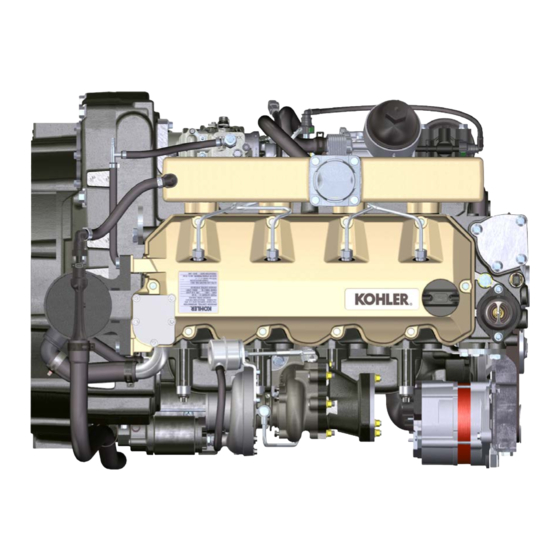
Kohler KDI 3404 TM Workshop Manual
Hide thumbs
Also See for KDI 3404 TM:
- Operation and maintenance manual (54 pages) ,
- Owner's manual (45 pages)
Table of Contents
Advertisement
Quick Links
Advertisement
Chapters
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for Kohler KDI 3404 TM
- Page 1 KDI 3404 TM WORKSHOP MANUAL TP-6983 04/16...
- Page 2 > KDI KOHLER DIESEL section > "TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION" > select "KDI 3404 TM" and download the latest version of this manual onto your device. NOTE: you can select the desired language before downloading the manual, as shown in the figure below.
- Page 3 INDEX OF CHAPTERS GENERAL INFORMATION Useful information 1.1.1 Useful Information -accident prevention - environmental impact Manufacturer and engine identification Name plate for EPA regulations Identification of the main internal components of the engine and operating reference (BASE CONFIGURATION) Identification of the external components of the engine (BASE CONFIGURATION) TECHNICAL INFORMATION Engine specifications Engine dimensions (mm)
- Page 4 INDEX OF CHAPTERS 2.15.8 Fuse 2.15.9 Control panel (optional) 2.16 Timing system and tappets 2.16.1 Components identification 2.16.2 Timing system phasing angles 2.16.3 Rocker arm pin 2.16.4 Rocker arms 2.16.5 Hydraulic tappets 2.16.5.1 Hydraulic tappet operation 2.16.5.2 Difficult operating conditions 2.17 Components handling 2.17.1...
- Page 5 INDEX OF CHAPTERS Oil vapour separator replacement 6.3.1 Disassembly 6.3.2 Assembly Oil cooler unit and oil filter replacement 6.4.1 Oil Cooler unit disassembly 6.4.2 Oil filter cartridge replacement 6.4.3 Oil Cooler unit assembly Fuel filter replacement 6.5.1 Disassembly 6.5.2 Assembly DISASSEMBLY INFORMATION Recommendations for disassembly Turbocharger disassembly...
- Page 6 INDEX OF CHAPTERS INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING Recommendations for overhauls and tuning Crankcase 8.2.1 Oil line check 8.2.2 Cylinder check 8.2.3 Camshaft housing check 8.2.4 Camshaft control 8.2.5 Camshaft control with internal EGR Tappets and tappet housings 8.3.1 Tappets check 8.3.2 Tappet housing check Crankshaft 8.4.1...
- Page 7 INDEX OF CHAPTERS Flange unit assembly 9.7.1 Flange housing 9.7.2 Flywheel Fuel system assembly 9.8.1 High-pressure injection pump 9.8.2 Injector 9.8.3 Fuel injector ricicle pipe 9.8.4 Rocker arm cover 9.8.5 Installation of the fuel injector pipes (injection pump/injectors) 9.8.6 Fuel filter Crankshaft pulley assembly 9.10 Coolant circuit assembly...
- Page 8 NOTES ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ED0053030410...
- Page 9 NOTES ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ED0053030410...
- Page 10 NOTES ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ED0053030410...
- Page 11 Therefore, the information in this manual is subject to change without notice. • KOHLER reserves the right to make, at any time, changes on the engines for technical or commercial reasons. • These changes do not require KOHLER to intervene on the production marketed up to that time and nor to consider this manual as inappropriate.
- Page 12 GENERAL INFORMATION 1.2 Manufacturer and engine identification The engine identification name plate is situated in the lower part of the crankcase; it is visible from the intake or exhaust side. Fig. 1.1 Fig. 1.2 Engine serial number Engine type Manufacturer identification Engine version Approval data and...
- Page 13 GENERAL INFORMATION 1.3 Name plate for EPA regulations Fig. 1.4 Tab. 1.1 POS. DESCRIPTION Model year in compliance with the rules Power category (kW) Engine displacement (Lt.) Particulate emission limit (g/kWh) Engine family ID Emission Control System = ECS Fuel with low sulphur content Injection timing Electronic injector opening pressure (bar) Production date (example: 2013.JAN)
- Page 14 GENERAL INFORMATION 1.4 Identification of the main internal components of the engine and operating reference (BASE CONFIGURATION) VIEW OF INTAKE SIDE Fig. 1.5 The following chapters contain operating references in order to clearly understand the engine. This paragraph illustrates these references that may be recognised by means of some main internal components.
- Page 15 GENERAL INFORMATION VIEW OF FLYWHEEL SIDE Fig. 1.6 ED0053030410...
- Page 16 GENERAL INFORMATION 1.5 Identification of the external components of the engine (BASE CONFIGURATION) VIEW OF PULLEY SIDE - INTAKE Fig. 1.7 VIEW OF FLYWHEEL SIDE - EXHAUST Fig. 1.8 ED0053030410...
- Page 17 GENERAL INFORMATION This paragraph illustrates all external components that are NOTE: The illustrated components may differ from those present in the base configuration of the engine. illustrated; the illustration is only as an example. For components present on engines that differ from those represented in these illustrations, refer to Chap.
- Page 18 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.1 Engine specifications Tab. 2.1 MANUFACTURER SPECIFICATIONS AND OPERATION UNIT OF GENERAL INFORMATION KDI 3404 TM MEASURE Operating cycle diesel - 4-stroke Cylinders Bore x stroke 96x116 Displacement 3359 Compression ratio 17:1 Intake Supercharged with Turbocharger Cooling Liquid...
- Page 19 TECHNICAL INFORMATION UNIT OF GENERAL INFORMATION KDI 3404 TM MEASURE Lubrication Recommended oil see Par. 2.4 Circuit forced Lobe pump Oil sump capacity (MAX) 15,6 Oil pressure switch Intervention pressure (MIN) 0.6±0.1 Oil filter Maximum operating pressure Degree of filtration 17 ±2...
- Page 20 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.2 Engine dimensions (mm) NOTE: Dimensions vary according to engine configuration. 579.5 734.4 Fig. 2.1 ED0053030410...
- Page 21 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.3 Performance without AFTER with AFTER COOLER COOLER 70HZ 60HZ 50HZ 63HZ 63HZ @1800 RPM @1800 RPM @1800 RPM @1500 RPM @1500 RPM POWER Stand-by power (kW/HP) 70 / 95.2 60 / 81.6 63 / 85.7 63 / 85.7 50 / 68 Prime power (kW/HP) 63 / 85.7...
- Page 22 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.4 Oil Important Danger • The engine may be damaged if operated with improper oil • Prolonged skin contact with the exhausted engine oil can level. cause cancer of the skin. • Do not exceed the MAX level because a sudden increase in •...
- Page 23 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.5 Fuel 2.5.1 Fuel for low temperatures Important • For the operation of the engine at temperatures lower than 0 ° C suitable for use fuels normally distributed by • Use the same type of diesel fuel as used in cars (EN 590 for the oil companies and in any case corresponding to the E.U.
- Page 24 2.6 Coolant Tab. 2.6 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS 50% ETYLENGLYCOL e 50% DECALCIFIED WATER 50% PROPYLENGLYCOL e 50% DECALCIFIED WATER 2.7 Battery features Battery not supplied by Kohler Tab. 2.7 RECOMMENDED BATTERIES AMBIENT TEMPERATURE BATTERY TYPE ≥ - 15°C 100 Ah - 800 CCA/SAE <...
- Page 25 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.8 Periodic maintenance The intervals of preventive maintenance in Tab. 2.8 and Tab. 2.9 with fuel and oil meeting the recommended specifications. refer to the engine operating under normal operating conditions Tab. 2.8 CLEANING AND CHECKING PERIODICITY (HOURS) OPERATION DESCRIPTION 1000 1500...
- Page 26 5. POS. DESCRIPTION Fuel tank NOTE: The representation of fuel tank is purely indicative. Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. Fuel supply hose from the tank to the injection pump Fuel filter Electrical fuel feed pump Injection pump...
-
Page 27: Table Of Contents
Fuel tank Fuel return pipe to the tank NOTE: The representation of fuel tank is purely indicative. Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. Fig. 2.3 2.9.3 Injection pump Pressure into the injection pump must be positive in all operating conditions. - Page 28 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.9.4 Injector It is a device used to introduce fuel, in the form of one or more jets that are adequately pulverised and suitably oriented directly into the combustion chamber. They consist of a metallic body that internally provides a mobile element that acts on the needle: this, rising against the action of a calibrated spring, allows the release of fuel under high pressure.
-
Page 29: Tab. 2.17
TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.9.6 Electric fuel pump (optional) When the electric fuel pump is installed in a diesel engine, one must: 1 - Remove any filters installed on the inlet of the electric injection pump; 2 - Insert a pre-filter between the tank and the electric pump; 3 - The electric pump may be assembled on application at a maximum height of 500 mm from the position of the fuel tank. - Page 30 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.10 Lubrication circuit 2.10.1 Lubrication circuit diagram The oil pump is driven by the crankshaft on the timing system side. On the parts of the systems shown in green on In the parts in green, the oil is in intake, in the parts in red, the oil is under pressure and in those in yellow the oil is returning towards the oil sump 2 (not under pressure).
- Page 31 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.10.2 Oil pump The oil pump rotors are trochoidal (with lobes) and are activated from the crankshaft by means of the key. The pump body is situated inside the distribution guard. It is imperative to assemble the rotors with reference visible by the operator.
- Page 32 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.10.3 Oil filter and Oil Cooler NOTE: unscrewing the cartridge holder cover makes the oil in support 7 flow towards the oil sump by means of the drain duct 4. Fig. 2.15 Tab. 2.21 POS. DESCRIPTION Oil arriving from the pump Oil cooling Oil filtering Oil drain duct (oil sump return)
- Page 33 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.11 Coolant circuit 2.11.1 Coolant circuit diagram Tab. 2.23 POS. DESCRIPTION Coolant pump Coolant intake Coolant, cylinder Coolant, cylinder head Coolant to radiator Coolant into radiator Coolant in the Oil Cooler Coolant input into the Oil Cooler Coolant output from the Oil Cooler Vent line from radiator (to 15) Return from compensation tank Compensation tank...
- Page 34 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.11.2 Coolant pump Tab. 2.24 POS. DESCRIPTION Coolant pump control pulley Coolant intake fitting Fig. 2.19 2.11.3 Thermostatic valve Tab. 2.25 POS. DESCRIZIONE Cylinder head Coolant outlet cover Thermostatic valve Gaskets Air bleeding hole Opening temperature +89° ± 3°C. Fig.
-
Page 35: Component Not Necessarily Supplied
(Fig. 2.21) NOTE: Nella Fig. 2.21 illustrates the radiator without Intercooler (the differences in POS. 10). Fig. 2.22 illustrates the radiator with Intercooler (the differences in POS. 8 - 9). Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. Fig. 2.22 ED0053030410... -
Page 36: Tab. 2.27
TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.12 Intake and exhaust circuit 2.12.1 Intake and exhaust circuit diagram with Intercooler Gas in exhaust Air in intake Tab. 2.27 POS. DESCRIPTION Air in intake from air filter Air in compression Air in intercooler flow Air cooling Air in intake manifold flow Cylinder head air... -
Page 37: Fig. 2.25
TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.12.2 Diagram, intake and exhaust circuit without Intercooler Gas in exhaust Air in intake Tab. 2.28 POS. DESCRIPTION Air in intake from air filter Air in compression Air in intake manifold flow Air in head intake Air in cylinder intake Gas in cylinder outlet Gas in head outlet... - Page 38 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.12.4 Air filter (optional) Tab. 2.30 POS. DESCRIPTION NOTE: Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. Air filter cartridge Important Filter cover • The air filter is a dry-type one, with a replaceable paper filter Filter support cartridge H (refer to Tab. 2.8 and Tab. 2.9 for procedure Dust exhaust valve frequency on components).
- Page 39 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.13 Electric system 2.13.1 Engine electrical wiring (opzional) Tab. 2.31 NOTE: Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. DESCRIPTION REF. Electrical wiring is supplied upon request, it interfaces with Engine panel connector interface (Fig. 2.27) the panel by means of 19-way Deutsch connectors (female Accessories panel connector interface (Fig.
- Page 40 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.13.1.1 Connector panel on the engine/machine Tab. 2.32 INLET SIGNALS TO THE PANEL PIN. The connector is a female 19-way Deutsch type. There is a list of all PIN connections in Tab. 2.32. Oil pressure switch Alternator indicator light Coolant temperature warning light Air cleaner clogging warning light Outlet indicator general alarm...
- Page 41 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.13.1.3 Wiring disconnection Some sensor connectors and electronic control devices are sealed. This tipe of connectors must be disconnected by means of pressure on tabs or unblock the retainers B, as illustrated from Fig. 2.29 to Fig. 2.33. Fig.
- Page 42 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.14 Sensors and switches 2.14.1 Fuel filter water detection sensor (optional) The water presence sensor in the fuel filter serves to indicate the presence of water in the fuel. The sensor closes the electrical circuit and the warning lamp in the panel board switches on the dashboard of the car on which the motor is mounted.
- Page 43 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.14.4 Air cleaner clogging switch NOTE: Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. The switch is assembled on the air cleaner. When the filter is clogged, it sends a signal to the panel. Features: • Operating temperature: -30 °C / +100°C •...
- Page 44 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.15.4 Electric fuel pump (optional) Tab. 2.36 POS. DESCRIPTION NOTE: Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. Electrical connection The electric pump A is located before the fuel filter. Prefilter pump Ingoing fitting (IN) from tank Characteristics: Outgoing fitting (OUT) to fuel filter •...
- Page 45 Fuse Device G is assembled on cylinder head P (flywheel side); it protects the electrical circuit in the event of an overload or short circuit. NOTE: Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. Fig. 2.46 2.15.9 Control panel (optional) Panel L can be assembled on the engine or machine.
- Page 46 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.16 Timing system and tappets The distribution system is equipped with hydraulic tappets that automatically recover the operation of the rocker rods assembly. No registration is therefore required. 2.16.1 Components identification Fig. 2.48 Tab. 2.40 POS. DESCRIPTION Crankshaft Camshaft Camshaft tappets Rocker arm control rod...
- Page 47 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.16.2 Timing system phasing angles VIEW OF FLYWHEEL SIDE (1 PTO) Important Crankshaft rotation • For information purposes, Tab. 2.41 reports the timing system diagram phasing angle values. Intake cicle • It should be noted that the said values may be verified by Exhaust cicle rotating the crankshaft (Pos.
- Page 48 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.16.5 Hydraulic tappets Tab. 2.44 POS. DESCRIPTION Low pressure chamber Hight pressure chamber Hydraulic tappets oil refill pipe Retaining ring Piston Unidirectional valve Tappet body Spring 2.16.5.1 Hydraulic tappet operation The operating principle of the hydraulic tappet is based on the incompressibility of the liquids and on controlled leakage.
- Page 49 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.17 Components handling 2.17.1 Injection pump - Only handle by means of the points marked by Y. - It is forbidden to handle using the points marked by N. Fig. 2.55 2.17.2 Injector - Only handle by means of the points marked by Y. - It is forbidden to handle using the points marked by N.
- Page 50 • Do not apply additives to the lubricating oil and fuel, unless • Check the engine oil level. instructed to do so by Kohler. • Before switching it off after it has been used, make the engine • Do not increase engine speed, or apply loads, immediately run idle, or without a load, for approximately 1 minute.
- Page 51 TECHNICAL INFORMATION 2.18.3 Before installing a new turbocharger Important • Do not lift the turbocharger with one hand from the FG box. • Do not lift turbocharger from Comp hsg side. • Lift the turbocharger with both hands from FG box. •...
- Page 52 Correct the cause of the breakage before replacing it with a new turbocharger. If in doubt, contact KOHLER service department. Important • Failure to comply with these instructions can cause damage to the turbocharger and void the warranty.
- Page 53 Any use of the • In the event KOHLER does not approve the type of machine other than that described cannot be considered as modification, KOHLER shall not be held responsible for any...
- Page 54 • The oil must be drained whilst the engine is hot. Particular care is required to prevent burns. Do not allow oil to come into • Only use the eyebolts A installed by KOHLER to move the contact with the skin because of the health hazards involved.
- Page 55 SAFETY INFORMATION 3.4 Safety signal description • To ensure safe operation please read the following statements • This manual contains safety precautions which are explained and understand their meaning. below. • Also refer to your equipment manufacturer's manual for other •...
- Page 56 State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm. 3.6 Safety and environmental impact In order to minimise the impact on the environment, KOHLER Every organisation has a duty to implement procedures to provides some indications to be followed by all those handling identify, assess and monitor the influence of its own activities the engine, for any reason, during its expected lifetime.
- Page 57 SAFETY INFORMATION 3.7 Location of safety signals on engine Fig. 3.2 ED0053030410...
- Page 58 STORAGE INFORMATION 4.1 Product preservation 11 - When cleaning the engine, if using a pressure washer or steam cleaning device, avoid directing the nozzle on Important electrical components, cable connections and sealed rings (oil seals etc). • If the engines are not to be used for 6 months, they must If cleaning engine with a pressure washer or steam be protected by carrying out the operations described in Engine storage (up to 6 months) (Par.
- Page 59 NOTES ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ED0053030410...
- Page 60 INFORMATION REGARDING DISCHARGE OF LIQUIDS 5.1 Coolant NOTE: Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. The representation of the radiator is purely indicative. Warning • Before proceeding with operation, carefully read Par. 3.3.2. • Presence of steam pressurized coolant danger of burns.
- Page 61 INFORMATION REGARDING DISCHARGE OF LIQUIDS 5.2 Engine oil Important • Before proceeding with operation, carefully read Par. 3.3.2. • The oil must be drained whilst the engine is hot, which requires particular care to prevent burns. Do not allow oil to come into contact with the skin because of the health hazards involved.
- Page 62 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.1 Injector and injection pump replacement Important • Before proceeding with operation, carefully read Par. 3.3.2. • Replace the high pressure pipes after two disassemblies. • The injectors cannot be repaired but must be replaced. •...
- Page 63 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.1.3 Fuel return pipes disassembly 1 - Undo the screws Q and remove hose R. Fig. 6.5 6.1.4 Injectors disassembly 1 - Undo the screw J and remove washer K and then bracket 2 - Remove the injector Z. NOTE: Should you be unable to remove the electronic injector (acting only on point BC), use an open-ended spanner (Ã...
- Page 64 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 2 - Disassemble the starter motor. ST_34 3 - Mount the tool ST_34 in the seat of the starter motor fit it with the two starter motor fixing screws. 4 - Rotate the crankshaft clockwise (Ref. A Par.
- Page 65 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 10 - Undo and remove the nut C1 fixing the injection pump control gear D1. Important • After removing the nut C1, ensure that the correct advance value has remained unchanged on ST_30. • Be careful that the nut C1 does not fall into the timing cover. Fig.
- Page 66 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.1.6 Injection pump assembly Important • Before assembling the new pump J1, make sure that plate F1 can move freely and that fastening capscrews E1 are not loose (the pump sold as a spare part is supplied with the cylinder injection timing blocked N°...
- Page 67 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 9 - Secure tube U1 by means of capscrew P1, inserting gasket T1. 10 - Fit quick coupling N1 onto pump J1. Fig. 6.20 11 - Secure plate B1 by means of capscrews A1, inserting gasket V1 onto carter S1 (tightening torque at 10 Nm).
- Page 68 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 3 - Assemble the parts P, Q, R. and fit the parts so assembled on the injector Z. Fig. 6.24 4 - Insert tool ST_52 on the injectors junctions Z (detail ST_52 X2). 5 - Tighten screw (tightening torque to 20 Nm - Fig.
- Page 69 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.1.9 Assembly Rocker arm cover ST_17 ST_17 Important • The gasket Z1 between the rocker arm cover and the cylinder head must always be replaced every time it is disassembled. 1 - Position tool ST_17 onto the head in correspondence with the two fastening holes 2 - Position gasket Z1 and cap P...
- Page 70 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.2 Coolant pump replacement 6.2.1 Disassembly NOTE: Perform the operations described in Par. 5.1. Important • Before proceeding with operation, carefully read Par. 3.3.2. • The coolant pump is not repairable. Fig. 6.32 1 - Loosen the screws A and B. 2 - Loosen capscrew C and disconnect voltage from belt D and remove belt D.
- Page 71 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.2.2 Assembly Important • Always replace the gaskets J, at each disassembly. • Always replace the belt D after each assembly. 1 - Fit the pump H with the screws G interposing the new gasket J (tightening torque at 25 Nm).
- Page 72 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.3 Oil vapour separator replacement Important • Before proceeding with operation, carefully read Par. 3.3.2. 6.3.1 Disassembly 1 - Remove quick fitting A. 2 - Release the clamps B and C. 3 - Remove hose D from breather body E. Fig.
- Page 73 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.4 Oil cooler unit and oil filter replacement 6.4.1 Oil Cooler unit disassembly Important • Perform the operations described in Par. 5.1 and Par. 5.2. • Oil Cooler unit E is not repairable. 1 - Release the clamps A. 2 - Remove the hoses B out of the Oil Cooler unit E.
- Page 74 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 5 - Lubricate and insert gaskets L, M and N in the L1, M1 and N1 seats of element holder cover H. 6 - Insert element P into element holder cover H. Fig. 6.45 6.4.3 Oil Cooler unit assembly Important...
- Page 75 INFORMATION FOR REPLACING THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS 6.5 Fuel filter replacement 6.5.1 Disassembly Warning • Before proceeding with operation, carefully read Par. 3.3.2. • The fuel filter is not always mounted in the engine. • When disassembling, use a suitable container to recover the fuel contained in the cartridge F.
- Page 76 NOTES ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ED0053030410...
- Page 77 • Where necessary, reference to special tools to use during disassembly operations is indicated (e.g. ST_05), refer to • Before disassembly, perform the operation described in KOHLER diesel special tools. Chap. 5. 7.2 Turbocharger disassembly 1 - Unscrew the fittings A and remove the pipe B with the relative gaskets C.
- Page 78 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.3 Coolant recirculation components disassembly 7.3.1 Oil Cooler manifold 1 - Release the clamps A. 2 - Undo the screws B and remove hoses C. Fig. 7.4 3 - Release the clamps D and remove hoses E. Fig.
- Page 79 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.4 Electric components disassembly 7.4.1 Starter motor Important • The motor is not repairable. 1 - Perform the operations from point 2 to 3 of Par. 6.1.5. 7.4.2 Alternator 1 - Undo the screws A1 and B1 and remove the alternator C1. Fig.
- Page 80 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.6 Fuel system disassembly Important • Seal all injection component unions as illustrated in Par. 2.9.8 during disassembly. 7.6.1 Injection fuel pipes 1 - Perform the operations of Par. 6.1.1. 7.6.2 Rocker arms cover 1 - Perform the operations of Par. 6.1.2. 7.6.3 Fuel return pipes 1 - Perform the operations of Par.
- Page 81 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.8 Flange unit disassembly 7.8.1 Flywheel Danger • The flywheel A is very heavy. Pay the utmost attention while removing it in order to prevent it dropping or falling, as this may have serious consequences for the operative. 1 - Undo the screws B and remove the flywheel A by means of tool ST_43.
- Page 82 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.10 Cylinder head unit disassembly 7.10.1 Rocker arm pin 1 - Undo the screws D. 2 - Remove the rocker arm pin unit E. Fig. 7.18 7.10.1.1 Rocker arm ( 1 - Remove the retainer ring F. 2 - Remove the shoulder rings G.
- Page 83 Fig. 7.21 Important • To lift cylinder head Q, only use both eyebolts Y provided by KOHLER (refer to Fig. 7.28). • When removing the cylinder head Q and subsequent disassembly, control, and assembly operations, it is necessary to protect the contact surface W of cylinder head Q and crankcase J against impacts..
- Page 84 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY Important • Before removing the valves, make some marks to record their original position, in order to avoid confusing them when re- assembling (if they are not replaced). 4 - Remove the valves V. Fig. 7.25 7.10.3.2 Electronic injector sleeves ( 1 - Unscrew and remove the sleeves Z from the head Q.
- Page 85 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.11 Oil sump unit disassembly Important • For the following operation, turn the engine by bringing the cylinder head surface downwards. 7.11.1 Oil sump 1 - Undo the screws A. 2 - Remove the oil sump B by inserting a plate between surface C of crankcase D and oil sump B.
- Page 86 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.12 Engine block disassembly 7.12.1 Piston unit / connecting rod Important • Mark some numerical references (cylinder n°) on the connecting rods, connecting rod caps N, pistons and gudgeon pins to prevent unintentionally confusing the components not replaced during assembly.
- Page 87 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 2 - Pull out the connecting rod - piston assembly from position by manually applying pressure on the connecting rod M in the direction of arrow AK. 3 - Couple the connecting rod big end caps L with the relevant piston and connecting rod unit M.
- Page 88 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.12.3 Lower semi-crankcase Important • The capscrews Q must be replaced every time they are disassembled. • Do NOT remove the capscrews completely, first loosen them by turning them a whole cycle following the order shown in the figure.
- Page 89 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.12.4 Crankshaft Remove: 1 - Crankshaft S. 2 - The shoulder semi-rings T. 3 - Remove gasket U from crankshaft S. Fig. 7.42 7.12.5 Piston ( 1 - Remove the retainer ring V. 2 - Remove the pin Z to separate the piston J from the connecting rod L.
- Page 90 INFORMATION FOR DISASSEMBLY 7.12.7 Camshaft 1 - Remove the lock ring C. 2 - Extract the camshaft F from the upper semi-crankcase D2. Fig. 7.46 7.12.8 Camshaft tappets 1 - With a magnet, remove the tappets Y from the upper semi- crankcase D2.
- Page 91 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.1 Recommendations for overhauls and tuning • The information is laid out in sequence, according to • Do not wash the components with steam or hot water. Use operational requirements, and the intervention methods have suitable products only. been selected, tested and approved by the manufacturer's •...
- Page 92 EPA name plate (refer to Par. 1.3). The grinding involved is of +0.20, +0.50 and + 1 mm. • Cylinder grinding operations must observe KOHLER • SPECIFICATIONS - cod. ED0035612500. Grinding must be strictly performed on all cylinders F.
- Page 93 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.2.3 Camshaft housing check Tab. 8.2 Housing and camshaft gudgeon dimensions. Use an internal dial gauge to measure the diameters of housings CLEARANCE REF. DIMENSIONS (mm) - Z. VALUE (mm) With a micrometer, measure the diameters of gudgeon pins 47.500 - 47.525 (Fig.
- Page 94 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.3 Tappets and tappet housings 8.3.1 Tappets check Use a surface plate and a dial gauge as shown in Fig. 8.5. Check the perpendicularity of the plate C, making the tappet D rotate in the direction of the arrow. The MAX value of wear allowed is 0.02 mm.
- Page 95 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.4 Crankshaft 8.4.1 Dimensional check and overhauling Tighten capscrews J (Fig. 9.9) and K (Fig. 9.10) observing Wash the crankshaft thoroughly using suitable detergent. the cycles, tightening, and subsequent rotation. Insert the pipe cleaner into all lubrication ducts and blow Cycle 1 - Screw J - Torx M14x1,5 - Torque 60 Nm.
- Page 96 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.4.2 Checking the axial clearance of the crankshaft Perform the operations described in Par. 9.3.1, 9.3.4 and. Par. 9.3.5 - except points 2, 3, 5, and 10. Tighten capscrew J (Fig. 9.9) observing the cycles, tightening, and subsequent rotation. Cycle 3 - Screw J - Torx M14x1,5 - Torque 45°.
- Page 97 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.5.2 Checking the gudgeon pin-pin axes are parallel Lubricate gudgeon pin A and bearing R (Fig. 8.10). Insert the gudgeon pin into bearing R. Use a dial gauge to check the axis parallelism of the connecting rod big end and small end. The parallelism deviation (value V) measured at the tip of the gudgeon pin, must be a MIN of 0,015 and MAX of 0,030 mm.
- Page 98 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING Important • With a feeler gauge, measure the clearance of the seal ring in the respective seat (value L1, e L3). • If the clearance does not comply with the values shown in the table (Tab. 8.9), replace the seal rings and the piston. Fig.
- Page 99 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.6.2 Valve seats check Thoroughly clean the valves and their seats with. Measure indentation of each valve with regard to the cylinder head surface C, which is to be a MIN of 0.50 mm and MAX of 0.53 mm. MAX indentation allowed on worn components is 0.90 If the measured value does not correspond with the values indicated, replace the worn component.
- Page 100 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.6.5 Valve guides replacement The intake and exhaust guides are both made out of grey iron with pearlitic phosphoric matrix and they have the same dimensions: The guides are press-fit assembled; assembly is possible by cooling the guides with the aid of liquid nitrogen. Before assembling a new guide, measure value and M, calculate the press-fit value, which must observe the values...
- Page 101 INFORMATION ABOUT OVERHAULING 8.7 Oil pump check 8.7.1 Dimensional and visual check Measure clearance value between the rotor teeth, the value of allowable wear is MAX 0.28 mm. Important • Should the results from checks carried out not be in accordance with the conditions described, replace the oil pump A.
- Page 102 • This chapter describes the installation procedures for the assemblies and/ or individual components which have already been checked, overhauled or possibly replaced with original spare parts. • Where necessary, reference to special tools during assembly operations refer to KOHLER diesel special tools. Here in after in Tab. 9.1 an example of a special tool (ST_05).
- Page 103 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.3 Engine block assembly 9.3.1 Crankshaft bushings Important • Execute the procedure in Par. 8.2.1 and 8.2.2, before proceeding with assembly. • The crankshaft half-bearings are made of special material. Therefore, they must be replaced every time they are assembled to prevent seizures.
- Page 104 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.3.4 Crankshaft Important • Carry out the checks described in Par. 8.4.1 and Par. 8.4.2. 1 - Check that the crankshaft half-bearings A1 are mounted correctly on the upper crankcase B1. 2 - Lubricate the main journal and crankpin J, with oil. 3 - Insert the crankshaft M into its seat on the upper crankcase 4 - Insert the 2 shoulder half-rings N1, between the crankshaft M and the upper crankcase B1 (Q detail).
- Page 105 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION Fig. 9.9 Fig. 9.10 Tab. 9.16 CYCLE SCREWS TORQUE J - Torx M14x1,5 60 Nm K - Torx M10x1.25 30 Nm J - Torx M14x1,5 45° J - Torx M14x1,5 45° Important • The fastening bolts J, K must be replaced every time they Fig.
- Page 106 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.3.6 Camshaft 1 - Lubricate the pins S2, the cams S3 of the camshaft S1, all the housing Q1 with oil. 2 - Insert the camshaft S1 all the way into its housing Q1. 3 - Fit the lock ring S4 on to the crankcase B to hold the position of the camshaft S1.
-
Page 107: Assembly Information
ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.3.8 Piston rings 1 - Perform the operations described in Par. 8.5.3. 2 - Put the scraper ring Z3 onto the piston Z. 3 - Put the 2° seal ring Z2 on the piston Z. 4 - Put the 1° seal ring Z1 onto the piston Z. 5 - Perform the operations described in Par. - Page 108 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.3.10 Piston and connecting rod assembly Important • Before assembling the piston and connecting rod assemblies, execute the controls described in Par. 8.5. 1 - Rotate the crankshaft M by moving the crankpin J1 to a TDC position of the affected cylinder. Fig.
-
Page 109: Cycle Screws Torque
ASSEMBLY INFORMATION Important • Leave the ring compressor assembled on the piston. 6 - Push piston Z downwards without introducing segments in the cylinder, rotate piston Z by 10° in a clockwise direction (value – correct assembly position). Fig. 9.24 7 - Push the piston Z downwards by centering the crankpin J1 with the connecting rod F2. - Page 110 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.4 Oil sump unit assembly 9.4.1 Oil drain pipe Important • It is mandatory to replace the gasket D after each assembly. • Always replace capscrews B with new ones or alternatively apply Loctite 2701. 1 - Secure the hose A on the crankcase C with the screws B inserting the gasket D (tightening torque 10 Nm).
- Page 111 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION Important • Tighten the screws L, strictly following the sequence and tightening torque indicated. 4 - Fix oil sump H by means of the screws L following the sequence indicated (tightening torque 25 Nm). 5 - After tightening of the screw n°...
- Page 112 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.5.3 Injectors projection 1 - Perform the operations of Par. 6.1.7. Fig. 9.35 Check, using ST_03 tool (Fig. 9.36), the projection of the injector, which must range between 1.68 ÷ 2.42 mm. ST_03 NOTE: if the value detected does not correspond, replace gasket Q with a different thickness Fig.
- Page 113 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 6 - Push the lever of the tool ST_07 downwards, in order to lower the valve disks S in the direction of the arrow AK, and insert the valve cotters AJ inside the disk S. 7 - Check that the valve cotters AJ are properly mounted on the valve seats X and release the tool ST_07.
-
Page 114: Failure To Adhere To The Bolt Fixing Procedures May
ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 7 - Check that the surface head W is free from impurities. 8 - Position the head F on the crankcase Z with reference to the centering bushings J. Important • The fastening bolts V must be replaced every time they are assembled. - Page 115 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.5.7 Rocker arms Important • The suction rocker arm AT is shorter than the discharge arm 1 - Fit the lock ring AM into the seat AN of the rocker arm pin 2 - Position the pin AH with the surface AP facing upwards and insert the 2 shoulder rings AQ.
- Page 116 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 3 - Secure the rocker arm pin BB tightening the screws BE (tightening torque to 40 Nm). Adhere to the screw tightening sequence BE as shown in Fig. 9.51. Fig. 9.51 9.6 Assembly lubrication circuit 9.6.1 Oil pressure relief valve 1 - Lubricate the piston N and fully insert it in the seat P.
- Page 117 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.7 Flange unit assembly 9.7.1 Bell housing Danger LOCTITE 5660 • Bell A is very heavy; pay special attention during assembly operations to avoid dropping and causing serious risks to the operator. 1 - Apply a bead of approx. 2.5 mm of sealant (Loctite 5660) on the surface B of the bell A.
- Page 118 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.8 Fuel system assembly Important • Remove the protective caps from all the components of the fuel circuit just before assembly just before assembly (Par. 2.9.8). 9.8.1 High-pressure injection pump 1 - Follow operations 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 of Par. 6.1.5. 2 - Follow operations 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 10 of Par.
- Page 119 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.10 Coolant circuit assembly 9.10.1 Thermostatic valve Important • Always replace the gasket A after each assembly. 1 - Check the condition of the seal gasket A and fit it on the thermostatic valve B. 2 - Position the thermostatic valve B in the seat on the head C (detail D).
- Page 120 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.11 Exhaust manifold assembly Important • Replace the metal gaskets A every time they are assembled. 1 - Check that the contact surfaces D are free from impurities. 2 - Position manifold E onto cylinder head G by manually tightening capscrews F, inserting: - gaskets A between cylinder head G and manifold E;...
- Page 121 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.13 Electric component assembly 9.13.1 Sensors and switches 9.13.1.2 Coolant temperature sensor 1 - Secure the sensor A onto the head B (tightening torque of 20 Nm). Fig. 9.68 9.13.1.3 Oil Pressure Switch 1 - Clamp the oil pressure switch C on the crankcase D (tightening torque at 35 Nm).
- Page 122 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION 9.14 Tightening torques and the use of sealants Tab. 9.20 Alternatively to the capscrew replacements, with "Dri-loc" BASE CONFIGURATION SHORT BLOCK Component Thread (mm) Torque (Nm) Sealer Oil sprays fastening capscrew M6x1 Lower crankcase fastening capscrew M14x1.5 3 cycles 1st Cycle 2nd Cycle +45°...
- Page 123 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION Alternatively to the capscrew replacements, with "Dri-loc" INJECTION SYSTEM Component Thread (mm) Torque (Nm) Sealer Fuel filter fastening capscrew M8x1.25 Injector brace fastening capscrew M8x1.25 Injector side injection tube nuts M12x1.5 Injection pump side injection tubes nuts M12x1.5 Injection pump fastening capscrew M8x1.25 Loctite...
- Page 124 ASSEMBLY INFORMATION Alternatively to the capscrew replacements, with "Dri-loc" OPTIONAL COMPONENTS (CHAP. 11) HEATER Component Thread (mm) Torque (Nm) Sealer Flange intake with heater fastening capscrew M8x1.25 COOLING CIRCUIT Component Thread (mm) Torque (Nm) Sealer Blower fastening capscrew M6x1 Radiator support fastening capscrew (on crankcase) M12x1.75 Shroud radiator fastening capscrew M6x1...
- Page 125 NOTES ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................in alternativa alle viti di ricambio con "Dri-loc" Alternatively to the capscrew replacements, with "Dri-loc" ED0053030470...
- Page 126 FLUIDS FILLING INFORMATION 10.1 Engine oil Warning • Before proceeding with operation, carefully read Par. 3.3.2. 1 - Loosen the oil filler cap A. 2 - Add the type and amount of oil recommended (Tab. 2.2). Fig. 10.1 3 - Remove the oil dipstick B and check that the level is up to but does not exceed the MAX.
- Page 127 FLUIDS FILLING INFORMATION 5 - Loosen the screw F on the head G, release any air and tighten the screw (Fig. 10.7); Tightening torque: - 8 Nm for screw M6 (Rev. 00); - 30 Nm for screw M12 (Rev. 01). 6 - Start the engine without the radiator cap D or the expansion tank cap B.
- Page 128 NOTES ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ED0053030410...
- Page 129 INFORMATION ABOUT OPTIONAL COMPONENTS 11.1 Heater (replacement) 11.1.1 Disassembly 1 - Undo the screws A and the relevant washers. 2 - Remove the flange C. 3 - Remove the heater E and the relevant gaskets F. Fig. 11.1 11.1.2 Assembly Important •...
- Page 130 INFORMATION ABOUT OPTIONAL COMPONENTS 11.3 Cooling circuit (replacement) 11.3.1 Radiator disassembly 1 - Release the clamp A1, A2. 2 - Disconnect hose B from radiator C. Fig. 11.5 3 - Release the clamp A3, A4. 4 - Disconnect hose D from radiator C. Fig.
- Page 131 INFORMATION ABOUT OPTIONAL COMPONENTS 11.3.2 Fan disassembly 1 - Undo the screws P and remove the fan R. Fig. 11.10 11.3.3 Fan assembly 1 - Assemble the fan R on the pulley U. 2 - Fasten the fan R by using the screws P (tightening torque at 10 Nm).
- Page 132 INFORMATION ABOUT OPTIONAL COMPONENTS 4 - Position floodgate G1 onto radiator C. 5 - Secure all capscrews E1. 6 - Place floodgate G2 onto radiator C. 7 - Secure all capscrews E3 and E2. Fig. 11.13 8 - Fit hose H1 onto radiator C, being careful not to deform tube J1.
- Page 133 INFORMATION ON ADJUSTMENTS Warning • Before proceeding with operation, carefully read Par. 3.3.2. 12.1 Waste Gate opening valve regulation Important • Regulation must not be carried out with the engine running. During the procedure in point 5, pay special attention not to bend rod H.
- Page 134 INFORMATION ON ADJUSTMENTS 12.2 Air filter check 1 - Hose A must be completely clean and not damaged. 2 - Air filter cartridge B and its housing C must be completely clean and free from impurities. Fig. 12.2 12.3 Oil steam separator check 1 - Loosen clamp B and remove hose C from separator A.
- Page 135 INFORMATION ON ADJUSTMENTS 12.5 Oil leak check Check that there are no leakages next to area A. 1 - Start the engine at idle speed or without a load and check whether there are any leakages next to area A. 2 - It is anyhow necessary to also check the seals of all main components and their surface contact, such as: - crankcase and gasket (side 2a PTO)
- Page 136 NOTES ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ED0053030410...
- Page 137 TOOLS INFORMATION 13.1 Information regarding specific tools For reference check the specific tools manual, cod. ED0053030770-S, to be found at: http://iservice.lombardini.it ED0053030470...
- Page 138 INFORMATION ABOUT FAILURES 14.1 Possible causes and trouble shooting IMMEDIATELY STOP THE ENGINE WHEN: Tab. 14.1 contains the possible causes of some failures, which may occur during operation. 1 - Engine rpm increases and decreases suddenly without Always perform these simple checks before removing or being able to control them;...
- Page 139 INFORMATION ABOUT FAILURES TROUBLES POSSIBLE CAUSE Oil level too high Oil level low Dirty or blocked pressure regulating valve Worn oil pump Air in the oil suction pipe Oil suction hose clogged Oil steam exhaust pipe clogged Damaged electronic injectors Damaged injection pump Wrong injector IMA codes Insufficient coolant...
- Page 140 Alternator: electrical energy. Authorised service station: KOHLER authorised workshop. Authorised workshop: Kohler authorised service centre. Base configuration: Engine having components represented in Para. 1.4 - 1.5. Bottom Dead Centre; a moment in which the piston is at the BDC: start of its stroke.
- Page 141 GLOSSARY Par.: Paragraph. Paraffin: Fatty and solid substance that may form inside the diesel. An instrument having a metal cylindrical body with bristles that jut outwards. It is similar to a brush and is used to clean Pipe cleaner: areas that are not easily accessible manually (e.g. oil ducts inside an engine).
- Page 142 GLOSSARY Tab. 15.1 SYMBOLS AND UNITS OF MEASUREMENT SYMBOL UNIT OF MEASUREMENT DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE α degree Rotation/inclination angle 1° square centimetre Area 1 cm millimetre Circumference Ø Ø 1 mm newton-metre Torque 1 Nm millimetre 1 mm Dimension 1/1000 of a millimetre μm 1 μm (micron)
- Page 143 TP-6983 04/16 Lombardini s.r.l. is a part of Kohler Group. E U R O P E U S A & C A N A D A F R A N C E Lombardini has manufacturing facilities Lombardini Srl Kohler Co.
















Need help?
Do you have a question about the KDI 3404 TM and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers