Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Advertisement
Table of Contents

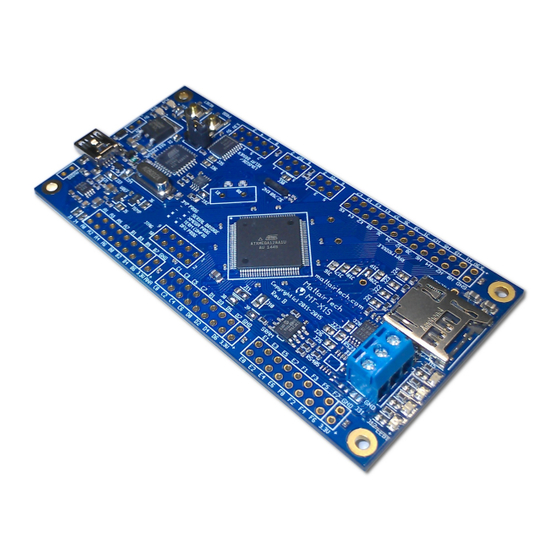
Summary of Contents for MattairTech MT-X1S
- Page 1 MT-X1S Manual March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 2: Table Of Contents
MT-X1S Manual Table of Contents Table of Contents Overview........................3 Introduction............................3 MTX1S Features..........................4 ATxmega128a1u Features........................ 5 Revision B Changes.....................7 Board Variants (Rev B only)..................7 MTX1S Hardware......................9 Solder Jumpers..........................9 Headers / Pin Descriptions......................10 Buttons / Jumper..........................13 Power / Status LEDs........................13 Power Supply..........................13 Clock Sources / RTC........................14 USB Serial Bridge........................... 15 MicroSD Card..........................15 32KB SPI SRAM..........................15 RS232 / RS485..........................15 Audio Amplifier..........................16 1.25V Precision Reference...................... -
Page 3: Overview
MT-X1S Manual Overview Overview Introduction The MTX1S is a flexible USB development board for the Atmel ATxmega128a1u microcontroller. Optionally available is a MicroSD card slot, 32KB SPI SRAM, audio amplifier, lowside / relay driver, temperature sensor, RS232 or RS485, 4 LEDs, and an onboard 1.25V precision reference for the ADC. The XMEGA can be programmed over USB using the optional onboard AVRISP mkII compatible PDI programmer. The XMEGA can communicate with a computer using the optional onboard USB to serial bridge (up to 2Mbps). The Atmel AT90USB162 USB AVR, which provides these features, will automatically sleep when USB is disconnected. Alternatively, the XMEGA can be connected directly to the USB connector. The board can be powered via USB or an external header. Voltage is regulated by a 3.3V, 1A LDO regulator. There are several clock options available onboard, including a 32.768KHz crystal, an external clock, an external HC49 crystal landing, and several internal clock options. Most XMEGA pins are routed to headers. The included peripheral devices are connected to the XMEGA via solder jumpers, which allows use of the pins if the device is not used. A demo program is preinstalled on the XMEGA demonstrating use of each peripheral device, as well as demonstrating sleep mode. March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/... -
Page 4: Mtx1S Features
MT-X1S Manual MTX1S Features Atmel XMEGA ATXMEGA128A1U, 128KB flash, 8KB RAM ● Optional onboard USB PDI programmer (no external programmer needed) ● AVRISP mkII compatible ● Program flash, EEPROM, fuses, lock bits, and more ● Supports AVR Studio 4 & 5, Atmel Studio 6 & 7, AVRDUDE, Codevision, and BASCOM ● Optional USB Serial Bridge ● Up to 2MHz baud rate (1MHz async) ● Synchronous or asynchronous operation ● XMEGA can be routed directly to the USB connector ● 3.3V, 1A LDO regulator ● Powered via USB or external header ● 32.768KHz crystal connected to TOSC (RTC) pins ● HC49 crystal landing connected to XTAL pins ● MicroSD card slot with pushpush spring action* ● 32KB SPI SRAM chip* ● 8 channel lowside / relay driver with kickback protection* ● Up to 70mA per channel ● 5V or 3.3V devices (relays, LCD backlights, etc.) ● Can be used as general purpose lowside driver ●... -
Page 5: Atxmega128A1U Features
MT-X1S Manual ATxmega128a1u Features Highperformance, lowpower Atmel AVR XMEGA 8/16bit Microcontroller ● Nonvolatile program and data memories ● l 64K 128KBytes of insystem selfprogrammable flash ● l 4K 8KBytes boot section ● l 2KBytes EEPROM ● l 4K 8KBytes internal SRAM ● l External bus interface for up to 16Mbytes SRAM ● l External bus interface for up to 128Mbit SDRAM ● Peripherall features ● Fourchannel DMA controller ● Eightchannel event system ● Eight 16bit timer/counters ● l Four timer/counters with 4 output compare or input capture channels ● l Four timer/counters with 2 output compare or input capture channels ● l High resolution extension on all timer/counters ● l Advanced waveform extension (AWeX) on two timer/counters ● One USB device interface ●... - Page 6 MT-X1S Manual I/O and packages ● l 78 Programmable I/O pins ● l 100 lead TQFP ● l 100 ball BGA ● l 100 ball VFBGA ● Operating voltage ● l 1.6 – 3.6V ● Operating frequency ● l 0 – 12MHz from 1.6V ● l 0 – 32MHz from 2.7V ● March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 7: Revision B Changes
MT-X1S Manual Revision B Changes Revision B Changes Revision B includes the following changes: 1) Add jumpers J33 and J34 to allow routing of the USB data lines to either the XMEGA or the AVR. Jumpers J10 and J11 were changed to 3pad to support this. The Serial RAM cannot be used when the XMEGA is connected to USB. 2) Add PTC fuse to USB Vbus 3) Change both crystals and buttons to SMT 4) Change 32.768KHz crystal load capacitors 5) Support a variant of the board without the onboard PDI programmer / serial bridge by adding J35 through J38: * J35 connects the STS_LED to TX (XMEGA F2) * J36 connects the PROG button to XCK (XMEGA F1) * J37 disconnects the debouncing capacitor of the Reset button for use with the XMEGA * J38 connects Reset button to XMEGA PDI_CLK (also reset) Board Variants (Rev B only) Board Variants (Rev B only) Revision B of the MTX1S is sold with two hardware options: 1) Onboard PDI Programmer / Serial Bridge 2) Onboard Peripheral Devices for a total of four board variants. The schematic shows the variant with both options installed. The peripheral devices include: 1) Micro SD card slot 2) Relay driver 3) Precision reference 4) Audio amplifier 5) Temperature sensor 6) Serial RAM 7) RS232 or RS485 The 4 LEDs are always installed The PDI programmer / serial bridge includes: 1) AT90USB162 and related parts (8MHz crystal, capacitors, etc) 2) bilateral switch (TC7W66) 3) PWR LED (STS LED is always installed) March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/... - Page 8 MT-X1S Manual Variant Jumper Configuration Variant Jumper Config With programmer J19: Installed J10 & J11: Any setting J33: Left*, J34: Up* J35 & J36: Not Installed J37: Installed, J38: Not Installed Without programmer J19: Not Installed J10 & J11: Disconnected* J33 & J34: Right & Down* J35 & J36: Installed J37: Not Installed, J38: Installed With programmer, but with J19: Not Installed J10 & J11: Disconnected* USB routed to XMEGA J33 & J34: Right & Down* J35: Not Installed, J36: Installed J37: Installed, J38: Not Installed * Direction indicates which pads are soldered when the board is viewed with the USB connector to the left. Disconnected means no solder connection from the center pad to either of the outer pads. If you have the programmer installed, you may switch the USB data connection between the programmer (AT90USB162) and the XMEGA. See the table above for jumper settings. Note that because the AT90USB162 is mounted, the XMEGA cannot control the STS LED, otherwise contention would occur. When the AT90USB162 detects that USB is disconnected, it will turn off both the STS and PWR LEDs and enter sleep. The RESET button should not be connected to the XMEGA. The AT90USB162 will reset the XMEGA after the button is pressed. Because the serial connection between the two chips is unused in this configuration, J19 should be disconnected (and optionally J18). Additionally, be sure that the Serial Mode is set to Asynchronous and the USB Ready Signal is Disabled in the AT90USB162 configuration (see the Configuration chapter). Finally, the XMEGA BOOTRST fuse bit must be changed so that the bootloader is run after reset. This can be done with ...
-
Page 9: Mtx1S Hardware
MT-X1S Manual MTX1S Hardware MTX1S Hardware Solder Jumpers Jumper Description USB Shield to gnd (not connected by default) ~5V to relay driver (5V header pin and kickback diodes common cathode) DACA0 (pin A2) to amplifier audio input AREF B (pin B0) to 1.25V reference AREF A (pin A0) to 1.25V reference ADCA1 (pin A1) to temperature sensor output Not present on MTX1S SPI D SS (pin D4) to SRAM chip select (external pullup) SPI D MOSI (pin D5) to SRAM SI (external pullup) SPI D SCK (pin D7) to SRAM clock input (external pullup) SPI D MISO (pin D6) to SRAM SO (external pulldown) Pin D0 to LED_1 Pin D1 to LED_2 Pin D2 to LED_3 Pin D3 to LED_4 SPI F SCK (pin F7) to relay driver clock input SPI F MOSI (pin F5) to relay driver SI input USART F0 RXD (pin F2) to AT90USB162 USART TX USART F0 TXD (pin F3) to AT90USB162 USART RX (shared with PDI_DATA) USART F0 XCK (pin F1) to AT90USB162 USART XCK (also USB ready signal) SPI E MISO (pin E6) to SD card SO (must enable XMEGA pullup) SPI E SCK (pin E7) to SD card clock input (external pullup) SPI E MOSI (pin E5) to SD card SI (external pullup) SPI E SS (pin E4) to SD card chip select (external pullup) Serial TX enable (pin E0) to RS232 _FORCEOFF_ or RS485 DE (external pulldown) Serial RX enable (pin E1) to RS232 _EN_ or RS485 _RE_ (external pullup) Serial RX (pin E2) to RS232 ROUT or RS485 RO March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/... -
Page 10: Headers / Pin Descriptions
MT-X1S Manual Serial TX (pin E3) to RS232 DIN or RS485 DI (external pullup) Serial Noninverting screwterminal to 680 ohm bias resistor to 3.3V (RS485 ONLY) Serial Nonnverting screwterminal to 120 ohm termination resistor to Inverting screw terminal (RS485 ONLY) Serial Inverting screwterminal to 680 ohm bias resistor to GND (RS485 ONLY) 3.3V to 33KOhm minimum current resistor to GND (MTX1S ONLY) Disconnect for lowest power consumption, but observe 3.3V regulator minimum load specification Jumpers J33 and J34 allow routing of the USB data lines to either the XMEGA or the A90USB162. Jumpers J10 and J11 were changed to 3pad to support this. The Serial RAM cannot be used when the XMEGA is connected to USB. See Board Variants section above. See J33 J35 connects the STS_LED to TX (XMEGA F2) . This allows the XMEGA to control the STS LED when the AT90USB162 in not installed. See Board Variants section above. J36 connects the PROG button to XCK (XMEGA F1) . This enables bootloader entry selection for the DFU bootloader on the XMEGA when the AT90USB162 in not installed. See Board Variants section above. The XMEGA reset line is also the PDI_CLK line used for programming/debugging. It cannot have a capacitor installed. J37 disconnects the debouncing capacitor of the Reset button for use with the XMEGA . See Board Variants section above. J38 connects Reset button to XMEGA PDI_CLK (also reset). This allows the XMEGA to be reset when the AT90USB162 in not installed. See Board Variants section above. Headers / Pin Descriptions Description External Power Header Under the default configuration, 5V should be supplied to this pin. Lower voltages may be used down to around 4V (or lower if using less current). Voltages greater than 5.5V require J2 to be disconnected. Disconnecting J2 will disable the 5V output pin and inductive kickback protection of the relay driver. But it will then allow voltages up to ~7.5V. This header is reverse polarity / reverse current protected using a schottky diode. 3.3V output headers (x4) There are four 2pin power output headers next to each port header group. The header next to the analog ports (ports A and B) comes from the analog 3.3V rail. Note that if these headers are installed, there will not be enough room to plug in IDC connectors next to each other. Relay Header 3.3V This can be used for the positive 3.3V side of a relay or other device. - Page 11 MT-X1S Manual Relay Header 5V This can be used for the positive 5V side of a relay or other device. This is also the common cathode of the kickback diodes in the relay driver. Both of these are disabled when J2 is diconnected. Relay Header 18 These are the 8 relay driver outputs. They are opendrain active low. When enabled, the output is connected to ground. When disabled, the pin is in a high impedance state. When driving inductive loads, like relays, freewheeling diodes provide kickback protection (when J2 connected). Noninductive loads can also be connected (ie: LCD backlight). Each output is capable of sinking 70mA. Outputs can be combined. Audio Header This is the singe channel output from the audio amplifier. It can drive 8 ohm loads. 4 ohm loads may also be connected, but under some conditions, distortion or automatic thermal shutdown may occur. JTAG Header JTAG header for the XMEGA which can be used for programming, debugging, and JTAG boundary scans. Disable JTAG to gain access to the four underlying analog/GPIO pins. PDI Header PDI header for the XMEGA which can be used for programming or debugging. When using this header, J19 MUST be disconnected. This is due to the fact that RX and PDI_DATA are shared. This means that the XMEGA serial TX won't be connected to the USB AVR RX. This doesn't affect programming, but may present a problem in certain situations when debugging. If serial TX is required when debugging, the JTAG header can be used. Alternatively, an external USB serial bridge can be connected. ISP Header ISP header for the USB AVR which can be used for programming or debugging. The USB AVR can be programmed over USB using the DFU bootloader. Port A All pins are routed to headers. The 1.25V precision reference can be connected to pin A0 (Vref input) through a solder jumper. The temperature sensor output and audio amplifier input are also connected to this port. Port B All pins are routed to headers. The 1.25V precision reference can be connected to pin B0 (Vref input) through a solder jumper. Note that JTAG is connected to pins B4 – B7. JTAG must be disabled to use these pins for other purposes like ...
- Page 12 MT-X1S Manual Pins Q0 and Q1 The 32.768KHz crystal is connected to these pins, which serve as the TOSC input pins of the RTC. Pins Q2 and Q3 Pin Q2 is routed to the chip select pin of the relay driver. Pin Q3 is routed to the audio amplifier powerdown pin. Neither pin is routed to a header. Pins R0 and R1 Both of these pins are routed to an HC49 crystal footprint. A 22pF capacitor is also connected to each line. If an external clock is used, connect it to R1. Serial Screw Terminal Pin 1, which is closest to the port F header, is ground. This should always be connected, with both RS232 and RS485. Pin 2 is RX (RS232) or inverting (, RS485). Pin 3 is TX (RS232) or noninverting (+, RS485). March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 13: Buttons / Jumper
MT-X1S Manual Buttons / Jumper There are four modes of operation which are selected using the PROG button and JMP jumper. The button and jumper are sampled when powering up or pressing reset. Additionally, the MT X1S can be switched between the AVRISP mkII programmer and the serial bridge during runtime by pressing the PROG button. This is useful, for example, to program the XMEGA, then switch to the serial bridge for printf() debugging. The reset button resets the USB AVR, which will in turn reset the XMEGA when it boots. The following table lists the mode selection during powerup and reset. Mode Selection During Powerup and Reset PROG Button JMP Jumper Mode Pressed Installed DFU Bootloader Not Pressed Installed Configuration Mode Pressed Not Installed AVRISP mkII PDI Programmer Not Pressed Not Installed USB Serial Bridge Power / Status LEDs There are two green LEDs that are used to indicate USB status, the mode of operation, communication activity, programmer status, and more. The following table lists LED functionality in each mode. Both LEDs are turned off in sleep mode. LED Functionality Mode STS LED PWR LED AVRISP mkII Programmer Programmer Activity PWM pulsing Configuration Mode... -
Page 14: Clock Sources / Rtc
MT-X1S Manual prevents VBUS from rising to the level of the external voltage. Note that there is a minimum load of 100uA for this regulator. The MTX1S can consume less than 75uA in the deepest sleep modes. An onboard load resistor between 3.3V and Gnd is provided to ensure that this requirement is met. A MicroSD card inserted may consume enough to meet the specification without the resistor, thus it can be disconnected by using solder jumper J32. The 3.3V regulator has thermal protection and foldback current limiting. There is a 10uF capacitor on both the input and output. Note that 10uF is the maximum allowed by the USB specification. When using the external header, additional capacitance may be needed with higher impedance voltage sources (ie: batteries, long cable runs). The regulator input can also be routed through J2 to the header pin labeled 5V (near the relay driver). Voltages greater than 5.5V on the external power input header require J2 to be disconnected, which will disable the relay driver kickback protection. Clock Sources / RTC By default, a 32.768KHz crystal is installed and connected to the TOSC pins of the XMEGA (R0 and R1). An HC49 crystal landing is available as well, with 22pF load capacitors preinstalled. An external clock can also be connected to pin R1. There are several internal clock options as well. The demo program makes use of the 32MHz internal RC oscillator. This oscillator is configured to be auto calibrated by a DFLL, which uses the 32.768KHz crystal as input. The crystal is also the source for the RTC. A 2MHz RC oscillator and two different 32KHz oscillators are also available. A PLL and prescalers can be used to obtain the various clocks. Be aware that the ATxmega128a1u requires both the 2MHz and 32MHz oscillators to be running and both DFLLs to be enabled for either DFLL to operate due to errata. Atmel ASF (Atmel Software Framework) does not support this arrangement, but the example code shows how to set this up. Also note that the DFLL calibrated oscillators will still not be as accurate as an external high speed crystal. If using an external crystal, it must be 0.4MHz to 16MHz. The PLL can be used to obtain higher clock speeds. Programming Headers The PDI header has the standard 6pin layout. Because an onboard programmer is provided, an external programmer is not necessary. However, debugging requires use of an external debugger connected to the PDI header or the JTAG header. Because the RX/D pin is shared with the XMEGA PDI_DATA pin, an external programmer/debugger cannot be used when using the serial bridge as this would cause contention. Jumper J19 can be disconnected to avoid this contention, but the onboard serial bridge will no longer be usable (an external bridge can be used if needed for debugging). Alternatively, the JTAG header can be used for debugging. When using an external debugger or programmer on the PDI header, the USB AVR should be in any mode other than the PDI programmer. -
Page 15: Usb Serial Bridge
MT-X1S Manual routed to a header, to be used for other purposes. External pull resistors are installed to keep the peripheral pins at a defined state during boot or when the peripheral is disconnected. They pull chip select lines to the deselected state to minimize power consumption. Most solder jumpers are connected by default. To disconnect for the first time, a small trace connecting the two jumper pads must be cut. To reconnect, create a solder bridge across the pads. Jumper J1 can be soldered to connect the USB shield to ground. The USB specification calls for the USB shield to be connected to ground on the host side only. However, it may be desired to ground this on the device side. An 0603 SMT component may be soldered on the solder jumper pads as well. USB Serial Bridge The USB Serial bridge allows the XMEGA to communicate with a computer over USB by simply using a USART. There is no need to learn the USB protocol or utilize a USB library. All USB functionality is handled by the USB AVR (AT90USB162). It simply relays bytes between the XMEGA and the host. The MTX1S uses two pins on USART F (RX and TX) in asynchronous mode and three pins (adding XCK) in synchronous mode. Optionally, a USB ready signal is available on the XCK pin. To minimize power consumption. TX should be tristated before entering sleep. This is due to the sharing of PDI_DATA and TX. PDI_DATA has a pulldown active, which will consume current when TX is set to output high. All three pins can be disconnected from the USB AVR using the solder jumpers. MicroSD Card The MicroSD card slot has a springloaded mechanism that locks the card in place when inserted (pushin, pushout). The contacts are goldplated. It is connected to SPI E using four pins. All pins have external 47Kohm pullups installed. All four pins can be disconnected from the MicroSD card slot using the solder jumpers. Note that when in the deepest sleep modes and a card is installed, it will likely consume the most current. Since the minimum load required by the regulator is 100uA, and the rest of the onboard components may consume less than 75uA, having a card installed may allow disconnection of the minimum load resistor (solder jumper), which itself consumes 100uA. 32KB SPI SRAM The 32KB SPI SRAM is the 23K256I/SN from Microchip. It has a very simple protocol, and can be quite fast operating at 16MHz with sequential access (ie: data capture). It is less suitable for storage that requires random access. It is connected to SPI D using four pins, all of which have 47Kohm external pull resistors. All four pins can be disconnected using the solder jumpers. A simple driver is provided in the ASF template. More more information, consult the datasheet. RS232 / RS485 The MTX1S comes with either an RS232 or RS485 interface IC installed. There are two different PCB footprints, but the screw terminals and I/O lines are shared. Therefore, only one can be installed on the PCB at a time. The RS232 IC is the MAX3221IPWR from Texas Instruments. The RS485 IC is the ISL3175EIUZ from Intersil. The IC is connected to USART E via four pins. They are RX, TX, RX enable, and TX enable. There are three 47Kohm pull resistors installed, a pullup on TX, and pull resistors on the enable lines that keep both disabled by default. All four pins can be ... -
Page 16: Audio Amplifier
MT-X1S Manual disconnected using the solder jumpers. The IC is connected to a 3pin screw terminal with 3.5mm pin spacing. The pin closest to header F is ground. The center pin is RX with RS232 installed, or Inverting () with RS485. The pin next to the MicroSD slot is TX with RS232 or NonInverting (+) with RS485. Note that the A/Y, B/Z naming is not used due to differing definitions among different manufacturers. When RS485 is installed, there is a 120ohm termination resistor installed between the inverting and noninverting pins, which can be disconnected using the solder jumper. Additionally, two 680 ohm resistors are installed that can be used to bias the inverting and noninverting pins to negative and positive voltages respectively. The IC does not require this biasing so the bias resistors are disconnected by default. When connecting wires to the screw terminal, take care not to short a wire to an LED as they are close in proximity. The location of the LEDs was chosen to minimize differences between the MTX1 and the MTX1S. When using RS232, be aware that the auto powerdown feature is enabled. This causes the TX driver to power down when the RX line is disconnected (no valid RS232 level present). One consequence of this is that a loopback test requires a pull resistor on RX to enable the TX driver, which will then keep RX at a valid level thereafter. For more information on either IC, consult the appropriate datasheet. Audio Amplifier The audio amplifier is the LM4889MM/NOPB from National Semiconductor. It is a single channel, class AB, 400mW @ 3.3V amplifier with depop and thermal protection. It is connected to the XMEGA DAC A0 on pin A2, which can be disconnected using a solder jumper. The shutdown pin is routed to pin Q3 and has a 47 Kohm pull resistor to keep the IC in shutdown when Q3 is not driven. The differential gain is set to 2, so the internal 1V reference or the external 1.25V reference can be used. An 8ohm or 16ohm speaker can be connected to the output which is routed to a two pin header. A 4ohm load can also be connected, but the amplifier may enter thermal shutdown if using a higher voltage reference and the signal magnitude remains large for a long enough period of time. For more information on this IC, please consult the datasheet. 1.25V Precision Reference The 1.25V precision reference is the ISL60002DIH312ZTK from Intersil. It is a lowpower FGA reference with a low 20ppm/C temperature coefficient. The initial accuracy is +/5mV. Because each MTX1S board is intended to be calibrated individually, the initial accuracy was deemed less important than the temperature coefficient. The reference is connected to both reference inputs, pins A0 and B0. It can be disconnected using the solder jumpers. The reference voltage of 1.25V was chosen as a workaround to the ADC errata of the ATxmega128a1. It is intended to be used with the ADC in differential mode and with signed conversions. The voltage to be measured is connected to the positive input, and the reference to the negative. This results in conversions in the ~0 to 2.5V range. See the source code for example setup and usage. For more information on this IC, please consult the datasheet. Temperature Sensor The temperature sensor is the MCP9701ATE/TT from Microchip. It is connected to pin A1, ... -
Page 17: 8Channel Lowside / Relay Driver
MT-X1S Manual temperature is limited to the maximum PCB temperature. It has an accuracy of +/ 2C (max.) and it outputs 19.5mV/C. It consumes only 6uA (typ.). For more information on this IC, please consult the datasheet. 8channel Lowside / Relay Driver The 8channel lowside / relay driver is the MAX4820 from Maxim. The outputs are opendrain. Each channel can drive low at 70mA each. Channels can be connected together to increase the current capability. All channels have kickback protection diodes, allowing them to driver relays. Note that solder jumper J2 must be connected for kickback protection to be available. All eight outputs, along with 3.3V (regulated Vcc) and ~5V (external voltage), are routed to a 10pin header. Thus, devices that use either 3.3V or 5V (ie: 5V relay, 5V LCD backlight) are supported. Voltages greater than 5.5V on the external power input header require J2 to be disconnected, which will disable the relay is connected to SPI F and can be disconnected using the solder driver kickback protection. The IC jumpers. Note that MISO is not connected, so the XMEGA cannot read from the IC. Also note that the SPI F SS line is not used as the chip select, but instead, Q2 is used. Thus, it is necessary to configure the SS pin as an output, or enable the pullup and leave it as an input so that SPI will operate as a master. The maximum operating speed is 2MHz. The protocol is very simple; essentially just a shift register. A simple driver is provided in the ASF template. For more information on this IC, please consult the datasheet. LEDs There are four LEDs connected to pins D0D3, and can be disconnected by using the solder jumpers. The LEDs are on when the outputs are high. The LEDs are connected to ground through 249 ohm series resistors. External 1MB lowpower SRAM (optional) An external 1 MB lowpower SRAM module is available separately. * 8Mbit (1024 x 8) static RAM * Cypress CY62158EV30 IC * 45ns * 2.2V3.6V * 18mA (25mA max) @ max speed * 2uA (8uA max) when not selected * 40C to +85C * 2 latches for address lines (20bit) * dedicated 8bit data lines... -
Page 18: Installation
MT-X1S Manual Installation Installation This section applies only to boards with the PDI Programmer / Serial Bridge option installed. Before plugging in the MTX1S for the first time, the latest software and drivers must be downloaded. The MTX1S is supported under Windows XP, Vista (32 and 64 bit), Windows 7 (32 and 64 bit), Windows 8, and Windows 10. The MTX1S appears as three different devices to the PC depending on which mode is selected by the button and jumper. These devices are the AVRISP mkII compatible programmer, the DFU bootloader for firmware updates of the USB AVR, and the USB CDC device (Virtual COM port) which is used for configuration mode and the USB Serial bridge. Therefore, three drivers are required. The DFU driver is included with software available on the Atmel website. The CDC driver is included with Windows, but requires an .inf file available on the MattairTech website. The following table lists the minimum versions of the required software. If the software provides a driver, is is listed as well. See the Firmware Updates section for installation of the DFU bootloader driver. Required Downloads Software Version Driver AVRISPmkII AVRISPmkII https://www.mattairtech.com/software/MattairTech_AVRISPmk latest Driver driver II_Driver_Signed.zip https://www.mattairtech.com/software/MattairTech_CDC_Driv CDC Driver latest CDC driver er_Signed.zip http://www.atmel.com/tools/atmelstudio.aspx OR AVR Studio / 4.19, 5.x, http://www.atmel.com/tools/studioarchive.aspx (AVR Studio) AVRISPmkII Atmel Studio 6.x, 7.x... - Page 19 MT-X1S Manual WinAVR / AVRDUDE WinAVR contains the GNU GCC compiler for C and C++, compiler tools, and libraries (including AVR Libc). It also includes AVRDUDE for Windows, which is a command line tool for transferring firmware to AVR microcontrollers. A graphical tool is included with AVR Studio. Download WinAVR from http://sourceforge.net/projects/winavr/files/WinAVR/20100110/ and install it first. To use AVRDUDE, you will need to download and install an update to libusbwin32 available at http://sourceforge.net/projects/libusbwin32/files/libusbwin32releases/. Choose the libusbwin32 develfilterx.x.x.x.exe file. Do this only after installing AVR Studio. You will also need to change the MTX1S AVRISP mkII Programmer host configuration to AVRDUDE. Note that WinAVR is outdated. It is not recommended for newer devices like the XMEGA series. AVRDUDE can also be installed separately. March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
- Page 20 MT-X1S Manual MTX1S Driver / Serial Configuration Next, the MTX1S CDC driver can be installed, which is used by the serial bridge and configuration mode. This driver allows the board to appear as a COM port. The driver itself is included with Windows, but an .inf file is needed to configure it. Download the .inf file from https://www.mattairtech.com/software/MattairTech_CDC_Driver_Signed.zip . Note that Windows Vista 64bit, Windows 7 64bit and Windows 8 require the signed driver. Now, plug in or reset the MTX1S with jumper JMP removed. This will run the USBserial bridge. Both LEDs should be lit. Windows will then prompt you for the MTX1S CDC driver. Point the installer to the directory where you downloaded the driver and install. Note that you may need to rename the driver in order for it to show up in the installer. Windows may add the .txt extension to the file after downloading. Rename it so that it ends with .inf. Ignore any warnings given by the installer (ie: unsigned driver). Once the driver is loaded, the device will appear as the MTX1S CDC device using a COM port in the device manager. There is no need to configure serial port parameters. The buad rate, for example, is ignored. The MTX1S will always communicate with the computer at full speed (up to 2Mbps). If you experience any buffering problems, for example, a delayed response to user input, then change both buffer sizes to 1. Terminal Emulator Finally, the terminal emulator can be configured. Windows XP includes HyperTerminal, which has been tested with the MTX1S and will be documented here. There are several other terminal emulators available freely on the Internet. If you wish to use any of them, it should be no trouble to adapt the instructions presented here. Next, start HyperTerminal. Create a new connection. You will refer to this connection again, so give it an appropriate name (after it is configured, you can copy it to your desktop). Select the MTX1S COM port (ie: COM4) and continue. It is not necessary to configure the baud rate or any other serial Now, click on the connect icon. parameters. After connecting, you may see garbage on the terminal screen. If this is the case, click on the configuration icon and change the emulation to ANSI (or ANSIW). The configuration mode requires an ANSI terminal to allow drawing of the menu system. Normally, when first entering a mode that uses the CDC driver, a message that reads “Press any Key” is printed periodically. If you do not see this message, just press any key to continue. Note that it may not be possible to switch between modes using the button until a key is pressed. It is important to always click the disconnect icon before switching to the PDI programmer. Then click the connect icon a couple seconds after returning. This is required because changing to the AVRISP mkII driver unloads the CDC driver, then loads the AVRISP mkII driver. In order for the terminal to use the same COM port as before, it must be disconnected when returning to the CDC driver so that it does not assign a new COM port.
- Page 21 MT-X1S Manual Linux Installation Linux is supported as well. You must download and build the toolchain from the latest script available at AVR Freaks on the AVR GCC Forum (Script for building AVR GCC sticky at http://www.avrfreaks.net/index.php?name=PNphpBB2&file=viewtopic&t=42631). All firmware written for the MTX1S is developed under Linux using this toolchain. Drivers TODO (drivers should already be installed) GCC Toolchain TODO (see opening paragraph) AVRDUDE TODO (ie: avrdude p x128a1 c avrisp2 P usb U flash:w:"myfirmware.hex") dfuprogrammer TODO (must use version 0.5.2 or higher) Terminal Emulator TODO (can use minicom, config port (ie: /dev/tty/ACM0), save config, run with minicom o) March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 22: Avrisp Mkii Compatible Pdi Programmer
MT-X1S Manual AVRISP mkII Compatible PDI Programmer AVRISP mkII Compatible PDI Programmer This section applies only to boards with the PDI Programmer / Serial Bridge option installed. However, most of the information on Atmel Studio usage still applies. The MTX1S onboard PDI Programmer is based on the AVRISP mkII compatible programmer written by Dean Camera (http://www.fourwalledcubicle.com/). AVR Studio 4.19, 5.x, Atmel Studio 6.x, and AVRDUDE are supported. Using Atmel Studio (AVR Studio) Start Atmel Studio and open or create a new project. An example project, which can be used as a template, is available for the MTX1S at http://www.mattairtech.com/software/MTX1S/MT X1S_Simple_Demo.zip. To install, click File>Import>Project Template. Once installed, open the template by clicking File>New>Project and selecting the MTX1S_Simple_Demo. Once loaded, you can read the main source file. Also have a look at the src/config and src/asf/xmega/boards/mtx1 directories using the solution explorer pane. You may also wish to view the toolchain options with Project>Properties. March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/... - Page 23 MT-X1S Manual Next, build the project. Then, click on the Device Programming button. In the Device Programming window, select the AVRISP mkII as the tool. If no tool appears, be sure that the MTX1S is plugged in and in programming mode (STS LED will be pulsing). Select the ATxmega128A1 as the device and PDI as the interface and click Apply. You should now be connected to the AVRISP mkII compatible programmer with serial number 000200012345. Now click Read next to Device signature. It should match the device if all is well. It is recommended to always perform this step first to verify the connection. The target voltage will always read 3.3V. March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
- Page 24 MT-X1S Manual Next, select the Memories page. In the Flash section, a hex file can programmed into the targets flash memory. Load your hex file, then click Program. The hex file for the MT X1S_Simple_Demo is located in the Debug folder. You will need to erase the target first if you do not have “Erase Flash before programming” checked. You should also verify the flash as well. March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
- Page 25 MT-X1S Manual Next, select the Fuses page. It is best to leave the fuse settings alone until you understand what they do. In particular, do not set the BOD (Brownout detection) voltage too close to 3.3V, as this could cause the target to be held perpetually in reset. Due to errata, the BOD should not be enabled in sampled mode when active or idle (BODACT). Sampled mode is OK for other sleep modes (BODPD). Now you may wish to look at the other pages. Note that any firmware upgrade feature should not be used. The MTX1S PDI Programmer is not an actual AVRISP mkII, it just emulates one, so you should not attempt to update the MTX1S firmware using Atmel Studio. Any firmware updates will be posted to the website and loaded using FLIP or dfuprogrammer. March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 26: Using Avrdude
MT-X1S Manual Using AVRDUDE TODO (ie: avrdude p x128a1 c avrisp2 P usb U flash:w:"myfirmware.hex") March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/... -
Page 27: Serial Bridge
MT-X1S Manual Serial Bridge Serial Bridge This section applies only to boards with the PDI Programmer / Serial Bridge option installed. The serial bridge can connect the XMEGA to a host application (ie: terminal emulator) over USB. The XMEGA simply uses one USART as it would with, for example, RS232. There is no need to learn the USB protocol or use a USB library. On the host side, the MTX1S will appear as a virtual COM port. Speeds of up to 2Mbps are supported. Configuration Before using the serial bridge, it must be configured to be compatible with the target. This configuration is stored in EEPROM. There is no need to duplicate the settings on the host side, as communication between the host and MT X1S will always be the maximum supported USB speed, and the other parameters are ignored by the host. Only the connection between the USB AVR and the XMEGA use these settings. Note that when configuring the speed to be manual, it is possible to set the speed higher than 2MHz, but the maximum speed supported by the USB link is 2MHz. The serial bridge is configured in configuration mode (jumper on, button not pressed). Serial Bridge Configuration Options Configuration Option Possible Values Speed 2M, 1M, 500K, 250K, 125K, 76.8K, 57.6K, 38.4K, 19.2K, 9600, 2400, manual Baud Rate Register 0x0000 0x0FFF (if manual selected as speed) Clock 2X 1X, 2X Clock Mode async, sync Data Bits 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 When in synchronous mode, the USB AVR is the master, so the XCK pin is enabled as an output. The XMEGA must enable its clock pin as an input and be configured as a slave. When using 9bit data frames, two bytes are sent or received for every frame. The first byte simply contains the 9th bit, thus the first byte will always be 0 or 1. The second byte contains the rest of the 8 bits. March 2, 2017... - Page 28 MT-X1S Manual Baud Rate Register Value (Manual Speed) Async 1X Async 2X Synchronous UBRR= UBRR= UBRR= −1 −1 −1 16∗BAUD 8∗BAUD 2∗BAUD BAUD= BAUD= BAUD= 16∗UBRR1 8∗UBRR1 2∗UBRR1 where =8000000 March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 29: Configuration
MT-X1S Manual Configuration Configuration This section applies only to boards with the PDI Programmer / Serial Bridge option installed. The MTX1S PDI programmer, serial bridge, and other features can be configured by entering configuration mode. This configuration is stored in nonvolatile EEPROM memory. Configuration mode requires an ANSI terminal emulator. Configuration options are highlighted by using the up and down arrow keys, and selected using the enter key. Some dialogs are for entering numbers in hexadecimal. Here, the left and right arrow keys and backspace are used. The menu system is structured as follows: Serial Speed (Serial bridge speed selection) ● List of selectable speeds: 2400, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 50.0K, 76.8K, 125K, 250K, 500K, 1M, 2M ● Manual (when selected, configure using Manual Settings below) ● Manual Settings ● Baud Rate Register (enter value in hex) ● Clock 2X (async mode only) ● Serial Mode ● Asynchronous or synchronous ● Sleep Mode (Which sleep mode is used when USB is disconnected or suspended) ● Power Down or Standby ● Ready Signal (USB ready signal is opendrain active low on XCK pin from USB AVR) ● Disabled or Enabled ●... -
Page 30: Xmega Demo Program
MT-X1S Manual XMEGA Demo Program XMEGA Demo Program Note: This page describes the preinstalled demo program. This program is primarily meant for testing. While the source code is available, it is not intended to be reused. The code is a collection of many code fragments. It is disorganized and complicated. It is recommended to use the Atmel Studio 6 ASF (Atmel Software Framework) template to get started (see Using Atmel Studio (AVR Studio)). The following relates to the preinstalled demo. Note2: This program is installed on all board variants, even those without the optional onboard peripheral devices. In these cases, most of the functionality will be useless except for the LED demo (the 4 LEDs are always installed). Additionally, if the optional onboard PDI programmer / serial bridge is not installed, communications must be made by connecting a USBserial converter to pins F2 (XMEGA TX) and F3 (XMEGA RX) at 1000000 baud (8N1). XMEGA uses serial bridge to display menu system on ANSI compatible terminal emulator screen. Remove the jumper and boot the board without pressing the button (remember that the terminal must be disconnected while resetting). Press any key, and the main demo menu will appear. Now, all interaction is with the XMEGA via the USB serial bridge. MicroSD Card Demo: The SD card demo makes use of the FatFS module from ChaN. FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32 are supported. Press 'h' for a help menu. Audio Demo: You can load wav files from the SD card and play them over an ~8 ohm speaker connected to the audio amplifier. You will need to use an audio program (like sox), to encode music or sound to 8bit or 16bit (recommended), 44.1KHz or less, mono uncompressed PCM. Then, in the audio demo, select the file chooser and pick a file. You can use the slider to adjust volume. When using the sleep demo, current measurements can be made using the external power header. Disconnect J2 to allow voltages above 5.5V. Supply 6.0V – 7.5V to this header so that current is drawn from this connector rather than from USB. Running the demo will put the XMEGA to sleep with the RTC running and waking the cpu every second to update the time. Most current consumption will then be from the USB AVR. Now unplug USB. The current consumption will drop further. Currently, ~75uA is consumed by the board in this state (without MicroSD card installed). Not all low power features are used, so this number can be lowered further. But note that a minimum load of 100uA should be present on the regulator output. The measured current at the external connector includes the regulator ground current, which will add to the 100uA minimum load. March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/... -
Page 31: Firmware Updates
MT-X1S Manual Firmware Updates Firmware Updates This section applies only to boards with the PDI Programmer / Serial Bridge option installed. The MTX1S firmware will be updated periodically to add new features and fix bugs. These updates will be available on the MattairTech website. The updates may include just a hex file (for programming flash), or both a hex file and eep file (for programming both flash and EEPROM). FLIP is a graphical utility for Windows used to load firmware updates onto the MTX1S. FLIP includes the DFU bootloader driver. Download FLIP 3.4.2 or higher from http://www.atmel.com/tools/FLIP.aspx and install. If required to install a signed driver, then consult the table below for the download link. Downloads required for Firmware Updates Software Version Driver MTX1S latest http://www.mattairtech.com/software/MTX1S/MT_X1S.hex Firmware (At90USB162) FLIP 3.4.2 + DFU driver http://www.atmel.com/tools/FLIP.aspx http://www.avrfreaks.net/index.php?module=Freaks Signed DFU latest DFU driver %20Academy&func=viewItem&item_type=project&item_id=219 Driver Once FLIP is installed, the DFU bootloader driver can be loaded. Plug in the MTX1S with jumper JMP installed and while holding down the PROG button. This will enter the DFU bootloader. LED_STS should be on and LED_PWR should be off. Windows will then prompt you for the AT90USB162 driver. By default, this is located in the Program Files/Atmel/Flip 3.4.2/usb directory. Once the driver is loaded, the device will appear as the AT90USB162 device under Atmel USB Devices in the device manager (note that ATmega32U2 is shown in screenshots). March 2, 2017... - Page 32 MT-X1S Manual FLIP Plug in the MTX1S with jumper JMP installed and while holding down the PROG button. This will enter the DFU bootloader. LED_STS should be on and LED_PWR should be off. Now launch the FLIP utility. When it has loaded, click on the chip icon and select the AT90USB162. Next, click on the USB icon, select USB, then connect. The screen should now show information about the AT90USB162. Click on the File menu, and open the appropriate hex file. More information will appear about the program. Be sure that erase is checked. The MTX1S firmware cannot be loaded unless the flash is erased first. Program must be checked. Verify should also be checked. Now click on the Run button in the lowerleft of the screen, and the firmware will be quickly loaded onto the MTX1S. If you encounter problems, you will need to unplug the MTX1S, disconnect FLIP, and start over making certain that the above settings are observed. March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
- Page 33 MT-X1S Manual You may also need to program the EEPROM. If so, click on Select EEPROM at the bottom. Then, click on the File menu and open the appropriate eep file. You will have to change the file filter to allow you to see the eep file. Note that eep files are just hex files but with the eep extension instead of hex. More information will appear about the file when selected. Both Program and Verify should be checked. Click run to program the EEPROM. dfuprogrammer TODO Must erase chip first. Cannot read flash. dfuprogrammer at90usb162 erase dfuprogrammer at90usb162 flasheeprom MT_X1S.eep (if applicable) dfuprogrammer at90usb162 flash MT_X1S.hex March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 34: Xmega Usb Dfu Bootloader (Rev B Only)
MT-X1S Manual XMEGA USB DFU Bootloader (Rev B Only) XMEGA USB DFU Bootloader (Rev B Only) USB enabled XMEGAs (ATXMEGA128A1U) come with a USB DFU bootloader preinstalled. The bootloader is from Atmel. Documentation can be found in AVR1916. Note that the MTX1S uses a different bootloader activation pin than the Atmel default. The hex files provided by Atmel (from AVR1916.zip) were patched directly to use the MTX1S PROG button. The patched hex files can be found at https://www.mattairtech.com/software/MTX1S/MTX1S_DFU_Bootloaders_104.zip. Installing FLIP / USB DFU Drivers FLIP is a graphical utility for Windows used to load firmware into the XMEGA. FLIP supplies the USB DFU bootloader driver. Download FLIP 3.4.7 or higher from http://www.atmel.com/tools/flip.aspx and install. Older versions may not support the latest XMEGA variants. Once FLIP is installed, the USB DFU drivers can be loaded. Press the PROG button while powering the board (or press reset), then release. This will start the DFU bootloader. Windows will then prompt you for the driver, which is located in the Program Files/Atmel/Flip 3.4.7/usb directory. Point the installer to that directory and install. Once the driver is loaded, the device will appear under Atmel USB Devices in the device manager. No driver is needed for Linux or OS X. Using FLIP Press the PROG button while powering the board (or press reset), then release. This will start the DFU bootloader. Now launch the FLIP utility. When it has loaded, click on the chip icon and select your XMEGA variant. Next, click on the USB icon, select USB, then connect. The screen should now show information about the XMEGA. Click on the File menu, and open the appropriate hex file. More information will appear about the program. Be sure that erase is checked. The firmware cannot be loaded unless the flash is erased first. Program must be checked. Verify should also be checked. Now click on the Run button in the lowerleft of the screen, and the firmware will be quickly loaded into the XMEGA FLASH. You may also program the EEPROM. If so, click on Select EEPROM at the bottom. Then, click on the File menu and open the appropriate eep file. You will have to change the file filter to allow you to see the eep file. Note that eep files are just hex files but with the eep extension instead of hex. More information will appear about the file when selected. Both Program and Verify should be checked. Click run to program the EEPROM. You can run your application without pressing reset by unchecking the reset box and pressing the “Start Application” button (lower right). Using dfuprogrammer dfuprogrammer is a Linux command line utility used to program the XMEGA memories. Driver installation is not required. Download version 0.6.2 or higher from http://dfu programmer.sourceforge.net/ . The following commands can be used: March 2, 2017... - Page 35 MT-X1S Manual dfu-programmer atxmega128a1u erase dfu-programmer atxmega128a1u flash Blink_128a1u.hex dfu-programmer atxmega128a1u flash-eeprom YourEep.eep (if applicable) dfu-programmer atxmega128a1u start (to jump to application section without reset) March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 36: Troubleshooting / Faq
MT-X1S Manual Troubleshooting / FAQ Troubleshooting / FAQ AVRDUDE 6.x does not yet support the MTX1S. A working patched version ● can be found at http://www.mattairtech.com/software/avrdude_6.0.1_patched_windows.zip. Thanks to Larry Viesse. For support on Linux 64bit, download http://www.mattairtech.com/software/avrdude_6.0.1_patched_Linux_64.zip. For support on other Linux (especially with xhci (USB 3.0)), replace the usb_libusb.c file from 6.0.1 with http://www.mattairtech.com/software/usb_libusb.c. If you are having problems communicating with the programmer using Atmel Studio 6.x, ● download the Zadig USB driver manager at http://zadig.akeo.ie/. Under options, List All Devices. The AVRISP mkII should show up in the list. Replace the current driver with libusbwin32 (v1.2.6.0), which comes embedded with Zadig. Alternatively, please use the procedure at https://www.olimex.com/forum/index.php? topic=4188.0 If you are having problems communicating with the programmer using Atmel Studio 7.x, please ● ensure that you are using the new AVRISPmkII driver, which now must be downloaded separately (see installation). Prior versions of Atmel Studio included this driver. Support Information Support Information Please check the MattairTech website (http://www.MattairTech.com/) for firmware and software updates. Email me if you have any feature requests, suggestions, or if you have found a bug. If you need support, please contact me (email is best). You can also find support information at the MattairTech website. A support forum is planned. Support for AVRs in general can be found at AVRfreaks (http://www.avrfreaks.net/). There, I monitor the forums section as the user physicist. Justin Mattair MattairTech LLC PO Box 1079 Heppner, OR 97836 USA 541-626-1531 justin@mattair.net... -
Page 37: Schematic
MT-X1S Manual Schematic Schematic March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/... - Page 38 MT-X1S Manual March 2, 2017 http://www.mattairtech.com/...
-
Page 39: Legal Notices
This document is intended only to assist the reader in the use of the product. MattairTech LLC shall not be liable for any loss or damage arising from the use of any information in this document or any error or omission in such information or any incorrect use of the product. - Page 40 MT-X1S Manual Licenses LUFA USB Library Copyright 2012 Dean Camera (dean [at] fourwalledcubicle [dot] com) Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee, provided that the above copyright notice appear in...
-
Page 41: Appendix A: Precautions
Manual Appendix A: Precautions Appendix A: Precautions CAUTION The MT-X1S contains static sensitive components. Use the usual ESD procedures when handling. CAUTION Improper fuse settings may result in an unusable AVR. Be certain that you know the effects of changing the fuses, that you... -
Page 42: Appendix B: Other Mattairtech Products
MT-X1S Manual Appendix B: Other MattairTech Products Appendix B: Other MattairTech Products ZeptoProg II AVRISP mkII Programmer ● AVRISPmkII compatible AVR Programmer ● Supports all AVRs with ISP, PDI, or TPI ● Optional 5V output via headers to target board, with ● standard jumper and PTC fuse 4channel Logic Analyzer ● Serial bridge / pattern generator / SPI interface ● GPIO / PWM / frequency input & output ● Atmel Studio / AVRDUDE support ● Target board voltage of 2V to 5.5V via levelshifted ● pins on two main headers MTDBU6 USB AVR development board ● AT90USB646 / AT90USB1286 USB AVR ● 64KB/128KB FLASH, 4KB/8KB SRAM ● 5V, 500mA LDO regulator (3V30V input) ● Auto power source selection IC (USB/External) ● 16MHz and 32.768KHz crystals ● Arduino compatible ● CDC or DFU bootloader ●...




Need help?
Do you have a question about the MT-X1S and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers