Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Copyright
Copyright © 2021 MITAC COMPUTING TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION. All rights
reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or translated without prior
written consent from MITAC COMPUTING TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION.
Trademark
All registered and unregistered trademarks and company names contained in this
manual are property of their respective owners including, but not limited to the
following.
®
TYAN
is a trademark of MITAC COMPUTING TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION.
®
AMD
is a trademark of AMD
Intel
®
is a trademark of Intel
AMI, AMI BIOS are trademarks of AMI Technologies.
®
Microsoft
, Windows
®
Nuvoton
is a trademark of Nuvoton Technology Corporation.
Notice
Information contained in this document is furnished by MITAC COMPUTING
TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION and has been reviewed for accuracy and reliability
prior to printing. MITAC assumes no liability whatsoever, and disclaims any express
or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of TYAN
or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose or merchantability. MITAC
retains the right to make changes to product descriptions and/or specifications at
any time, without notice. In no event will MITAC be held liable for any direct or
indirect, incidental or consequential damage, loss of use, loss of data or other
malady resulting from errors or inaccuracies of information contained in this
document.
S7126
Version 1.0d
®
Corporation.
®
Corporation.
®
are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
http://www.tyan.com
®
products including liability
1
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for TYANO S7126
- Page 1 S7126 Version 1.0d Copyright Copyright © 2021 MITAC COMPUTING TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or translated without prior written consent from MITAC COMPUTING TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION. Trademark All registered and unregistered trademarks and company names contained in this manual are property of their respective owners including, but not limited to the following.
- Page 2 http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Contents Before you begin… ..................4 Chapter 1: Instruction ................5 1.1 Congratulations ................. 5 1.2 Hardware Specifications ..............5 1.3 Software Specifications ..............7 Chapter 2: Board Installation ..............9 2.1 Board Image ..................10 ... -
Page 4: Before You Begin
1 x M.2 Latch Kit 1 x Rear I/O Shield 2 x CPU Carrier 1 x S7126 Quick reference guide IMPORTANT NOTE: Sales sample may not come with the accessory listed above. Please contact your sales representative to help order accessory for your evaluation. -
Page 5: Chapter 1: Instruction
32 and 64-bit computing, high-bandwidth memory design, and lightning-fast PCI-E bus implementation. The S7126 not only empowers you in today’s demanding IT environment but also offers a smooth path for future application upgradeability. All of these rich feature sets provides the S7126 with the power and flexibility to meet demanding requirements for today’s IT environments. - Page 6 Q'ty / Port (2) GbE ports + (1) GbE dedicated for IPMI Controller Intel I210-AT Realtek RTL8211E Connector (14) SATA Storage SATA Speed 6Gb/s RAID RAID 0/1/10/5 (Intel RSTe) Connector (M.2) (1) 22110/2280/2242 (by PCIe interface) Storage NVMe Connector (U.2) (4) SFF-8654 for (8) NVMe ports Storage VROC Support...
-
Page 7: Software Specifications
90%, non-condensing at 35° C RoHS RoHS 6/6 Compliant Operating OS supported list Please refer to our AVL support lists. System Motherboard (1) S7126 Motherboard Manual (1) Quick Installation Guide Package Contains I/O Shield (1) I/O Shield Cable SATA (2) SATA signal cables 1.3 Software Specifications... - Page 8 NOTE http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 9: Chapter 2: Board Installation
Chapter 2: Board Installation You are now ready to install your motherboard. How to install our products right… the first time The first thing you should do is reading this user’s manual. It contains important information that will make configuration and setup much easier. Here are some precautions you should take when installing your motherboard: (1) Ground yourself properly before removing your motherboard from the antistatic bag. -
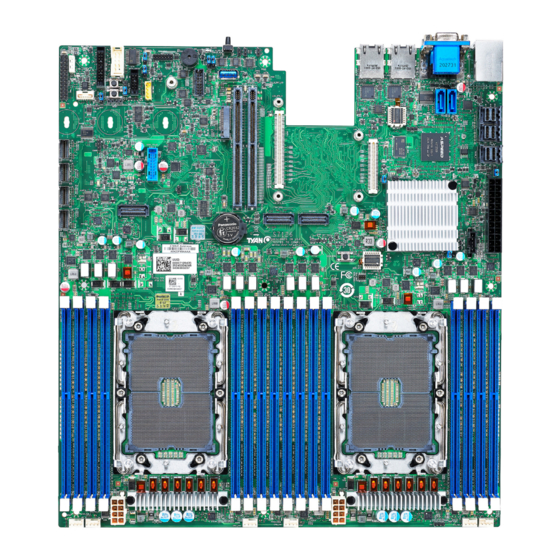
Page 10: Board Image
2.1 Board Image S7126 This picture is representative of the latest board revision available at the time of publishing. The board you receive may not look exactly like the above picture. http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 11: Block Diagram
2.2 Block Diagram S7126 Block Diagram http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 12: Mainboard Mechanical Drawing
2.3 Mainboard Mechanical Drawing http://www.tyan.com... -
Page 13: Board Parts, Jumpers And Connectors
2.4 Board Parts, Jumpers and Connectors This diagram is representative of the latest board revision available at the time of publishing. The board you receive may not look exactly like the above diagram. But for the DIMM number please refer to the above placement for memory installation. For the latest board revision, please visit our web site at http://www.tyan.com. - Page 14 Jumpers & Connectors Connectors 1 Dedicated IPMI port + USB3.0x2 (J112) 19 IPMB pin header (IPMB_HD1) 20 Vertical SLIMSAS connector 2 sSATA connector (sSATA4) (SLIMSAS1) 21 Vertical SLIMSAS connector 3 VGA + COM port (VGA_COM1) (SLIMSAS2) 22 Vertical SLIMSAS connector 4 sSATA connector (sSATA5) (SLIMSAS3) 23 Vertical SLIMSAS connector...
- Page 15 LEDS BMC Debug LED (BMC_LED1) Memory Error LED-CPU1 (LED69) M.2 LED (LED75) XVII Memory Error LED-CPU1 (LED70) REAR IO ID LED BTN (IDLED_BTN1) XVIII Memory Error LED-CPU1 (LED67) REAR ID LED (ID_LED1) Memory Error LED-CPU1 (LED68) On board BMC IPMI ALERT LED Memory Error LED-CPU0 (LED64) (IPMI_LED1) BMC Heartbeat LED (BMC_LED4)
- Page 16 FAN1~6 (CPU0_FAN, CPU1_FAN, SYS_FAN_1~4): 4-pin FAN Connector Signal P12V FAN_TACH FAN_PWM Use this header to connect the cooling fan to your motherboard to keep the system stable and reliable. FPIO_1: Front Panel Pin Header Signal Signal FP_ PWER FP_PW_LED_PW (VCC3_Aux) FP_ID_LED_PW FP_PW_LED_GND FP_ID_LED_N...
- Page 17 DBG_HD1: TYAN Module Header Signal Signal VCC3 FRAME_N LAD0 LAD1 PLT_RST_N LAD2 LAD3 CLK_33M DBG_SERIRQ DBG_PRES_N VCC3_AUX TPM_ADDR_MB PCH_TPM_PP_EN FAN_HD1: Fan Connector (Reserved for Barebone) Signal Signal TACH1 TACH6 TACH2 TACH7 TACH3 TACH8 TACH4 TACH9 TACH5 TACH10 PWM2 PWM1 TACH11 TACH12 PWM3 USB3_FPIO1: Front USB3.0 Header...
- Page 18 SSATA_SGPIO1: SATA SGPIO Pin Header for SSATA4-5 Signal Signal SDATA IN SDATA OUT- SLOAD SCLOCK VCC3_AUX HD_ERROR_LED FPIO_VGA3: Front Panel VGA Header Signal Signal VGA2_5V HD_VGA_R HD_VGA_G HD_VGA_B HD_VGA_DAT HD_VGA_HS HD_VGA_CLK HD_VGA_VS HD_COM2: COM Port Header Signal Signal COM2_DCD COM2_DSR COM2_RXD COM2_RTS COM2_TXD...
- Page 19 IDLED_BTN1: Rear IO ID LED Button Signal Signal FP_IDLED_BTN_N PWR_BTN1: System Power Button Signal Signal PWR_BTN1 RST_BTN1: System Reset Button Signal Signal FP_RST_BTN_N sSATA4: 7-pin Vertical SATA Connector PIN Define SSATA4_TXP_C Connects to the Serial SSATA4_TXN_C ATA ready drives via the Serial ATA cable.
- Page 20 TYPEA_USB3: Vertical Type-A USB3.0 Connector Signal Signal USB3_N3_RX_TYPEA VCC5 USB3_P3_RX_TYPEA USB2_N8_TYPE_A_R USB2_P8_TYPE_A_R USB3_N3_TX_TYPEA USB3_P3_TX_TYPEA CLEAR_BTN1: RTC Reset Button for Clear CMOS You can reset the CMOS settings by using this button, if you have forgotten your system/setup password or need to clear system BIOS setting.
- Page 21 NGFF1: M.2 Connector Signal Signal VCC3 VCC3 VCC3_AUX M2_LED_N VCC3 VCC3 VCC3 VCC3 PCH_PE1_M2_1_RX_N P12V_IN P12V_IN PCH_PE1_M2_1_RX_P P12V_IN P12V_IN PCH_PE1_M2_1_TX_N PCH_PE1_M2_1_TX_P M2_SMB_CLK_R PCH_PE0_M2_0_RX_N M2_SMB_DAT_R PCH_PE0_M2_0_RX_P PCH_PE0_M2_0_TX_N M2_PERST_N_R PCH_PE0_M2_0_TX_P M2_2_PEWAKE_N CLK_100M_M2_DN CLK_100M_M2_DP PE_M.2_DETECT_N VCC3 VCC3 VCC3 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 22 PCH_SSATA_0_3: 36-pin Vertical Mini SAS Connector (SATA 3.0 signals) Signal Signal PCH_SSATA_0-3_A1 SGPIO_SSATA_CLK SGPIO_SSATA_LOAD SSATA1_RXP_C SSATA0_RXP_C SSATA1_RXN_C SSATA0_RXN_C SSATA3_RXP_C SSATA2_RXP_C SSATA3_RXN_C SSATA2_RXN_C SSGPIO_DO_0R SSGPIO_DI_0R SAS1_CTYPE SSATA1_TXP_C SSATA0_TXP_C SSATA1_TXN_C SSATA0_TXN_C SSATA3_TXP_C SSATA2_TXP_C SSATA3_TXN_C SSATA2_TXN_C http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 23 PCH_SSATA_0_7: 72-pin Vertical Mini SAS Connector (SATA 3.0 signals) Signal Signal PCH_SATA_0-7_A1 SGPIO_SATA_CLK SGPIO_SATA_LOAD SATA1_RXP_C SATA0_RXP_C SATA1_RXN_C SATA0_RXN_C SATA3_RXP_C SATA2_RXP_C SATA3_RXN_C SATA2_RXN_C SGPIO_DO_0R SGPIO_DI_0R SAS0_CTYPE SATA1_TXP_C SATA0_TXP_C SATA1_TXN_C SATA0_TXN_C SATA3_TXP_C SATA2_TXP_C SATA3_TXN_C SATA2_TXN_C NC_PCH_SATA_0-7_A10 SGPIO_SATA_CLK SGPIO_SATA_LOAD SATA5_RXP_C SATA4_RXP_C SATA5_RXN_C SATA4_RXN_C SATA7_RXP_C SATA6_RXP_C SATA7_RXN_C...
- Page 24 SlimSAS1: Vertical Slim SAS 8x Connector Signal Name Signal Name CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN0 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP0_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DP0 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DN0_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN1 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP1_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DP1 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DN1_C BP_TYPEA PE_HD0_SMB_CLK PE_WAKE_N0 PE_HD0_SMB_DAT SLIMSAS_NVME0_DP PCIE_SLIMSAS_RST_N SLIMSAS_NVME0_DN CPRSNTA- CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN2 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP2_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DP2 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DN2_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN3 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP3_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DP3 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DN3_C SlimSAS2: Vertical Slim SAS Connector Signal Name Signal Name CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN4 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP4_C...
- Page 25 SlimSAS3: Vertical Slim SAS Connector Signal Name Signal Name CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN8 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP8_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DP8 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DN8_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN9 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP9_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DP9 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DN9_C BP_TYPEC PE_HD2_SMB_CLK PE_WAKE_N2 PE_HD2_SMB_DAT SLIMSAS_NVME2_DP PCIE_SLIMSAS_RST_N SLIMSAS_NVME2_DN CPRSNTA- CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN10 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP10_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DP10 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DN10_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN11 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP11_C CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DP11 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DN11_C SlimSAS4: Vertical Slim SAS Connector Signal Name Signal Name CPU1_PE2_ABCD_RX_DN12 CPU1_PE2_ABCD_TX_DP12_C...
- Page 26 J125: PSU Throttling Function Jumper Signal Signal PSU_SMB_ALERT_BUFF_N_R 10K to VCC3_AUX Pin1-2 closed: Normal Mode (Default) Pin2-3 closed: Enable PSU Throttling Function J118: BMC COM Port Jumper Signal Signal BMC_COM2_RXD RXD_2 BMC_COM5_RXD Pin1-2 closed: BMC COM PORT2 (Default) Pin2-3 closed: BMC CONSOLE PORT5 J119: BMC COM Port Jumper Signal Signal...
- Page 27 J133: Select PECI to BMC or PCH Jumper Signal Signal 1KK to VCC3_AUX 10K to GND Pin1-2 closed: PP-PECI to BMC (Default) Pin1-2 open: NI-PECI to PCH J120: System Buzzer Jumper VCC5_BZ BUZ_1 BUZ_2 Pin3-4 closed: Normal Mode (Default) Pin2-3 closed: Disable PC Beep Pin1-4 closed: Use the external speaker http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 28: Led Definitions
2.5 LED Definitions Signal +VCC3_SB State Description BMC Heart The LED shuts off when the BMC_LED4 Beat LED BMC controller cannot be detected or properly initiated. The LED blinks per second to Blinking Green indicate that the BMC controller is working normally Signal + VCC3 CPU0... - Page 29 The LED lights up when the Green power of CPU0 is normally. Signal + VCC3 CPU1 State Description P1_PG_LED1 PWOK The LED shuts off when the power of CPU1 is abnormal. The LED lights up when the Green power of CPU1 is normally. Signal + VCC3_AUX PSU Alert...
-
Page 30: Installing The Processor And Heat Sink
2.6 Installing the Processor and Heat sink ® The S7126 supported Intel processors are listed in section 1.2 Hardware Specifications on page 5. Check our website at http://www.tyan.com for latest processor support. NOTE: MITAC TYAN is not liable for damage as a result of operating an unsupported configuration. - Page 31 NOTE: A new heatsink comes with pre-applied thermal grease. Once the heatsink has been removed from the processor, you need to clean the processor and heatsink using an alcohol solvent. Then apply new thermal grease before reinstalling the heatsink. 3. Remove the CPU cover. 4.
- Page 32 5. Press down on the retention clips to fix the heatsink assembly to the CPU socket. 6. To secure the heatsink assembly, use a T30 Security Torx to tighten the screws in a sequential order (1234). NOTE: When disassembling the heatsink, loosen the screws in reverse order (4321).
-
Page 33: Tips On Installing Motherboard In Chassis
2.7 Tips on Installing Motherboard in Chassis Before installing your motherboard, make sure your chassis has the necessary motherboard support studs installed. These studs are usually metal and are gold in color. Usually, the chassis manufacturer will pre-install the support studs. If you are unsure of stud placement, simply lay the motherboard inside the chassis and align the screw holes of the motherboard to the studs inside the case. - Page 34 http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 35: Installing The Memory
2.8 Installing the Memory Before installing memory, ensure that the memory you have is compatible with the http://www.tyan.com motherboard and processor. Check the TYAN Web site at for details of the type of memory recommended for your motherboard. DDR4/DDR-T Memory Population Guidelines The Whitley Ice Lake processor has up to eight channel memory interfaces ®... - Page 36 General Population Requirements DIMM Mixing Rules All DIMMs must be either all DDR4 DIMMs and/or DDR4 and PMem 200 series DIMMs. x4 and x8 RDIMMs can be mixed in the same channel. Mixing of non-3DS and 3DS RDIMMs is not allowed in the same channel, across different channels, and across different sockets.
- Page 37 DDR4 Memory Configuration This section highlights the memory configuration for DDR4 DIMM population for Ice Lake processor based systems. Note #1 – rank sparing, ADDDC, channel mirroring, hemisphere modes and 2LM not supported with Intel SGX There should be at least one DDR4 DIMM per socket ...
- Page 38 ® DDR4 and Intel Optane PMem 200 series Socket Level Population Requirements This section highlights the memory configuration for DDR4 DIMM population and ® Intel Optane PMem 200 series DIMM population for Ice Lake processor based systems. There should be at least one DDR4 ...
- Page 39 For MM, NM/FM ratio is between 1:4 and 1:16. (NM=Near Memory; FM=Far Memory) Matrix targets configs for optimized PMem to DDR4 cache ratio in MM mode For a bring-up purpose, (1 DDR4 and 1 PMem) per socket or (2DDR4 and ...
- Page 40 DIMM Location http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 41 Recommended Memory Population Table Quantity of memory installed Single CPU Installed (Reference Intel Memory Population #574174) √ √ P0_MC0_DIM_CH_A0 √ √ √ P0_MC0_DIM_CH_B0 √ √ P0_MC1_DIM_CH_C0 √ √ √ P0_MC1_DIM_CH_D0 √ √ P0_MC2_DIM_CH_E0 √ √ √ P0_MC2_DIM_CH_F0 √ √ P0_MC3_DIM_CH_G0 √...
- Page 42 Quantity of memory installed Dual CPU Installed (Reference Intel Memory Population #574174) √ √ P0_MC0_DIM_CH_A0 √ √ √ P0_MC0_DIM_CH_B0 √ √ P0_MC1_DIM_CH_C0 √ √ √ P0_MC1_DIM_CH_D0 √ √ P0_MC2_DIM_CH_E0 √ √ √ P0_MC2_DIM_CH_F0 √ √ P0_MC3_DIM_CH_G0 √ √ √ P0_MC3_DIM_CH_H0 √...
- Page 43 Memory Installation Procedure Follow these instructions to install memory modules into the S7126. Unlock the clips as shown in the illustration. Insert the memory module firmly into the socket by gently pressing down until it sits flush with the socket.
-
Page 44: Attaching Drive Cables
2.9 Attaching Drive Cables Attaching Serial ATA Cables S7126 is equipped with two (2) Serial ATA (SATA) channel. Connections for the drives are very simple. There is no need to set Master/Slave jumpers on SATA drives. If you are in need of SATA/SAS cables or power adapters please contact your place of purchase. -
Page 45: Installing Add-In Cards
2.10 Installing Add-In Cards Before installing add-in cards, it’s helpful to know if they are fully compatible with your motherboard. For this reason, we’ve provided the diagrams below, showing the slots that may appear on your motherboard. PCIe Gen3 x16 OCP 2.0 (Slot A) PCIe Gen3 x16 OCP 2.0 (Slot B) (2) PCIe Gen3/Gen4 x32 slots Simply find the appropriate slot for your add-in card and insert the card firmly. -
Page 46: Connecting External Devices
2.11 Connecting External Devices Connecting external devices to the motherboard is an easy task. The motherboard supports a number of different interfaces through connecting peripherals. See the following diagrams for the details. NOTE: Peripheral devices can be plugged straight into any of these ports but software may be required to complete the installation. -
Page 47: Installing The Power Supply
2.12 Installing the Power Supply There are three (3) power connectors on your S7126 motherboard. The S7126 supports EPS 12V power supply. PWR1: ATX 24-pin Main Power Connector Signal Signal VCC3 VCC3 VCC3 VCC12N VCC5 ATX_PS_ON_N VCC5 ATX_PG NC_PWR1_20 VCC5_SB... -
Page 48: Finishing Up
2.13 Finishing Up Congratulations on making it this far! You have finished setting up the hardware aspect of your computer. Before closing up your chassis, make sure that all cables and wires are connected properly, especially IDE cables and most importantly, jumpers. -
Page 49: Chapter 3: Bios Setup
Chapter 3: BIOS Setup 3.1 About the BIOS The BIOS is the basic input/output system, the firmware on the motherboard that enables your hardware to interface with your software. The BIOS determines what a computer can do without accessing programs from a disk. The BIOS contains all the code required to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial communications, and a number of miscellaneous functions. - Page 50 3.1.2 Getting Help Pressing [F1] will display a small help window that describes the appropriate keys to use and the possible selections for the highlighted item. To exit the Help Window, press [ESC] or the [Enter] key again. 3.1.3 In Case of Problems If you have trouble booting your computer after making and saving the changes with the BIOS setup program, you can restart the computer by holding the power button down until the computer shuts off (usually within 4 seconds);...
-
Page 51: Main Menu
3.2 Main Menu In this section, you can alter general features such as the date and time. Note that the options listed below are for options that can directly be changed within the Main Setup screen. System Language Choose the system default language. English / Simplified Chinese / Japanese System Date Set the Date. -
Page 52: Advanced Menu
3.3 Advanced Menu This section facilitates configuring advanced BIOS options for your system. NOTE: This is a sample screenshot of the Advanced Menu. The HII network drivers displayed here depend on the card(s) you installed and the functions you enabled. Option ROM Dispatch Policy Option ROM Dispatch Policy. - Page 53 Power Management Power Management. Serial Port Console Redirection Serial Port Console Redirection. PCI Subsystem Settings PCI, PCI-X and PCI Express Settings. Socket Configuration Socket Configuration. Memory Topology Memory Topology. Server ME Configuration Configure Server ME Technology Parameters. SATA Configuration SATA devices and settings. PCH Configuration SATA Device Information.
- Page 54 Hardware Health Configuration Hardware health Configuration Parameters. NVDIMM ADR Configuration NVDIMM ADR Configuration. CPU Registration This item support INTEL CPU, sign the CPU will record current CPU. Once BIOS checked different with registered CPU, show WRNING message on POST screen. Memory Registration Sign the Memory will record current Memory.
- Page 55 MAC: XXXXXXXXXXXX --- IPV4 Network Configuration Configure network parameters. (MAC: XXXXXXXXXXXX) MAC: XXXXXXXXXXXX --- IPV6 Network Configuration Configure IPV6 network parameters. (MAC: XXXXXXXXXXXX) Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU This formset allows the user to manage Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU Driver Health Provides Health Status for the Drivers/Controllers.
- Page 56 3.3.1 Option ROM Dispatch Policy On Board LAN1 (I210) Onboard Device has: UEFI [X]. Legacy [ ] Embedded ROM(s). VIDx8086;DIDx1533 @ s0/[Bx2/Dx0/Fx0] Enabled / Disabled On Board LAN2 (I210) Onboard Device has: UEFI [X]. Legacy [ ] Embedded ROM(s). VIDx8086;DIDx1533 @ s0/[Bx3/Dx0/Fx0] Enabled / Disabled Slot #1~10 Empty...
- Page 57 3.3.2 S5 RTC Wake Settings Wake system from S5 Enable or disable System wake on alarm event. When enabled, System will wake on the day::hr::min::sec specified. Disabled / Fixed Time / Dynamic Time When Wake system from S5 is set to [Fixed Time] Wake up hour Select 0-23.
- Page 58 3.3.3 Trusted Computing Security Device Support Enables or Disables BIOS support for security device. O.S. will not show Security Device. TCG EFI protocol and INT1A interface will not be available. Enabled / Disabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 59 3.3.4 ACPI Settings Enable ACPI Auto Configuration Enable or Disable BIOS ACPI Auto Configuration. Disabled / Enabled Enable Hibernation Enable or Disable System ability to Hibernate (OS/S4 Sleep State). This option may not be effective with some operating system. Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 60 3.3.5 AST2500 Super IO Configuration Super IO Chip Read only. Serial Port 1 Configuration Set Parameters of Serial Port 1 (COMA). Serial Port 2 Configuration Set Parameters of Serial Port 2 (COMB). http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 61 3.3.5.1 Serial Port 1 Configuration Serial Port Enable or disable Serial Port (COM). Enabled / Disabled Change Settings Select an optimal setting for Super IO Device. Auto / IO=3F8h; IRQ=4; / IO=3F8h, IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12; / IO=2F8h;...
- Page 62 3.3.5.2 Serial Port 2 Configuration Serial Port Enable or disable Serial Port (COM). Enabled / Disabled Change Settings Select an optimal setting for Super IO Device. Auto / IO=3F8h; IRQ=4; / IO=3F8h, IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12; / IO=2F8h;...
- Page 63 3.3.6 Power Management CPU Power and Performance Policy CPU Power and Performance Policy. Performance / Balanced Power / Power http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 64 3.3.7 Serial Port Console Redirection Console Redirection / Console Redirection EMS Console redirection enable or disable. Disabled / Enabled Legacy Console Redirection Settings Legacy Console redirection settings. Console Redirection Settings The settings specify how the host computer (which the user is using) will exchange data.
- Page 65 3.3.7.1 COM1 Console Redirection Settings Terminal Type Emulation: ANSI: Extended ASCII char set. VT100: ASCII char set. VT100+: Extends VT100 to support color, function keys, etc. VT-UTF8: Uses UTF8 encoding to map Unicode chars onto 1 or more bytes. VT100+ / VT100 / VT-UTF8 / ANSI Bits per Second Select serial port transmission speed.
- Page 66 Stop Bits Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start bit indicates the beginning). The standard setting is 1 stop bit. Communication with slow devices may require more than 1 stop bit. 1 / 2 Flow Control Flow Control can prevent data loss from buffer overflow.
- Page 67 3.3.7.2 COM2 Console Redirection Settings Terminal Type Emulation: ANSI: Extended ASCII char set. VT100: ASCII char set. VT100+: Extends VT100 to support color, function keys, etc. VT-UTF8: Uses UTF8 encoding to map Unicode chars onto 1 or more bytes. VT100+ / VT100 / VT-UTF8 / ANSI Bits per Second Select serial port transmission speed.
- Page 68 Stop Bits Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start bit indicates the beginning). The standard setting is 1 stop bit. Communication with slow devices may require more than 1 stop bit. 1 / 2 Flow Control Flow Control can prevent data loss from buffer overflow.
- Page 69 3.3.7.3 Legacy Console Redirection Settings Legacy Serial Redirection Port Select a COM port to display redirection of Legacy OS and Legacy OPROM Messages. COM1 / COM2 Resolution On Legacy OS, the Number of Rows and Columns supported redirection. 80x24 / 80x25 Redirect After POST When BootLoader is selected, then Legacy Console Redirection is disabled before booting to legacy OS, When Always Enable is selected, then Legacy Console...
- Page 70 3.3.7.4 Serial Port for Out-Of-Band Management/Windows Emergency Services (EMS) Console Redirection Settings Out-of-Band Mgmt Port Microsoft Windows Emergency Management Services (EMS) allows for remote management of a Windows Server OS through a serial port. COM1 / COM2 Terminal Type VT-UTF8 is the preferred terminal type for out-of-band management. The next best choice is VT100+ and then VT100.
- Page 71 Flow Control Flow Control can prevent data loss from buffer overflow. When sending data, if the receiving buffers are full, a ‘stop’ signal can be sent to stop the data flow. Once the buffers are empty, a ‘start’ signal can be sent to restart the flow. Hardware flow control uses two wires to send start/stop signal.
- Page 72 3.3.8 PCI Subsystem Settings Above 4G Decoding Enables or Disables 64bit capable Devices to be Decoded in Above 4G Address Space (Only if System Supports 64 bit PCI Decoding). Enabled / Disabled SR-IOV Support If system has SR-IOV capable PCIe Devices, this option Enables or Disables Single Root IO Virtualization Support.
- Page 73 3.3.9 Socket Configuration Processor Configuration Displays and provides option to change the Processor Settings. Common RefCode Configuration Displays and provides option to change the Common RefCode Settings. UPI Configuration Displays and provides option to change the Uncore Settings. Memory Configuration Displays and provides option to change the Memory Settings.
- Page 74 3.3.9.1 Processor Configuration Hyper-Threading [All] Enables Hyper Threading (Software Method to Enable/Disabled Logical Processor threads). Disabled / Enabled Enable Intel® TXT Enable Intel® TXT. Disabled / Enabled Intel® Virtualization Technology Intel® Virtualization Technology allows a platform to run multiple operating systems and applications in independent partitions.
- Page 75 3.3.9.1.1 Per-Socket Configuration CPU Socket 0 Configuration CPU Socket 0 Configuration. CPU Socket 1 Configuration CPU Socket 1 Configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 76 3.3.9.1.1.1 CPU Socket 0 Configuration Core Disable Bitmap (Hex) 0: Enable all cores. FFFFFFFFFF: Disable all cores. NOTE: At least one core per CPU must be enabled. Disabling all cores is an invalid configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 77 3.3.9.1.1.2 CPU Socket 1 Configuration Core Disable Bitmap (Hex) 0: Enable all cores. FFFFFFFFFF: Disable all cores. NOTE: At least one core per CPU must be enabled. Disabling all cores is an invalid configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 78 3.3.9.2 Common RefCode Configuration MMCFG Base Select MMCFG Base. 1G / 1.5G / 1.75G / 2G / 2.25G / 3G / Auto MMCFG Size Select MMCFG Size. 64M / 128M / 256M / 512M / 1G / 2G / Auto MMIO High Base Select MMIO High Base.
- Page 79 Numa Enable or Disable Non uniform Memory Access (NUMA). Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 80 3.3.9.3 UPI Configuration UPI General Configuration Displays and provides option to change the UPI General Settings. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 81 3.3.9.3.1 UPI General Configuration Link Speed Mode Select the UPI link speed as either the POR speed (Fast) or default speed (Slow). Slow / Fast Link Frequency Select Allows for selecting the UPI Link Frequency. 9.6GT/s / 10.4GT/s / 11.2GT/s / Auto / Use Per Link Setting Link L0p Enable Enable --- Set the c_l0p_en, Disable --- Reset it,...
- Page 82 SNC (Sub NUMA) SNC disable will support 1-cluster (XPT/KTI Prefetch enable) 4-IMC may interleave. SNC2 Enable supports 2-clusters SNC and 2-way IMC interleave. SNC4 Enable supports 4-clusters SNC and 1-way IMC interleave. Enable SNC2 or SNC4 will gray out IMC-interleave knob and UmaBasedClustering knob. Disabled / Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 83 3.3.9.3.1.1 UPI Status Read only http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 84 3.3.9.4 Memory Configuration Enforce POR Enable --- Enforces Plan Of Record restrictions for DDR4 frequency and voltage programming. Disable --- disables this feature and user is able to run at higher frequencies, specified in the DDR Frequency Limit field (limited by processor support).
- Page 85 Interleave NVDIMMs Controls if NVDIMMs are interleaved together or not. Enabled / Disabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 86 3.3.9.4.1 Memory RAS Configuration Mirror Mode Full Mirror Mode will set entire 1LM memory in system to be mirrored, consequently reducing the memory capacity by half. Partial Mirror Mode will enable the required size of memory to be mirrored. If rank sparing is enabled partial mirroring will not take effect.
- Page 87 3.3.9.5 IIO Configuration Intel® VT for Directed I/O (VT-d) Press <Enter> to bring up the Intel® VT for Directed I/O (VT-d) Configuration menu. Intel® VMD Technology Press <Enter> to bring up the Intel® VMD for Volume Management Device Configuration menu. PCIe Hot Plug Enable/Disable PCIe Hot Plug globally.
- Page 88 Skip PCIe retimers detection Skip PCIe retimers detection to speedup the boot. Retimers are present only in specific HW configurations. Disabled / Enable http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 89 3.3.9.5.1 Socket 0 Configuration IOU0 (IIO PCIe Port 1) Selects PCIe port Bifurcation for selected slot(s). x4x4x4x4 / x4x4x8 / x8x4x4 / x8x8 / x16 IOU1 (IIO PCIe Port 2) Selects PCIe port Bifurcation for selected slot(s). x4x4x4x4 / x4x4x8 / x8x4x4 / x8x8 / x16 NOTE: The default setting is x16 for MB, x8x8 for TS65-B7126.
- Page 90 3.3.9.5.1.1 Port 1A/2A/4A/5A PCI-E Port In auto mode the BIOS will remove the EXP port if there is no device or errors on that device and the device is not HP capable. Disable is used to disable the port and hide its CFG space. Auto / Disabled / Enabled Hot Plug Capable This option specifies if the link is considered Hot Plug capable.
- Page 91 Override Max Link Width Override the max link width that was set by bifurcation. Auto / x1 / x2 / x4 / x8 / x16 PCIE Port DeEmphasis De-Emphasis control (LNKCON2[6]) for this PCIe port. -6.0 dB / -3.5 dB PCI-E Port MPSS Configure Max Payload Size supported in PCIe Device Capabilities register.
- Page 92 3.3.9.5.2 Socket 1 Configuration IOU0 (IIO PCIe Port 1) Selects PCIe port Bifurcation for selected slot(s). x4x4x4x4 / x4x4x8 / x8x4x4 / x8x8 / x16 IOU1 (IIO PCIe Port 2) Selects PCIe port Bifurcation for selected slot(s). x4x4x4x4 / x4x4x8 / x8x4x4 / x8x8 / x16 NOTE: The default setting is x16 for MB, x8x8 for TS65-B7126.
- Page 93 3.3.9.5.2.1 Port 1A/2A/4A/4B/4C/4D/5A/5C PCI-E Port In auto mode the BIOS will remove the EXP port if there is no device or errors on that device and the device is not HP capable. Disable is used to disable the port and hide its CFG space. Auto / Disabled / Enabled Hot Plug Capable This option specifies if the link is considered Hot Plug capable.
- Page 94 Override Max Link Width Override the max link width that was set by bifurcation. Auto / x1 / x2 / x4 / x8 / x16 PCIE Port DeEmphasis De-Emphasis control (LNKCON2[6]) for this PCIe port. -6.0 dB / -3.5 dB PCI-E Port MPSS Configure Max Payload Size supported in PCIe Device Capabilities register.
- Page 95 3.3.9.5.3 Intel® VT for Directed I/O (VT-d) Intel® VT for Directed I/O (VT-d) Enable/Disable Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (VT-d) by reporting the I/O device assignment to VMM through DMAR ACPI Tables. Enabled / Disabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 96 3.3.9.5.4 Intel® VMD Technology http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 97 3.3.9.5.4.1 Intel VMD for Volume Management for Socket 0 VMD Config for PCH ports Enable/Disable VMD in this Stack. Disabled / Enabled VMD Config for IOU0 Enable/Disable VMD in this Stack. Disabled / Enabled VMD Config for IOU1 Enable/Disable VMD in this Stack. Disabled / Enabled VMD Config for IOU2 Enable/Disable VMD in this Stack.
- Page 98 VMD Config for IOU4 Enable/Disable VMD in this Stack. Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 99 3.3.9.5.4.2 Intel VMD for Volume Management for Socket 1 VMD Config for IOU0 Enable/Disable VMD Enable/Disable VMD in this Stack. Disabled / Enabled VMD Config for IOU1 Enable/Disable VMD Enable/Disable VMD in this Stack. Disabled / Enabled VMD Config for IOU2 Enable/Disable VMD Read only.
- Page 100 VMD Port A Enable/Disable Intel® Volume Management Device Technology on specific root port. Disabled / Enabled VMD Port B Enable/Disable Intel® Volume Management Device Technology on specific root port. Disabled / Enabled VMD Port C Enable/Disable Intel® Volume Management Device Technology on specific root port.
- Page 101 MemBar2 size Setup VMD Memory BAR2 size (in bits Min=20), ex: 20bits=1MB, 22bits=4MB, 26bits=64MB. MemBar2 attribute Set up VMD Memory BAR2 attribute, like 64-bit or prefetchable. 32-bit non-prefetchable / 64-bit non-prefetchable / 64-bit prefetchable VMD for Direct Assign Enable/Disable VMD for Direct Assign. Disabled / Enabled VMD Config for IOU4 Enable/Disable VMD...
- Page 102 3.3.9.6 Advanced Power Management Configuration CPU P State Control P State Control Configuration Sub Menu, include Turbo, XE and ete. Hardware PM State Control Hardware P-State setting. CPU C State Control CPU C State setting. Package C State Control Package C State setting. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 103 3.3.9.6.1 CPU P State Control SpeedStep (Pstates) Enable/Disable EIST (P-States). Disabled / Enabled Dynamic SST-PP Support Dynamic SSTPP Select. Disabled / Enabled Intel SST-PP Intel SST-PP Select allows user to choose from up to two additional base frequency conditions. Base / Config 3 / Config 4 Energy Efficient Turbo Energy Efficient Turbo Disable, MSR 0x1FC [19].
- Page 104 Perf P Limit Enable/Disable Performance P-Limit. Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 105 3.3.9.6.2 Hardware PM State Control Hardware P-States Disable: Hardware chooses a P-state based on OS Request (Legacy P-States). Native Mode: Hardware chooses a P-state based on OS guidance. Out of Band Mode: Hardware autonomously chooses a P-state (no OS guidance). Disabled / Native Mode / Out of Band Mode / Native Mode with No Legacy Support http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 106 3.3.9.6.3 CPU C State Control Package C State Package C State limit. C0/C1 state / C2 state / C6 (non Retention) state / Auto CPU C6 report Enable/Disable CPU C6 (ACPI C3) report to OS. Disabled / Enabled / Auto Enhanced Halt State (C1E) Core C1E auto promotion Control.
- Page 107 3.3.9.6.4 SOCKET RAPL Config PL1 Limit Enable/Disable PL1. If this option is disabled, BIOS will program the default values for PL1 Power Limit and PL1 Time Window. Disabled / Enabled PL1 Power Limit PL1 Power Limit in Watts. The value may vary from 0 to Fused value. If the value is 0, the fused value will be programmed.
- Page 108 PL2 Limit Enable/Disable PL2. If this option is disabled, BIOS will program the default values for PL2 Power Limit and PL2 Time Window. Disabled / Enabled PL2 Power Limit PL2 Power Limit in Watts. The value may vary from 0 to Fused value. If the value is 0, BIOS programs 125% * TDP.
- Page 109 3.3.10 Memory Topology Read only. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 110 3.3.11 Server ME Configuration Altitude The altitude of the platform location above the sea level, expressed in meters. The hex number is decoded as 2’s complement signed integer. Provide the 8000h value if the altitude is unknown. 8000 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 111 3.3.12 SATA Configuration SATA Configuration SATA devices and settings. SSATA Configuration sSATA devices and settings. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 112 3.3.12.1 SATA Configuration SATA Controller Enable or Disable SATA Controller. Disabled / Enabled Configure SATA as Identify the SATA port is connected to Solid State Drive or Hard Disk Drive. AHCI / RAID Support Aggressive Link Power Management Enables/Disables SALP. Disabled / Enabled Port 0/1/2/3/4/5/6/7 Enable or Disable SATA Port.
- Page 113 Configure as eSATA Configures port as External SATA (eSATA). Disabled / Enabled Spin Up Device If enabled for any of ports Staggered Spin Up will be performed and only the drives witch have this option enabled will spin up at boot. Otherwise all drives spin up at boot.
- Page 114 3.3.12.2 sSATA Configuration sSATA Controller Enable or Disable sSATA Controller. Disabled / Enabled Configure sSATA as Identify the sSATA port is connected to Solid State Drive or Hard Disk Drive. AHCI / RAID Support Aggressive Link Power Management Enables/Disables SALP. Disabled / Enabled Port 0/1/2/3/4/5 Enable or Disable sSATA Port.
- Page 115 Configure as eSATA Configures port as External SATA (eSATA). Disabled / Enabled Spin Up Device If enabled for any of ports Staggered Spin Up will be performed and only the drives witch have this option enabled will spin up at boot. Otherwise all drives spin up at boot.
- Page 116 3.3.13 PCH Configuration PCH Devices Enable/Disable Intel® IO Controller Hub devices. PCI Express Configuration PCI Express Configuration settings. USB Configuration USB Configuration Settings. ADR Configuration Automatic DIMM Refresh (ADR) Configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 117 3.3.13.1 PCH Devices Restore AC Power Loss Select S0/S5 for ACPI state after a G3. Power On / Power Off / Last State http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 118 3.3.13.2 PCI Express Configuration PCI Express Root Port 1~20 PCI Express Root Port 1~20 Settings. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 119 3.3.13.2.1 PCI Express Root Port 1 ~ 20 PCI Express Root Port 1~20 Control the PCI Express Root Port. Disabled / Enabled ASPM Support Set the ASPM Level: Force L0s: Force all links to L0s state AUTO: BIOS auto configure DISABLE: Disables ASPM Disable ASPM / ASPM L1 / ASPM Auto L1 Substates...
- Page 120 Max Payload Size PCIE Max Payload Size Selection. MPL128B / MPL256B http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 121 3.3.13.3 USB Configuration XHCI Idle L1 Enabled XHCI Idle L1. Disabled to workaround USB3 hot plug will fail after 1 hot plug removal. Please put the system to G3 for the new settings to take effect. Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 122 3.3.13.4 ADR Configuration Enable/Disable ADR Enable or disable Automatic DIMM Refresh (ADR). This is not available if eADR is enabled since eADR requires ADR to be enabled. Platform-POR / Enabled / Disabled ADR GPIO Select between GPIO_B or GPIO_C. GPIO_B / GPIO_C Host Partition Reset ADR Enable Enables/Disables ADR on Host Partition Reset.
- Page 123 ADR timer multiplier Select proper ADR timer multiplier: x1, 8, 24, 40, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88, 96. Platform-POR / x1 / x8 / x24 / x40 / x56 / x64 / x72 / x80 / x88 / x96 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 124 3.3.14 Miscellaneous Configuration Active Video Select active video type. Onboard Device / Offboard Device http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 125 3.3.15 Runtime Error Logging System Errors System Error Enable/Disable setup options. Disabled / Enabled Memory Error Enabling Press <Enter> to view or change the Memory errors enabling options. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 126 3.3.15.1 Memory Error Enabling Memory Error Enable/Disable Memory Error. Disabled / Enabled Spare Interrupt Spare Interrupt Selection. Disabled / SMI / Error Pin / CMCI http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 127 3.3.16 USB Configuration Legacy USB Support Enables USB legacy support. AUTO option disables legacy support if no USB devices are connected. DISABLE option will keep USB devices available only for EFI applications. Disabled / Enabled / Auto XHCI Hand-off This is a workaround for OSes without XHCI hand-off support. The XHCI ownership change should be claimed by XHCI driver.
- Page 128 USB transfer time-out The time-out value for Control, Bulk and Interrupt transfers. 1 sec / 5 sec / 10 sec / 20 sec Device reset time-out USB mass storage device Start Unit command time-out. 10 sec / 20 sec / 30 sec / 40 sec Device power-up delay Maximum time the device will take before it properly reports itself to the Host Controller.
- Page 129 3.3.17 NVMe Configuration This page shows the Device Name you installed. Press Enter to read the device information. If no NVME device is installed, it shows no NVME device is found. Read only. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 130 3.3.18 Onboard Device Configuration Onboard VGA Enable or disable onboard VGA. Enabled / Disabled Onboard LAN 1 (I210) LAN Enable/Disable control function. Enabled / Disabled Onboard LAN 2 (I210) LAN Enable/Disable control function. Enabled / Disabled ICC Clock Spread Spectrum Turn on/off Spread Spectrum Setting for IsCLK.
- Page 131 NMI Button Enable or Disable NMI button. Enabled / Disabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 132 3.3.19 Redfish Host Interface Settings Redfish Enable/Disable AMI Redfish. Enabled / Disabled Authentication mode Select authentication mode. Basic Authentication / Session Authentication IP Address Enter IP address. IP Mask Address Enter IP Mask address. IP Port Enter IP Port. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 133 3.3.20 Network Stack Configuration NOTE: The BIOS will automatically read the onboard LAN controller. Network Stack Enable/Disable UEFI Network Stack. Disabled / Enabled NOTE: The following items are available when Network Stack is set to [Enabled]. Ipv4 PXE Support Enable Ipv4 PXE Boot Support. If disabled IPV$ PXE boot option will not be created. Disabled / Enabled Ipv4 HTTP Support Enable Ipv4 HTTP Boot Support.
- Page 134 Ipv6 HTTP Support Enable Ipv6 HTTP Boot Support. If disabled IPV6 HTTP boot option will not be created. Disabled / Enabled PXE boot wait time Wait time to press ESC key to abort the PXE boot. Media detect count Number of times presence of media will be checked. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 135 3.3.21 Hardware Health Configuration Fan Speed Control Fan Speed Control. Manual / Full Speed NOTE: Change the Fan Speed Control BIOS setting from [Manual] to [Full Speed] when installing the Nvidia GeForce / Quardro GPU and any VGA card. PWM Minimal Duty Cycle PWM Minimal Duty Cycle (%).
- Page 136 3.3.21.1 Sensor Data Register Monitoring NOTE: SDR can not be modified. Read only. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 137 3.3.22 NVDIMM ADR Configuration Enable ADR Enables the detecting and enabling of ADR. This is not available if eADR is enabled since eADR requires ADR to be enabled. Enabled / Disabled Assert ADR on Reset Assert ADR on Reset. Enabled / Disabled Assert ADR on Shutdown Assert ADR on Shutdown.
- Page 138 3.3.23 CPU Registration Sign-up the current CPU This item support INTEL CPU, sign the CPU will record current CPU. Once BIOS checked different with registered CPU, show WARNING message on POST screen. Deregistration / Sign-up / Keep Current Status http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 139 3.3.24 Memory Registration Sign-up the current Memory Sign the Memory will record current Memory. Once BIOS checked different with registered Memory, show WARNING message on POST screen. Deregistration / Sign-up / Keep Current Status http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 140 3.3.25 T1s Auth Configuration Server CA Configuration Press <Enter> to configure Server CA. Client Cert Configuration Press <Enter> to configure Client Cert. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 141 3.3.25.1 Server CA Configuration Enroll Cert Press <Enter> to enroll cert. Delete Cert Press <Enter> to delete cert. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 142 3.3.25.1.1 Enroll Cert Enroll Cert Using File Enroll Cert Using File. Cert GUID Input digit character in 11111111-2222-3333-4444-1234567890ab format. Commit Changes and Exit Commit Changes and Exit. Discard Changes and Exit Discard Changes and Exit. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 143 3.3.25.1.2 Delete Cert FE9C6606-8B49-44A3-8B6B-DEA3A0E032 GUID for CERT. Disabled / Enabled http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 144 3.3.26 iSCSI Configuration Please follow the instructions to initiate the iSCSI function. Step 1. Select Advanced CSM Configuration Network [UEFI]. Step 2. Select Advanced Network Stack Configuration Network Stack [Enabled] Step 3. Save changes and reboot. Host iSCSI Configuration Host iSCSI Configuration http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 145 3.3.26.1 Host iSCSI Configuration iSCSI Initiator Name The worldwide unique name of iSCSI Initiator. Only IQN format is accepted. Enter [iqn.xxx]. xxx ranges from 4 to 223. Add an Attempt Add an Attempt. Delete Attempts Delete one or more attempts. Change Attempt Order Change the order of Attempts using +/- keys.
- Page 146 3.3.26.1.1 Add an Attempt NOTE: Only LAN1 supports iSCSI function. MAC xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx (Intel® I210 Gigabit Network Connection) PFA: Bus 2 / Dev 0 / Func 0. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 147 3.3.26.1.1.1 MAC xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx (Intel® I210 Gigabit Network Connection) iSCSI Attempt Name The human name defined for this attempt. Maximum length is up to 12 characters. Attempt 1 / Attempt # iSCSI Mode Disabled, Enabled, Enabled for MPIO. Disabled / Enabled / Enabled for MPIO Internet Protocol Initiator IP address is system assigned in IP6 mode.
- Page 148 Connection Establishing Timeout The timeout value in milliseconds. The minimum value is 100 milliseconds and the maximum is 20 seconds. Configure ISID OUI-format ISID in 6 bytes, default value is derived from MAC address. Only last 3 bytes are configurable. Example: update 0ABBCCDDEEFF to OABBCCF07901 by input F07901.
- Page 149 3.3.26.1.2 Delete Attempts Attempt 1 MAC xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx, PFA: Bus 2 / Dev 0 / Func 0, iSCSI mode: Disabled, IP version: IPv4. Disabled / Enabled Attempt 2 MAC xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx, PFA: Bus 2 / Dev 0 / Func 0, iSCSI mode: Disabled, IP version: IPv4.
- Page 150 3.3.26.1.3 Change Attempt Order Change Attempt Order Change the order of Attempts using +/- keys. Use arrow keys to select the attempt then press +/- to move the attempt up/down in the attempt order list. Attempt 1 / Attempt 2 Commit Changes and Exit Commit Changes and Exit.
- Page 151 3.3.27 VLAN Configuration (MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx) Enter Configuration Menu Press ENTER to enter configuration menu for VLAN configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 152 3.3.27.1 Enter Configuration Menu VLAN ID VLAN ID of new VLAN or existing VLAN, valid value is 0~4094. Priority 802.1Q Priority, valid value is 0~7. Add VLAN Create a new VLAN or update existing VLAN. Remove VLAN Remove selected VLANs. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 153 3.3.28 MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx - IPv4 Network Configuration Configured Indicate whether network address configured successfully or not. Disabled / Enabled Save Changes and Exit Save Changes and Exit. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 154 3.3.29 MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx - IPv6 Network Configuration Enter Configuration Menu Press ENTER to enter configuration menu for IPv6 configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 155 3.3.29.1 Enter Configuration Menu Interface ID The 64 bit alternative interface ID for the device. The string is colon separated, e.g. ff:dd:88:66:cc:1:2:3 xx:xx:x:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx DAD Transmit Count The number of consecutive Neighbor Solicitation messages sent while performing Duplicate Address Detection on a tentative address. A value of zero indicates that Duplicate Address Detection is not performed.
- Page 156 3.3.29.1.1 Advanced Configuration New IPv6 address Manual IP address can only be configured under manual policy. Separate the IP address with blank space to configure more than one address. e.g. 2002::1/64 2002::2/64 New Gateway addresses Gateway IP address can only be configured under manual policy. e.g. 2002::3. Separate the IP address with blank space to configure more than one address.
- Page 157 3.3.30 Intel® I210 Gigabit Network Connection – xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx NIC Configuration Click to configure the network device port. Blink LEDs Blink LEDs for a duration up to 15 seconds. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 158 3.3.30.1 NIC Configuration Link Speed Specifies the port speed used for the selected boot protocol. Auto Negotiated / 10 Mbps Half / 10Mbps Full / 100Mbps Half / 100Mbps Full Wake On LAN Enables power on of the system via LAN. Note that configuring Wake on LAN in the operating system does not change the value of this setting, but does override the behavior of Wake on LAN in OS controlled power states.
- Page 159 3.3.31 VLAN Configuration (MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx) Enter Configuration Menu Press ENTER to enter configuration menu for VLAN configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 160 3.3.31.1 Enter Configuration Menu VLAN ID VLAN ID of new VLAN or existing VLAN, valid value is 0~4094. Priority 802.1Q Priority, valid value is 0~7. Add VLAN Create a new VLAN or update existing VLAN. Remove VLAN Remove selected VLANs. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 161 3.3.32 MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx - IPv4 Network Configuration Configured Indicate whether network address configured successfully or not. Disabled / Enabled Save Changes and Exit Save Changes and Exit. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 162 3.3.33 MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx - IPv6 Network Configuration Enter Configuration Menu Press ENTER to enter configuration menu for IPv6 configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 163 3.3.33.1 Enter Configuration Menu Interface ID The 64 bit alternative interface ID for the device. The string is colon separated, e.g. ff:dd:88:66:cc:1:2:3 xx:xx:x:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx DAD Transmit Count The number of consecutive Neighbor Solicitation messages sent while performing Duplicate Address Detection on a tentative address. A value of zero indicates that Duplicate Address Detection is not performed.
- Page 164 3.3.33.1.1 Advanced Configuration New IPv6 address Manual IP address can only be configured under manual policy. Separate the IP address with blank space to configure more than one address. e.g. 2002::1/64 2002::2/64 New Gateway addresses Gateway IP address can only be configured under manual policy. e.g. 2002::3. Separate the IP address with blank space to configure more than one address.
- Page 165 3.3.34 Intel® I210 Gigabit Network Connection – xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx NIC Configuration Click to configure the network device port. Blink LEDs Blink LEDs for a duration up to 15 seconds. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 166 3.3.34.1 NIC Configuration Link Speed Specifies the port speed used for the selected boot protocol. Auto Negotiated / 10 Mbps Half / 10Mbps Full / 100Mbps Half / 100Mbps Full Wake On LAN Enables power on of the system via LAN. Note that configuring Wake on LAN in the operating system does not change the value of this setting, but does override the behavior of Wake on LAN in OS controlled power states.
- Page 167 3.3.35 VLAN Configuration (MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx) Enter Configuration Menu Press ENTER to enter configuration menu for VLAN configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 168 3.3.35.1 Enter Configuration Menu VLAN ID VLAN ID of new VLAN or existing VLAN, valid value is 0~4094. Priority 802.1Q Priority, valid value is 0~7. Add VLAN Create a new VLAN or update existing VLAN. Remove VLAN Remove selected VLANs. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 169 3.3.36 MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx - IPv4 Network Configuration Configured Indicate whether network address configured successfully or not. Disabled / Enabled Save Changes and Exit Save Changes and Exit. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 170 3.3.37 MAC:xxxxxxxxxxxx - IPv6 Network Configuration Enter Configuration Menu Press ENTER to enter configuration menu for IPv6 configuration. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 171 3.3.37.1 Enter Configuration Menu Interface ID The 64 bit alternative interface ID for the device. The string is colon separated, e.g. ff:dd:88:66:cc:1:2:3 xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx DAD Transmit Count The number of consecutive Neighbor Solicitation messages sent while performing Duplicate Address Detection on a tentative address. A value of zero indicates that Duplicate Address Detection is not performed.
- Page 172 3.3.37.1.1 Advanced Configuration New IPv6 address Manual IP address can only be configured under manual policy. Separate the IP address with blank space to configure more than one address. e.g. 2002::1/64 2002::2/64 New Gateway addresses Gateway IP address can only be configured under manual policy. e.g. 2002::3. Separate the IP address with blank space to configure more than one address.
- Page 173 3.3.38 Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU NOTE: This is a sample screenshot of the Intel Virtual RAID on CPU. The information displayed in this page may vary in accordance with the cards you installed. Please follow the instructions to initiate the Intel Virtual RAID on CPU function. Step 1.
- Page 174 Step 3. Save changes and reboot to BIOS. Select Advanced to setup Intel Virtual RAID on CPU. All Intel VMD Controllers Select to see more information about the Intel VMD Controllers. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 175 3.3.39 Driver Health NOTE: This is a sample screenshot of the Driver Health. The information displayed in this page may vary in accordance with the cards you installed. Intel® PRO/1000 8.5.21 PCI-E Provides Health Status for the Drivers/Controllers. Healthy Intel® PRO/1000 8.5.21 PCI-E Provides Health Status for the Drivers/Controllers.
- Page 176 3.3.38.1 Intel® PRO/1000 8.5.21 PCI-E NOTE: This is a sample screenshot of the Driver Health. The information displayed here may vary in accordance with the card you installed. Controller 6136CF98 Provides Health Status for the Drivers/Controllers. Healthy Intel® I210 Gigabit Network Connection Provides Health Status for the Drivers/Controllers.
- Page 177 3.3.38.2 Intel® PRO/1000 8.5.21 PCI-E NOTE: This is a sample screenshot of the Driver Health. The information displayed here may vary in accordance with the card you installed. Controller 61375698 Child 0 Provides Health Status for the Drivers/Controllers. Healthy Intel® I210 Gigabit Network Connection Provides Health Status for the Drivers/Controllers.
- Page 178 3.3.38.3 Intel® VROC with VMD Technology 7.5.0.1152 NOTE: This is a sample screenshot of the Driver Health. The information displayed here may vary in accordance with the card you installed. Controller 612FDB18 Child 0 Provides Health Status for the Drivers/Controllers. Healthy http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 179: Server Management
3.4 Server Management BMC Logo Enable or Disable BMC Logo. Enabled / Disabled FRB-2 Timer Enable or Disable FRB-2 timer (POST timer). Enabled / Disabled NOTE: FRB-2 Timer timeout and FRB-2 Timer Policy are available when FRB-2 Timer is set to [Enabled]. FRB-2 Timer timeout Enter value Between 3 to 6 min for FRB-2 Timer Expiration value. - Page 180 OS Watchdog Timer If enabled, starts a BIOS timer which can only be shut off by Management Software after the OS loads. Helps determine that the OS successfully loaded or follows the OS Boot Watchdog Timer policy. Enabled / Disabled NOTE: OS Wtd Timer timeout and OS Wtd Timer Policy are available when OS Watchdog Timer is set to [Enabled].
- Page 181 3.4.1 BMC Network Configuration Configuration Address Source Select the configure LAN channel parameters statically or dynamically (by BIOS or BMC). Unspecified option will not modify any BMC network parameters during BIOS phase. Unspecified / Static / DynamicBmcDhcp / DynamicBmcNonDhcp Management Port 2 Enable/Disable BMC Share NIC.
- Page 182 3.4.2 BMC User Settings Add User Press <Enter> to Add a user. Delete User Press <Enter> to Delete a user. Change User Settings Press <Enter> to change User Settings. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 183 3.4.2.1 Add User User Name Enter BMC User Name. User Password Enter New Password to change. Password at least 8 characters. User Access Enable/Disable the BMC User’s Access. Enabled / Disabled Channel No Enter BMC Channel Number. N/A / 1 / 8 User Privilege Limit Enter BMC User Privilege Limit for Selected Channel.
- Page 184 3.4.2.2 Delete User User Name Enter BMC User Name. User Password Enter New Password to change. Password at least 8 characters. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 185 3.4.2.3 Change User Settings User Name Enter BMC User Name. User Password Enter New Password to change. Password at least 8 characters. Change User Password Enter New Password to change. Password at least 8 characters. User Access Enable/Disable the BMC User’s Access. Enabled / Disabled Channel No Enter BMC Channel Number.
-
Page 186: Security
3.5 Security Administrator Password Set administrator password in the Create New Password window. After you key in the password, the Confirm New Password window will pop out to ask for confirmation. User Password Set user password in the Create New Password window. After you key in the password, the Confirm New Password window will pop out to ask for confirmation. - Page 187 3.5.1 Secure Boot Secure Boot Secure Boot feature is Active if Secure Boot is Enabled. Platform Key (PK) is enrolled and the System is in User mode. The mode change requires platform reset. Enabled / Disabled Secure Boot Mode Secure Boot mode selector: Standard/Custom. In Custom mode Secure Boot Variables can be configured without authentication.
- Page 188 Key Management Enables expert users to modify Secure Boot Policy variables without full authentication. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 189 3.5.1.1 Key Management Factory Key Provision Install factory default Secure Boot keys after the platform reset and while the System is in Setup mode. Enabled / Disabled Restore Factory Keys Force System to User Mode. Install factory default Secure Boot key databases. Press ‘Yes’...
- Page 190 Enroll Efi Image Allow the image to run in Secure Boot mode. Enroll SHA256 Hash certificate of a PE image into Authorized Signature Database (db). Remove ‘UEFI CA’ from DB Device Guard ready system must not list ‘Microsoft UEFI CA’ Certificate in Authorized Signature database (db).
- Page 191 Forbidden Signatures Enroll Factory Defaults or load certificates from a file: 1. Public Key Certificate in: a) EFI_SIGNATURE_LIST b) EFI_CERT_X509 (DER) c) EFI_CERT_RSA2048 (bin) d) EFI_CERT_SHAXXX 2. Authenticated UEFI Variable 3. EFI PE/C0FF Image (SHA256) Key source: Factory, External, Mixed Details / Export / Update / Append / Delete Authorized TimeStamps Enroll Factory Defaults or load certificates from a file:...
-
Page 192: Boot
3.6 Boot Setup Prompt Timeout Number of seconds to wait for setup activation key. 65535 (0xFFFF) means indefinite waiting. Bootup NumLock State Select the keyboard NumLock state. Off / On Quiet Boot Enable or disable Quiet Boot option. Enabled / Disabled Endless Boot Enable or disable Endless Boot. - Page 193 Wait for ‘ESC’ If Error Wait for ‘ESC’ key to be pressed if error occurs. Enabled / Disabled Boot Option Priorities Boot Option #1~#4 Select the system boot order. Device Name / Disabled Delete Boot Option Remove an EFI boot option from the boot order. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 194 3.6.1 Delete Boot Option Delete Boot Option Remove an EFI boot option from the boot order. Select one to delete / Device Name http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 195: Save & Exit
3.7 Save & Exit Save Changes and Exit Exit system setup after saving the changes. Discard Changes and Exit Exit system setup without saving any changes. Save Changes and Reset Reset the system after saving the changes. Discard Changes and Reset Reset system setup without saving any changes. - Page 196 Restore Defaults Restore/Load Default values for all the setup options. Save as User Defaults Save the changes done so far as User Defaults. Restore User Defaults Restore the User Defaults to all the setup options. Boot Override Read only. http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 197: Chapter 4: Diagnostics
Chapter 4: Diagnostics NOTE: if you experience problems with setting up your system, always check the following things in the following order: Memory, Video, CPU By checking these items, you will most likely find out what the problem might have been when setting up your system. -
Page 198: Amibios Post Code (Aptio)
4.2 AMIBIOS Post Code (Aptio) The POST code checkpoints are the largest set of checkpoints during the BIOS pre- boot process. The following table describes the type of checkpoints that may occur during the POST portion of the BIOS: Checkpoint Ranges Status Code Range Description 0x01 –... - Page 199 SEC Error Codes 0x0C – 0x0D Reserved for future AMI SEC error codes 0x0E Microcode not found 0x0F Microcode not found SEC Beep Codes None PEI Phase Status Code Description Progress Codes 0x10 PEI Core is started 0x11 Pre-memory CPU initialization is started 0x12 Pre-memory CPU initialization (CPU module specific) 0x13...
- Page 200 Status Code Description 0x38 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific) 0x39 Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific) 0x3A Post-Memory North Bridge initialization (North Bridge module specific) 0x3B Post-Memory South Bridge initialization is started 0x3C Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific) 0x3D Post-Memory South Bridge initialization (South Bridge module specific) 0x3E...
- Page 201 Recovery Progress Codes 0xF0 Recovery condition triggered by firmware (Auto recovery) 0xF1 Recovery condition triggered by user (Forced recovery) 0xF2 Recovery process started 0xF3 Recovery firmware image is found 0xF4 Recovery firmware image is loaded 0xF5 – 0xF7 Reserved for future AMI progress codes Recovery Error Codes 0xF8 Recovery PPI is not available...
- Page 202 Status Code Description 0x76 South Bridge DXE initialization (South Bridge module specific) 0x77 South Bridge DXE initialization (South Bridge module specific) 0x78 ACPI module initialization 0x79 CSM initialization 0x7A – 0x7F Reserved for future AMI DXE codes 0x80 – 0x8F OEM DXE initialization codes 0x90 Boot Device Selection (BDS) phase is started...
- Page 203 Status Code Description 0xAF Exit Boot Services event 0xB0 Runtime Set Virtual Address MAP Begin 0xB1 Runtime Set Virtual Address MAP End 0xB2 Legacy Option ROM initialization 0xB3 System Reset 0xB4 USB hot plug 0xB5 PCI bus hot plug 0xB6 Clean-up of NVRAM 0xB7 Configuration Reset (reset of NVRAM settings)
- Page 204 Status Code Description 0x40 System is waking up from the S4 sleep state 0xAC System has transitioned into ACPI mode. Interrupt controller is in PIC mode. 0xAA System has transitioned into ACPI mode. Interrupt controller is in APIC mode. http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 205: Appendix I: How To Recover Uefi Bios
Appendix I: How to recover UEFI BIOS Important Notes: The emergency UEFI BIOS Recovery process is only used to rescue a system with a failed or corrupted BIOS image that fails to boot to an OS. It is not intended to be used as a general purpose BIOS flashing procedure and should not be used as such. - Page 206 5.The system will boot to BIOS setup. A new menu item will appear at the far right of the screen. Scroll to the 'Recovery' tab, move the curser to “Proceed with flash update” and press the "Enter" key on the keyboard to start the BIOS recovery process.
-
Page 207: Appendix Ii: Fan And Temp Sensors
Appendix II: Fan and Temp Sensors This section aims to help readers identify the locations of some specific FAN and Temp Sensors on the motherboard. A table of BIOS Temp sensor name explanation is also included for readers’ reference. Figure 1: Sensor Location NOTE: The red spot indicates the sensor. - Page 208 BIOS Temp Sensor Name Explanation: http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 209 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 210 BIOS Temp Sensor Name Explanation CPU0_Temp CPU0 Tempterature CPU1_Temp CPU1 Tempterature SYS_Air_Inlet Sensor connected to the Front Panel MB_Air_Inet Temperature of the M/B Air Inlet Area SYS_Air_Outlet Temperature of the System Air Outlet Area PCH_Temp Temperature of the PCH P0_MOSFET Max Temperature of CPU0_MOSFET P1_MOSFET Max Temperature of CPU1_MOSFET...
- Page 211 PSU0_FAN Fan Speed of PSU0 PSU1_STATUS Current status of PSU1 PSU1_Temp Temperature of PSU1 PSU1_FAN Fan Speed of PSU1 http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 212 NOTE http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 213: Appendix Iii: M.2 Latch Installation
Appendix III: M.2 Latch Installation This section provides a step-by-step demonstration on how to install a M.2 latch. 1. Take out the M.2 latch packs from the Accessory Box. 2. Insert the M.2 latch into the hole and then turn 90 degrees to the left as shown below. - Page 214 NOTE: The arrow sign on the blue knob is now turned left. 3. Push the blue knob slightly to the left as the arrow shows to lock the M.2 card in place. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 215 4. The installation of the M.2 latch is now complete. http://www.tyan.com...
- Page 216 NOTE http://www.tyan.com...
-
Page 217: Glossary
Glossary ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface): a power management specification that allows the operating system to control the amount of power distributed to the computer’s devices. Devices not in use can be turned off, reducing unnecessary power expenditure. AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): a PCI-based interface which was designed specifically for demands of 3D graphics applications. - Page 218 Bus: a data pathway. The term is used especially to refer to the connection between the processor and system memory, and between the processor and PCI or ISA local buses. Bus mastering: allows peripheral devices and IDEs to access the system memory without going through the CPU (similar to DMA channels).
- Page 219 DRAM (Dynamic RAM): widely available, very affordable form of RAM which looses data if it is not recharged regularly (every few milliseconds). This refresh requirement makes DRAM three to ten times slower than non-recharged RAM such as SRAM. ECC (Error Correction Code or Error Checking and Correcting): allows data to be checked for errors during run-time.
- Page 220 I/O (Input/Output): the connection between your computer and another piece of hardware (mouse, keyboard, etc.) IRQ (Interrupt Request): an electronic request that runs from a hardware device to the CPU. The interrupt controller assigns priorities to incoming requests and delivers them to the CPU. It is important that there is only one device hooked up to each IRQ line;...
- Page 221 RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): a way for the same data to be stored in different places on many hard drives. By using this method, the data is stored redundantly and multiple hard drives will appear as a single drive to the operating system.
- Page 222 Standby mode: in this mode, the video and hard drives shut down; all other devices continue to operate normally. UltraDMA-33/66/100: a fast version of the old DMA channel. UltraDMA is also called UltraATA. Without a proper UltraDMA controller, your system cannot take advantage of higher data transfer rates of the new UltraDMA/UltraATA hard drives.
-
Page 223: Technical Support
Technical Support If a problem arises with your system, you should first turn to your dealer for direct support. Your system has most likely been configured or designed by them and they should have the best idea of what hardware and software your system contains. - Page 224 NOTE: A receipt or copy of your invoice marked with the date of purchase is required before any warranty service can be rendered. You may obtain service by calling the manufacturer for a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number. The RMA number Should be prominently displayed on the outside of the shipping carton and the package should be mailed prepaid.

Need help?
Do you have a question about the S7126 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers