Table of Contents
Advertisement
Advertisement
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for MST ImPact NS5004
- Page 1 NS50 Wireless Network Switch User Guide Revision C NS50_UG_EN_C...
-
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Contents Revision History............................7 Contact Information............................9 About this Manual............................11 Chapter 1: Understanding the NS50 Wireless Network Switch...13 1.1 Hardware Overview........................14 1.2 System Layout...........................16 1.3 Connectivity..........................16 1.3.1 Composite Fibre Ports....................17 1.3.2 Ethernet Ports......................18 1.3.3 Wireless Access......................18 Chapter 2: Network System Design............19 2.1 Installation Types and Coverage....................20 2.2 Power Requirements........................20 2.3 Choosing Antennas........................20 2.4 Placement of NS50 Units......................21... - Page 4 4.1.1 Trunk Ports.........................44 4.1.2 Access Ports........................44 4.1.3 Port Allocation......................45 4.2 VLANs and Wireless Networks....................46 4.3 Native VLAN ...........................46 Chapter 5: Configuration Using the Web Interface ......49 5.1 Logging onto the Web Browser Interface..................50 5.2 Configuration screen........................50 5.3 Status Tab...........................51 5.3.1 Obtaining Device Information..................51 5.3.2 Wireless Client Information..................52 5.3.3 Viewing System Logs....................53 5.3.4 Viewing Network Traffic Statistics................54...
- Page 5 Appendix A: Troubleshooting Guide............93 Appendix B: Composite Cable Testing............95 B.1 Visual Inspection of the Fibre Optic Cable................95 B.2 Measuring and Testing for Power Loss..................95 Appendix C: Ethernet Cable Specifications...........97 Appendix D: Device Discovery..............99 Appendix E: Time Zone Indices and Offsets ........101 Appendix F: Connecting a PC to an ImPact Network Device....105 Appendix G: Maintenance Check-list...........109 Appendix H: Acronyms................111...
- Page 6 NS50 User Guide Revision C...
-
Page 7: Revision History
Revision History Revision Change Date User Manual for NS50 hardware and firmware 2.22.16 February 2012 Updated for firmware 2.24.2 September 2012 Updated Centralised Configuration Management December 2012 © Copyright 2012 Mine Site Technologies Pty Ltd. All rights reserved. Mine Site Technologies Pty Ltd reserves the right to make changes to specifications and information in this manual without prior notice. -
Page 9: Contact Information
Contact Information AUSTRALIA - Sydney 113 Wicks Road North Ryde NSW 2113 AUSTRALIA Tel: +61 2 9491 6500 CANADA - Sudbury 1085 Kelly Lake Road Sudbury Ontario P3E 5P5 CANADA Tel: +1 705-675 7468 CHINA - Hangzhou 4F, Building 1 1413 Moganshan Road Hangzhou CHINA 310011 Tel: +86 571 85803320x206... -
Page 11: About This Manual
Note: The information provided in this document ("Information") is presented in good faith and believed to be correct as at the date of this document. MST makes no representations as to the accuracy or completeness of the Information. The Information is supplied on the condition that the recipient will make their own determination as to the suitability of the Information for their purposes prior to use. -
Page 13: Chapter 1: Understanding The Ns50 Wireless Network Switch
Chapter Understanding the NS50 Wireless Network Switch Topics: This chapter presents the features and functions of the ImPact NS50 Wireless Network Switch and shows how it is integrated within a • Hardware Overview network. • System Layout Mine Site Technologies' ImPact NS50 consists of a managed fibre •... -
Page 14: Hardware Overview
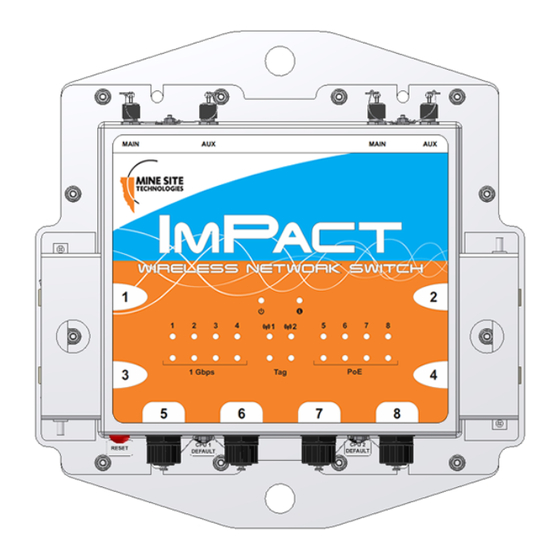
Understanding the NS50 Wireless Network Switch 1.1 Hardware Overview The features and functions of the NS50 are illustrated below. Note: The NS50 has four slightly different models: • NS5001 - 1 Radio port, 2 Fibre ports • NS5002 - 2 Radio ports, 2 Fibre ports •... - Page 15 Understanding the NS50 Wireless Network Switch Description Function Power indicator LED • Green: when power is applied to the NS50. • Red: when the power drops below 12V. Status indicator LED • Flashing Red: startup in progress. • Flashing Green: normal operation. •...
-
Page 16: System Layout
Understanding the NS50 Wireless Network Switch Description Function Default button for CPU 2 Button to reset Radio 2's configuration back to factory defaults. Refer to Manual Reset and Reboot on page 40 for details. Mounting holes Holes for mounting the NS50. Composite fibre port retention Protective arm to lock fibre port covers and cable connectors. -
Page 17: Composite Fibre Ports
Understanding the NS50 Wireless Network Switch • Wireless 1.3.1 Composite Fibre Ports Each side of an NS50 unit has two composite fibre port connectors with a crush protection cover. Each connector consists of two electrical contacts and a duplex LC single mode optic fibre (SMOF) receptacle. Note: A protective cover or a mating cable connector must be attached to unused ports to maintain the IP65 (Ingress Protection) rating of the unit. -
Page 18: Ethernet Ports
Understanding the NS50 Wireless Network Switch Due to the difference in the fibre orientation, MST composite cable and fibre optic cable can only be connected between ports on NS50 devices marked with a tick in the matrix below. Port 1... -
Page 19: Chapter 2: Network System Design
Network System Design Topics: This chapter describes network system design for underground mines. An MST System Engineer will usually design and preconfigure a • Installation Types and Coverage network based on the requirements and layout of each mine site. This •... -
Page 20: Installation Types And Coverage
NS50 units, PoE devices, branches in the network and composite cable lengths. Note: A site inspection conducted by a MST System Engineer will help determine the power requirements for your network. -
Page 21: Placement Of Ns50 Units
Network System Design Antenna Type Illustration Description Omnidirectional A lower gain antenna that radiates equally in all 5.5 dBi rubber directions. It provides direct coverage in an open area. whips Panel antenna A panel antenna is a directional antenna, with a wide horizontal beamwidth and narrower vertical beamwidth. - Page 22 Network System Design Tip 2: Obstructions Antennas should be mounted to avoid signal obstruction from rock, vehicles, equipment and machinery. Tip 3: RF Field Overlap Multiple antennas should be mounted to avoid crossing signal paths. The positioning of the antennas is crucial when AeroScout tags are used for asset tracking and location services.
-
Page 23: Determining Distances Between Wireless Network Switches
Network System Design 2.6 Determining Distances between Wireless Network Switches Line of Sight Distances In line of sight, each NS50 has a maximum wireless range of 300 metres (984 feet) using high gain directional antennas. NS50 units are generally installed with a 100 metre (328 feet) overlap of the radio field. -
Page 25: Chapter 3: Installation
Chapter Installation Topics: This chapter describes mounting options, installation schemes, and antenna and cable connections. Fibre connector assembly and cable • NS50 Mounting Options termination are beyond the scope of this manual. • Antenna Mounting Options Important: The electronic components in each NS50 have been •... -
Page 26: Ns50 Mounting Options
Installation 3.1 NS50 Mounting Options Standard mounting options for the NS50 are described in the table below. Application Installation Mounting the NS50 to a rock bolt The NS50 has two 25mm holes to mount to a rock bolt in the mine's rock face. It is secured to the rock bolt with a 25mm nut. -
Page 27: Installation Schemes
Installation Mounting Option Description Picture Mounting a panel The panel antenna is cable tied the antenna on the mesh. rockface. 3.3 Installation Schemes The installation and placement of antennas and NS50 units will depend on the wireless coverage type, rock type and tunnel topology. A few examples of installation schemes in a mine are described and illustrated in the following sections. -
Page 28: Installation In A Curved Decline / Incline
Installation 3.3.2 Installation in a Curved Decline / Incline • A Yagi antenna is positioned at the end of the curve for directional wireless coverage. • The Yagi antenna is clamped to a mounting pole, and is chemically adhered into the mine roof. •... -
Page 29: Installation In A Stope
Installation 3.3.3 Installation in a Stope • A panel antenna is clamped to a mounting pole, and is chemically adhered into the mine roof. • The panel antenna is angled down into the stope to provide wide wireless coverage. • A Yagi antenna is installed in the roof providing directional coverage down a straight drive. •... -
Page 30: Installation At An Intersection
Installation 3.3.4 Installation at an Intersection • A panel antenna is clamped to a mounting pole, and is chemically adhered into the mine roof. • The panel antenna is angled to provide wide wireless coverage at an intersection. • A Yagi antenna is installed in the roof providing directional coverage down a straight drive. Each antenna is connected to a WAC in the NS50. -
Page 31: Connecting Power To The Ns50
Installation 3.4 Connecting power to the NS50 A pre-deployment power-up test of NS50 units is recommended. To conduct a power-up test: 1. Connect the composite fibre/power cable to a DC power source with correct termination. Note that the DC supply must be between 10 and 50VDC. Revision C NS50 User Guide... -
Page 32: Handling Composite Cable During Installation
Installation 2. Turn on the DC power supply and verify that the green power light is on. If there is no green light, refer to Troubleshooting Guide on page 93. Power can be applied to cabling whilst additional NS50 units are being installed. Power usage levels should be evaluated prior to adding more units downstream to ensure that the voltage rail does not drop too low. - Page 33 Installation Step Procedure Illustration Loosen the thumbscrew on the retention arm. Slide out the retention arm from the NS50. Push down on the locking catch for the port and remove the cover. Align the pins on the connector to the composite fibre port. Revision C NS50 User Guide...
-
Page 34: Standard Composite And Fibre Cable Lengths
Connecting a NS50 to a branch NS50 requires simply connecting composite cables to the additional fibre ports. The connected fibre ports will cause the corresponding fibre port LEDs to become active. If you are adding NS50 units to an existing system, please consult your MST System Engineer to ensure power requirements are being met. -
Page 35: Connecting Ethernet Cable To The Ns50
Installation Part Number Composite Cable Length W-CFC-006-T125 125m W-CFC-006-T175 175m W-CFC-006-T250 250m W-CFC-006-T325 325m Table 2: Fibre-Only Cable Part Number Fibre Cable Length W-CFC-007-T100 100m W-CFC-007-T175 175m W-CFC-007-T325 325m W-CFC-007-T650 650m 3.8 Connecting Ethernet Cable to the NS50 The external Ethernet ports are located on the underside of the NS50, and are used to connect to Ethernet devices (such as computers, Ethernet controlled PLCs, hard-wired Ethernet Phones and IP video devices). -
Page 36: Connecting F-Link Terminated Composite Cable To The Ns50
Connecting NS50 units to networks with existing WNS units requires a JB14 Junction Box, supplied by MST, to act as an adaptor between the existing F-LINK terminated cable and the revised MST Composite connector. The JB14 has four 10mm mounting holes and can be bolted to a flat surface or cable-tied to the mesh in a tunnel. - Page 37 Installation Step Procedure Illustration Release the catch on the composite fibre/power cable port and remove the cover. Align the pins on the connector to the composite port. Insert the cable into the composite port, and push the locking catch to the connector.
-
Page 38: Connecting Antennas To The Ns50
Installation Step Procedure Illustration Align the F-LINK connector with the port. Insert the connector and spin the connector cover clockwise to secure the cable to the port. Attach the JB14 to a flat surface or tunnel mesh using the mounting holes. - Page 39 Installation Step Procedure Illustration Remove the dust cap from the antenna port. Connect the coaxial cable plug to the RP-TNC jack on the NS50 and tighten the outer sleeve. Insulate the connection using self-amalgamating rubber tape. Start at the base of the connection and pull back the rubber tape backing.
-
Page 40: Manual Reset And Reboot
Installation Step Procedure Illustration Wind the rubber tape at an angle back down towards the base of the connection and cut the tape. Cable tie and mount the coaxial cable(s) so it is free from obstructions. Important: Check that all unused antenna ports remain covered with the supplied dust caps. - Page 41 Installation Step Description Picture To reset the NS50 (i.e. power cycle), press and release the Reset button whilst the unit is powered up. To reset to factory default settings whilst the unit is powered up, press and hold both the Reset and CPU Default button.
-
Page 43: Chapter 4: Understanding Vlans
Chapter Understanding VLANs Topics: This chapter explains the principles behind a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN). It is important to understand VLANs to properly • Understanding Trunk and configure the wireless network switch. Access Ports A VLAN is a collection of nodes grouped according to their function •... -
Page 44: Understanding Trunk And Access Ports
Understanding VLANs 4.1 Understanding Trunk and Access Ports VLANs can be assigned to trunk ports and access ports on a network. These two types of allocation determine how data is transmitted and relayed. 4.1.1 Trunk Ports Trunk ports typically provide a connection between network switches, and can carry data for multiple VLANs. -
Page 45: Port Allocation
Understanding VLANs 1. A PC sends an untagged frame into access port 6 (Control VLAN) on wireless network switch 1. The frame is sent to other access ports on the Control VLAN (access port 5). 2. Wireless network switch 1 tags the frame with VLAN ID = 4 and Priority = 5 and sends it through the trunk ports to Wireless network switch 2. -
Page 46: Vlans And Wireless Networks
Understanding VLANs 4.2 VLANs and Wireless Networks The wireless network switch can have up to four wireless Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs) per WAC. Each SSID is associated with a single VLAN and functions as an access port on that VLAN. 1. - Page 47 Understanding VLANs 1. The PC sends an untagged frame to Trunk port 3 on wireless network switch 1. 2. The frame is allocated to the Infrastructure VLAN. 3. The management CPU of wireless network switch 1 is always an Access port on the Infrastructure VLAN and will receive the frame.
-
Page 49: Chapter 5: Configuration Using The Web Interface
• Settings Tab on page 105. The IP address of the network device can be located and configured using the MST Device Scanner tool. For more information on how to use the Device Scanner, see Device Discovery on page 99. -
Page 50: Logging Onto The Web Browser Interface
Each WAC has a unique MAC address and should be configured with a unique IP address. • By default, the NS50 is configured to use DHCP. To find the IP address of a newly connected device, use the MST Device Scanner. • Devices running firmware 2.24.0 or earlier may default to 192.168.1.90. -
Page 51: Status Tab
Configuration Using the Web Interface The configuration screens are divided into three section tabs across the top: • STATUS — Displays device information, wireless clients, system logs, network traffic statistics and the most AeroScout Engine data and tag reads. • TOOLS — Web screens to configure password access, time settings, restoring factory defaults, and firmware upgrades. -
Page 52: Wireless Client Information
Configuration Using the Web Interface Note: Changes in status display are dependent on the web browser. Some web browsers may report an error when obtaining WLAN status, or require to refresh the web browser screen. 5.3.2 Wireless Client Information The Wireless status screen displays current information about wireless clients connected to the access point. -
Page 53: Viewing System Logs
Configuration Using the Web Interface • MAC Address: The address of the client device. • Mode: Indicates if the client device is in 802.11b or 802.11g mode. • Rate: The data rate for the connection in Mbps. • Signal: The percentage signal strength of the client device, as received by the access point. Note: The Wireless Client Device List groups the devices by the wireless SSID with which they are associated. -
Page 54: Viewing Network Traffic Statistics
Configuration Using the Web Interface To define LOG OPTIONS: 1. In the What to View fields, select the System check box. 2. In the View Levels field, select the check boxes on the reporting levels required. 3. Click Apply Log Settings Now. To view LOG DETAILS: 1. - Page 55 Configuration Using the Web Interface To view statistics: 1. Click Refresh Statistics to update the statistics. 2. Click Clear Statistics to clear displayed statistics. A reset confirmation dialog box is displayed. 3. Click OK. The following parameters are displayed: • LAN STATISTICS •...
-
Page 56: Viewing Ethernet Switch Information
Configuration Using the Web Interface 5.3.5 Viewing Ethernet Switch Information The Switch status screen displays general switch information. Switch information can only be accessed for the WAC in slot 1 of the Network Switch. It displays the following parameters: • The temperature inside the switch processor •... -
Page 57: Viewing Tracking Information
Configuration Using the Web Interface 5.3.7 Viewing Tracking Information The Tracking status screen displays the status of the tracking servers that are registered to the network device. Revision C NS50 User Guide... -
Page 58: Viewing Recent Tag Reports
Configuration Using the Web Interface 5.3.8 Viewing Recent Tag Reports The Tags status screen displays the last ten AeroScout tag reads when asset tracking and location services are enabled. The following information is displayed: NS50 User Guide Revision C... -
Page 59: Tools Tab
Configuration Using the Web Interface • MAC Address: MAC address of the tag being read. • RSSI: Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) is a measurement of the quality of the received radio signal. • Sequence: The sequence number of the tag transmission. This screen assists to verify the following: •... - Page 60 Configuration Using the Web Interface 1. Under ADMIN PASSWORD, enter the administrator password in the Password and the Verify Password fields. Administrators have full access to the web browser interface. 2. Under USER PASSWORD, enter the user password in the Password and the Verify Password fields. Users have read-only access to the web browser interface.
-
Page 61: Setting The Time
Configuration Using the Web Interface 2. Select the file and click Open. 3. Click Restore Configuration from File. The device will upload the configuration file. The SUCCESS screen is displayed. 4. Click Reboot the Device and then OK to reboot or click Continue to return to the previous configuration screen. - Page 62 Configuration Using the Web Interface To set the time configuration settings: 1. Select the appropriate time zone from the Time Zone drop-down box. 2. Click Enable Daylight Saving check box if the selected region has daylight saving. Daylight saving options will be displayed. 3.
-
Page 63: Rebooting Or Restoring The Network Device
Configuration Using the Web Interface 5.4.3 Rebooting or Restoring the Network Device The System configuration screen enables the device to be rebooted or restored to the factory default settings. Click Reboot the Device to reboot the device. Any unsaved settings on the device will be lost and the connection will terminate. - Page 64 It is recommended that a client device (PC or laptop) has a wired connection to the network device to upgrade the firmware. Please contact your MST System Engineer for firmware files. To upgrade the firmware: 1. Click Choose File. A dialog box will open.
- Page 65 Configuration Using the Web Interface 2. Select the binary (.bin) firmware file and click Open. 3. Click Upload, then OK on subsequent dialogue boxes to confirm. The firmware will upload to the device. 4. When the firmware has been successfully uploaded, the UPLOAD SUCCEEDED screen will appear. The network switch will reboot after 60 seconds.
-
Page 66: Settings Tab
Configuration Using the Web Interface 5.5 Settings Tab 5.5.1 Managing Automatic TFTP Configuration The Config Management screen is used to configure how the device retrieves its configuration from a TFTP server on the network. For more information on TFTP, see Centralised Configuration Management on page 85. -
Page 67: Setting Up The Lan
Configuration Using the Web Interface The following settings are available, which may affect 3rd party SNMP tools: • Name: The name or ID of the device • Contact: The name of the person to be notified of any alarms • Location: The location of the device •... -
Page 68: Configuring Wireless Radio
Configuration Using the Web Interface Field Description Recommended Settings Get LAN IP from DHCP (Dynamic) or Static IP (Manual) Default is DHCP. If Static IP is selected, the following fields must be filled in. The IP address of the WAC. A different IP address is required for each IP Address WAC in a network. - Page 69 Configuration Using the Web Interface To configure the wireless radio: 1. Select the Enable Wireless Radio check box to enable wireless. 2. To change wireless radio settings, edit the required fields. A description and recommended settings are shown below. 3. Click Save Settings. Field Description Recommended Settings...
- Page 70 Configuration Using the Web Interface Field Description Recommended Settings Transmission Settings to configure how fast data is transmitted. Leave the default setting as Best Rate (automatic) for data transmission at the best possible speed. A drop-down box to select the 802.11 mode from If there are 802.11b wireless client 802.11 Mode mixed 802.11g and 802.11b to 802.11g.
-
Page 71: Configuring Wireless Networks
Configuration Using the Web Interface AG with Dynamic Turbo enabled. In Turbo mode, the access point doubles the channel bandwidth to increase the throughput. • Super AG with Static Turbo – Channel 6 ONLY - Capable of Packet Bursting, FastFrames, Compression, and Static Turbo. - Page 72 Configuration Using the Web Interface A description of the wireless network parameters are described in the table below. Field Description Recommended Settings Enable Enables or disables the wireless network. Click on the Enable check box to enable the wireless network. Visibility Enables or disables visibility of the wireless network Click on the Visible option button...
- Page 73 The SSID of the wireless network that is used by Enter a network name that relates Network client devices. closely to its function. For Name example, "MST-VOICE". Security Mode Four security modes exist: WPA-Personal is recommended. Selecting the wireless security • None: No wireless authentication is required and mode will display configuration traffic is not encrypted.
-
Page 74: Configuring Eap (Extensible Authentication Protocol)
Configuration Using the Web Interface Configuring WEP Security Settings To configure WEP security settings: 1. Click on the WEP option button. 2. In the WEP Key Length drop-down box, select 64bit or 128bit. 128bit is a more secure encryption type. 3. - Page 75 Configuration Using the Web Interface To configure wireless EAP, click on the drop-down boxes in the supplied fields. Click Save Settings to save settings. A description of the fields and settings are described in the table below. Field Description Recommended Settings Authentication Timeout Amount of time in minutes before Setting is at 120 minutes by...
-
Page 76: Wds (Wireless Distribution System) Settings
The Tracking configuration screen establishes where AeroScout tag reports are sent as shown below. An ImPact network device can communicate with an AeroScout Positioning Engine and / or a MST Tracker Engine. Configuration of the Access Point is not required when communicating with an AeroScout Positioning Engine as the device configuration is performed via AeroScout server tools. - Page 77 Configuration Using the Web Interface If the Access Point is sending tag reports to an MST Tracker Engine, the Tracker Engine's IP address must be entered into each Access Point. There are four sections on the Tracking configuration screen: Enable Check Enable Wi-Fi Tracking to view other settings.
-
Page 78: Configuring Ethernet Switch Ports
Tracker Engine List This section is used to configure the MST Tracker Engine(s) that the access point will send information to. The available settings are listed below. Note that data can be passed to up to 2 MST Tracker Engine instances. - Page 79 Configuration Using the Web Interface The Switch ports have the following configuration options: Field Description Recommended Settings Name Used to provide a convenient name for the port. Naming is specific to each device. It is often used to name the device connected to it.
-
Page 80: Enabling The Mac Address Filter
Configuration Using the Web Interface 5.5.10 Enabling the MAC Address Filter The MAC Address Filter configuration screen specifies MAC addresses to be allowed or denied access to the network. To enable MAC address filtering: 1. Click on the Enable MAC Address Filter check box to view settings. 2. -
Page 81: Defining Vlans
Configuration Using the Web Interface To edit a device in the list, click on the icon. 9. Click Save Settings. 5.5.11 Defining VLANs The VLAN LIST screen displays VLANs and the priority that will be assigned to traffic on each VLAN. For more information, see Understanding VLANs on page 43. -
Page 82: Configuring The Vlan Port Map
Configuration Using the Web Interface 5.5.12 Configuring the VLAN Port Map The VLAN Port Map screen assigns the VLAN(s) to each physical switch port, and each wireless network. Physical switch ports can be assigned as Trunk or Access ports. Wireless networks always act as Access ports on the selected VLAN. - Page 83 Configuration Using the Web Interface All ports pass through a single switch processor, but VLAN membership for some ports is configured on WAC 1 and others on WAC 2. All physical ports can be assigned to be either a trunk port or access port. Revision C NS50 User Guide...
- Page 84 Configuration Using the Web Interface To configure a port: 1. Set the Mode to be either Trunk or Access (for physical ports). 2. Select the VLAN Membership(s). For an Access port only one VLAN can be selected. For a trunk port multiple VLANS can be selected.
-
Page 85: Chapter 6: Centralised Configuration Management
Chapter Centralised Configuration Management Topics: Centralised configuration management is an alternative configuration method to the web interface. It uses Trivial File Transfer Protocol • Device Management Overview (TFTP) to enable devices to read and apply configuration files from • TFTP Server Overview a TFTP server. -
Page 86: Device Management Overview
Some familiarity with the ICA Administration Console is assumed here. For more information, see the ICA Administration Console User Manual available from MST. There are three editors in the ICA Administration Console with relevant settings: •... - Page 87 Centralised Configuration Management the Site Configuration editor. This template cannot be deleted, but new templates can be copied from it and modified separately. Note: Once a template is applied to an AP, any manual changes made to settings listed in the template will be reverted automatically to the template default.
-
Page 88: Access Point
Centralised Configuration Management • Parameter Value: To edit a parameter, click on the parameter value and either enter a new value (e.g. names and IP addresses) or select a new value from the dropdown menu (e.g. ENABLED / DISABLED). When all required changes have been made, click OK to close the dialog box. The Managed status of all available parameters can be changed at once using the Manage All and Manage None checkboxes below the list. - Page 89 Centralised Configuration Management List of Access Points The Managed column shows CURRENT for managed devices with up-to-date settings, or PENDING for devices awaiting newly updated settings. To edit an existing entry: Click on that entry, fill in the relevant fields on the right, then click the Save button or press Ctrl+S: Manage Configuration To have an AP's configuration managed by the ICA, tick the Manage Configuration checkbox, and...
-
Page 90: Tftp Server Overview
Note: This configuration method is not commonly used. For more information on TFTP server and configuration file requirements for ImPact access points, please contact MST. Centralised configuration management using ICA v1.3.1 or earlier, or a 3rd party TFTP server, involves... -
Page 91: Tftp Parameters
Configuration is not required when communicating with an AeroScout positioning engine. • tracking.tracker.x.* - These settings configure up to two MST Tracker Engines that the access point will send information to. The "x" in each parameter is replaced by the tracking engine number. - Page 92 Centralised Configuration Management Wireless Radio and Networking • wireless.radio.1.* - General wireless radio settings. • wireless.radio.1.ap.x.* - Each WAC in a device can have up to four wireless SSIDs (where "x" is replaced with 1-4), each with different security settings and different VLAN mapping. •...
-
Page 93: Appendix A: Troubleshooting Guide
Appendix Troubleshooting Guide This chapter assists in the diagnosis and resolution of problems with NS50 installation and operation. Problem Possible Causes Solution The power light Insufficient power supplied to the An additional DC power supply is required to boost the on the NS50 NS50. - Page 94 Troubleshooting Guide Problem Possible Causes Solution Security settings do not match on each Disable security on WDS link using the web interface. side of the WDS link. Signal loss in the Composite connector or fibre port is Check the connectors and fibre ports are clean. Clean fibre optic cable.
-
Page 95: Appendix B: Composite Cable Testing
Appendix Composite Cable Testing This appendix describes fibre optic cable continuity and testing. Fibre optic cable testing includes visual inspection and power loss testing. B.1 Visual Inspection of the Fibre Optic Cable Fibre optic cable can be inspected by visually tracing and inspecting the connector. Visual Tracing Checking for continuity diagnoses whether the fibre optic cable is damaged or broken. - Page 96 Composite Cable Testing Component Power loss Connector 0.5 dBi Multi-mode fibre 1 dBi / km @ 1300nm Single-mode fibre 0.5 dBi / km @ 1300nm 0.4 dBi / km @ 1550nm NS50 User Guide Revision C...
-
Page 97: Appendix C: Ethernet Cable Specifications
Appendix Ethernet Cable Specifications Ethernet cable must conform to the following specifications when connecting to ImPact network devices: • Polyethylene jacket • 5.0-6.5mm outer diameter • Stranded cable for lengths less than 30m • Solid core cable for lengths greater than 30m Cable and Parts Description Description Order Code... -
Page 99: Appendix D: Device Discovery
Appendix Device Discovery The MST Device Scanner can be used to discover and change the IP address of ImPact devices from any PC connected to the same network. Upon opening, the Device Scanner will automatically scan for devices. To use the Device Scanner, navigate to the folder where the program is stored, and double click devicescanner.exe. - Page 100 Device Discovery NS50 User Guide Revision C...
-
Page 101: Appendix E: Time Zone Indices And Offsets
Appendix Time Zone Indices and Offsets The table below specifies time-zone indices and offset values entered in the site configuration file. time.timezone.index Country time.timezone.offset Value Value Eniwetok, Kwajalein -43200 Midway Island, Samoa -39600 Hawaii -36000 Alaska -32400 Pacific Time (US/Canada), Tijuana -28800 Arizona -25200... - Page 102 Time Zone Indices and Offsets time.timezone.index Country time.timezone.offset Value Value Amsterdam, Berlin, Bern, Rome, Stockholm, Vienna 3600 Belgrade, Brastislava, Budapest, Ljubljana, Prague 3600 Brussels, Copenhagen, Madrid, Paris 3600 Sarajevo, Skopje, Sofija, Vilnus, Warsaw, Zagreb 3600 West Central Africa 3600 Athens, Minsk, Istanbul 7200 Bucharest 7200...
- Page 103 Time Zone Indices and Offsets time.timezone.index Country time.timezone.offset Value Value Taipei 28800 Osaka, Sapporo, Tokyo 32400 Seoul 32400 Yakutsk 32400 Adelaide 32400 Darwin 32400 Brisbane 36000 Canberra, Melbourne, Sydney 36000 Guam, Port Moresby 36000 Hobart 36000 Vladivostok 36000 Magadan, Solomon Is., New Caledonia 39600 Auckland, Wellington 43200...
-
Page 105: Appendix F: Connecting A Pc To An Impact Network Device
Appendix Connecting a PC to an ImPact Network Device This Appendix specifies how to set up a PC connection (with Windows XP operating system) to connect to an ImPact Wireless Network Switch or WAP. 1. Connect a PC to the device's Ethernet port with an Ethernet cable. If the PC is already part of the network, note its TCP/IP configuration settings. - Page 106 Connecting a PC to an ImPact Network Device 4. On the General tab, scroll down to Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then click Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box is displayed. 5. Click the Use the following IP address option button. NS50 User Guide Revision C...
- Page 107 Connecting a PC to an ImPact Network Device 6. In the IP address field, enter a fixed (static) IP address within the Subnet range of the target device's IP address (for example 192.168.1.100). 7. In the Subnet mask field, enter 255.255.255.0. Click OK. Revision C NS50 User Guide...
-
Page 109: Appendix G: Maintenance Check-List
2. Using a MinePhone handset, verify the signal strength is within specification. (Refer to commissioning data). Testing RF RX path for WAC 1 1. Stand 50M away from the ImPact NS50 with two MST RFID tags. 2. Open NS50 web browser interface and select the STATUS > TAGS web page. - Page 110 (Refer to commissioning data). Testing RF RX path for WAC 2 1. Stand 50M away from the ImPact NS50 with two MST RFID tags. 2. Open the NS50 web browser interface and select the STATUS > TAGS web page.
-
Page 111: Appendix H: Acronyms
Appendix Acronyms Acronym Meaning Alternating Current Access Point Direct Current IP address Internet Protocol address IPxx Ingress Protection rating MAC address Media Access Control address Mine Site Technologies Network Switch Power Over Ethernet Power Supply Unit Radio Frequency SSID Service Set Identifier. Small Form-factor Pluggable (optical transceiver module) User Datagram Protocol VLAN... -
Page 113: Appendix I: Impact Ns50 Specifications
Dimensions 410mm x 327mm x 69mm Weight 5.9kg packaged Connectivity 4 x MST composite fibre ports (1000Base-LX) 4 x PoE ports 2 x 802.11b/g Radio ports 4 x RP-TNC antenna ports (with diversity support) Enclosure Ingress Powder-coated stainless steel enclosure, sealed to comply with an Ingress Protection... - Page 114 ImPact NS50 Specifications NS5003 1 x Access Point Radio, 4 x Gbps 10.4 11.5 12.3 Fibre Ports NS5004 2 x Access Point Radio, 4 x Gbps 11.2 12.0 13.9 14.7 Fibre Ports Ethernet Port Crossover Auto MDI/MDIX crossover Auto negotiation 10 BASE-T / 100 BASE-TX Network Information Network...
- Page 115 802.11b: +19dBm 802.11g: +19dBm @6Mbps + 14dBm @54Mbps Receive sensitivity 802.11b: -94dBm @1Mbps -87dBm @ 11Mbps 802.11g: -87Bm @ 6Mbps -70dBm @ 54Mbps Compliance Note: Please contact MST for the latest available compliance information if required. Revision C NS50 User Guide...
-
Page 117: Appendix J: Hardware Warranty
Appendix Hardware Warranty Mine Site Technologies provide a 12 month warranty for hardware supplied to the original purchaser. Mine Site Technologies warrants that the hardware supplied will be free from material defects in workmanship and materials from the date of original purchase. Mine Site Technologies will repair or replace the defective hardware during the warranty period at no charge to the original owner.


Need help?
Do you have a question about the ImPact NS5004 and is the answer not in the manual?
Questions and answers