Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Off. 10-03 Zero-speed control P.151 function selection DC voltage braking 10-04 Voltage at zero-speed 5.0% 7.5K/11KF and below model 0~30.0% P.152 control 2.0% 11K/15KF and above model Setting Zero-speed control...
- Page 148 Application parameter group 10 5.10.4 Restart mode selection Select suitable start mode according to different load conditions. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content No frequency search. Reserved Decrease voltage mode 10-08 Restart mode Power on once. P.150 selection Start each time. Only instantaneous stop and restart Only valid when the inverter resets in fire mode 10-09...
- Page 149 Application parameter group 10 5.10.5 Remote setting function selection If operation box is located away from control cabinet, without analog signal, variable speed can still be realized through digital input. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Remote control function, frequency save in memory Remote control function, frequency won’t save Remote control function, frequency won’t save, clear 10-11...
- Page 150 Application parameter group 10 If 10-11 (P.61)=1~4, the target frequency of inverter = (frequency set during RH and RM operation + external set frequency other than multi-speed/PU set frequency); If 10-11 (P.61)=11~14, the target frequency of inverter = frequency set during RH and RM operation. Frequency save ...
- Page 151 Application parameter group 10 5.10.6 Auto reset function This function allows inverter to reset itself and restart when alarm occurs. Choose which alarm to reset. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Off. When over-voltage, inverter will reset. 10-12 Auto reset function When over-current, inverter will reset.
- Page 152 Application parameter group 10 5.10.7 Forward and reverse rotation dead time During the process of inverter output forward -reverse transition, set the transition time at 0Hz. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content Forward Off. 10-16 reverse rotation 0.0s P.119 Waiting and holding time during forward -reverse switch, dead time 0.1~3000.0s...
- Page 153 Application parameter group 10 5.10.9 Dwell function V/F During acceleration /deceleration, this function can solve the backlash problem caused by stopping acceleration /deceleration, through frequency and time set by this parameters. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content None. 10-18 Dwell function Backlash compensation function.
- Page 154 Application parameter group 10 Acceleration and deceleration interrupt waiting function(10-18(P.229)=2) When 10-18 (P.229) = 2, enable acceleration and deceleration interrupt waiting function. When accelerating to the frequency set in 10-19 (P.230), wait for the time set in 10-20 (P.231) before accelerating to the target; when decelerating to the frequency set in 10-21 (P.232), wait for the time set in 10-22 (P.233) before decelerating to the target.
- Page 155 Application parameter group 10 Setting Triangular wave function If 10-23(P.234) set to 1, triangular wave function will be on when terminal function TRI is triggered. Please set one of 03-00(P.83)~03-01(P.84), 03-03(P.80)~03-04(P.81) to “36”, and then give TRI signals to the digital input terminal.
- Page 156 Application parameter group 10 Setting eciprocating machine function Start button Stop button Left limit switch Right limit switch System wiring diagram Please wire according to the above diagram, connect a limit switch between M0 and SD, M1 and SD, and connect ...
- Page 157 Advanced parameter group 11 5.11 Advanced parameter group 11 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 11-00 P.320 Slip compensation gain 0~200% 11-01 P.321 Torque boost filter coefficient 0~2000 Cutoff frequency point of 11-02 P.322 0~30.00Hz 4.00Hz current filter time 1 According 11-03 P.323...
- Page 158 Special Adjustment Parameter Group 13 5.12 Special Adjustment Parameter Group 13 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 13-00 P.89 Slip compensation coefficient 0~10 High frequency vibration 0.2K~5.5K model:0~1515 13-03 P.286 suppression factor 7.5K/11KF and above: 0~1515 5.12.1 Slip Compensation V/F This parameter can set the compensation frequency so that the motor running speed at the rated current can be ...
- Page 159 User registered parameter 15 5.13 User registered parameter 15 Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 15-00 P.900 User registered parameter 1 99999 15-01 P.901 User registered parameter 2 99999 15-02 P.902 User registered parameter 3 99999 15-03 P.903 User registered parameter 4 99999 15-04...
- Page 160 User registered parameter 15 5.13.1 User registered parameter The user parameter group is used to register the number of the parameter that does not require the user to restore the factory default value. Parameter Name Default Setting Range Content 15-00 User registered parameter 1 99999...
- Page 161 User registered parameter 15 Setting User registered parameter The parameter values set in this parameter group will not be restored to the factory default value when performing 00-02=5/6(P.999=2/3) The parameter value set in this parameter group is the parameter number required to be registered by the user. ...
- Page 162 Inspection item 6. INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE 6.1 Inspection item 6.1.1 Daily inspection item Inverter is mainly composed of semiconductor components. In order to prevent faults caused by influence of environment such as temperature, humidity, dust and vibration, or aging and service life of used parts, users must do daily inspections 1.
- Page 163 Inspection item 6.1.3 Ways to measure voltage, current, power on main circuit When testing, please first remove the external wiring of the main circuit terminals (R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3), and measure by resistance mode of the meter. Positive Negative Normal situation...
- Page 164 Inspection item 6.1.5 Replacement parts Inverter is composed of many electronic components such as semiconductor components. Due to the composition or physical characteristics, the following components will age within a certain period of time, thus reducing the inverter performance and even causing faults. Therefore, it is necessary to replace them on a regular basis.
- Page 165 Ways to measure voltage, current, power on main circuit 6.2 Ways to measure voltage, current, power on main circuit 6.2.1 Selecting measurement instruments Since inverter voltage and current on input side and output side includes harmonics, measurement data result may ...
- Page 166 Ways to measure voltage, current, power on main circuit 6.2.5 Measurement of insulation resistance Inverter insulation resistance 1. Before measuring the inverter insulation resistance, first dismount the wiring of all the main-circuit terminals and control board. Then do the wiring as shown in the right picture 2.
- Page 167 Appendix 1 Parameter table 7. Appendix 7.1 Appendix 1 Parameter table 7.1.1 Parameter in P sequence Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0.75K and under :0~30.0% 6.0% 1.5K~3.7K model:0~30.0% 4.0% 01-10 Torque boost 5.5K~7.5K/11KF model:0~30.0% 3.0% 11K/15KF and above model:0~30.0% 2.0% 01-00 Maximum frequency...
- Page 168 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0~1000.0V P.19 01-04 Base voltage 99999 99999:Change according to the input voltage 50Hz system setting: 1.00~650.00Hz 50.00Hz Acceleration/deceleration P.20 01-09 reference frequency 60Hz system setting: 1.00~650.00Hz 60.00Hz Acceleration/deceleration 0: Time increment is 0.01s P.21 01-08...
- Page 169 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Setting Range Group Name Default Page Number 0: In communication mode, run signal and frequency Communication mode is given by communication. P.35 00-19 selection 1: In communication mode, run signal and frequency is given by external signal. Inverter communication P.36...
- Page 170 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number XXX0: Use wheel on built-in keypad or external keypad to set frequency XXX1: Use keypad knob on external keypad to set frequency X0XX: Frequency change done and setting saves in 30 seconds Built-in keypad set target P.59...
- Page 171 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number Special regenerative brake P.70 06-06 0~100.0% 0.0% duty 0: Idling brake P.71 00-13 Idling brake / DC brake 1: DC brake 11K/15KF and below model:1~15kHz P.72 00-11 Carrier frequency 15K/18.5KF and above Heavy Duty:1~15kHz 5kHz 15K/18.5KF and above Normal Duty:1~10kHz...
- Page 172 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 10:STF+EXJ 11:STR+EXJ 12:STF+RT 13:STR+RT 14:STF+RL 15:STR+RL 16:STF+RM 17:STR+RM 18:STF+RH 19:STR+RH 20:STF+RL+RM 21:STR+RL+RM 22:STF+RT+RL 23:STR+RT+RL 24:STF+RT+RM 25:STR+RT+RM 26:STF+RT+RL+RM 27:STR+RT+RL+RM 28: RUN(Inverter runs forward) 29: STF/STR(use with RUN signal, when ON, motor runs Terminal P.83 03-00...
- Page 173 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: RUN(Output when inverter running) 1: SU(Output when reach target frequency) 2: FU(Output when reach 03-21 03-22 value ) 3: OL(Output when overload) 4: OMD(Output when output current is zero) 5: ALARM(Output when alarm) 6: PO1(Output when in program operation step) 7: PO2(Output when in program operation cycle)
- Page 174 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number Programmed operation minute / 0: Select minute as the time increment. P.100 04-15 second selection 1: Select second as the time increment. Programmed operation mode P.101 04-27 0~6000.0s 0.0s speed 1 operating time Programmed operation mode...
- Page 175 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number Programmed operation mode speed 2 P.112 04-36 0~600.00s/0~6000.0s 0.00s Acc/Dec time Programmed operation mode speed 3 P.113 04-37 0~600.00s/0~6000.0s 0.00s Acc/Dec time Programmed operation mode speed 4 P.114 04-38 0~600.00s/0~6000.0s 0.00s...
- Page 176 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number X0:No frequency search. X1:Reserved X2:Decrease voltage mode P.150 10-08 Restart mode selection 0X:Power on once. 1X:Start each time. 2X:Only instantaneous stop and restart 3X: Only valid when the inverter resets in fire mode 0: Off.
- Page 177 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 11: Forward reverse rotation signal. Built-in keypad: Frd is forward,rEv is reverse,STOP is not operating status. External keypad:1 is forward , 2 is reverse, 0 is not operating status.. 12: NTC temperature (℃) P.161 00-07...
- Page 178 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number P.180 08-12 Wake-up level 0~200.0% 90.0% P.181 08-13 Stop level 0~120.00Hz 40.00Hz 50Hz system:0~120.00Hz 50.00Hz P.182 08-14 Upper integral limit 60Hz system:0~120.00Hz 60.00Hz Deceleration step length when P.183 08-15 0~10.00Hz 0.50Hz...
- Page 179 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number P.208 06-85 Frequency setting in fire mode 0~650.00Hz 60.00Hz Accumulated times in fire Read P.209 06-88 Read only mode only 0:Use default acc/dec time(same as regular Remote function acc/dec time mode)...
- Page 180 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: Off P.242 10-05 DC brake before inverter start 1: Before starting operate DC brake first. P.243 10-06 DC brake time before inverter start 0~60.0s 0.5s DC brake voltage before inverter 7.5K/11KF and below model:0~30.0% 4.0% P.244...
- Page 181 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number XX0:Off XX1:Detect leakage current of ground when inverter starts Short circuit to ground protection P.280 06-18 0X1:Detect leakage current of ground only function when start for the first startup 1X1:Detect leakage current of ground for every startup.
- Page 182 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number According 0~99.98Ω: P.309 05-08 IM motor stator resistance to kw P.320 11-00 Slip compensation gain 0~200% P.321 11-01 Torque boost filter coefficient 0~2000 Cutoff frequency point of current P.322 11-02 0~30.00Hz...
- Page 183 Appendix 1 Parameter table 7.1.2 Group mode Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 00-00 P.90 Inverter model Read only 00-01 P.188 Firmware version Read only 0: Off 1: Clear alarm history (P.996=1) 2: Reset inverter (P.997=1) P.996 Parameter 00-02 ~...
- Page 184 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 9: Output power (kW). 10:Reserved 11: Forward reverse rotation signal. Built-in keypad: Frd is forward,rEv is reverse,STOP is not operating status. External keypad:1 is forward , 2 is reverse, 0 is not operating Multi-function status..
- Page 185 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: Forward/reverse rotation are both permitted. Prevent 1: Prevent reverse rotation (Giving reverse signal 00-15 P.78 forward/reverse decelerates and stops the motor). rotation selection 2: Prevent forward rotation (Giving forward signal decelerates and stops the motor).
- Page 186 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: Linear acceleration /deceleration curve Acceleration/decelerati 1: S shape acceleration /deceleration curve 1 01-05 P.29 on curve selection 2: S shape acceleration /deceleration curve 2 3: S shape acceleration /deceleration curve 3 3.7K and below:0~360.00s/0~3600.0s 5.00s 5.5K model:0~360.00s/0~3600.0s...
- Page 187 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0~360.00s/0~3600.0s 01-23 P.45 Second deceleration time 99999 99999:Off 0~30.0% 01-24 P.46 Second torque boost 99999 99999:Off 0~650.00Hz 01-25 P.47 Second base frequency 99999 99999:Off 01-26 P.98 Middle frequency 1 0~650.00Hz 3.00Hz Output voltage 1 of middle...
- Page 188 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0: Signal sampling range from 4~20mA. Terminal signal 02-20 P.17 1: Signal sampling range from 0~10V. range selection 2: Signal sampling range from 0~5V. Terminal 3-5 maximum 50Hz system:1.00~650.00Hz 50.00Hz 02-21 P.39...
- Page 189 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 13:STR+RT 14:STF+RL 15:STR+RL 16:STF+RM 17:STR+RM 18:STF+RH 19:STR+RH 20:STF+RL+RM 21:STR+RL+RM 22:STF+RT+RL 23:STR+RT+RL 24:STF+RT+RM 25:STR+RT+RM 26:STF+RT+RL+RM 27:STR+RT+RL+RM 28: RUN(Inverter runs forward) 29: STF/STR(use with RUN signal, when ON, motor runs reverse; when OFF, motor runs forward) 30: RES(External reset function) 31: STOP(Use as three line control with RUN signal and Terminal STF input...
- Page 190 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number Terminal M0 input 03-03 P.80 Same as 03-00 function Terminal M1 input 03-04 P.81 Same as 03-00 function 0: RUN(Output when inverter running) 1: SU(Output when reach target frequency) 2: FU(Output when reach 03-21 03-22 value ) 3: OL(Output when overload) 4: OMD(Output when output current is zero)
- Page 191 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0.05~100.00s 03-24 P.63 Zero current detection time 0.50s 99999: Off 04-00 Speed 1 (high speed) 0~650.00Hz 60.00Hz 04-01 Speed 2 (medium speed) 0~650.00Hz 30.00Hz 04-02 Speed 3 (low speed) 0~650.00Hz 10.00Hz 0~650.00Hz...
- Page 192 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number Programmed operation mode 04-27 P.101 0~6000.0s 0.0s speed 1 operating time Programmed operation mode 04-28 P.102 0~6000.0s 0.0s speed 2 operating time Programmed operation mode 04-29 P.103 0~6000.0s 0.0s speed 3 operating time Programmed operation mode...
- Page 193 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Setting Range Default Page Group Name Number According 0~500.0A 05-05 P.306 Motor rated current to kw 50Hz system:0~65000r/min 1410r/min 05-06 P.307 Motor rated rotation speed 60Hz system:0~65000r/min 1710r/min According 0~500.00A 05-07 P.308 IM Motor excitation current to kw According 0~99.98Ω:...
- Page 194 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number XX0:Off XX1:Detect leakage current of ground when inverter starts Short circuit to ground protection 06-18 P.280 0X1:Detect leakage current of ground only for function when start the first startup 1X1:Detect leakage current of ground for every startup.
- Page 195 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 0:baud rate :4800bps 1:baud rate :9600bps 2:baud rate :19200bps 07-02 P.32 Serial communication baud rate 3:baud rate :38400bps 4:baud rate :57600bps 5:baud rate :115200bps 0:8bit 07-03 P.48 Data length 1:7bit 0:1bit 07-04...
- Page 196 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Group Name Setting Range Default Page Number 08-06 P.174 Differential time 0~1000ms 08-07 P.175 Abnormal deviation 0~200.0% 0.0% 08-08 P.176 Abnormal duration time 0~600.0s 30.0s 0: Stop freely 08-09 P.177 Abnormal processing mode 1: Slow down to stop 2: Alarm and continue operation 08-10 P.178...
- Page 197 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Setting Range Group Name Default Page Number 0~30.0s 10-09 P.57 Restart idling time 99999 99999: Off. 7.5K/11KF and below model : 0~60.0s 5.0s 10-10 P.58 Restart rising time 11K/15KF and above model : 0~60.0s 10.0s 0: Off X1:Remote control function, frequency save in memory...
- Page 198 Appendix 1 Parameter table Parameter Setting Range Group Name Default Page Number 10-27 P.238 Amplitude acceleration time 0~360.00s/0~3600.0s 10.00s 10-28 P.239 Amplitude deceleration time 0~360.00s/0~3600.0s 10.00s 220V : 155~410V 380V 10-46 P.268 Voltage stall level 440V : 310~820V 760V Reciprocating machine function 0:Off 10-55 P.226...
- Page 199 Appendix 2 Alarm code list 7.2 Appendix 2 Alarm code list Code Keypad screen display Cause Troubleshooting 1.Low input voltage. 1.Use a better power supply. 2.The reset function “RES” is on. 2.Shut off “RES”. 3.Bad connection between the 3.Ensure the keypad is connected firmly. external keypad and main body.
- Page 200 Appendix 2 Alarm code list Code Keypad screen display Cause Troubleshooting 1.It is recommended to increase the deceleration time P.8 (01-07) The output current is two times 2.It is recommended to set the base voltage larger than the rated current of Over-current parameter P.19 (01-04) equal to power supply during...
- Page 201 Appendix 2 Alarm code list Code Keypad screen display Cause Troubleshooting 1.Check whether the inverter specifications match the motor specifications 2.Check whether the load of the system is too heavy, and whether the output current 1. IGBT module thermal relay displayed by the inverter exceeds the rated actuate.
- Page 202 Appendix 2 Alarm code list Code Keypad screen display Cause Troubleshooting If the alarm repeated, send the unit back to the dealer or the manufacturer to repair. Avoid frequent parameters modification and ROM malfunction saving target frequency to EEPROM, please Memory error refer to 07-11 (P.34) and target frequency address H1002 to prevent damage.
- Page 203 Appendix 3:Warning code list 7.3 Appendix 3:Warning code list Code Built-in keypad status Reason Action When the output current is 1. Check whether the greater than the stall level, the setting of 06-01 (P.22), glitter three small lights at the top 06-02 (P.23), 06-03 (P.66) right of the built-in keypad will Current stall...
- Page 204 Appendix 4:Troubles and solutions 7.4 Appendix 4:Troubles and solutions Troubles Check points •Is the voltage between terminals R/L1-S/L2-T/L3 normal? Main circuit •Is the wiring between the inverter and the motor correct? •Is the load too heavy? Load •Is the motor rotor locked? •Is the startup frequency (01-11(P.13)) set too high? •Is the operation mode (00-16(P.79)) correct? •Is the upper limit frequency (01-00(P.1)) set to zero?
- Page 205 Appendix 5 Optional equipment 7.5 Appendix 5 Optional equipment 7.5.1 PU301 Keypad PU301 appearance Order number Model Name Order code PU301 LED Keypad SNKPU301 Outline <Outline drawing> 4 × M3 10.95 92.8 114.7 26.9 Appendix 203...
- Page 206 Appendix 5 Optional equipment Panel mounting hole size 7.72 14.48 17.1 17.2 92.8 61.22 4- 3.5 Snap-in installation hole size < Card buckle installation: panel cutting dimension drawing > Cutout Area Panel thickness 1.2mm 1.6mm 2.0mm 66.4 110.2 111.3 112.5 * Allowable error: ±0.15mm...
- Page 207 Appendix 5 Optional equipment 7.5.2 DU06 Keypad DU06 appearance 42.4000 72.0000 Order number: Model Name Order code DU06 DU06 keypad SNKDU06 DU06 dimention: <Outline drawing> 52.4 2×M3 9.45 15.8 Effective depth of screws hole 2.9mm 38.65 DU06 Recommended screw installation size: <Screw installation:panel cutting dimension drawing>...
- Page 208 Appendix 5 Optional equipment 7.5.3 DU08 Keypad DU08 appearance DU08 DU08S Order number: Model Name Order code DU08 DU08 keypad SNKDU08 DU08S DU08S keypad SNKDU08S Appendix 206...
- Page 209 Appendix 5 Optional equipment DU08 outline: <Outline dimensional drawing> 15.0 30.0 60.0 37.7 14.4 78.0 66.0 2-M3 < Panel mounting hole size >< Flange mounting hole size > 17.3 66.0 63.0 20.3 29.0 15.0 20.3 30.0 Note: For flange installation, the fixed installation base is not standard and needs to be purchased separately, order code: SNKDUMH02 (DU08S already includes this fixed installation base).
- Page 210 Appendix 5 Optional equipment 7.5.4 DU10 Keypad DU10 appearance Order number: Model Name Order code DU10 DU10 keypad SNKDU10 DU10 outline: < Outline drawing > 33.4 36.4 29.8 13.5 Appendix 208...
- Page 211 Appendix 5 Optional equipment 18.0 7.5.5 PU302 Keypad Order number: Model Name Order code PU302 LED keypad SNKPU302 Outline 27.9 52.6 42.7 26.3 2-M3 18.0 Recommended screw installation size <螺丝安装面板开孔尺寸图> 33.7 19.3 open hole 52.4 Recommended installation size ...
- Page 212 Appendix 5 Optional equipment Spring installation pan head screw M3×5 steel plate * Allowable error: ±0.15mm * If the customer's drilling accuracy cannot meet the above tolerance, please purchase the accessory SMK301 (spring installation kit) for installation. 7.5.6 CBL:Data transmission line (for use with the above keypads) Model: SNKCBLxxGTN2 (xx means 1R5,3,5,10) Item NO.
- Page 213 Appendix 6 European Specification Compatibility Description 7.6 Appendix 6 European Specification Compatibility Description This inverter qualifies the CE label. Specifications: Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU & Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive 2014/30/EU 1. Electromagnetic compatibility command (EMC): (1). EMC compatibility description: For system integration, inverter is not a functionally independent device unit. It is usually a unit in the control box.
- Page 214 Appendix 6 European Specification Compatibility Description Appendix 212...
- Page 215 Appendix 6 European Specification Compatibility Description Appendix...
- Page 216 REVISION RECORD 8. REVISION RECORD Published Date Edition of the Manual Revision Content First edition July 2015 V1.00 modify: 1. Modification of factory values and setting ranges of some parameters February 2016 V1.01 2. Add Appendix 5: Compatibility Description of European Standards modify: 1.
- Page 217 REVISION RECORD Published Date Edition of the Manual Revision Content add: 1. frame C/D support 2. 3.4.2 Frame C/D May 2022 V1.14 3. 3.8.2 Frame C/D 4. 5.1.12 Motor types selection modify : Improve and optimize the description of some parameters Version:...










Need help?
Do you have a question about the SC3-043-7.5K/11KF and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers